GEOL 1010- Final Ohio University
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
how much of earths water is freshwater?
2.8%
how much of our fresh water is glacier water?
2.15%
Longest, largest, and muddiest river on the earth.
the nile
What is dischagre?
Volume of water flowing past a specific point
How do we estimate discharge?
Height x Width x Speed
laminal flow
Water flows smoothly, in straight line paths with no mixing or crossing of layers
turbulent flow
Stream paths mix, cross, and form swirls in a chaotic fashion
headwaters/source
• Farthest point upstream
• Usually in the hills or mountain
mouth
• Farthest point downstream
• Usually where the stream empties into a bigger stream, lake, or the ocean
longitudinal profile
Decrease in slope of the stream as it approaches the mouth
base level
Lowest level a stream erodes
how do rocks erode?
- Removal of rock debris
- Down cutting by abrasion
- Headwater erosion
two types of streams in floodplains
meandering and braided streams
meandering stream
A single channel with a sinuous pattern and are the most common pattern on floodplains
braided stream
Interwoven network of converging and diverging channels that thread their way among numerous islands and gravel bars
cut bank
side of stream that is eroded
point bar
side of stream where minerals are deposited
drainage basin
Total land that empties water into one stream system
drainage divide
Boundary separating one drainage basin from another
identify types of drainage patterns
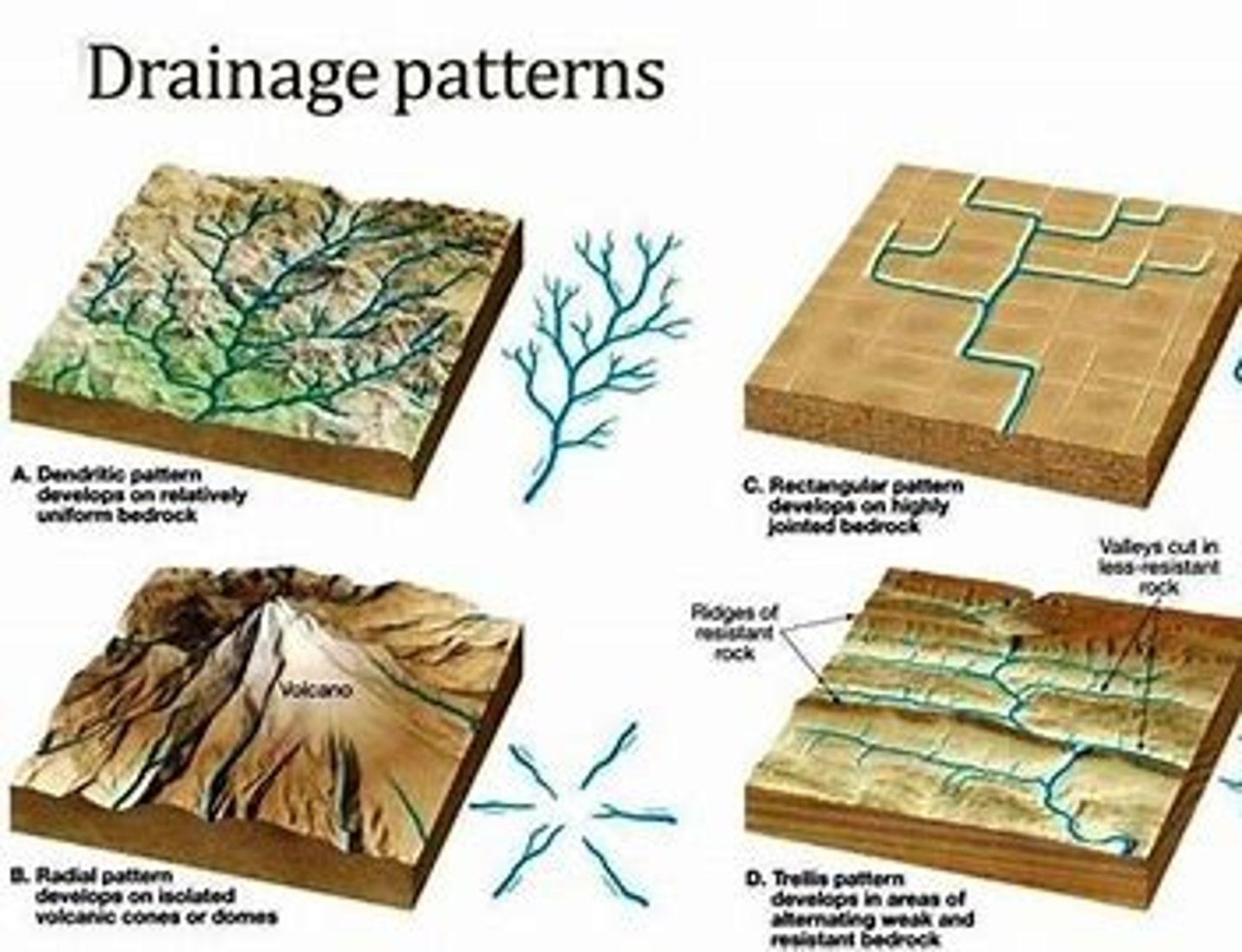
What are the different ways stream transport sediments?
- Suspended Load
- Bed Load
- Dissolved Loa
natural levee
• Ridge of coarse-grained sediment adjacent to a stream channel in a floodplain deposited during flooding events
What is a delta?
- Stream speed decreases when it reaches the ocean
- Deposits most of the sediment being transported
types of deltas
stream dominated
wave dominated
tide dominated
great flood of 1993
- Mississippi & Missouri Rivers
- 6 months of rain and floods
- 80% of levees failed
-20 million acres flooded
-15-20 billion in damages
What is an aquifer?
• Rock body or layer of sediment that easily transports and stores water
unconfined aquifers
- Aquifers with upper surfaces that coincide with the water table
confined aquifer
- Water-bearing rocks or sediments are sandwiched between impermeable layers
porosity
The volume of empty space relative to the volume of sediment particles
permeability
Measure of how well a fluid flows through a network of pores and cracks in sedimentary material
zone of aeration
Sediment is under saturated and pore spaces contains both air and water
zone of saturation
sediment has all pore space filled with water
Water Table
• Boundary between the zone of aeration and saturation
• Water wells must be below this level
aquitard
Rock body or layer of sediment that allows the transport and storage of water, but not easily
aquiclude
Rock body or layer of sediment that does not allow the transport or storage of water
Means of groundwater contamination by manmade activities
saltwater intrusion, landfill, agriculture, industrial waste, sewage
hot spring
Heated ground water rises to the surface quickly and naturally creating a pool of hot water
fumarole
Steam vent where heated groundwater is converted to steam
geysar
Cyclic and explosive emissions of super-heated groundwater
Consequences of excessive groundwater withdrawal
Surface Subsidence
commonly occurred heated groundwater systems
hot fumarole, geyser
what states use the most water per day?
California, Florida, and Texas
where do earthquakes occur?
plate boundaries
divergent boundary earthquake
- Least damaging
- Caused by tension
tranform boundary earthquake
- Intermediate damage
- Caused by shear
convergent boundary earthquake
- MOST damaging
- Caused by compression
intraplate earthquakes
- Earthquakes occurring in plate interiors
hypocenter/focus
Point on the fault where motion first occurs
epicenter
Location on the surface above the hypocenter
body waves
Seismic waves that travel through Earth's interior
Primary (P) Waves
- Travel through compression of material along travel direction
- 6-8 kilometers per second
- Travels through solids,
secondary (S) Waves
-Travel through compression of material perpendicular to the travel direction
- 4-5 kilometers per second
- Only travels through solids
surface waves
Seismic waves that travel along Earth's surface
rayleigh waves
-Contain both compressional and transverse waves
- Like ripples in water
love waves
-Contain both transverse waves that shear the surface
- Like a snake slithering
Damages caused by earthquakes
- Collapse
- Fire Damage
- Landslides
- Flood
- Tsunami
What is tsunami?
Movement of seafloor during an earthquake produces a surge of water
How do we know that outer core is liquid?
behavior of seismic waves
How many minimum numbers of stations are required to locate an epicenter?
3
non-renewable energy sources
- Resource that is being consumed faster than nature can replenish it
-coal, oil, gas
renewable energy sources
- A resource that can be used at it's current rate without exhausting the supply
- Sun, Wind, Wat
how is oil separated?
density
heat and pressure break down hydrocarbons
natural gas
- Gaseous petroleum consisting predominantly of methane
- Used for heating, cooking, and general electricity
- "Cleanest" fossil fuel
oil
- Liquid petroleum consisting of a complex mixture of liquid hydrocarbons
- Used as sources of energy (heating & gasoline) and lubricants (motor oil & grease)
oil trap
• Geologic structure that allows many reservoirs of oil and gas to collect in one area
where is petroleum stored
• Source Rock
• Reservoir Rock
• Seal
• Oil Trap
coal
most abundant fossil fuel
uranium
nuclear resource with very low abundance
types of renewable energy
- Geothermal Energy
- Water Energy '
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Biomass Ener
metallic minerals
-Minerals that have metals combined with other metals or other elements
non-metallic minerals
-Minerals that may be commercially exploited but not as a source of metal
-gypsum, halite, sulfur
abundant metals
Metals that occur commonly in Earth's crust
aluminum, iron, magnesium, titanium
scarce metals
Metals that do not occur commonly in Earth's crust
copper, zinc, chromium, gold
techniques for mineral exploration
-Geophysical
- Geochemical
- Drilling
- Remote Sensin
chemical separation
Separation based on differences in reactivity of substances
physical separation
Separation based on differences in material properties of substances
use of raw chemicals
production of fertilizers, detergents, drugs, lubricants, and batteries
hardest of all minerals
diamond, used for drilling and cutting equipment
Ore of Aluminium
bauxite
Ross Marble Quarry, Knoxville,
full of industrial materials such as stone, sand, gravel