Chapter 6 Microbiology Notes
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is a pure culture
a single strain of a species of bacteria, they are genetically identica to one another
What are 2 methods that can easily be utilized to obtain pure cultures of bacteria?
Streak method and spread plate
What is serial dilution
a procedure that can be used to enumerate bacterial cultures.
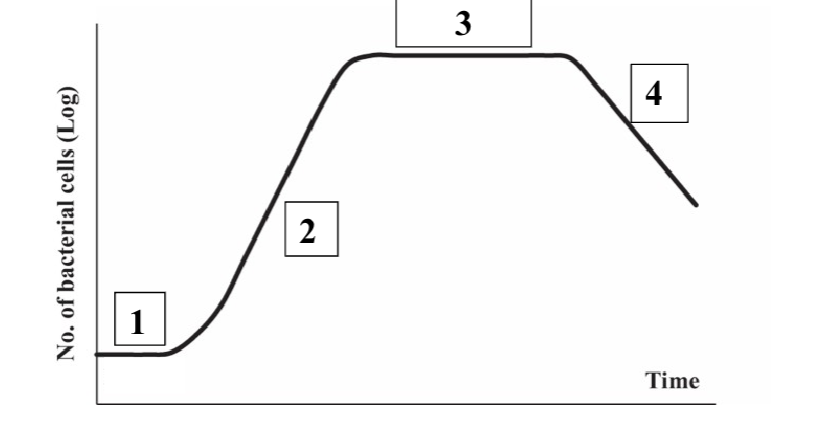
What is 1?
Lag
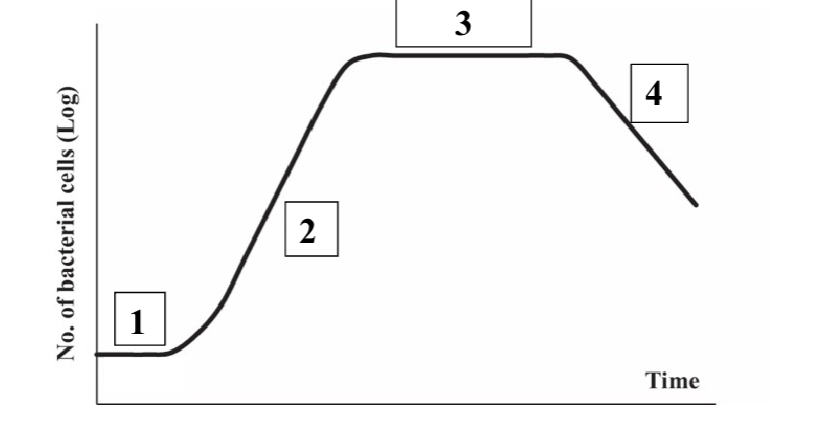
What is 2?
Log
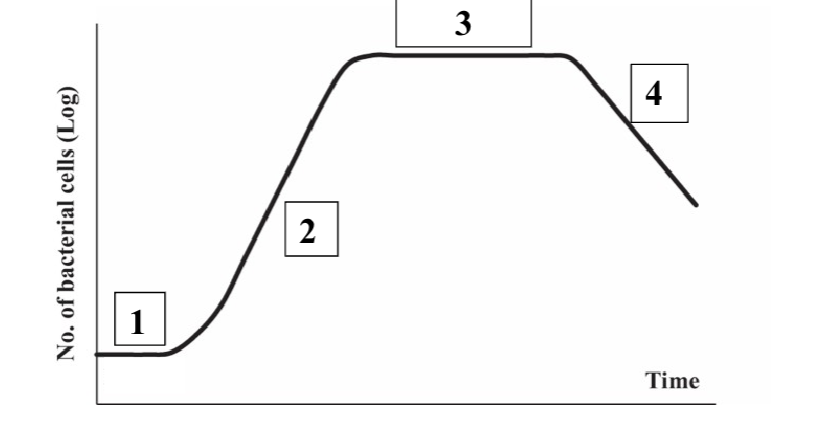
What is 3?
Stationary
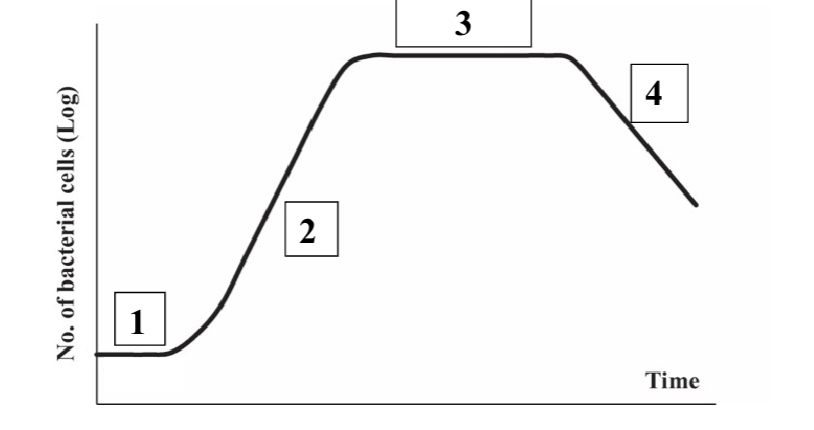
What is 4?
Death
Bacteria grows at what kind of rate?
Exponential
A growth medium in which there are ingredients included which are designed to exclude or stop growth of a certain type of organism
Selective growth medium
A growth medium that only has the bare minimum needed nutrients and ingredients to permit organisms to grow
Minimal growth medium
A nutrient-rich medium that specifically is created to help culture and grow organisms that are fastidious and difficult to culture on artificial growth media
Enriched growth medium
A growth medium that is designed to use ingredients and nutrients that a wide variety of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and fungi, are able to metabolize
General growth medium
A growth medium that distinguishes different biochemical abilities by microorganisms, by turning a different color which will define the characteristics of that organism
Differential growth medium
Carbon source:
Heterotroph and Autotroph
Heterotroph
Needs to consume already biologically fixed carbon sources
Autotroph
Can fix or make its own carbon source, typically from CO2
Energy source
Phototroph and Chemotroph
Phototroph
Energy source comes from light
Chemotroph
energy source comes from the consumption of chemical compoundsE
Electron source
Lithotroph and Organotroph
Lithotroph
electon source for energy comes from inorganic compounds
Organotroph
electron source for energy comes from organic compounds
If an organism gets its carbon from consuming previously fixed compounds and energy, and its electron source comes from organic chemicals, how would you classify this organism?
Chemoorganoheterotroph
First step of the nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen fixation
what is Nitrogen fixation?
Make N2 into NH4
What is the 2nd step in the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrification
What is nitrification?
NH4 is converted into NO3
What is the 3rd step of the nitrogen cycle?
Denitrification
What is Denitrification?
Nitrate is broken down into other nitrogen forms until it is back to N2 gas
the minimum or coldest the temp needs to be for the microbes to still grow
Minimal growth temperature
The temp at which the rate of reproduction is the fastest for that microbe
Optimal growth temperature
The max or the hottest the temp can be before the bacteria start to die due to the denaturing of proteins and enzymes
Maximum growth temperature
True or False: The optimal growth temperature is the ideal temperature for reproduction and all enzymatic activity in a cell
False
Why is it possible for organisms to stay alive if they are below their minimum growth temperature for a prolonged period, but tend to die very quickly when they are placed above their maximum growth temperature?
When cells are placed below their minimum, their metabolism and biological enzymes essentially freeze. Still, the shape and structure of the cells may be maintained, so when cells are brought back to their optimal range, growth may continue. When cells are placed above their maximum for too long, proteins and enzymes, and cell structures denature, and this is a permanent conformational change, and it cannot be fixed so the cell dies
Acidophile
an organism that thrives at a pH of 2-3
Neutrophile
an organism that thrives in a pH of around 7 and cannot withstand major shifts in either acidic or basic direction
Alkalophile
and organism that thrives in a pH of 10-11
Aerotolerant Anerobe
Does not utilize oxygen at all for any metabolic process, relies exclusively on fermentation to obtain energy, but is also not killed by reactive oxygen molecules
Obligate aerobe
Requires oxygen to be present in order to survive
Obligate anergobe
Requires the absence of oxygen in order to survive - O2 is toxic to these organisms
Facultative anaerobe
Grows the fastest and most abundantly with oxygen present; however, has other energy-deriving pathways that does not use oxygen, and so it can still grow with little to no oxygen present M
Microaerophile
Requires oxygen to be present, but not at atmospheric levels, too much oxygen is toxic to them, but they cannot survive in anoxic conditions either
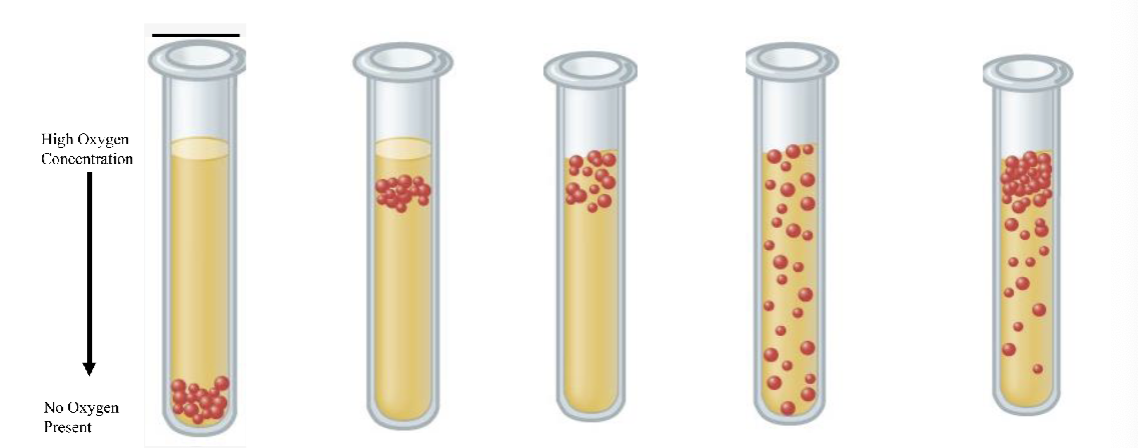
What is the first test tube
Obligate anaerobe
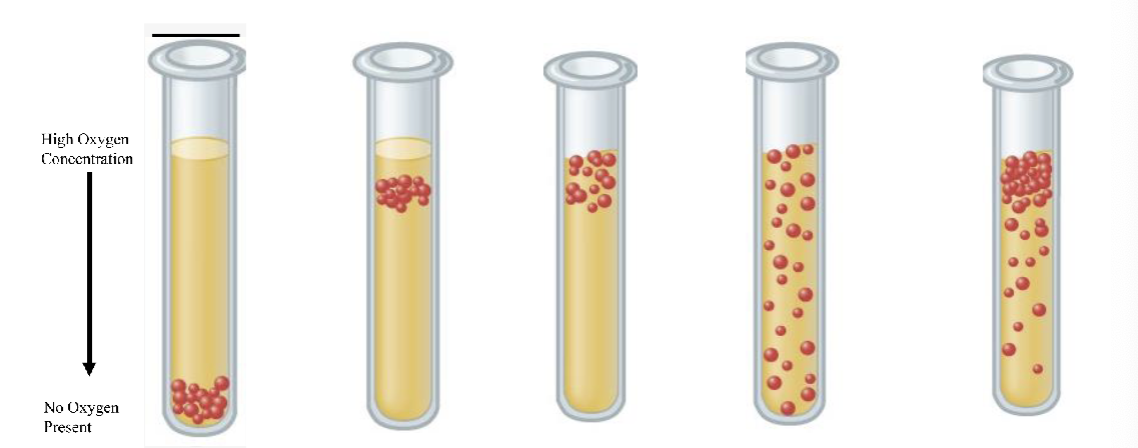
What is the second test tube
Microaerophile
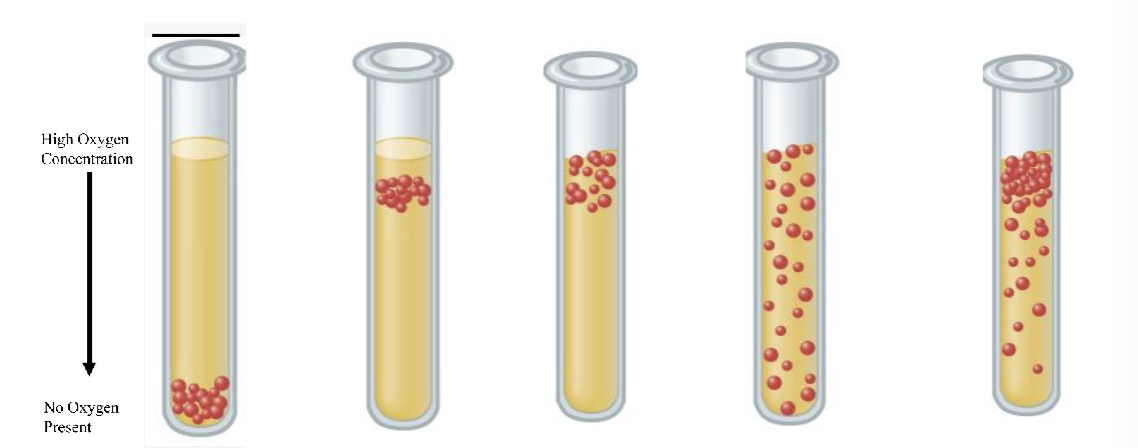
What is the third test tube
Obligate aerobe
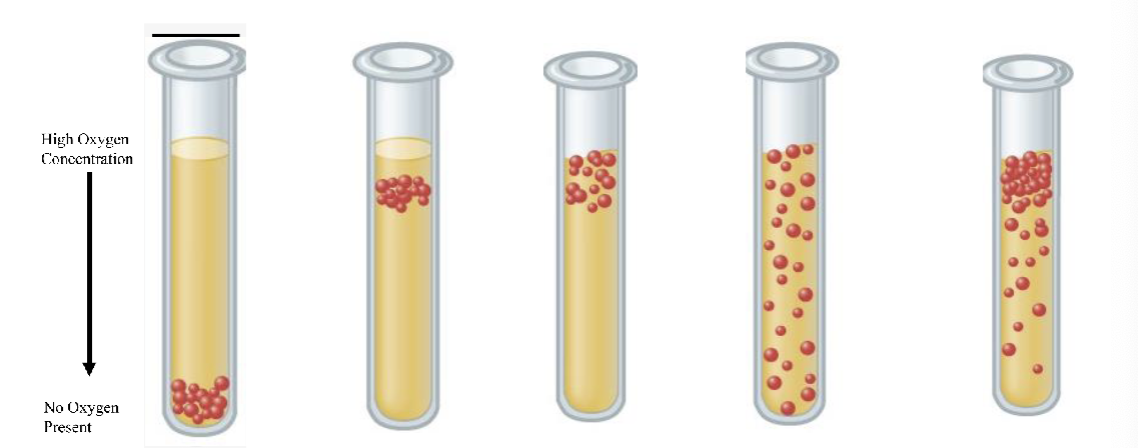
what is the fourth test tube
Aerotolerant anaerobe
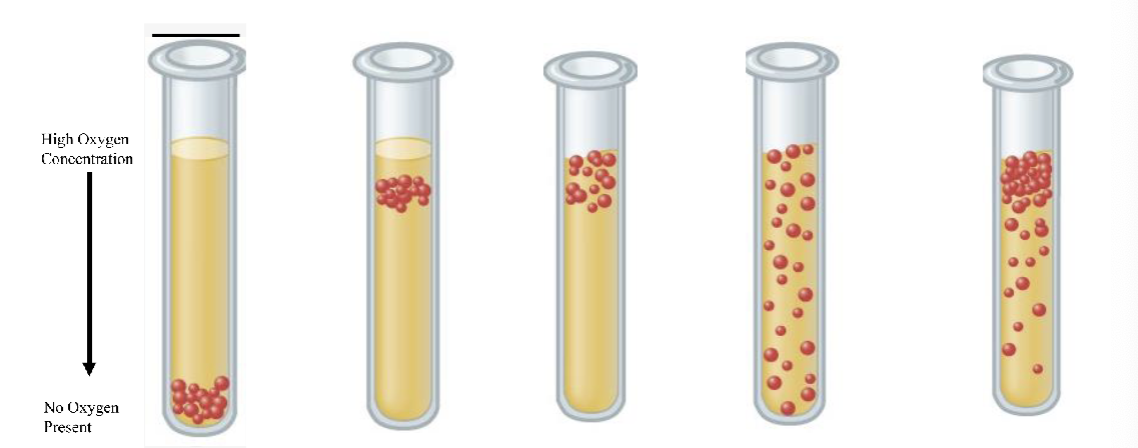
What is the last test tube
Facultative anerobe
What is a biofilm
A mass of bacteria that may be made up of multiple different species of bacteria that stick to and multiply on a solid surface.
When will a biofilm form
when nutrients are plentiful on a surface
What is quorum sensing?
how the biofilm communicates, they release different chemicals called autoinducers and till trigger different responses from the microbe
The thick sticky matrix that is extremely resistant to physical changes in the environment and destruction that holds a biofilm together is called
extracellular polymeric substances