Perioperative Nursing
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Perioperative Care
Provided before, during, and after surgery
Three phases:
Preoperative phase
Intraoperative phase
Postoperative phase
Preoperative phase
starts when the patient and surgeon mutually decide surgery is needed and ends with the patient is transferred to the operating room (OR).
Intraoperative phase
begins when the patient is transferred to the OR bed and ends when the patient is transferred to the post anesthesia care unit (PACU).
Postoperative phase
starts with admission to PACU or recovery area ands ends with recovery from surgery and last post op appointment with the surgeon.
Surgery is classified based on..
Urgency
Degree of risk
Purpose
Based on Urgency
Elective: surgery is preplanned and based on choice and availability.This surgery is non-urgent.
Examples: Tonsillectomy, hernia repair, scar revision, hip prosthesis
Urgent: must be done within a short time frame for patient health but is not emergent.
Examples: colon resection, amputation, removal of gallbladder,
Emergency: must be done immediately to preserve a patient’s life, body part, or function.
Examples: trauma, tracheostomy, control of hemorrhage
Based on Degree of risk
Major
May require hospitalization and has a higher degree of risk
Minor
Usually in outpatient setting
Surgery based on Purpose
Diagnostic
Ablative
Palliative
Reconstruction
Transplantation
Constructive
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is used to make uncomfortable intervention tolerable and safe.
Types:
General
Moderate Sedation/Analgesia
Regional Sedation
Topical and Local
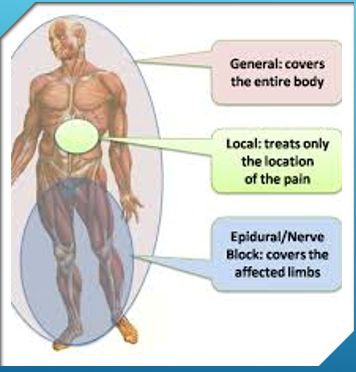
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia is typically Intravenous and inhalation of anesthetics.
General anesthesia goal is to have loss of consciousness, analgesia, relaxed muscles and depressed reflexes.
Risks: respiratory depression, N/V, thermoregulation.
Can be used at any age.
Children and young adults wake up more aggressive.
Three Phases of General Anesthesia
Induction
Maintenance
Emergence
Moderate Sedation
Used for short term and minimally sedation.
The patient can still respond to verbal commands and maintains cardiorespiratory function.
IV administration
Regional Anesthesia
When anesthetic agent is injected near a nerve or nerve pathway.
Inhibits transmission of sensory stimuli.
Patient awake but loses sensation in that area.
Can use major nerve blocks, spinal block, caudal, or epidural.
Regional is also helpful in reducing risks of general anesthesia for post surgical pain, bowel dysfunction, and hospital stay.
Topical
Injection of local anesthetics such as lidocaine and bupivacaine.
Loss of feeling or sensation where topical anesthesia is applied.
Examples: used for tissue biopsy
Epinephrine may be mixed to stop bleeding.
Can also be used during general anesthesia procedures.
Informed Consent
A informed consent must be signed, dated and timed before surgery.
Is a legal document.
Informed consent is patient voluntary agreement to undergo surgery/procedure.
Informed consent should have: description of procedure, disease process, person performing procedure, risks, patient right to refuse, and expected outcomes.
Advanced Directive
Advances directive is a legal document that allows patient to specify health care treatment they wish to have when unable to communicate.
Common forms are living wills and durable power of attorney.
Important to know and document if patient wishes to be a DNR before surgery.
Preoperative Assessment
Health History – assess medical history, risk factors, and developmental considerations, physical and psychosocial status.
Developmental – younger and older are at greater risk.
Physical – assess patient for cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases , kidney and liver diseases, endocrine diseases.
Surgical history – assess previous surgical complications
Nutrition Status – a malnourished patient is at risk of delay wound healing and infection.