computer science - networks
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
networks
group of computer systems and hardware linked together
LAN
Local Network Area
covers a local area
based on Ethernet - set of protocols for exchanging data
devices can use a single Internet connection, share files with one another, print to shared printers, and be accessed and even controlled by one another
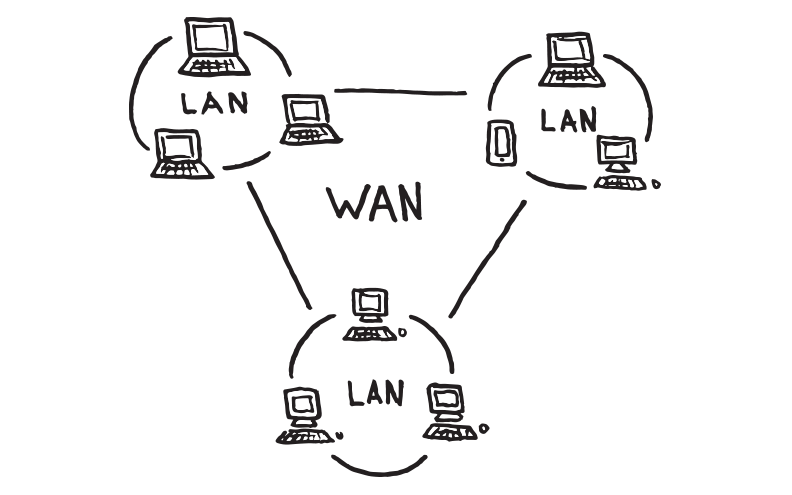
WAN
Wide Area Network
covers an area composed of LANs
popular WAN is Internet
enables a user or organization to connect with the world very easily and allows to exchange data and do business at global level
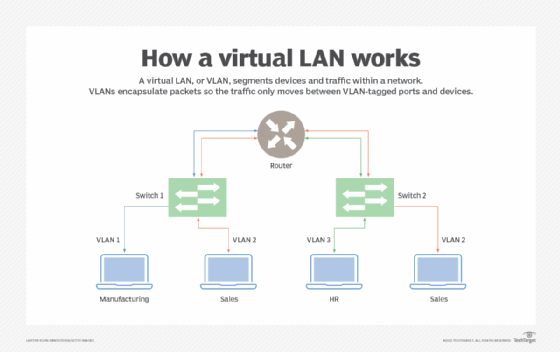
VLAN
Virtual Local Area Network
a logical group of workstations, servers, network devices (same as LAN)
creates a stimulated environment
improves performance
tightens security
eases administration
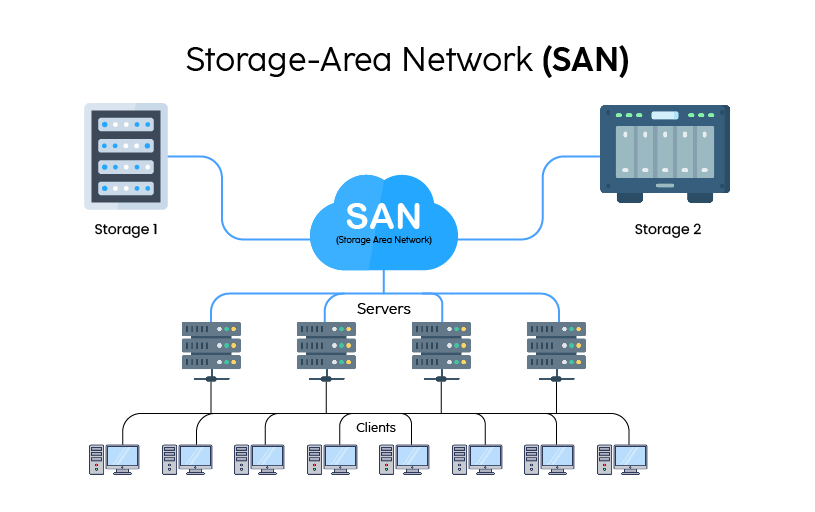
SAN
Storage Area Network
secures high-speed data transfer network
accessible to multiple servers
appear as attached drives
introduces networking flexibility that enables one server, or many heterogeneous servers across multiple data centers, to share a common storage utility
WLAN
Wireless Local Area Network
wireless method of distributing data between devices
allows users to move around
often called Wi-Fi network (can include other)
increases productivity and provide convenience

Internet
globally connected network system
Extranet
controlled private network
a private part of a website
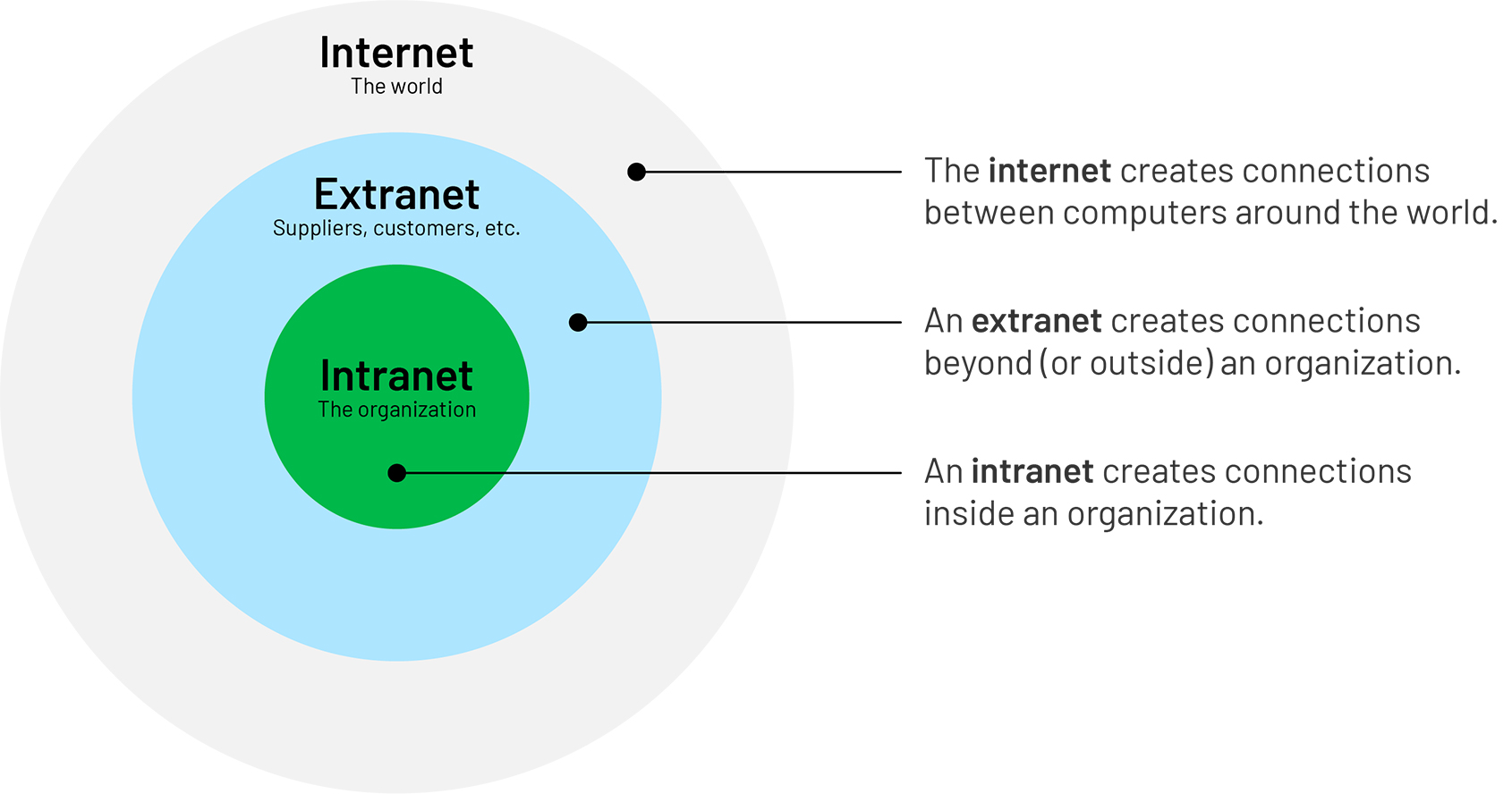
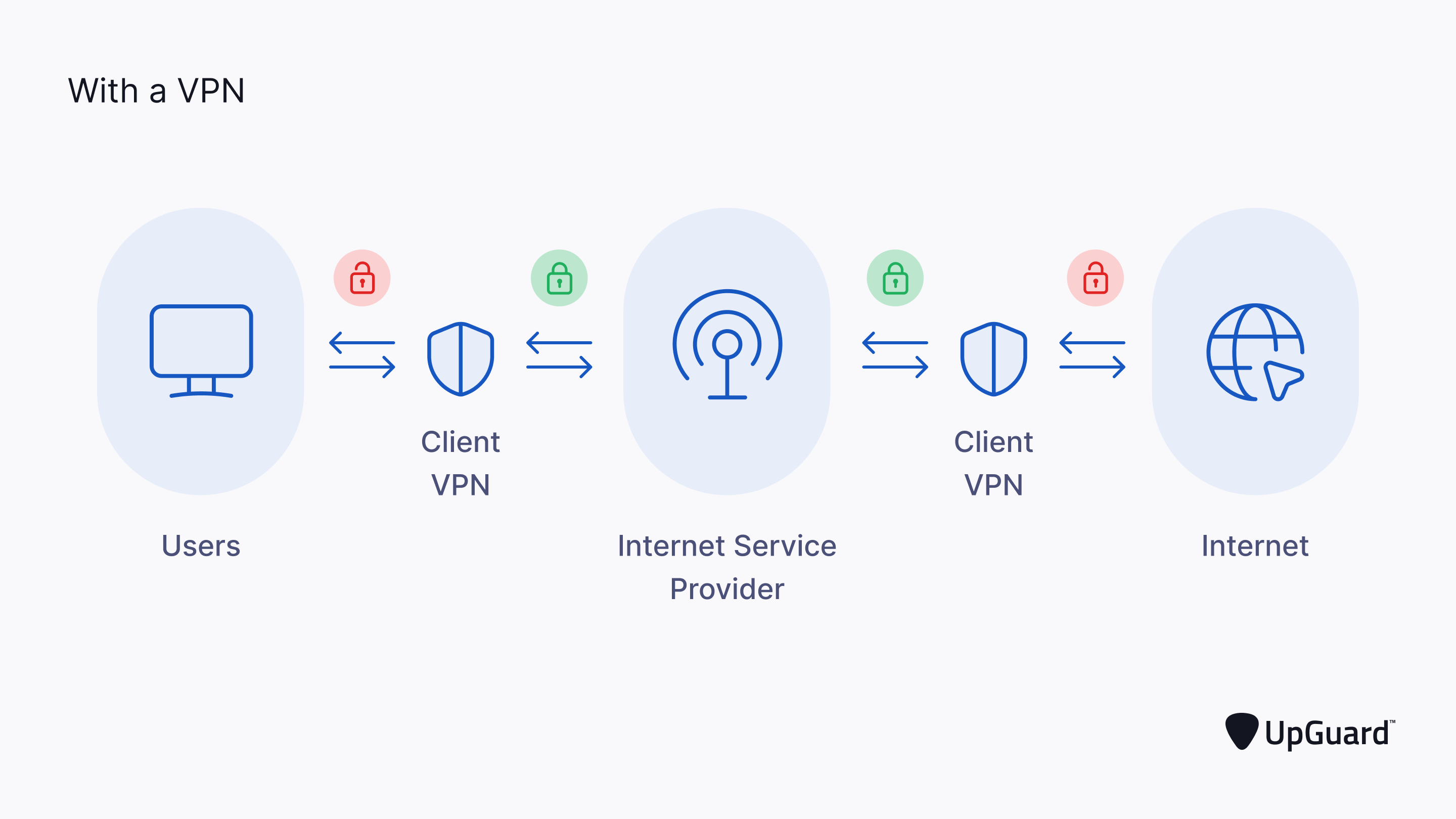
VPN
Virtual Private Network
allows establishment of an encrypted remote connection between two computers or networks
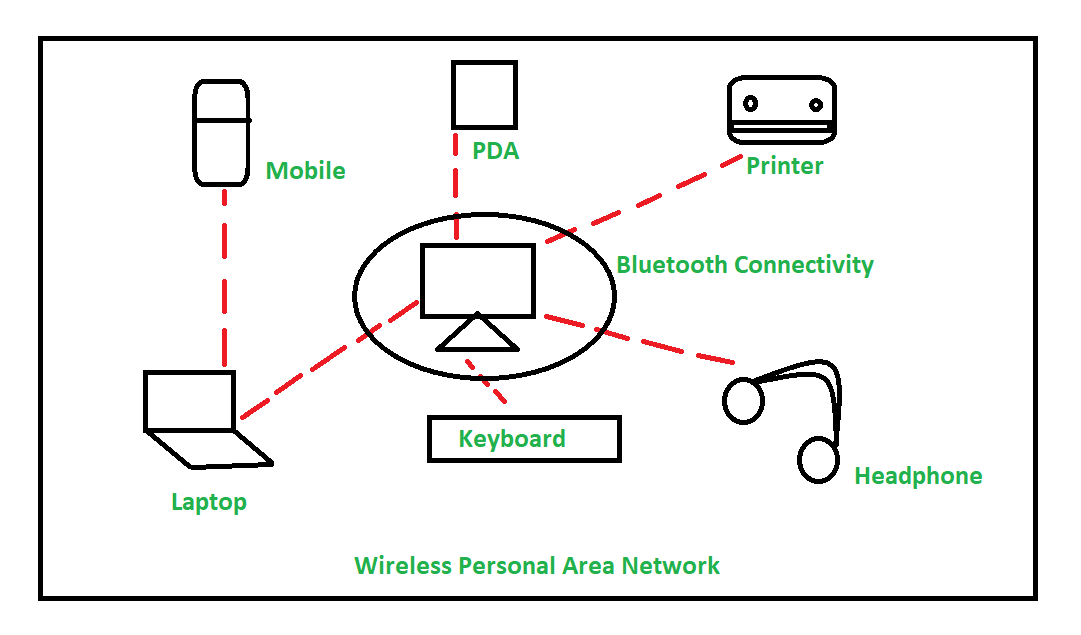
PAN
Personal Area Network
covers a very small area
examples: Bluetooth, USB
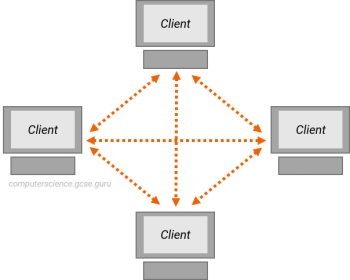
P2P
Peer-to-Peer
network model in which exchange of files happens
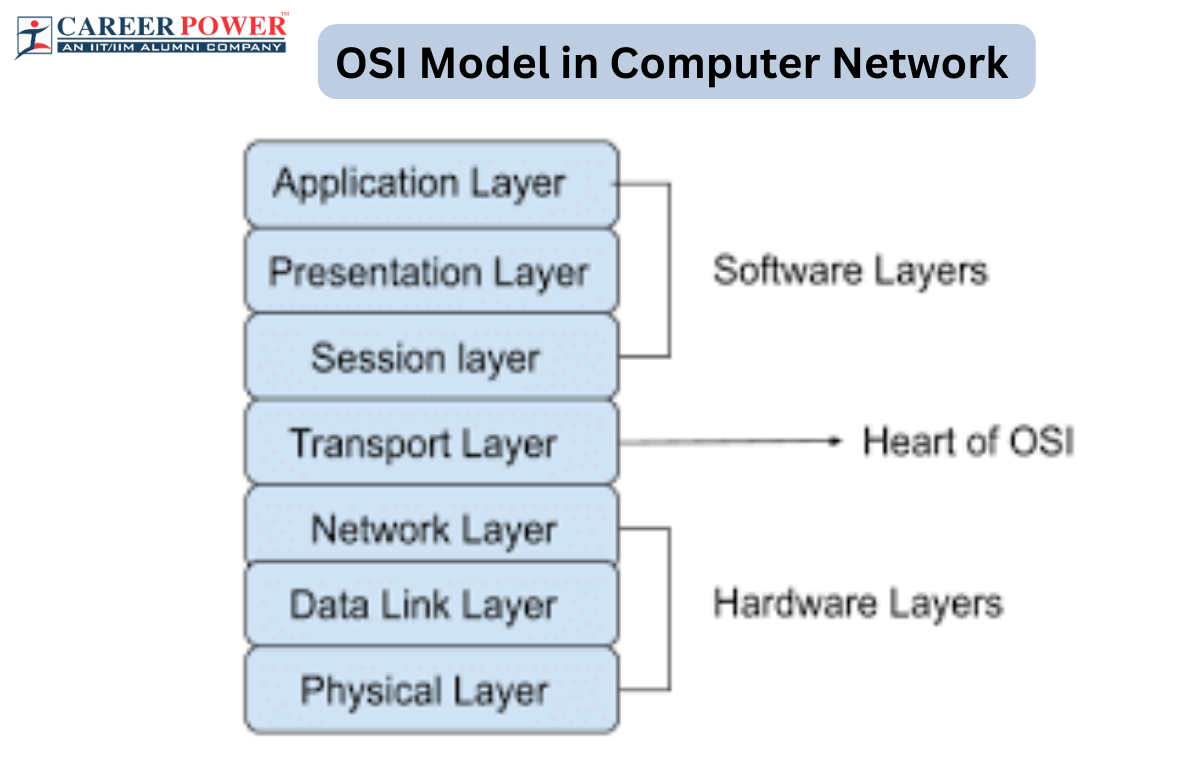
OSI model for communication over networks
» Open Systems Interconnection (theoretical)
physical layer - transmitting and receiving raw bitstream over a physical medium
data link layer - reliable transfer of data on a network (responsible for errors)
network layer - routing data between networks
transport layer - communication between applications on different hosts
session layer - manages the dialogue between applications
application layer - provides application services to users
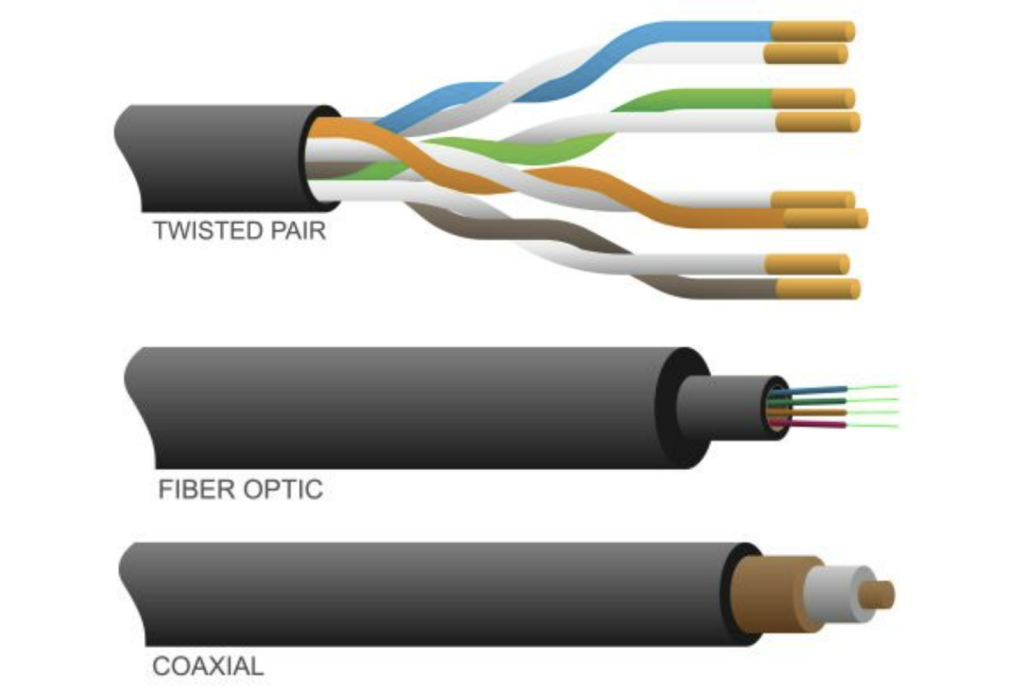
transmission media
» UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
secure
quite reliable
low cost per meter
speed: 100Mbps - 1Gbps
» fiber-optic
very secure
not reliable
costly per meter
speed: 5-100G
» radio waves
very unsecure
quite reliable
free
speed: 5-200Mbps
wireless networks
» Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity)
used in laptops
slow data transmission
backwards compatible
small transmitting radius
» WiMAX
large distance
high speed internet access
cheap
» 3G (Third Generation)
fast
primary way for mobile phones