BIO 312 exam 2 pt 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:56 PM on 3/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
CNS Structure
consists of the brain and spinal cord
2
New cards
CNS function
acts as control center for nervous system; processes information; provides short-term control over activities of other systems
3
New cards
PNS structure
cranial nerves and spinal nerves
4
New cards
PNS function
communication lines between the CNS and the rest of the body
5
New cards
4 supporting cells of CNS
1. Astrocytes
2. Microglia
3. Ependymal cells
4. Oligodendrocytes
6
New cards
2 supporting cells in the PNS
1. Satellite cells
2. Schwann cells
7
New cards
Astrocyte Function (CNS)
maintains blood brain barrier, structural support, regulate ion, nutrient, helps anchor things to the CNS, recycle and absorb neurotransmitters, form scar tissues
8
New cards
Microglia function (CNS)
remove cell debris, wastes, and pathogens by phagocytosis
9
New cards
ependymal cells (CNS)
lines ventricles (brain) and central canal (spinal cord), circulation, monitoring of cerebrospinal fluid
10
New cards
oligodendrocytes (CNS)
myelinate CNS axons, provide structural framework
11
New cards
Satellite cells (PNS)
surround neuron cell bodies in ganglia, regulation O2, CO2, nutrient and neurotransmitter levels around neurons in ganglia
12
New cards
Schwann cells (PNS)
create myelin sheath in PNS, surround all axons in PNS, responsible for myelination of peripheral axons, participate in repair process after injury
13
New cards
oligodendrocytes vs schwann cells
Oligo - in CNS, work on many axons; Schwann - in PNS, work on one axon, wrap around many times
14
New cards
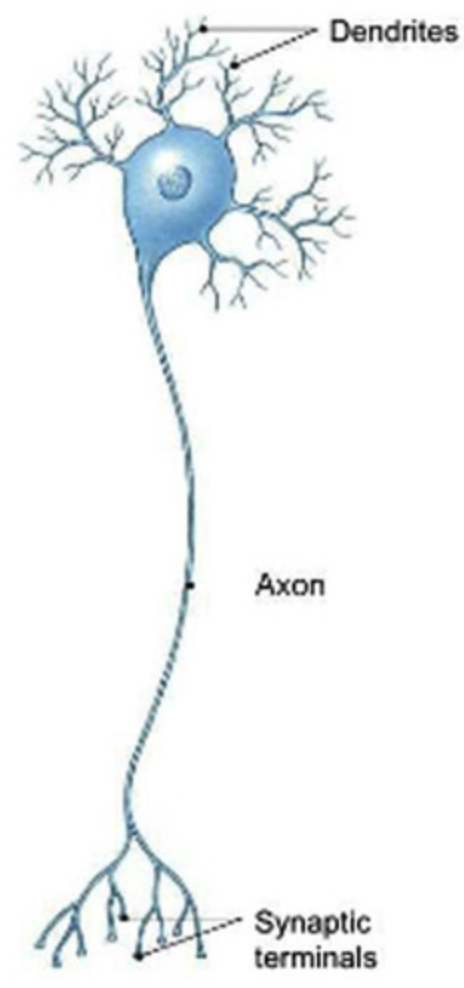
neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
15
New cards
synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
16
New cards
presynaptic neuron
neuron that sends the signal
17
New cards
postsynaptic neuron
the neuron on the receiving end of the synapse
18
New cards
axolemma
cell membrane of axon
19
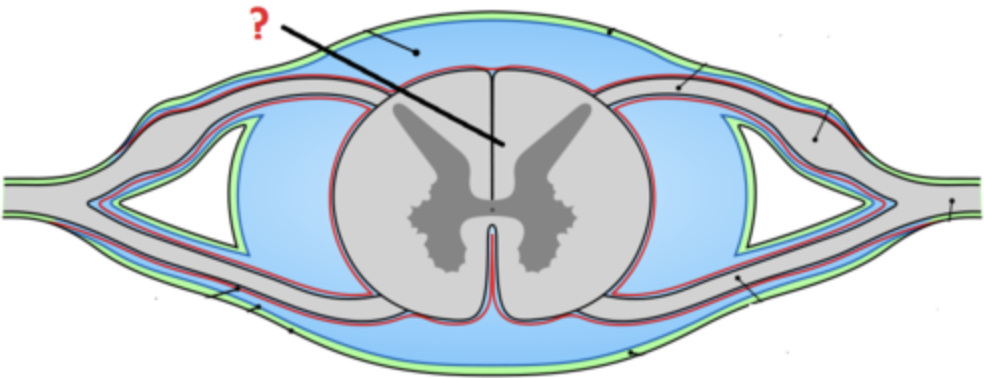
New cards
perikaryon (soma)
cell body of a neuron
20
New cards
dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
21
New cards
axons
a part of a neuron that carries impulses away from the cell body
22
New cards
Telodendria
Series of fine, terminal extensions branching from the axon tip.
23
New cards
terminal boutons
Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons
24
New cards
anaxonic neuron
many dendrites but no axon, help in visual processes
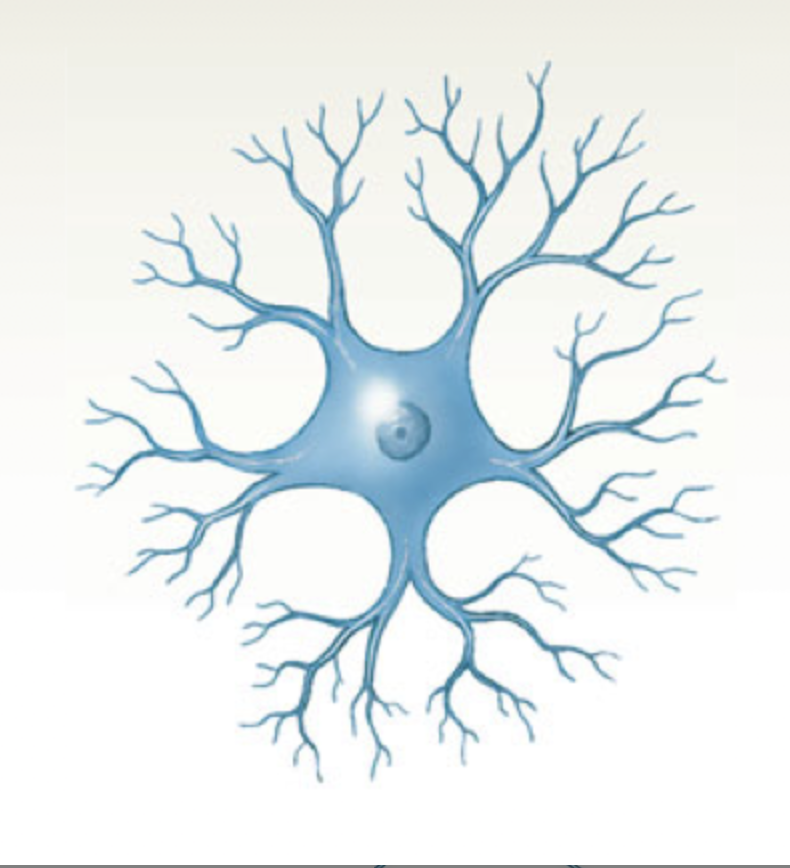

25
New cards
bipolar neuron
a nerve cell that has a single dendrite at one end and a single axon at the other end
26
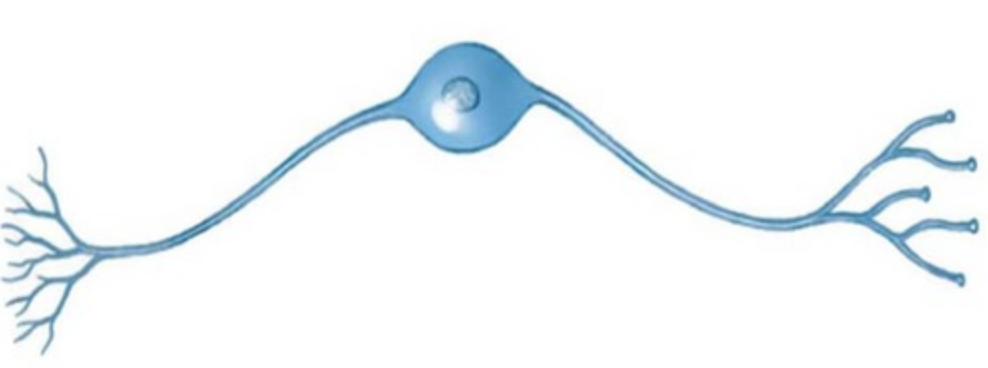
New cards
unipolar neuron
a neuron with one process extending from its cell body
27
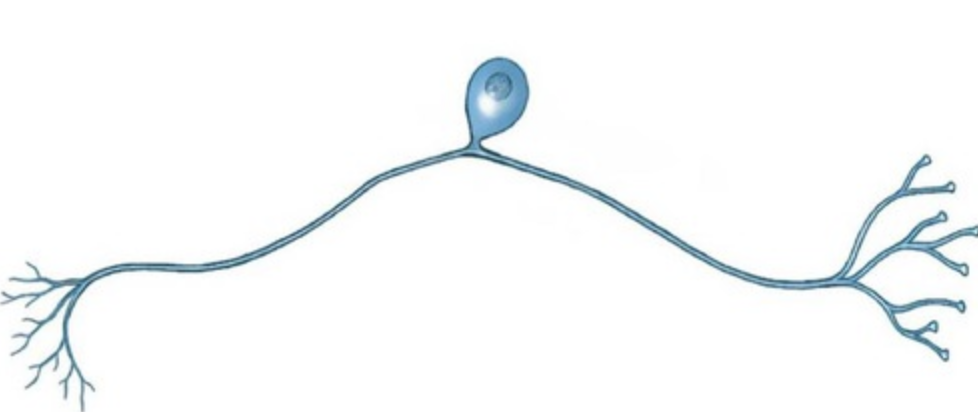
New cards
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites; the most common type of neuron in the nervous system.
28
New cards
myelinated
has multiple wrappings of schwann cells or oligodendrytes
29
New cards
unmyelinated
does NOT have multiple wrappings of schwann cells or oligodendrytes
30
New cards
sensory neuron
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
31
New cards
motor neuron
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
32
New cards
interneuron
Central nervous system neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
33
New cards
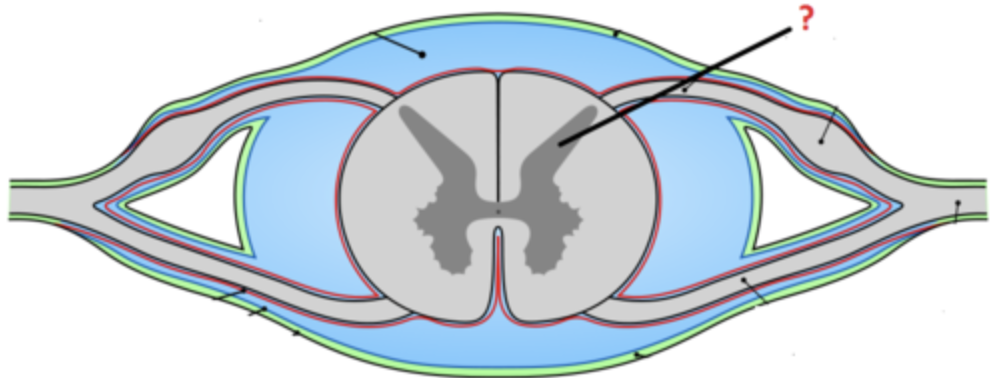
gray matter
Brain and spinal cord tissue that appears gray with the naked eye; consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and unmyelinated axons
34
New cards
white matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths.
35
New cards
gyri
ridges of the brain (brain convolutions)
36
New cards
sulci
shallow grooves (brain convolutions)
37
New cards
nerves
nerves are collections of neurons in the PNS and may contain multiple diff types of info (sensory or motor) with cell bodies in ganglia
38
New cards
Tracts
collections of neurons in the CNS with only one type of info; cell bodies in nuclei
39
New cards
cortex of brain
outer layer of gray matter; Formed from neuronal cell bodies; Located in cerebrum and cerebellum;
40
New cards
nuclei of brain
clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system
41
New cards
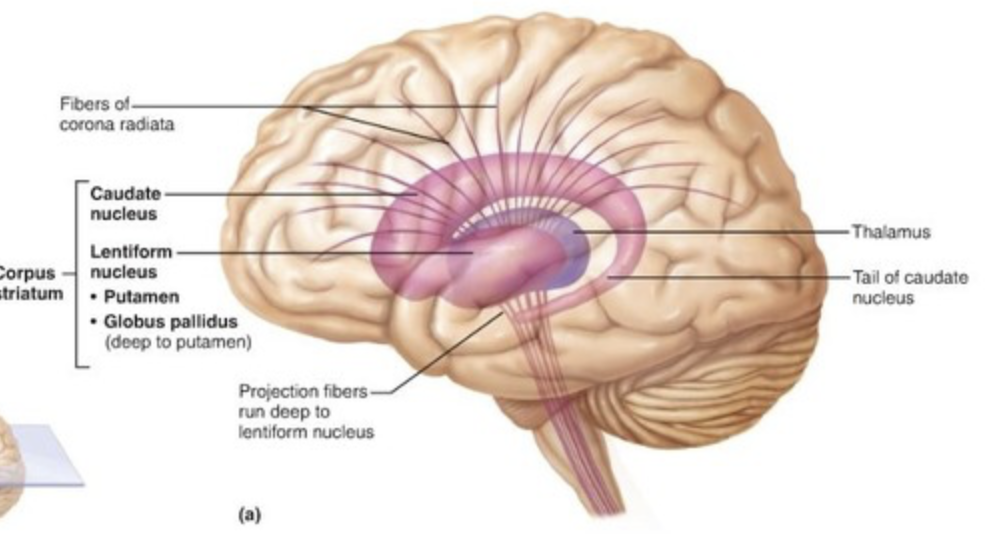
ganglia
clusters of neuron cell bodies in PNS
42
New cards
afferent pathway
Sensory pathway that relays information to the central nervous system.
43
New cards
efferent pathway
A motor pathway that relays information from the central nervous system to the rest of the body.
44
New cards
excitable cells
cells that are able to respond to certain stimuli by producing electric signals; can conduct/propagate electrical charges
45
New cards
basic neuron characteristics
highly differentiated, amitotic, incapable of regeneration, long-lived, high metabolic rate, dependence on glucose and O2
46
New cards
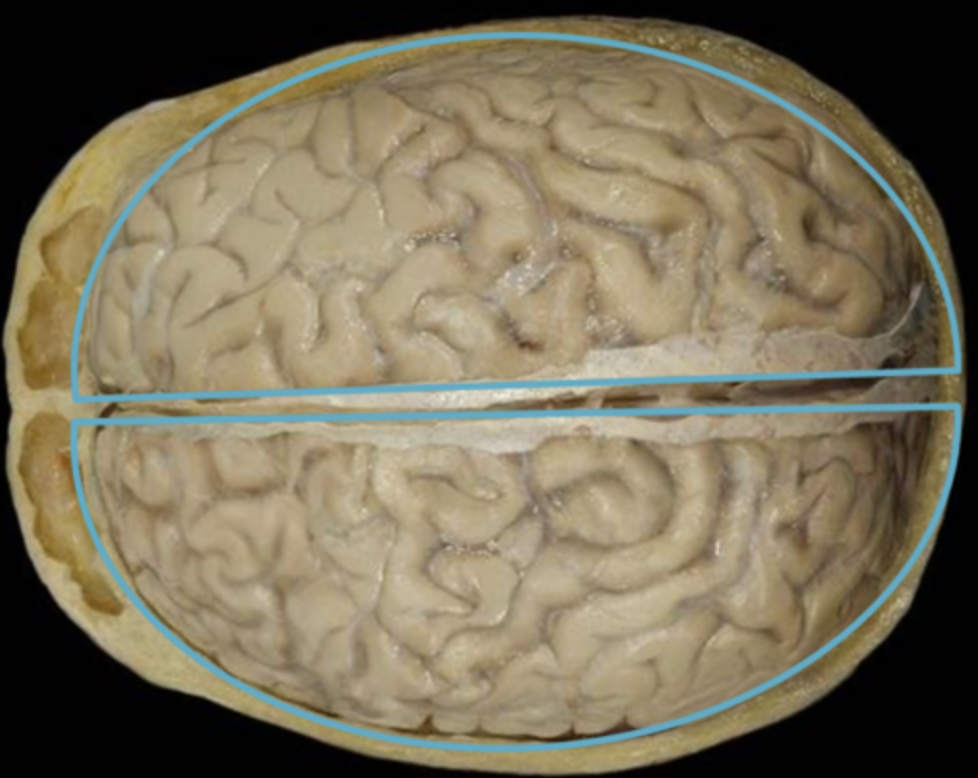
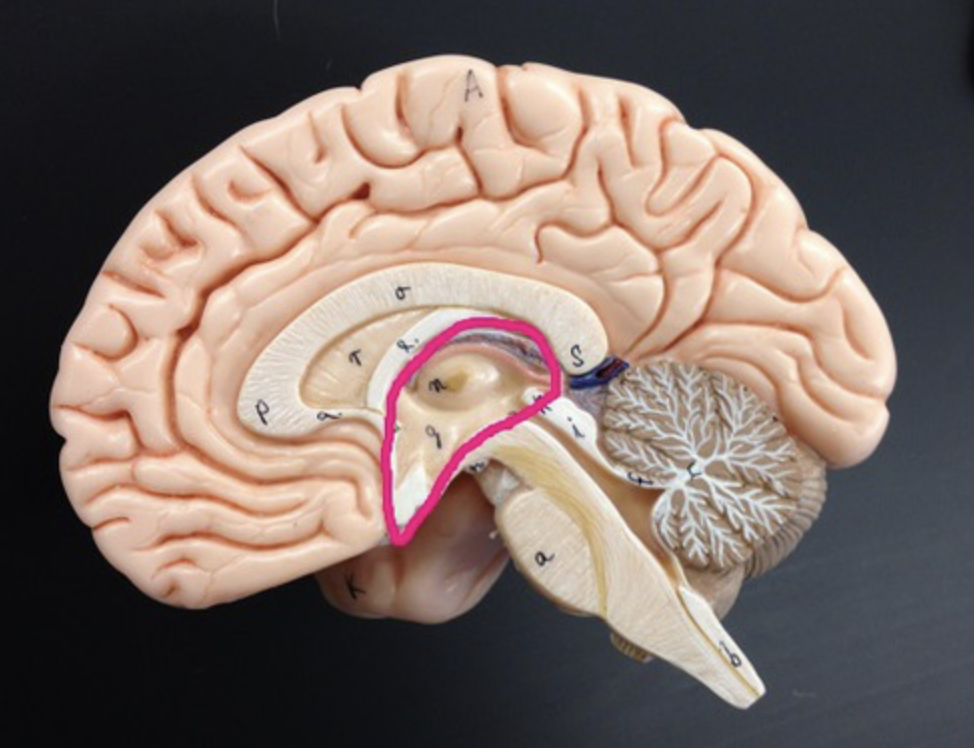
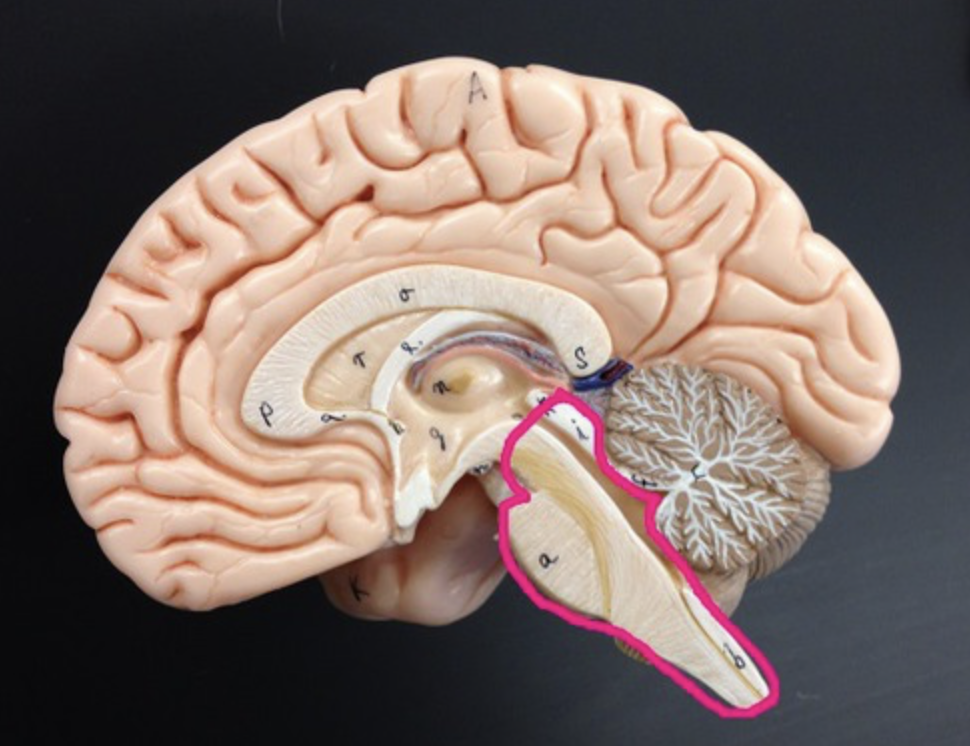
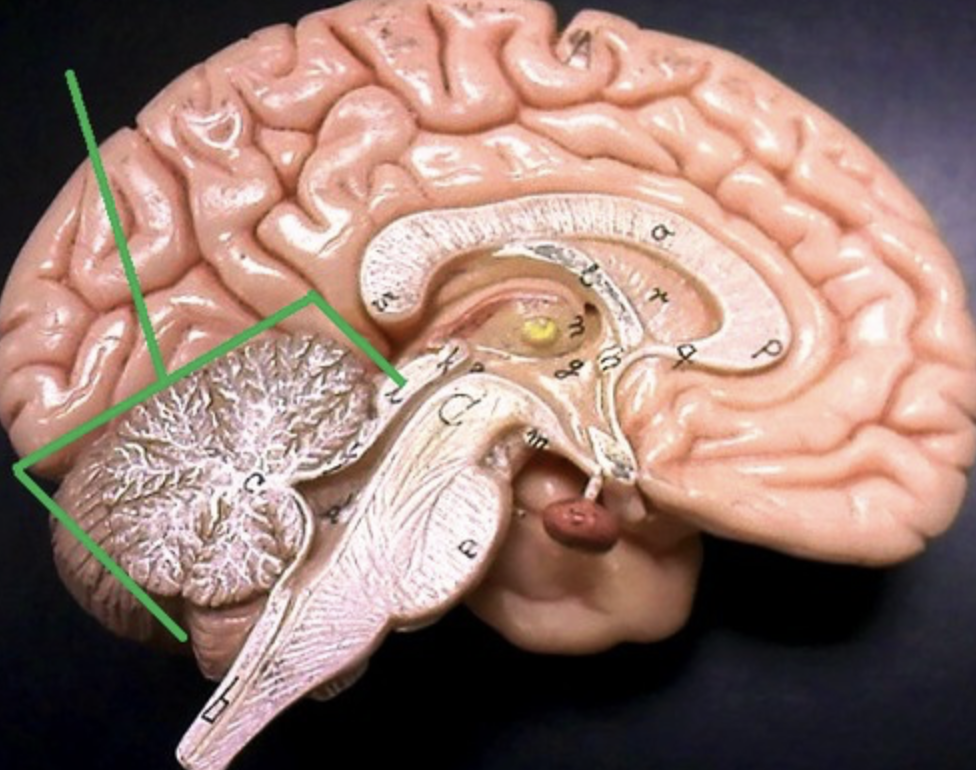
4 regions of the brain
1. Cerebral hemispheres; 2. Diencephalon; 3. Brain stem; 4. Cerebellum
47
New cards
cerebral hemispheres function
The "thinking parts" and the fiber tracts connecting those to each other and to brain-stem
48
New cards
diencephalon function
memory processing and emotional response
49
New cards
brain stem
Connects the brain and spinal cord
50
New cards
cerebellum function
process and store information, coordinates voluntary movements (posture, balance, speech)
51
New cards
kinetic energy
energy due to motion
52
New cards
potential energy
Energy that is stored and held in readiness
53
New cards
what is the charge of inside the cell
70mV
54
New cards
Where is K+ more concentrated?
inside the cell
55
New cards
Where is Na+ more concentrated?
outside the cell
56
New cards
Where is Cl- more concentrated?
outside the cell
57
New cards
where is ca2+ more concentrated?
outside the cell
58
New cards
Ohm's law
V \= IR: V: voltage; I: current; R: resistance
59
New cards
what is the definition of current?
flow of charged ions in body fluids
60
New cards
how does diameter affect resistance of flow?
the larger the diameter the less resistance there is to flow
61
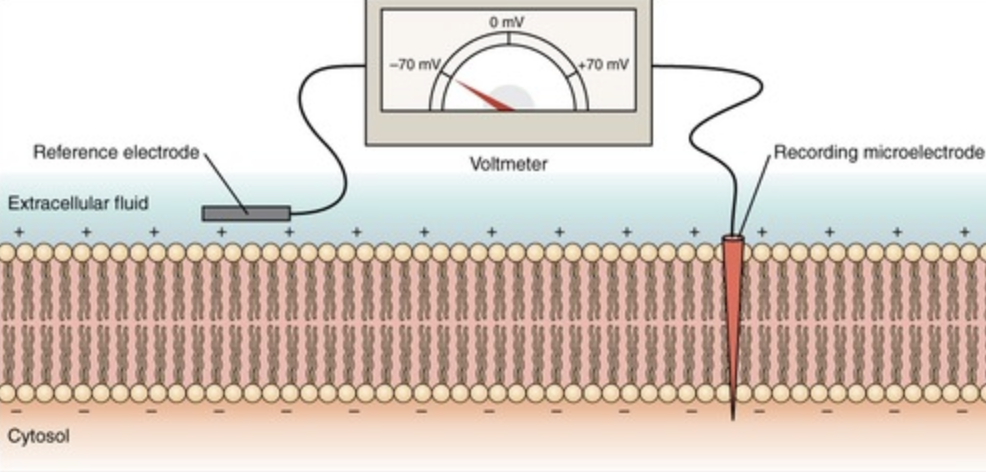
New cards
reference electrode
located outside of the cell membrane
62
New cards
recording electrode
recording tip inside the neuron
63
New cards
in to out convention
describe the membrane potential from the perspective of the recording electrode
64
New cards
voltmeter
A device used to measure voltage, or electrical potential energy difference
65
New cards
what 3 things does the resting membrane depend on?
1. the gradients for Na+ and K+ between cytosol and ECF; 2. Permeability of the membrane to Na+ and K+; 3. Activity of the 3Na+ 2K+ ATPase
66
New cards
depolarization
becomes less negative than rest (more positive); Na+ or Ca2+ channels are open and flowing into cell
67
New cards
hyperpolarization
becomes more negative than rest Cl- or K+ channels are openelectrical potential opposes this chemical potential favors this
68
New cards
Repolarization
returns to rest
69
New cards
chemically (ligand) gated channels
open or close depending on the presence or absence of a specific chemical that binds to the channel protein
70
New cards
location of ligand gated channels
dendrites and soma membrane
71
New cards
voltage gated channels
open or close in response to changes in membrane potential
72
New cards
location of voltage gated channels
axonal membrane
73
New cards
Graded potential
fizzle out along membrane; result form opening ligand fated channesl; amplitude caries with stimulus intesisty; 2 types (EPSP, IPSP)
74
New cards
Action potential
at axonal membranes allow transmission over long distances
75
New cards
EPSP
Excitatory postsynaptic potential; a slight depolarization of a postsynaptic cell, bringing the membrane potential of that cell closer to the threshold for an action potential; Na+ channels open
76
New cards
IPSP
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential; a slight hyperpolarization of the postysynaptic cell, moving the membrane potential of that cell further from threshold; K+ channels open
77
New cards
Temporal summation
Summation by a postsynaptic cell of input (EPSPs or IPSPs) from a single source over time; one channel opens multiple times
78
New cards
Spatial summation
The sum of multiple synapses firing at different locations at one time to create a net effect.
79
New cards
threshold potential
The minimum membrane potential that must be reached in order for an action potential to be generated.
80
New cards
threshold stimulus
stimulation level that must be exceeded to elicit a nerve impulse or a muscle contraction
81
New cards
absolute refractory period
the period immediately following the firing of a nerve fiber when another action potential cannot be stimulated no matter how great a stimulus is applied
82
New cards
relative refractory period
A period after firing when a neuron is returning to its normal polarized state and will fire again only if the incoming message is much stronger than usual
83
New cards
continuous conduction
the step-by-step depolarization and repolarization of each adjacent segment of the plasma membrane; nmyelinated axons; slow
84
New cards
saltatory conduction
the propagation of action potentials along myelinated axons from one node of Ranvier to the next node, increasing the conduction velocity of action potentials; jumping of action potentials from node to node
85
New cards
why does an action potential occur?
b/c of summation of graded potentials at trigger zones
86
New cards
Substrates of metabolism
glucose + O2 ; aerobic metabolism ; Fatty acids -\> TCA cycle(liver) -\> TCA cycle (brain) ; get glutamate, glutamine and GABA (neurotransmitters)
87
New cards
choroid plexuses function
produce cerebrospinal fluid
88
New cards
ependymal cells function
produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid
89
New cards
three layers of membrane that protect the brain?
meninges
90
New cards
inner layer of meninges
pia mater (very delicate)
91
New cards
middle layer of meninges
arachnoid mater
92
New cards
Outer layer of meninges
dura mater (tough mother)
93
New cards
ventricles of the brain
canals in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid
94
New cards
hydrocephalus
accumulation of fluid in the cavities deep within the brain
95
New cards
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
plasma-like clear fluid circulating in and around the brain and spinal cord
96
New cards
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
physiological barrier between the circulatory system and the central nervous system that establishes a privileged blood supply, restricting the flow of substances into the CNS
97
New cards
axon hillock (trigger zone)
initial segment of axon where the action potential is initiated
98
New cards
4 phases of action potential
1) depolarization; 2) overshoot; 3) repolarization; 4) undershoot
99
New cards
2 periods of action potential
1) absolute refractory period; 2)relative refractory period
100
New cards
Hodgkin positive feedback cycle
occurs when inward and capacitive current through voltage-gated Na+ channels bring the next patch of axonal membrane to threshold potential; triggers the opening of more voltage-gated Na+ channels