The Self
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
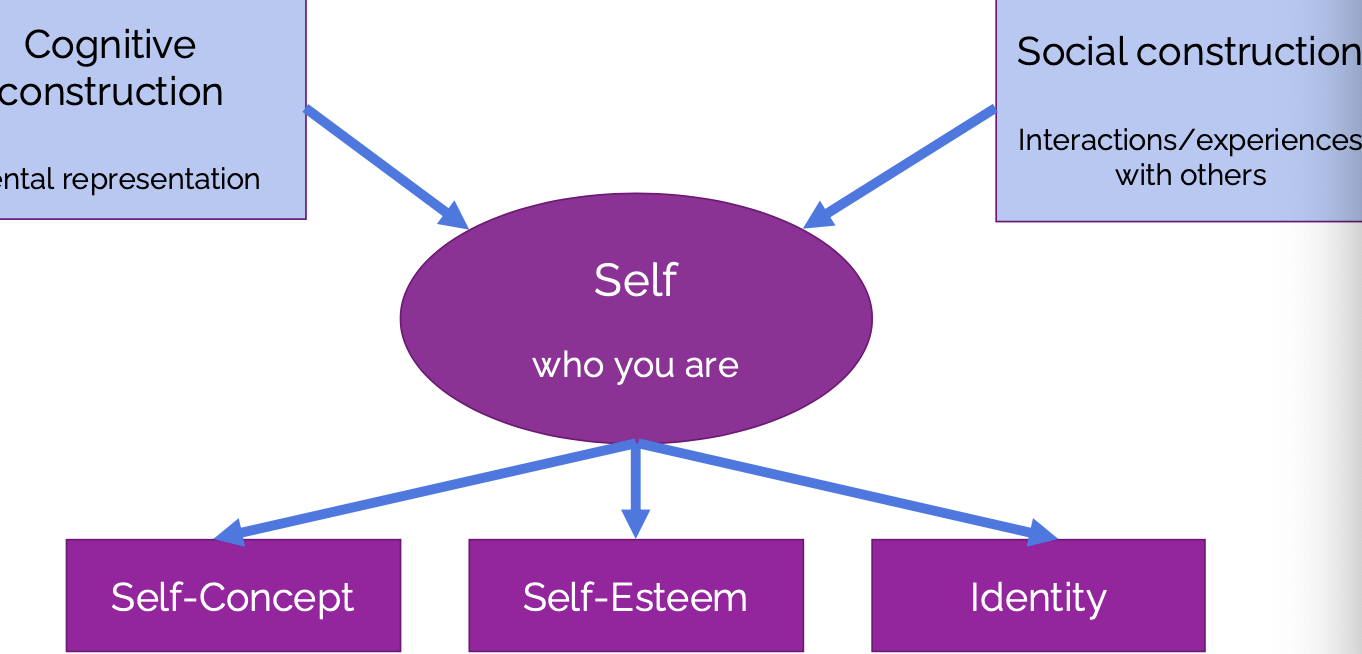
The Self (Who You Are)
Cognitive Construction: mental representation
+
Social Construction: interactions/experiences with others
= Self
which leads to….
Self Concept
Self Esteem
Identity
Self-Concept During Infancy
~18 months
Pass rouge test
Before 18 months kids with dots on their nose will look at themselves in mirror and will rub the mirror to get the dot off them, but kids around 18 understand they are the ones with the dot on their nose and they are the person in the mirror
~2 years:
Recognize self in pictures;
Label self using own name/“me”
Use category labels for self (“categorical self”)
Self Concept During Early Childhood
Can describe self
Focus on concrete, observable, stable characteristics/features
e.g. I have brown hair, you have 10 fingers
Unrealistically positive sense of self concept
E.g. I can be Simone biles
Self Concept During Middle Childhood
More integrated; begin to refer to global characteristics
E..g I’m creative, i’m not good at sports, not just I have or you have
More realistic and balanced
Linked to actual competencies/evaluation
How am I doing compared to other people
Social comparisons
Self Concept During Adolescence
Nuanced view of self
Understand role of situations, context, and perspective
My parents see me this way, my friends see me this way
More abstract and psychological/internal
Begin to think about the future; possible selves
Begin to develop coherent/integrated self
Stress around this
Self Concept During Adolescence Part 2
False self behaviour: intentionally presents a false impression to others
Least likely to do this with their friends, most likely with parents
Personal fable: belief that one’s own experience is unique and novel
Imaginary audience: the belief that everyone else is focused on you
Influences on Self-Concept
Cognitive Development
Perspective taking, abstract thinking
Parents
Warmth & Support
Family narratives (stories)
Peers
Culture
Individualistic vs collectivist
Neurodivergence
Autistic individuals → Less focus on self as seen through others; less focus on possible selves
Organization vs Abstraction Self Descriptions (European America vs Chinese)
Private vs Collective
Specific vs Abstract
Organization
Private descriptors more common in euro america
Collective descriptors more common in chinese cultures
Public descriptors second most common across the board
Everyone from all cultures are doing pretty similar on all of this though, but think in terms of relativity of who uses it more
Abstraction
Chinese Culture: Specific abstraction is much more common
European America: Specific is ALSO used more
BUT Abstract abstraction is used more commonly in European America than China
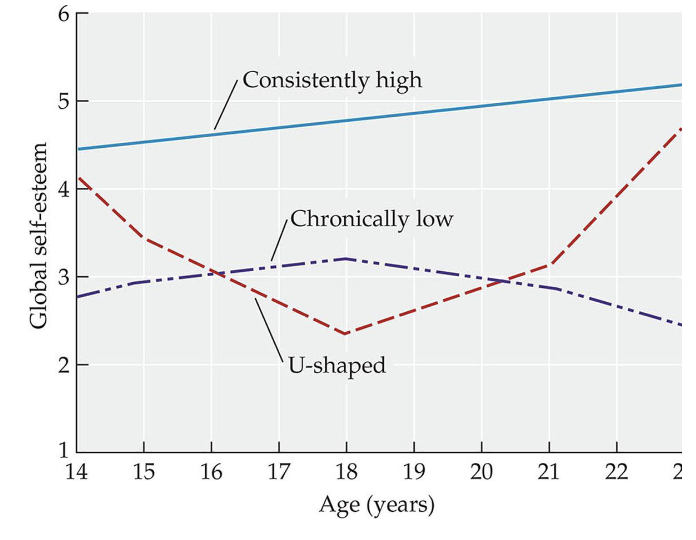
Self Esteem
Starts high, decline through childhood
Overall, seems to increase beginning in mid-adolescence
But lots of individual differences?
10 percent of individuals has a U shape trajectory of self esteem
Influences on Self-Esteem
Gender
Higher for cisgender boys than girls
For transgender youth –> importance of gender-affirming care
Culture
Different meanings of self esteem
Fairly consistent small increase in self esteem across cultures
Even pertaining to boys to girls, even with countries with strong/weak gender roles
Individualistic cultures: individuals accomplishments
Collectivistic volutes: self esteem from community
Race
Black ppl have higher self esteem then bi/multiracial, then latino, then asian american
Approval of others –> parents. peers, teachers
Societal standards
Physical attractiveness
Strongest predictor of your overall self esteem is how good you feel about your physical appearance, stronger for girls
Impact of Self-Esteem
High self-esteem → better in school, better well-being
Low self-esteem → emotional and behavioural problems
Self-Esteem Movement: programs designed to boost self-esteem in order to boost
academic performance/well-beingNot effective!
Identity
A description or definition of the self; a theory of oneself
The extent to which individuals feel secure about who they are, who they were, who they can become
Ethnic racial socialization
where children learn about the values, attitudes, behaviours, and perceptions associated with race/ethnicity
Influences on ERI (Sladek et al details)
“So, like, it’s all a mix of one”: Intersecting contexts of adolescents’ ethnic-racial socialization
• Qualitative study → focus group interviews with teenagers
• Asked about how they experienced and learned about their ethnic-racial background
Influences on ERI (Sladek et al) RESULTS
Learning about ERI through family → in connection with community, peers, media, school
Learning about ERI from peers in context of school, community; from media in the context of school
Teens discussed ERI development occurring within systems of racism/oppression
ERI comes from these broader systems and levels
Ethnic-racial identification
How someone labels their race and/or ethnicity
labeling and knowledge seems to develop in childhood
Ethnic racial Identity
A persons thoughts and feelings about their race and ethnicity and the process of developing those thoughts and feelings
Questions of identity seem to be heightened in adolescence
ERI Development in Multiracial Youth?
May be particularly challenging!
More likely to report ERI exploration, but less affirmation/positive ERI, less ERI centrality
Parents may not have experience with all aspects of a child’s ERI; may have different attitudes in socializing multiracial children
May experience racial/ethnic invalidation
May be more fluid, changing over situations and time
May gain asset of learning to be reflective about identity
May carry assets: reflection on identity; flexible thinking?
Cognitive benefits
Limited research!
ERI Development in White Youth?
White youth tend to discuss ERI as less important to their identity, and white parents engage in less ERI socialization
White youth also tend to report less positive ERI → less exploration, affirmation, centrality
Researchers have raised questions about the impact of “positive” and “negative” ERI in white youth
need to consider other dimensions of ERI (ie, “white guilt”, racial consciousness)
More pride about whiteness is correlated with less positive feelings towards other race
LIMITED RESEARCH
ERI Development Outside of North American Contexts?
Social stratification exists across societies!
Which domains distinguish access to power/resources/etc. can vary → race, migration status, language, religion, skin colour, etc.
Should ERi be taught in school?
Identity Project Curriculum
8 week program developed for teachers
Shows positive results
1 year later = kids are doing better in self esteem, grades, less depressive symptoms
this applies to kids from all races
ERI Development in Context
The ethnic-racial context we grow up in matters!
How homogenous/heterogenous schools and communities are…
Outside of North American
Social stratification exists across societies!
Which domains distinguish access to power/resources/etc. can vary → race, migration status, language, religion, skin colour, etc.
Identity pt 2 Erikson
Erikson: adolescence a crisis of identity vs role confusion
Suggests the need/concept of:
Psychosocial moratorium: time in which individuals are free from excessive obligations and can experiment with different roles
Not everyone experiences this because its a privilege to be able to have the space and time to explore this
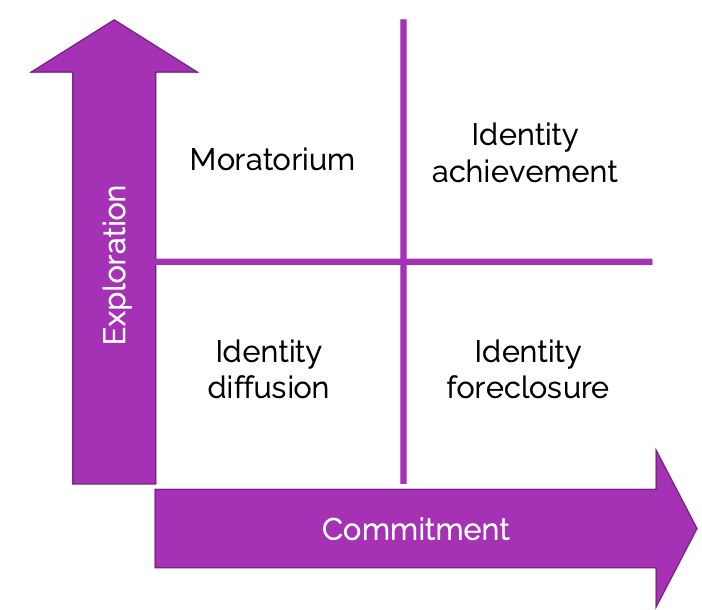
Identity Status (James Marcia)
James Marcia: need to consider both exploration (Y) and commitment (X)
Have you tested out, tried out different ways of being to see who you are?
Have you committed to who you are, do you have a sense of your identity/how you define yourself?
4 Different Identity States: Moratorium, diffusion, achievement, foreclosure
Often a continuous process! It is common to move between statuses multiple times
Across the lifespan too
A lot of movement between moratorium and identity achievement
Identity Diffusion
Most common early in Adolescence (which is ok)
If identity confusion continues later on then:
Associated with higher levels of behavioural and emotional problems, difficulties with relationships
More likely to report low levels of parental warmth/support
Identity Foreclosure
More common in early adolescence
Committed on who they are, yet haven’t tested it out to see if this is who you are
e.g. becoming a doctor, mother
Outcomes:
Tend to show low anxiety and general life satisfaction
Associated with higher levels of prejudice, inflexibility, need for social approval, lower sense of autonomy
More common with controlling or overly protective parents
Identity Moratorium
Most common for 17-19 year olds
Where you are searching to find out who you are
e.g. joining clubs, changing majors
If moratorium persists later in life:
Can be associated with high levels of anxiety, conflict with authority
Correlates may depend on the length of exploration, and amount of rumination about exploration
Identity Achievement
More common in young adulthood
“Ive taken these courses and classes and know what I want to do”
Outcomes:
Associated with high achievement, maturity, intimacy
Agency → a sense of control and responsibility for one’s own actions
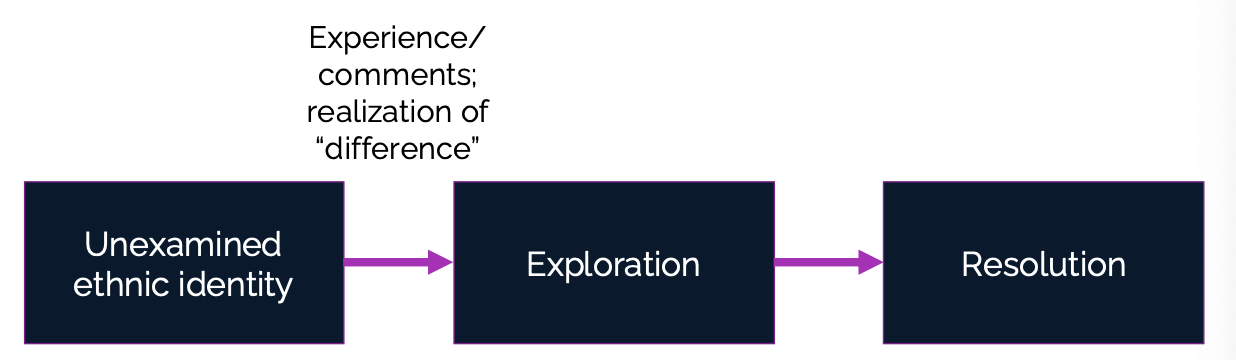
Ethnic-Racial Identity Process
Unexamined ethnic identity: Starts as what does it mean to be this race?
Exploration: Then we begin to think about learning about our heritage and talking with others of a similar heritage
Realization of “difference”
Testing things out
Resolution: integrated into our sense of self
Ethnic-Racial Identity Context
Affirmation (private regard): how good/bad a person feels about being part of their ethnic/racial group
Tends to be a protective factor
Public regard: how positively a person believes other people view their ethnic/racial group
Centrality: how important a person’s ethnic/racial group is to their identity
High centrality may make you more vulnerable to facing stereotypes and discrimination
Salience: how important a person feels their ethnic/racial group is to a particular situation
Bottom 3: Affirmation may depend on other aspects of ERI, like if you have a high public regard and centrality and salient
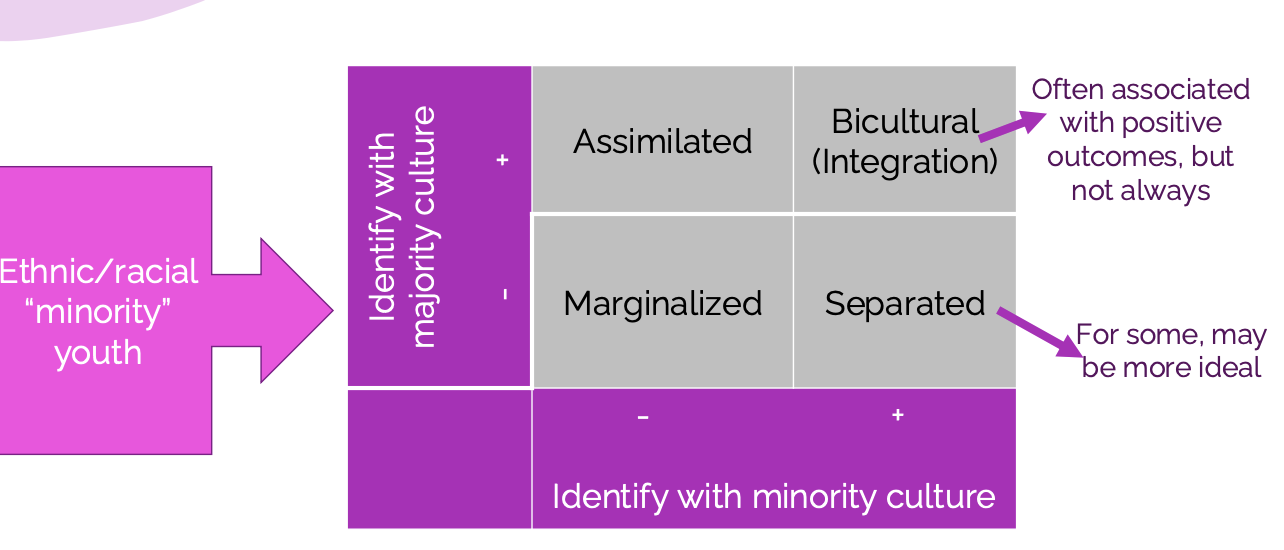
Berry’s Model of Acculturation; Galan’s Multidimensional Model (Ethnic Racial Identity)
minority youth and their indemnity with the majority culture
assimilation
marginalized
bicultural (integration)
associated with positive outcomes, but not always
separated
For some, may be more ideal
Especially for indigenous youth because dominant Canadian culture tries to erase your culture/heritage
In adolescents and young adults, positive ERI tends to be associated with….
Lower levels of depressive symptoms
Higher self-esteem
Positive academic outcomes
Protection in the face of discrimination
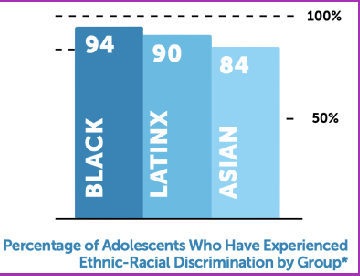
Discrimination is pervasive for youth from ethnic-racial minorities/marginalized groups
Linked to less ideal adjustment –> mental health, academic, social, etc.
Discrimination —> Maladjustment
BUT, a strong ERI may be protective
Discrimination -/→ Maladjustment
ERI in the middle, blocking the two
Influences on ERI/ Developing a positive ERI
Ethnic racial socialization: where children learn about the values, attitudes, behaviours, and perceptions associated with race/ethnicity
Much more common in marginalized groups
The “talk” in black families with their kids about police
Common themes:
Understanding/valuing ones’ culture
Dealing with racism
Succeeding in mainstream society