[02-PRELIMS-ANALYSIS-LAB] BOTTLE AND CLOSURE INSPECTION
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Yes
Are bottles a primary packaging?
Physical Evaluation
Visually check the presence of bottle defects.
Critical
Major
Minor
What are the three (3) physical evaluations for defects in primary packaging?
Critical Defects
Physical Evaluation:
Prevents the glass bottle from performing their intended function of safely holding the product causing danger to consumers.
Major Defects
Physical Evaluation:
Make handling of the bottle difficult (ex. durability).
Minor Defects
Physical Evaluation:
Adversely affect the appearance but not the function of the bottle.
Vernier Caliper
Measure the height and diameter of bottles.
Closures
A device that seals a bottle to protect its contents. They can be caps, lids, plugs, or liners.
Biological
Shallow CT
Roll On
Brandy Cork
Pry Off
Pilfer Proof
What are the six (6) types of closures?
Continuous Thread
The CT in “Shallow CT” stands for?
Biological
Identify what type of closure:
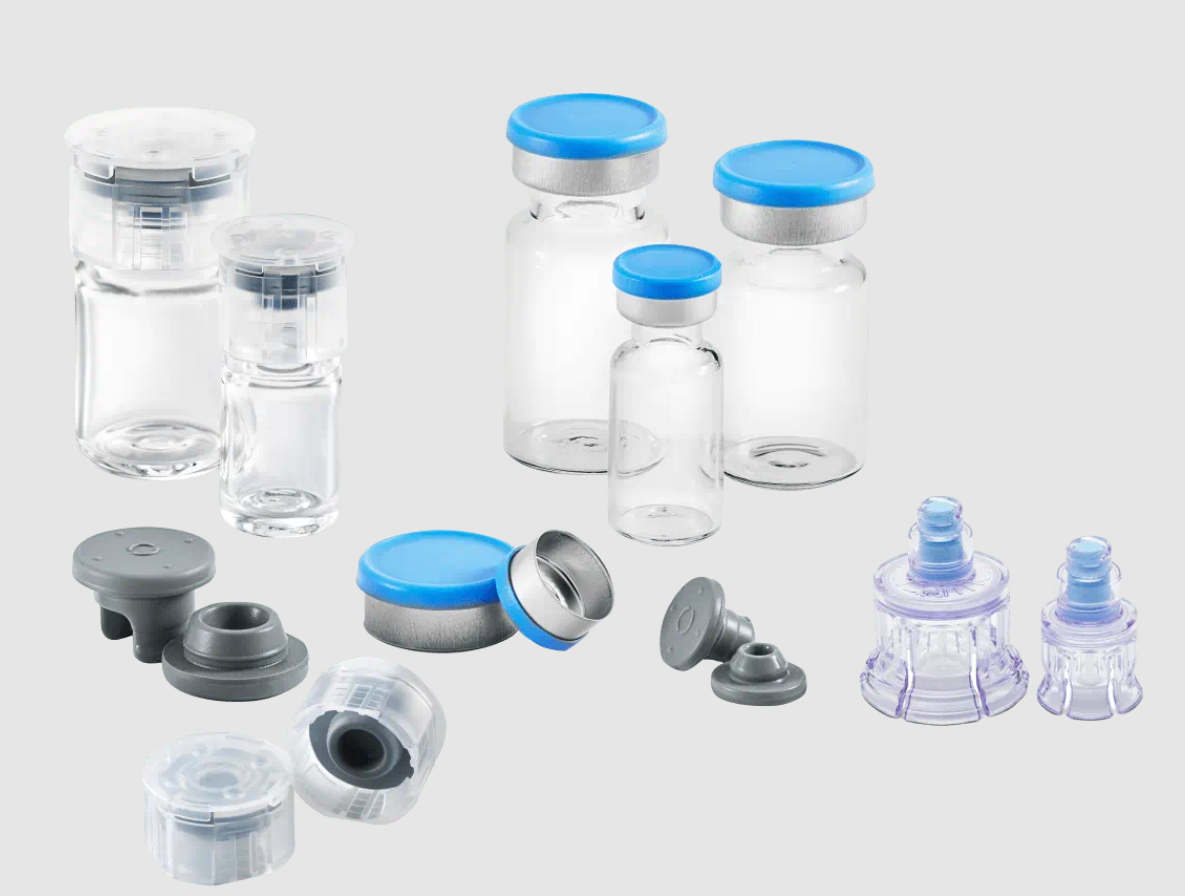

Shallow CT
Identify what type of closure:

Roll On
Identify what type of closure:

Brandy Cork
Identify what type of closure:

Pry Off
Identify what type of closure:
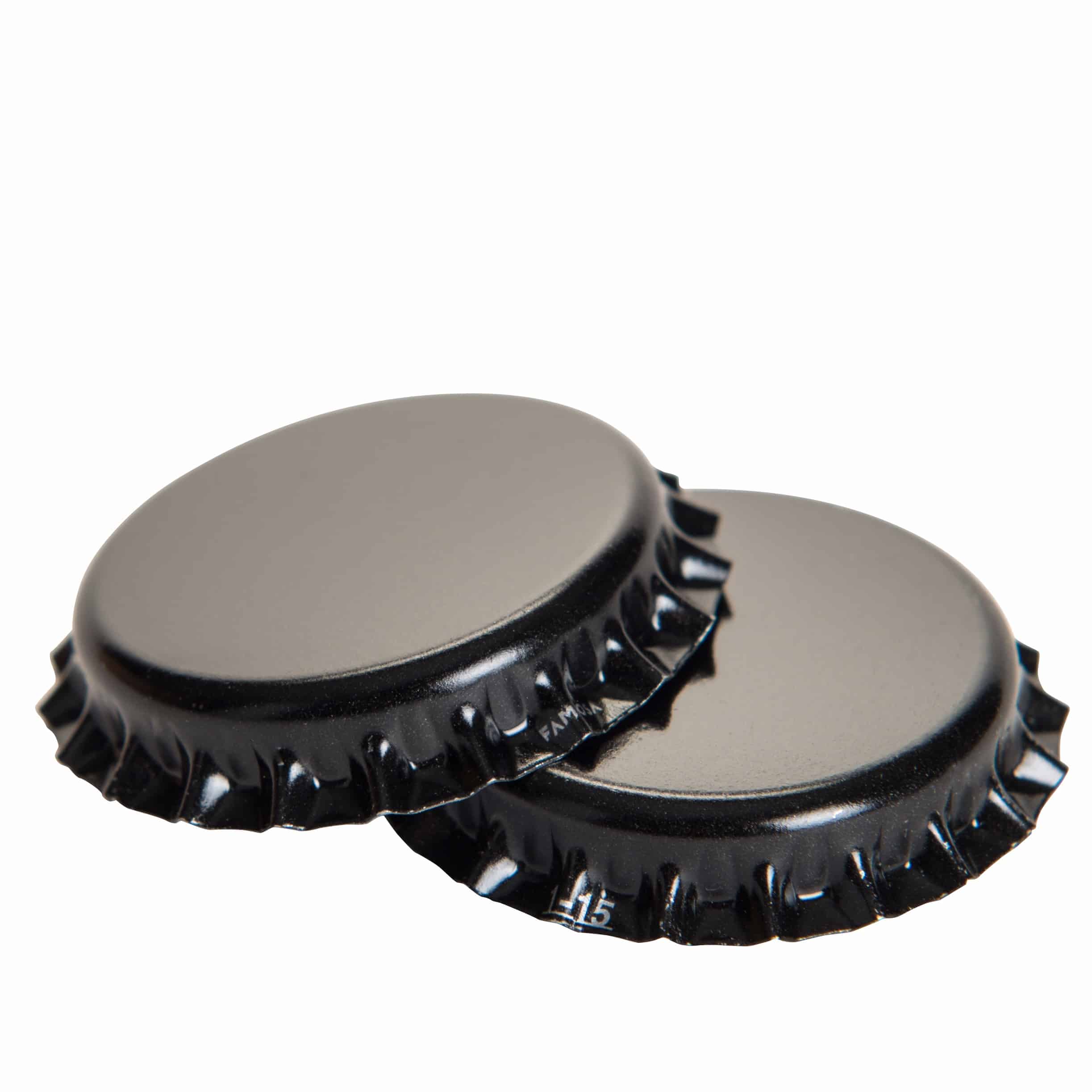

Pilfer Proof
Identify what type of closure:
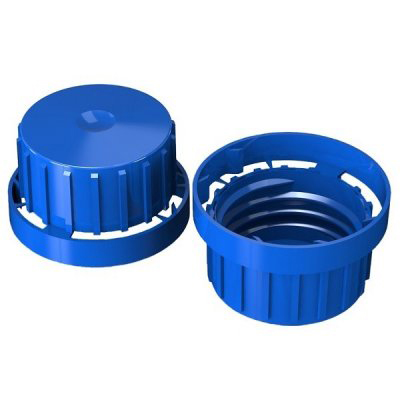

Finish
Neck
Body
Bottom
What are the four (4) parts of bottle?
Finish
Parts of Bottle:
Top of the container above the neck ring parting line.
Neck
Parts of Bottle:
Part which extends from the parting line to the curve at the base of the ____.
Body
Parts of Bottle:
Main part which holds the product.
Bottom
Parts of Bottle:
Part of the container on which it stands when upright.
Bird-Swings and Spikes
Critical Defect:
Long thin strands of glass inside the bottle would probably break off when bottle is filled.

Overpress
Critical Defect:
Small ridge of glass has been formed on the sealing surface of the finish.
Filament
Critical Defect:
Hair-like string inside the bottle.
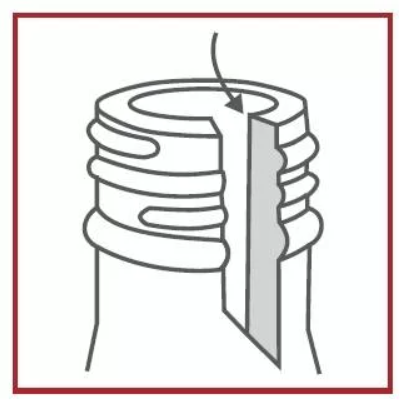
Split
Critical Defect:
An open crack staring at the top of the finish (top) and extending downward.
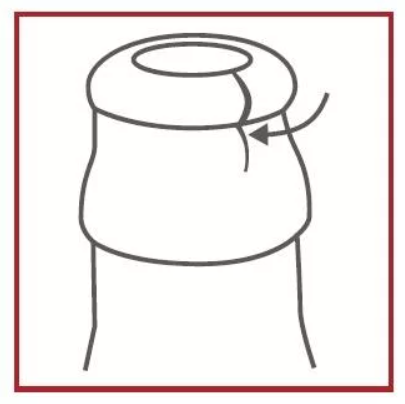
Poor Distribution
Critical Defect:
Uneven thickness of glass.

Soft Blister
Critical Defect:
A thin walled bubble in glass.
Cracks
Critical Defect:
Partial fractures.
Pinhole
Critical Defect:
Any opening causing leakage.
Chipped Finish
Critical Defect:
Pieces broken out of the top edge in the manufacturing process.
Contamination of foreign materials
This occurs when unintended substances are present in the product or its packaging, potentially compromising quality and safety.
Mismatch
Major Defects:
When the bottle and its closure do not fit properly.
Fin
Major Defects:
A thin, raised edge of excess glass on the bottle surface.
Out of round finish
Major Defects:
A pinch, flattened, or oval finish.
Stone
Major Defects:
Small inclusion of nonmelted material.
Rocker Bottom
Major Defects:
Warped bottoms which makes bottle unstable when placed on a flat surface.
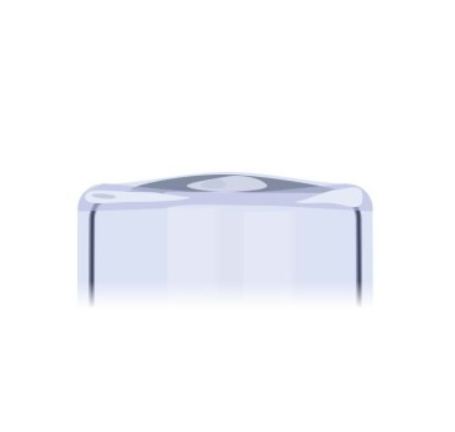

Sunken (Dropped Shoulder)
Minor Defects:
Shoulder not fully blown, sagged after blowing.
Tear
Minor Defects:
A small crack or split in the bottle that does not affect its overall integrity.
Washboard
Minor Defects:
A wavy condition of horizontal lines in the bottle.
Heeltap
Minor Defects:
Heavy glass on one side of the bottom.
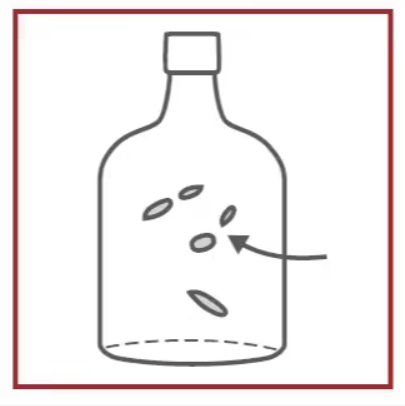
Seeds
Minor Defects:
Small bubbles in the glass.
Critical Defects
Defects that can cause serious harm or product failure and make the item unsafe for use.
Major Defects
Defects that affect product functionality or quality but are not immediately dangerous.
Minor Defects
Defects or small imperfections that do not significantly affect product performance or safety.