Principles of science- protein
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
what is meant by a protein structure hierarchy
-primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary(eg 2 beta and 2 alpha globin polypeptides with a heme group)
structure, properties and influence of a peptide bond
mammalian proteins are alpha amino acids
20 amino acids
carboxyl group reacts with amino group to form a peptide bond and lose a water molecule
catalysed by peptidyl transferase (28s ribozyme-ribonucleic acid enzymes)
within a polypeptide chain, individual amino acids = residues
when >50 amino acids are in a polypeptide is a protein
peptide bond is planar (partial double bond between carbonyl O and N)
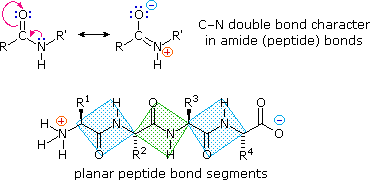
bonding determining protein structure
covalent primary
hydrogen secondary
hydrophobic+VDW tertiary
electrostatic within tertiary helps maintain
VDW/ electrostatic quaternary
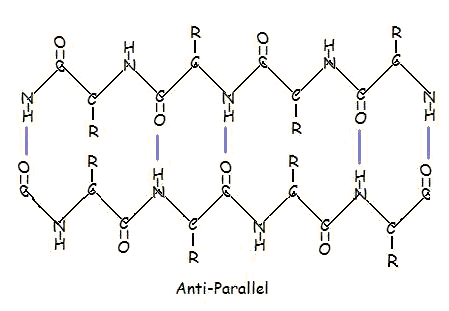
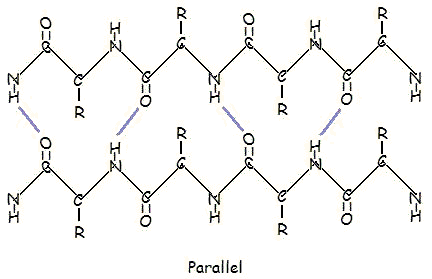
secondary structure
alpha helix- H bonds run parallel to helix axis. alpha carbon backbone winds around an axis so that each carbonyl O atom is H bonded to each amino N of the amino acid located 4 residues closer to C terminus
The standard alpha helix has approximately 3.6 amino acid residues per complete turn
beta sheets- H bonds run perpendicular to chain direction
parallel and antiparallel
types of r groups
nonpolar, polar, electrically charged
cysteine
can form disulphide bonds as it has an SH group
examples of tertiary proteins
-catalase
-triose phosphate isomerase
-actin
tertiary domain
the smallest stable unit of a tertiary structure. a domain is defined as that region of a polypeptide chain that can fold into an autonomous stable tertiary structure
domain shuffling- when domains have been switched around between proteins through evolution
quaternary
haemoglobin- needs to deliver oxygen tissues. needs high enough affinity to pick up oxygen but low enough to release it.
t state- oxygen unbound
r state- oxygen bound. so that the 3 other units have higher affinity
small changes in oxygen concentration can dramatically affect binding to haemoglobin giving a sigmoidal curve of oxygen binding
collagen
extracellular fibrous protein but not an alpha helix
3 helical chains that wind around a central axis
general structure is Gly-X-Y where X can be any amino acid especially proline lysine or hydroxyproline
Glycine is small so glycines from each chain fit at the centre of each helix
H bonds between the chains