Genomics: Plasmid Vectors, Cloning, and DNA Libraries
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are plasmids?
Naturally-occurring extra-chromosomal DNA elements that can replicate within cells.
What is the structure of plasmids?
Plasmids are double-stranded, circular, and much smaller than the main chromosome.
What are vectors in the context of cloning?
Artificially constructed DNA molecules that can replicate in a host organism and are used for cloning.
From what are most cloning vectors derived?
Genetically engineered plasmids with features useful for cloning DNA.
What are the three main components of an E. coli plasmid vector?
Ori (origin of replication), selectable marker, and MCS (multiple cloning site).
What is the function of the Ori in a plasmid vector?
It is a sequence required for DNA replication in the cell.
What is a selectable marker in a plasmid vector?
A gene that gives the cell a selectable phenotype, such as an ampicillin-resistance gene.
What is the purpose of the MCS in a plasmid vector?
It is a region containing unique restriction enzyme (RE) sites where foreign DNA can be inserted.
What is pBluescript II (pBSII)?
A plasmid vector with a high copy number and an MCS that is part of the lacZ+ gene.
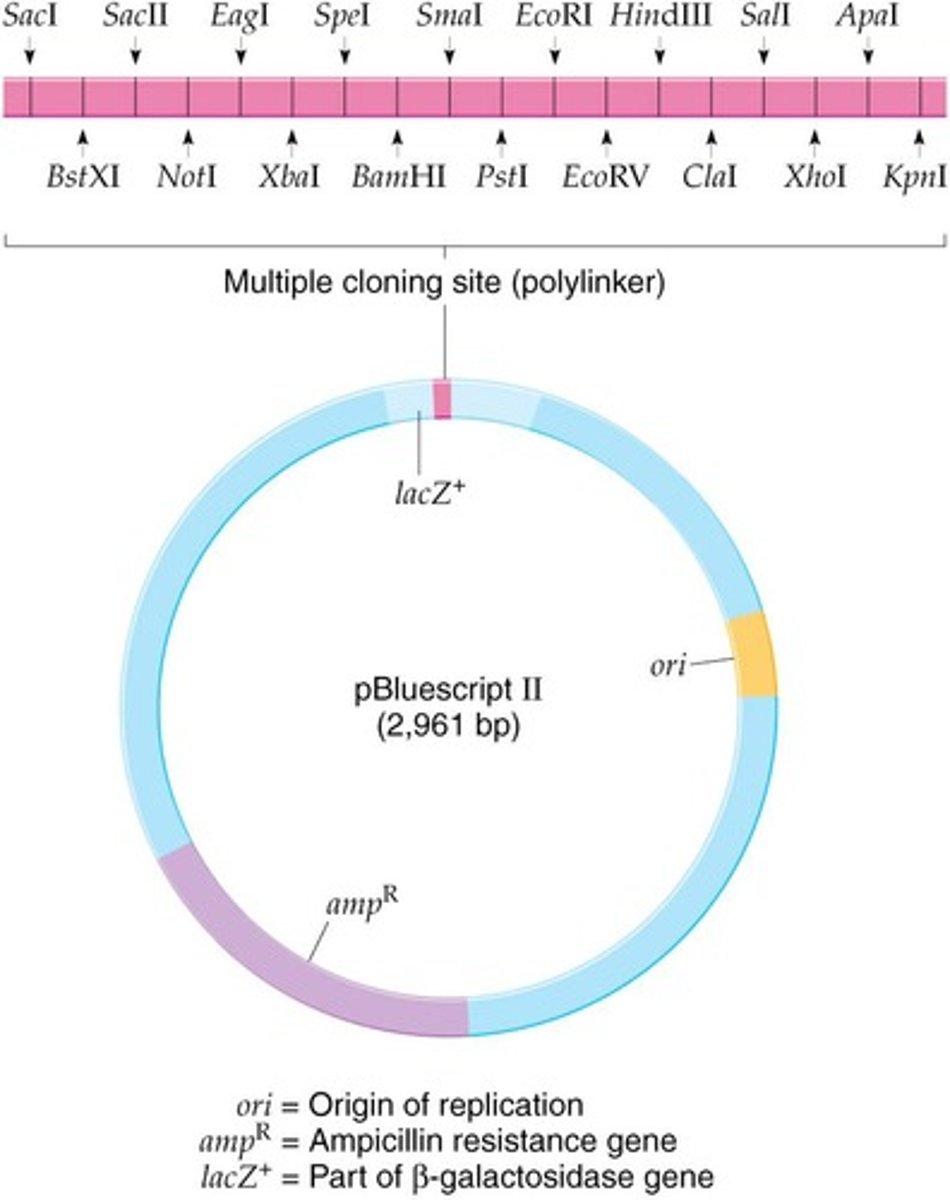
What happens when DNA is cloned into the MCS of pBSII?
The lacZ+ gene is disrupted, making the plasmid lacZ- and unable to complement E. coli.
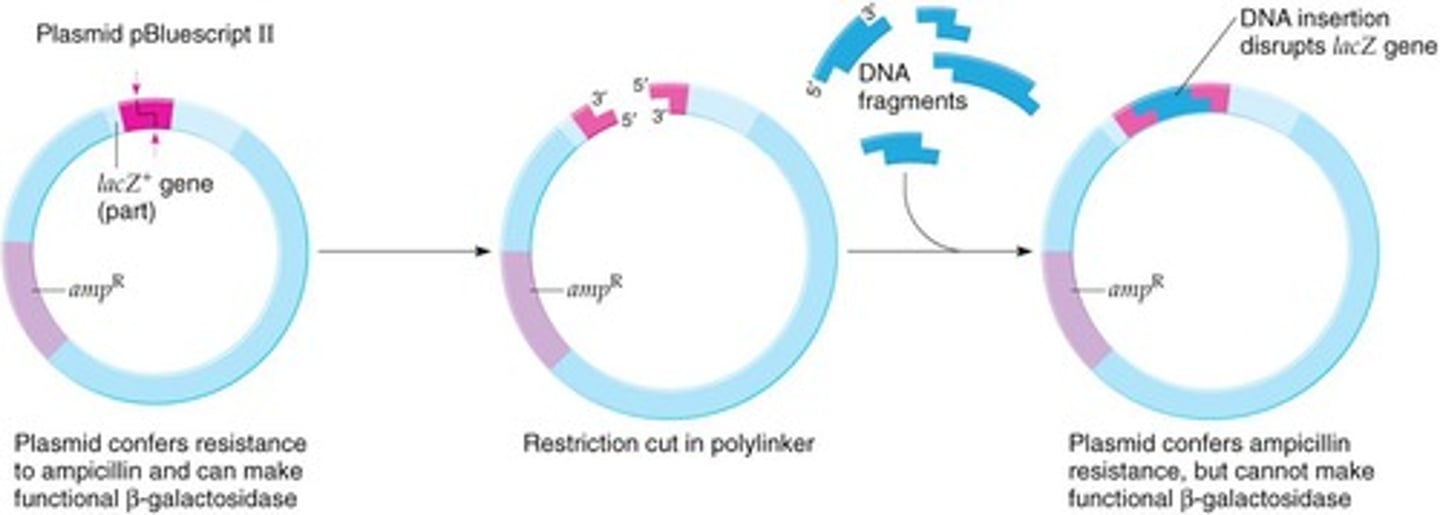
What is the significance of blue-white colony screening?
It distinguishes colonies with inserts (white colonies) from those without (blue colonies) based on lacZ activity.
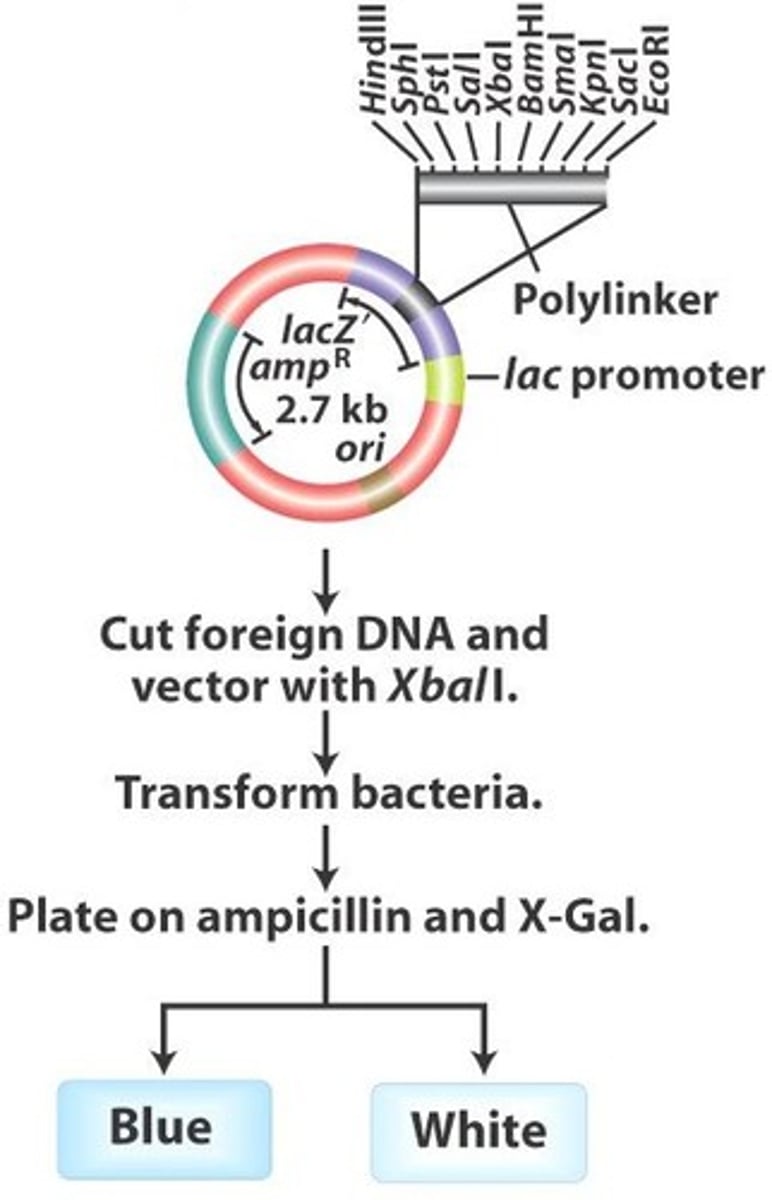
How does lacZ protein function in the context of blue-white colony screening?
It digests lactose into galactose and glucose and can also digest X-gal into a blue product.
What is a genomic library?
A collection of clones containing at least one copy of every DNA sequence in a genome.
What is the purpose of a genomic library?
To identify a cloned DNA containing a gene or sequence of interest.
How is a genomic library constructed?
By partially digesting genomic DNA with a restriction enzyme to generate overlapping fragments.
What is the process for cloning fragments into a genomic library?
Collect desired size fragments, ligate them to a cut vector, transform bacteria, and plate on selective medium.
What is a cDNA library?
A library created by copying a cell's mRNA molecules into complementary DNA (cDNA).
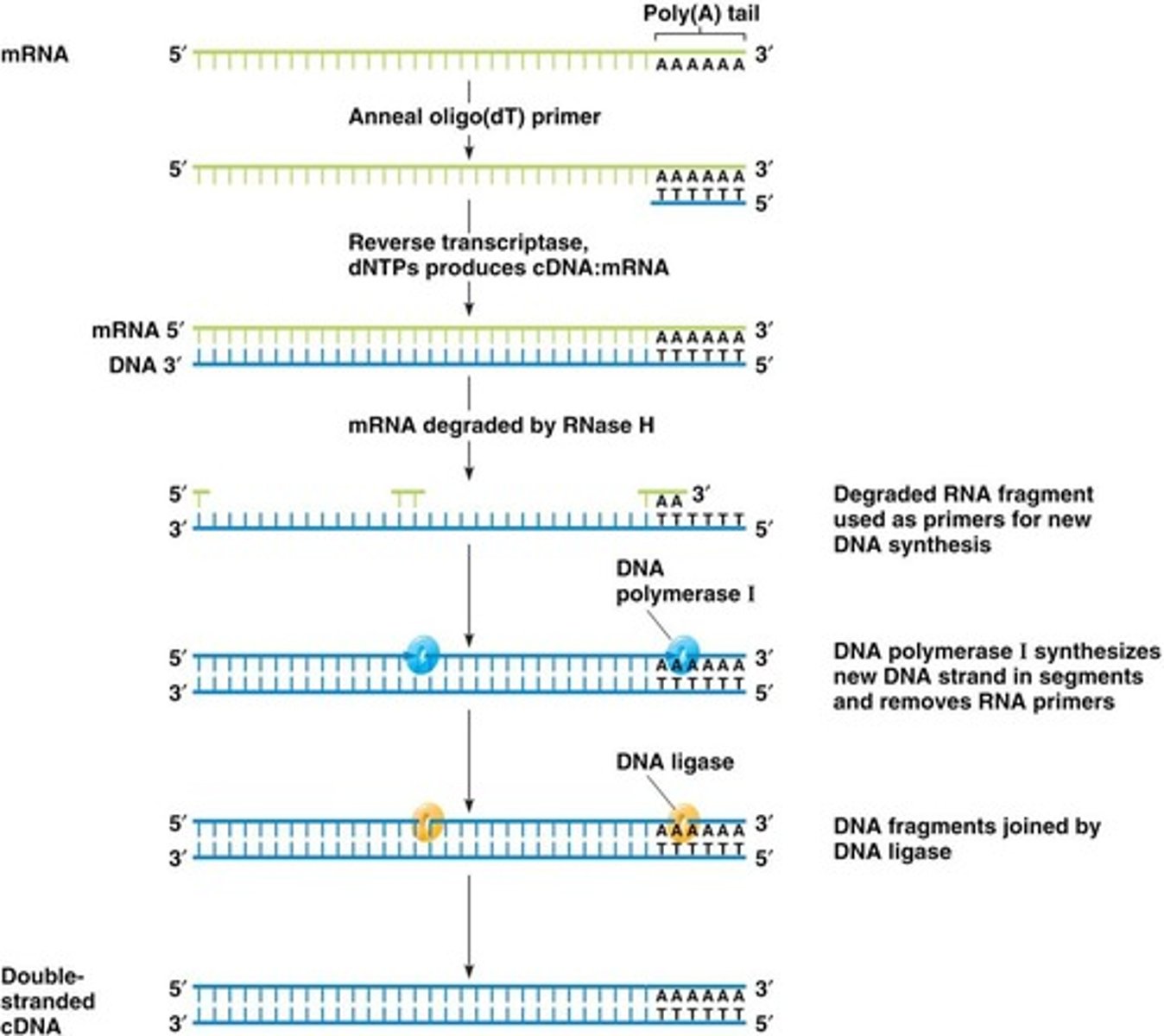
What does a cDNA library represent?
Only the genes being expressed in a given cell type at a specific condition or time point.
Why are cDNA libraries smaller than genomic libraries?
They represent only the protein-coding regions of the genome.
When is cDNA cloning usually done?
As a prelude to genomic cloning since genomic clones have more information, such as promoters and introns.