Quiz 16 med term- pharmacology
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
addiction
physical and psychlogic dependence on and craving for a drug
aerosol
particles of drug suspended in air and inhaled
anaphylaxis
exaggerated hypersensitivity reaction to a previouslt encountered drug or foreign protein
antidote
agent given to counteract an unwanted effect of a drug
brand name
commercial name for a drug; trademark or trade name
chemical name
chemical formula of a drug
contraindications
factors that prevent the use of a drug or treatment
controlled substances
drugs that produce tolerance and dependence and have potential for abuse or addiction
dependence
physiologic need for a drug with prolonged use
dose
amount of drug administered, usually measured in milligrams
generic name
legal noncommercial name for a drug
iatrogenic
condition caused by treatment given by physicians or medical personnel
inhalation
administration of drugs in gaseous or vapor form through the nose or mouth
oral administration
drugs are given by mouth
parenteral administration
drugs are given by injection into the skin, muscles, or veins
receptor
target substance with which a drug interact in the body
rectal administration
drugs are inserted through the anus into the rectum
resistance
lack of beneficial response; seen when drugs are unable to control the disease process
response
desired and beneficial effect of a drug
side effect
adverse reaction, usually minor, that routinely results from the use of a drug
sublingual administration
drugs are given by placement under the tongue
syringe
instrument (tube) for introducing or withdrawing fluids from the body
tolerance
larger and larger drug doses must be given to achieve the desired effect. the patient becomes resistant to the action of a drug as treatment progresses
topical application
drugs are applied locally on the skin or mucous membranes of the body; ointments, creams, and lotions are applied topically
toxicity
harmful effects of a drug
transport
movement of a drug across a cell membrane into body cells
analgesic
relieves pain
anesthetic
reduces or eliminates sensation; general and local
diuretic
increased the production of urine and thus reduces the volume of fluid in the body; antihypertensive
narcotic
habit forming drug that relieves pain by producing stupor or insensibility; morphine and opium are examples
sedative
mildly hypnotic drug that relaxes without necessarily producing sleep
a.c.,ac
before meals
b.i.d., bid
two times a day

without
cc
cubic centimeter
h.s., hs
IT
intrathecal
IV
intravenous
mg
milligram
ml, mL
milliliter
NPO
nothing by mouth
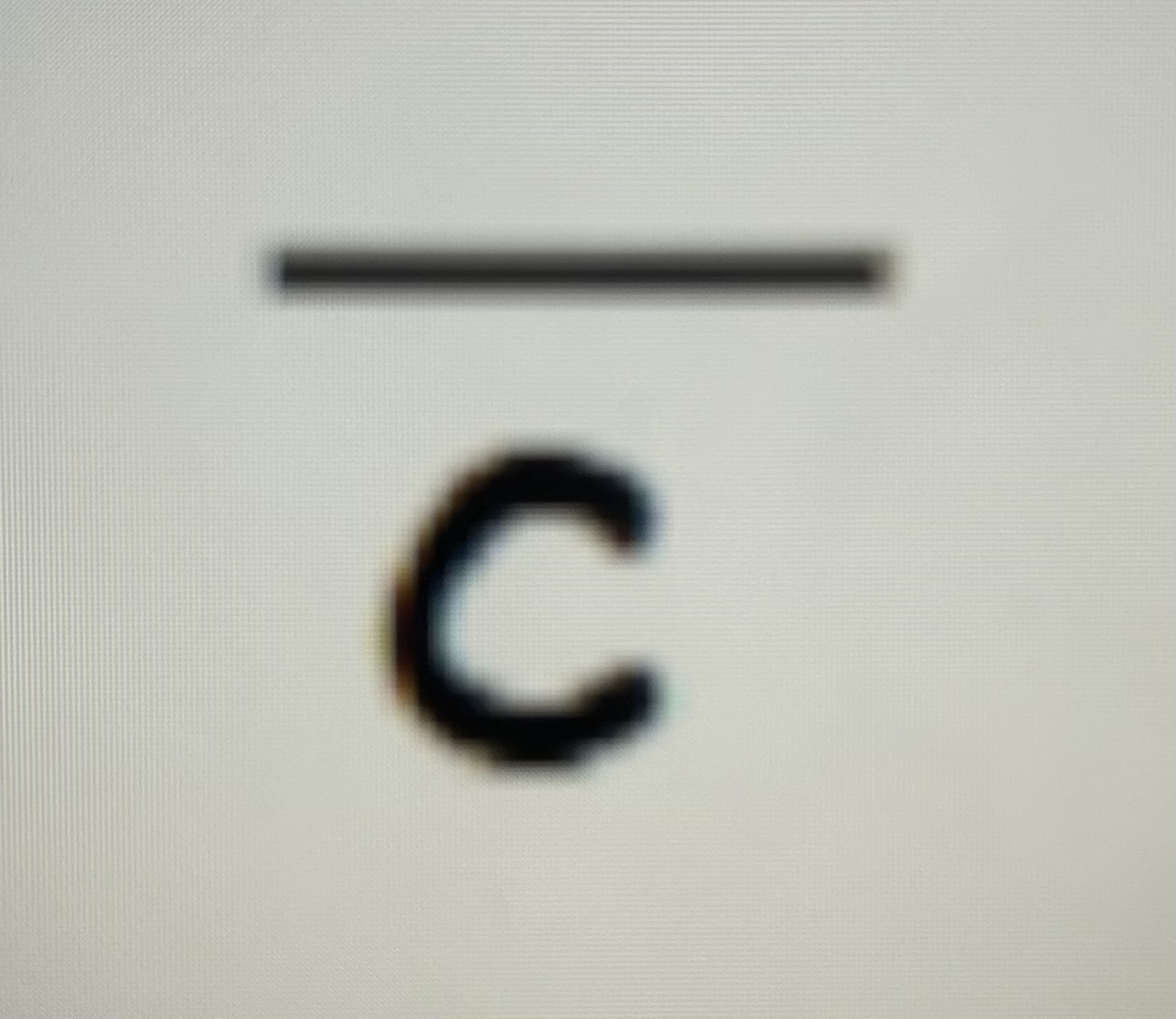
with
p.c., pc
after meals
PICC
peripherally inserted central catheter
PO, p.o., po
by mouth
p.r.n., prn
as needed
Pt
patient
q
every
q.h., qh
every hour
q2h
every 2 hours
q.i.d., qid
four times a day
qAM
every morning
qPM
every evening
Rx
prescription
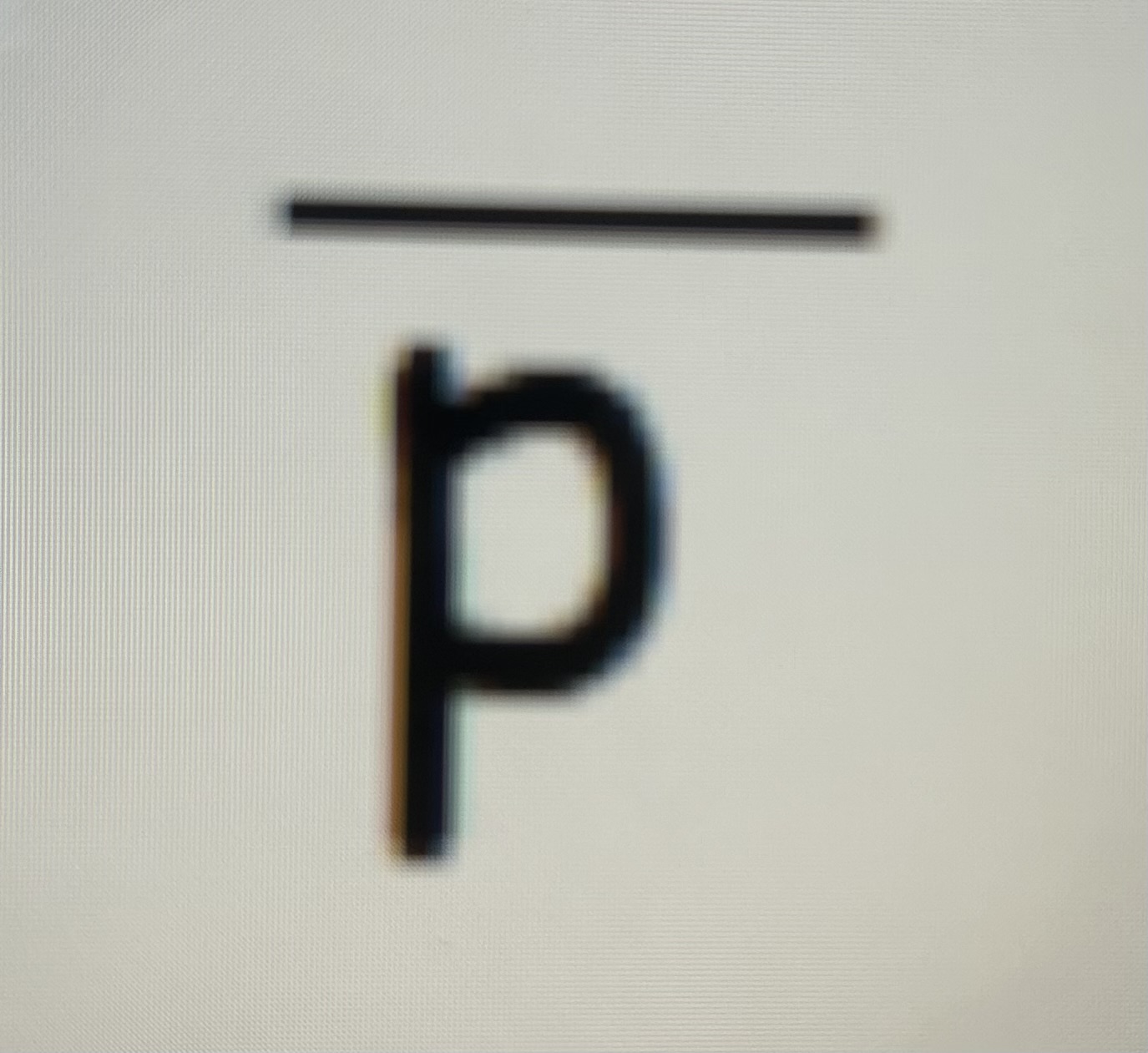
after
s.o.s
if it is necessary
subQ
subcutaneous
t.i.d., tid
three times daily
aa
of each
cm
centimeter
D/C
discontinue
hr
hour
ID
intradermal
inj
injection
kg
kilogram
L
liter
q.h.s.
at bedtime
ss
one half
VO
verbal order