Neuroscience Unit I Exam
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what makes up the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
it consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves, their associated ganglia, and peripheral end organs
what makes up the central nervous system (CNS)?
brain (cerebrum, basal ganglia, diencephalon, brainstem, and cerebellum) and spinal cord
how are the PNS and CNS continuous with one another?
the CNS is formed by the nervous system structures inside the bony vertebral column and skull and connects to the PNS that is formed by structures outside the vertebral column and skull
what is the autonomic nervous system?
it is a functionally separate entity from the CNS and PNS that is a system of specialized structures withint the CNS and PNS the functions to provide internal homeostasis (ex: blood pressure, digestive function, HR, breathing rate)
what are the general directional terms in regard to the brain?
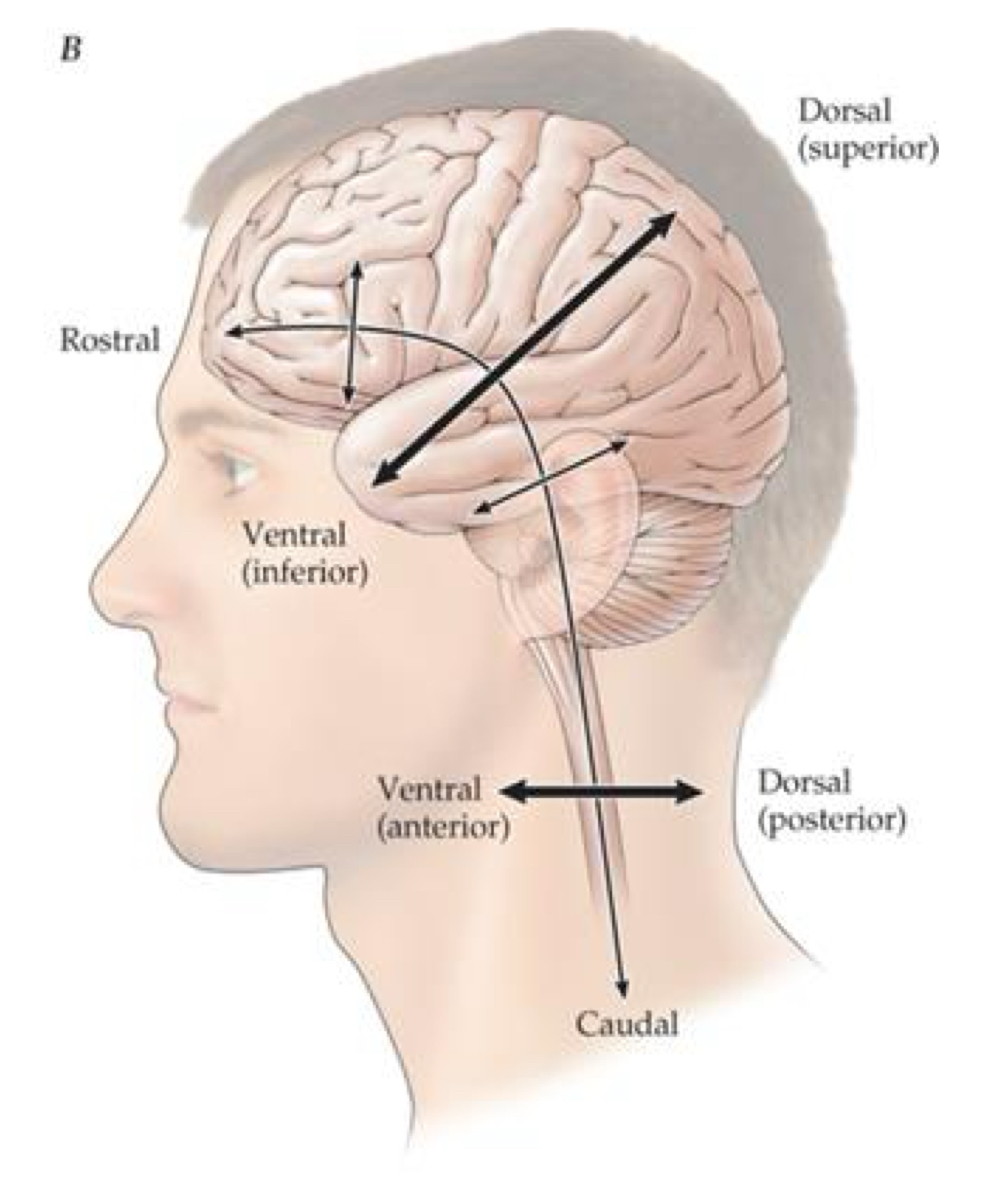
what are neurons and glia?
specialized cells that make up the nervous system
what are the parts and functions of a neuron?
dendrite: recieves input
cell body: integrates information from other neurons
axon: conducts information
synapse: outputs information
what are the types of glial cells and where are they located?
astrocytes: CNS
oligodendrocytes: CNS
microglia: CNS
ependymal cells: CNS
scwann cells: PNS
what is the function of astrocytes?
form supporting network in the brain
metabolic function
form scars in response to injury
provides a connection between the neuron and the vascular system
what is the function of oligodendrocytes?
forms the myelin sheath around axons of nerves in the CNS
what is the function of microglia?
engulfs and removes cellular debris
what is the function of ependymal cells?
lines the ventricles to direct CSF flow
what is the function of schwann cells?
forms myelin sheaths around axons of nerves
what makes up grey matter?
nuclei (neuronal cell bodies) of the CNS and ganglia (neuronal cell bodies) of the PNS
peripheral nerves are just a collection of what?
axonal bundles
what forms white matter?
neuronal axons in the CNS that carry electrical signals. they are also known as tracts or fascicules in the CNS or peripheral nerves in the PNS
if a cross sectional picture or the brain is stained, what does this mean?
white matter will look black and gray matter will look yellow
what is the difference between afferent and efferent?
afferent: the structure has a sensory function. the neuron sends signals from the senses, skin, muscles, and internal organs towards the CNS. brings information toward the reference cell.
efferent: the structure has a motor function. neurons transmit commands away from the CNS to the muscles, glands, and organs. brings information away from the reference cell.
what are the 5 vesicles of the brain?
myelencephalon: medulla
metencephalon: pons and cerebellum
mesencephalon: midbrain
diencephalon: thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, epithalamus
telencephalon: cerebrum and most of basal ganglia
discuss the stages of development of the CNS.
it forms from the neural tube is a collection of cells developing in an embryo
the shape of the neural tube is C shaped as it develops due to the flexed position in which the baby develops in
the outside of the 5 vesicles eventually become neurons while the inside of them becomes our ventricles
when is the CNS susceptible to damage until and why?
teratogens such as alchohol, drugs, or chemicals can cause teratogenesis in in the embryo or baby in the wound and lead to congenital malformation
however, the CNS is still susceptible to camage into early adolesence because even though the macrostructures are fully developed at birth, the microsctructures don’t fully develop until the early 20s.