Aquatic Biomes: Marine
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
these are ocean ridges formed by marine invertebrates living in warm shallow waters within the photic zone of the ocean
among the most biologically diverse and economically important ecosystems
foundation for many marine species
grow in shallow clear water
coral reefs
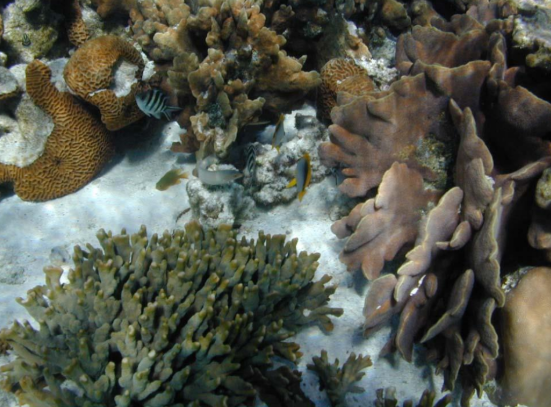

posses zooxanthellae
are reef builders
Hermatypic corals

no zooxanthellae
rely on tentacular feeding
can live in aphotic zone
Ahermatypic corals
what is an example of hermatypic coral?
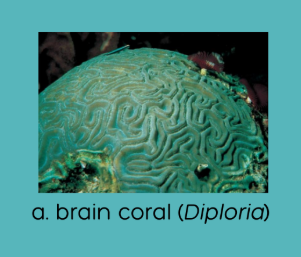
what is an example of non-hermatypic coral?

hawaiian coral zonation: high light levels, moderate wave energy
0m
cauliflower coral (Pocillopora meandrina)

hawaiian coral zonation: moderate light level, occasional storm wave energy
6m
Lobe coral (Porites lobata)

hawaiian coral zonation: low light level, low wave energy
13 m
Finger coral (Porites compressa)

hawaiian coral zonation: very low light, primarily downwelling, no wave energy
25 m
Plate coral (Porites rus)

what are the types of reef?
fringing, barrier, atoll, drowned



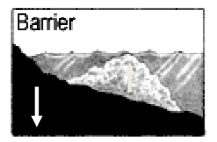

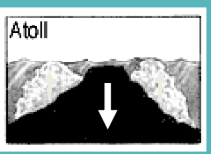
growth on reefs are often limited by tidal action
fringe reef


The great barrier reef
volcanic left-overs
atoll reefs

atoll reef fulanga
what are the environmental factors affecting corals?
water motion
depth: photic vs aphotic zone and water motion
sedimentation
salinity: 32-35 ppt
temperature: 18-32 0C
tidal fluctuations
nutrients: eutrophic vs. oligotrophic
the largest marine biome with relatively uniform chemical composition
the physical diversity of the ocean is a significant influence on plants, animals, and other organisms
open ocean
the ocean is categorized into different zones based on how far light reaches into the water. Each zone has a distinct group of species adapted to the biotic and abiotic conditions particular to that zone
submerged area of continents
Continental margin
the continental margin includes?
continental shelf
continental slope
continental rise
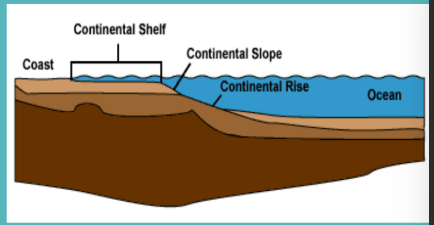
(flat gradually sloping seafloor) from shoreline to ~200m; end shelf is called the shelf break
continental shelf
(steeply sloping seafloor) seaward of shelf break
continental slope
(moderately sloping seafloor) seaweed of slope
continental rise
one simple ocean zone classification is between the water and the ocean floor
the water is referred to as the?
pelagic zone
one simple ocean zone classification is between the water and the ocean floor
the ocean floor is referred to as the?
Benthic zone
in the pelagic zone the organisms that swim through the water column are known as?
Nekton

in the benthic zone what are the organisms that live here
organisms that live here are benthic organisms or benthos

what are the benthic zone divisions? (seafloor zones)
supralittoral
littoral
sublittoral
Bathyl
Abyssal
Hadal
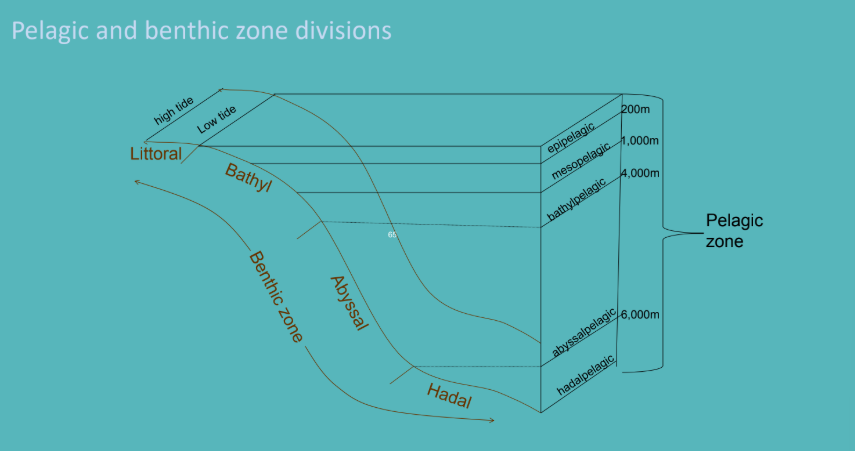
shore above high tide
Supralittoral
the intertidal zone (sometimes submerged and sometimes above water)
Littoral
Epipelagic (0-200m)
seafloor of the continental shelf (from low tide to the shelf break)
Sublittoral
Mesopelagic (200-1,000m)
seafloor of the continental slope to the deep ocean bottom
Bathyl
Bathypelagic (1,000-4,000m)
deep ocean bottom between the base of the slope and 6,000m
Abyssal
Abyssopelagic (4,000-6,000m)
the deepest zone, below 6,000m
hadal
Hadalpelagic (6,000-10,000m)
what are the differences of saltwater swamp and saltwater marsh
saltwater swamps are regions dominated with trees, whereas salt marshes are covered with grasses

what are the commonly found water species of saltwater wetland ecosystem?
amphibians
reptiles
some migratory birds
shellfishes
few fishes
are coastal wetlands that are flooded and drained by salt water brought in by the tides
they are marshy because the soil may be composed of deep mud and peat
saltwater marsh
is made of decomposing plant matter that if often several feet thick
is waterlogged, root-filled, and very spongy
peat
are a group of trees and shrubs that live in the coastal intertidal zone
Mangroves

what are the threats to marine environments
illegal and unregulated fishing
tourism and recreational activities
global trade and shipping
noise pollution
climate change and ocean acidification
overfishing and bycatch
pollution and plastic waste
habitat destruction
what continues to affect the state of the marine environment?
climate change continues to affect the state of the marine environment; oceans are continuing to acidify, sea levels are rising, and sea- surface temperatures continue to increase
what may impact marine species and ecosystems?
The state of the marine environment has impacts on marine species, habitats, ecosystems, and people. increases in sea-surface temperature, ocean acidification, and sea-level rise may impact marine species and ecosystems, coastal infrastructure and communities and sites of significance
what risks can pose to marine ecosystems?
Excess sediment and nutrients, plastics, and a non-indigenous introductions can pose risks to marine ecosystems. Changes to biodiversity and ecosystems have potential to influence connections to our marine environements