Lecture 4: Hemorrhagic strokes and non-traumatic intracerebral hemorrhage
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
-sudden
-symptoms worsen in a short period of time
is the onset of intracerebral hemorrhage sudden or gradual?
-severe HA
-seizure
-alteration of consciousness
-increased intracranial pressure
symptoms of intracerebral hemorrhage:
-increased ICP--->intracerebral hemorrhage
blown pupils is a sign of
herniation
how come intracerebral hemorrhage can be rapidly fatal?
-hemorrhagic stroke deficits may worsen within minutes to hours
How do you differentiate an ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke?
-sudden onset, focal deficit
-HA often present
clinical features of hemorrhagic stroke:
-neuro exam
-Head CT without contrast
-lumbar puncture
-assess GP
how should you evaluate a potential hemorrhagic stroke?
high blood pressure
what is the major risk factor for primary hemorrhagic stroke?
anticoagulants, or lytics like r-tPA
what should you NOT treat a pt with a hemorrhagic stroke with?
keep blood pressure lower than for ischemic stroke (160s/mid 80s)
in treating a hemorrhagic stroke, what blood pressure should you try to maintain
neurological decompression
treatment for hemorrhagic stroke if there is an abrupt increase in pressure and worsening condition
-loss of consciousness with focal findings
-"worst head ache of life"
-subarachnoid bleeding
clinical features of an intracerebral aneurysm
Thunderclap headache
classic HA associated with intracerebral aneurysm
breathing irregularities, pupillary abnormalities (dilated/fixed), extraocular movement abnormalities
if an intracerebral aneurysm results in increased ICP, what symptoms may manifest?
subarachnoid hemorrhage on CT
White blood in cisterns and 4th ventricle
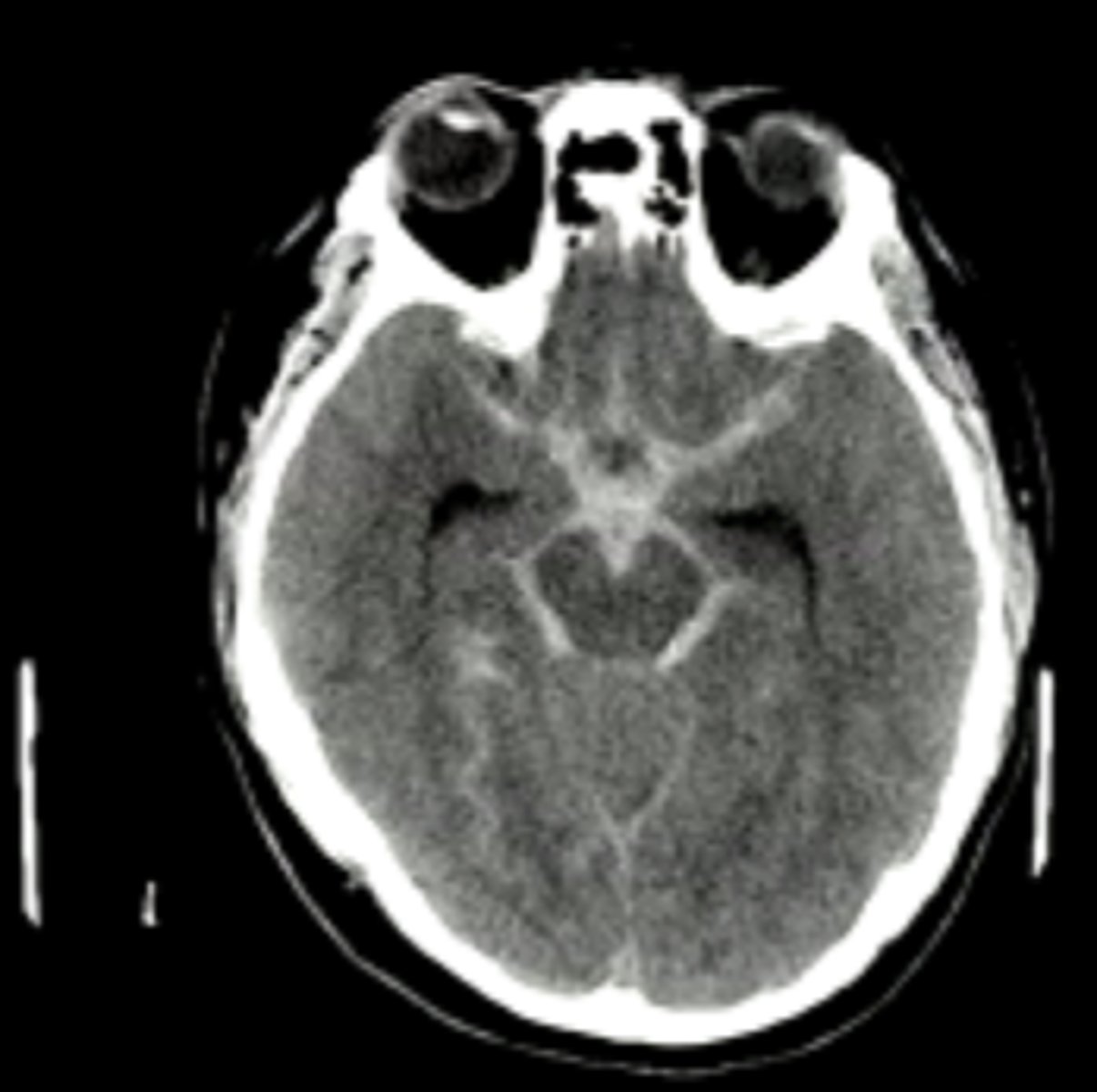
-CT without contrast
-if CT negative, lumbar puncture
-angiography may locate aneurysms >5 mm
how do you evaluate /work up a suspected intracerebral aneurysm?
aneurysm on angiogram
ID pathology
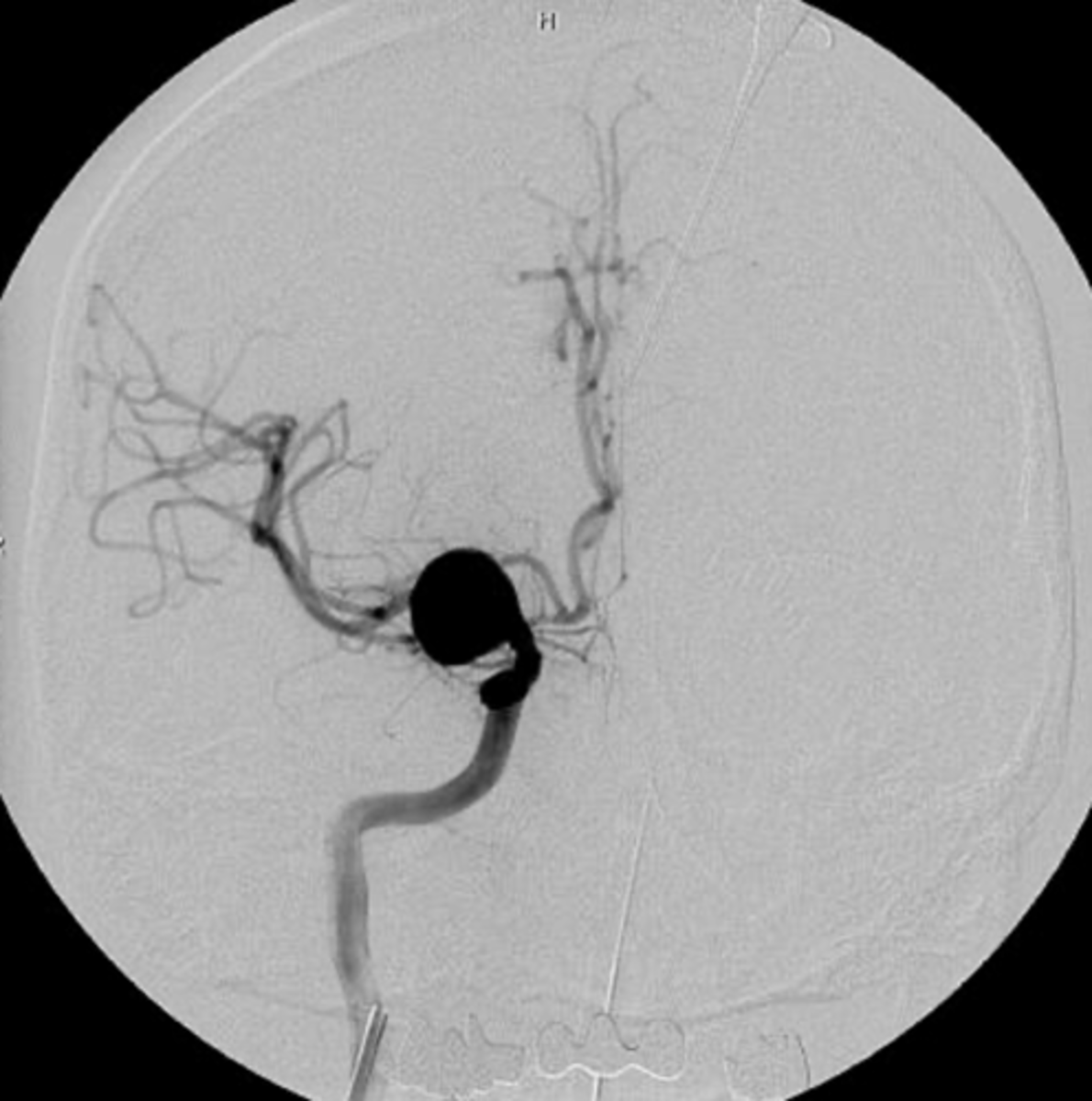
-neurosurgical aneurysm clipping or coiling for bleeding aneurysm
-seizure prevention
-medications to prevent arterial spasm
how do you treat an intracerebral aneurysm?
intubation, blood pressure monitoring and stabilization
supportive therapy recommended for intracerebral aneurysm
when the aneurysm is greater than 8mm in diameter
for an asymptomatic aneurysm, at what point do you treat with a clip or coil/
berry aneurysm
what type of aneurysm is associated with polycystic kidney disease?
berry aneurysm
-located in the circle of willis
-size varies from 2-25 mm
-usually multiple
-saccular
sudden subarachnoid hemorrhage or ICH without SAH
ruptured berry aneurysm casues
-anterior communicating artery most common
-typically at weak points of circle of willis
where do berry aneurysms most commonly occur?
Charcot-Bouchard aneurysms
what type of aneurysm?
-associated with chronic hypertension
-commonly occur in arterioles in basal ganglia, thalamus, brainstem
-when small arterioles rupture, causes a hemorrhagic stroke
charcot-bouchard pseudo-aneurysm
charcot bouchard aneurysm that is usually less than 1 mm diameter
arterial dissection
-most commonly in middle aged patients
-may be spontaneous or traumatic
can occur in any of the cerebral vessels, but carotid most common
in what artery is an arterial dissection most common?
subarachnoid hemorrhage
intracerebral dissections are associated with
arterial dissection
clinically associated with pain, headache, focal euro deficits and HORNER SYNDROME
angiogram, CTA, MRA, lumbar puncture showing blood
what can be used to diagnose an arterial dissection?
heparin, transition to coumadin
what is the initial treatment for an arterial dissection?
arterial bypass; vein grafting close to intimal flap
how do you treat an arterial dissection with persistent embolization?
-clip the involved portion of the vessel
-intra arterial balloons and grafts
-reverse flow through vertebral artery
how do you treat a vertebrobasilar and intracranial dissection?
cavernous hemangioma
venous angioma
vein-vein malformations result in
higher pressure
why are arterial malformations more likely to bleed?
seizures, HA, intracerebral hemorrhage
clinical features of vascular malformations
usually no treatment-- low risk for major bleed
how do you treat cavernous hemangiomas?
usually monitor-- low risk for major bleed
how do you treat venous angiomas?
small AVMs are more dangerous than large
what is the most dangerous type of AV malformation?
embolization, radiation, and resection
how do you treat AVMs?
-recurrent lobar hemorrhages
-petechial lobar hemorrhages
clinical features of amyloid angiopathy:
-cerebral biopsy stained for amyloid
how do you diagnose amyloid angioathy?
-no available treatment-- prognosis is grim, patients will continue to have recurrent hemorrhages
-avoid anticoagulants and anti-platelet agents that could expand hemorrhages
how do you treat amyloid angiopathy?
hemorrhagic brain tumors
-glioblastoma
-primary CNS lymphoma
-melanoma
-renal cell carcinoma
bronchogenic carcinoma
what cancer is less likely to hemorrhage but more likely to metastasize/