DSA25 - Acute and Chronic Diarrheas
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
290 - 2(Na + K)
How is the Osmolar Gap calculated?
<50; >100
Secretory Diarrhea occurs when the osmolar gap is (<50/>100), while Osmotic Diarrhea occurs when the (<50/>100)
-Blood (Melena, Hematochezia)
-Weight Loss
-Fever
-Severe Abdominal Pain
-Nocturnal Symptoms (Organic)
-Elevated CRP/ESR
-FHx of colon cancer
What are Alarm Sx a/w Diarrhea?
> CBC/CMP (Anemia, Electrolyte abns)
> CRP/ESR (inflammation, but non-specific)
> TSH/Free T4
What labs should be drawn with the main Sx of Diarrhea?
> Electrolytes (Na, K, Mg, Phos)
> Calprotectin/Lactoferrin
> Stool Culture and sensitivity
> Ova & Parasite (if indicated)
> WBCs
> C diff
What should be examined in Stool Studies for Diarrhea?
Preformed toxin of Staphylococcus aureus or Bacillus cereus
If the concern is Infectious Diarrhea, Diarrhea occurring within 6 hours of other sx (aka N/V) indicates ingestion of what?
Clostridium perfringens
If the concern is Infectious Diarrhea, Diarrhea occurring within 8-16 hours of other sx indicates infection of what?
Viral Infex or other bacterial infex (ETEC, EHEC, etc)
If the concern is Infectious Diarrhea, Diarrhea occurring > 16 hrs of other sx indicates infection of what?
Salmonella
Diarrhea after exposure to animals (poultry, turtles, petting zoos) has been associated with ____ infection
parasitic
Travel to a resource-limited setting increases the risk of bacterial diarrhea and informs the risk of certain ____ infections
daycare centers
Occupation in ____ has been associated with infections with Shigella, Cryptosporidium, and Giardia
> Laxatives (MgSO4, Lactulose, Fiber)
> Chemotherapy (disrupt mitosis in intestinal lining)
> PPIs (less stomach acid, less defense)
What medication types can cause Acute Diarrhea?
> Fever
> Stomach Discomfort
> Bloody/Mucus-containing stools
What are typical signs of Inflammatory Diarrhea (often caused by bacteria or parasites)?
> Wt Loss
> Vitamin/Mineral Deficiences
What are general Sx of Malabsorption Diarrhea?
> Pale (if bile absent/no bilirubin)
> Voluminous stool
> Floating stool
> Greasy, foul smelling
> Loss of ADEK vitamins
What is a/are specific characteristic(s) of Fat Malabsorption?
WATERY Diarrhea (Osmotic effect of sugar)
What is a/are specific characteristic(s) of Carb Malabsorption?
Diarrhea + EDEMA
What is a/are specific characteristic(s) of
Protein Malabsorption?
Lactose Intolerance
Define Condition:
GI symptoms after ingesting lасtosе or lactοѕе-containing food
-Sx/PE:
> Abdominal Pian
> Bloating
> Nausea
> Diarrhea (OSMOTIC, Gap > 125 d/t carbs)
-Dx: Hydrogen Breath Test (measures H2 levels after lactose ingestion)
-Tx:
> Lactose restriction
> Ca & Vit D supplementation
> Lactose Enzyme Supplementation
Chronic Pancreatitis
Define Condition:
Inflammation, fibrosis, and loss of acinar and islet cells
-Sx/PE:
> Epigastric pain radiating to back
> Steatorrhea
-Dx:
> Labs =
>> Exocrine/Endocrine Insufficiency
>> Soluble Vitamin Deficiency
> Imaging = (CT Abd/EUS)
>> Dilated pancreatic duct
>> Pancreatic duct calcifications
-Tx:
> Pancreatic enzyme replacement
> Pain Mgmt
> Surgery
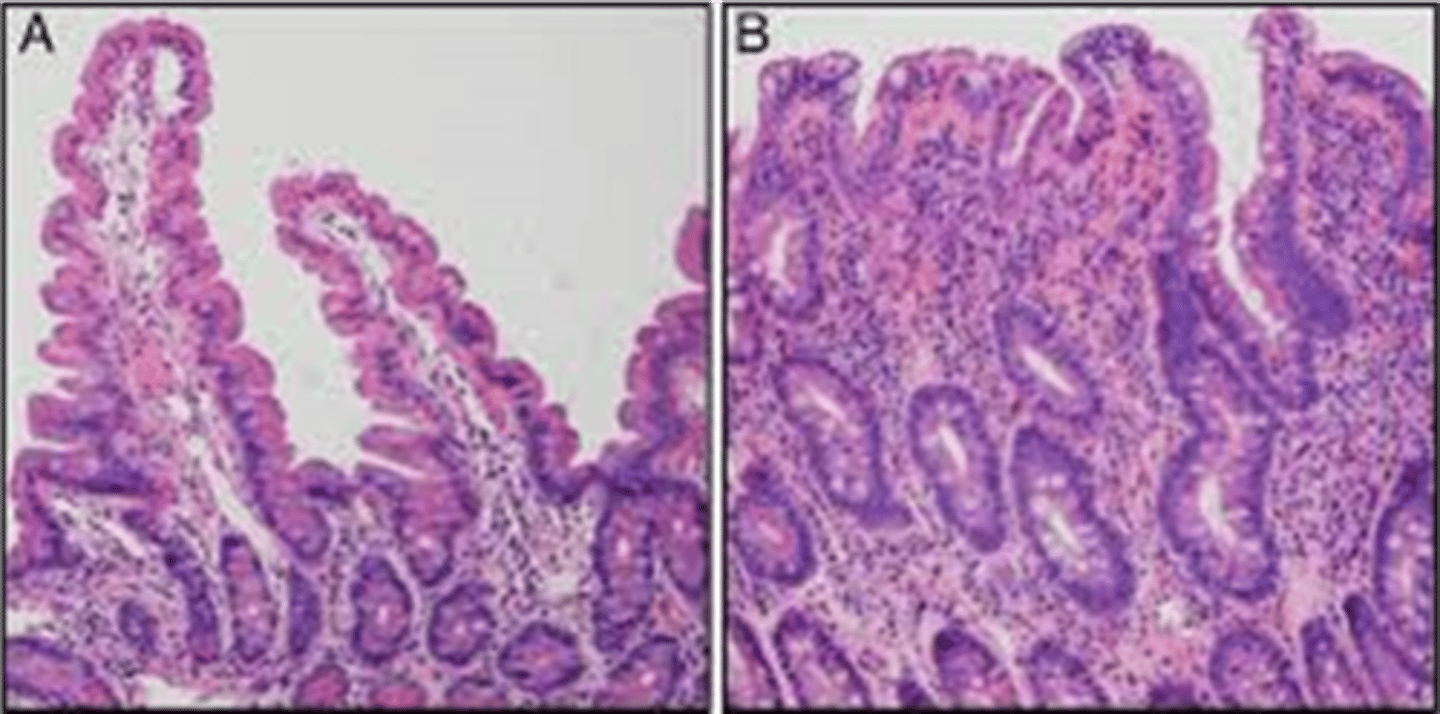
Celiac Disease
Define Condition:
Immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the small intestine caused by sensitivity to dietary gluten and related proteins
-Hx: A/w...
> Down's Syndrome
> Type 1 DM
-Path: Allergy to gluten (BROW = Barley, Rye, Oats, Wheat)
-Sx:
> Diarrhea (Bulky, foul smelling, floating = Steatorrhea)
> Flatulence
> Malabsorption:
>> Wt Loss
>> Severe Anemia
>> Neuro Sx (Vit B9/B12)
>> Osteopenia (Ca/Vit D)
> Oral Ulcers
> ALCs
> Rash
-Dx:
> CONFIRM = GLUTEN CHALLENGE + Upper Endoscopy/Bx
> Biopsy: FLATTENED VILLI
> Endoscopy:
>> Blunted villi
>> Crypted hyperplasia
>> Lymphocytic infiltrate of crypts
> Labs:
>> IDA
>> Electrolyte imbalance
>> Vit Deficiency (ADEK)
> Serology:
>> IgA endomysial
>> Anti-tTG Ab
>> HLA-DQ2/DQ8
-Tx:
> Exclude gluten
> DEXA Scan + Appropriate Tx
> Tx Anemia
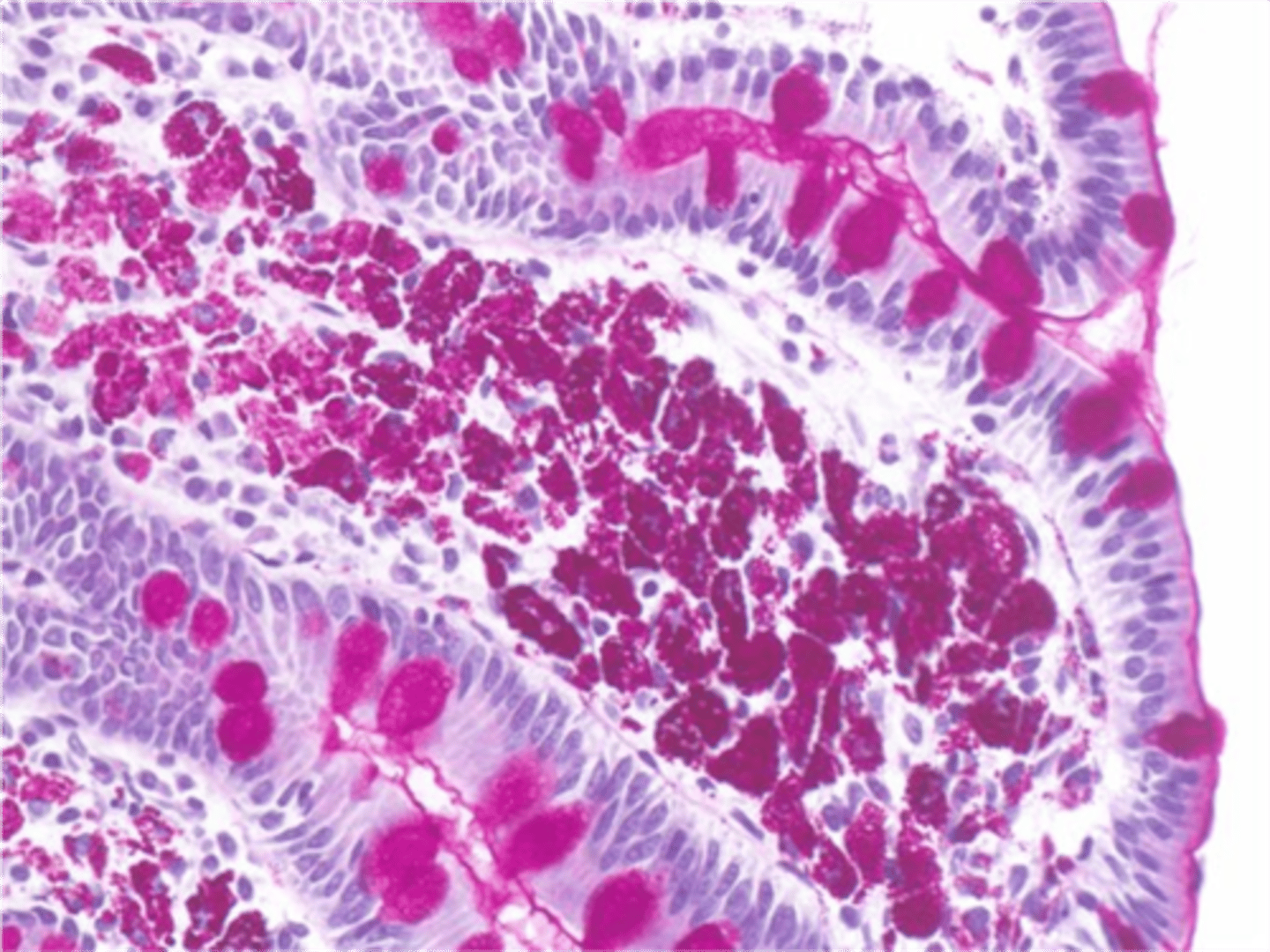
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)
Define Condition:
Small bowel is colonized by an excessive number and/or abnormal type of aerobic and anaerobic microbes that are usually found in the colon - usually by E. coli and Klebsiella
-Hx:
> Post-surgery (Blind Loop Syndrome after Gastric Bypass)
> RADIATION
-Path: Maldigestion in intestinal lumen or malabsorption at microvillus membrane d/t enterocyte damage
-Sx/PE:
> BLOATING
> Flatulence
> Abdominal Discomfort
> Chronic Watery Diarrhea (Carb)
> From Malabsorptions:
>> Steatorrhea (Fat)
>> Edema (Protein)
>> Peripheral Neuropathy & Macrocytic Anemia (Vit B12)
>> Coagulation Issues (Elevated Vit K & B9 d/t bacterial synthesis)
-Dx: Carb Breath Test (H2 & CH4 made by bacteria)
-Tx:
> Abx
> Severe --> Surgical Reversal
Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
Define Condition:
D/t Mutations in the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein, a regulatory protein found in all exocrine tissues
-Sx/PE: (d/t Pancreatic Insufficiency)
> Chronic Diarrhea
> Steatorrhea
> Frequent, bulky, foul-smelling stools (may be oil)
> FTT
> Poor Wt Gain (malabsorption of fat/protein)
Whipple's Disease
Define Condition:
Caused by T. whipplei (gram-positive bacillus)
-Sx/PE:
> Chronic (Intermittent) Diarrhea (Diarrhea = Watery & Steatorrhea) + Colicky Abdominal Pain
> Gross GI Bleeding
> Malabsorption
> Wt Loss
> CNS Issues
> Derm Issues
> Pulm Issues
> Cardiac Issues
-Dx: EGD w/ Small Bowel Bx
> Accumulation of macrophages in lamina propria; PAS (+)
-Tx: Abx after C & S
Crohn Disease
Define Condition:
Transmural inflammation of GI tract and skip areas of involvement (Segments of normal-appearing bowel interrupted by areas of disease)
-Hx:
> BIMODAL AGE
>> 15-30 y/o
>> 55-65 y/o
-Path: Involves ILEUM & PROXIMAL COLON usually
-Sx/PE:
> Severe Abd Pain
> Wt Loss
> Chronic Diarrhea > 8 loss stools a day
> Nocturnal Sx
> Cutaneous lesions + Abdominal Abscess + Fistulas
> Extraintestinal
>> Large Joint arthritis
>> Pyoderma Gangrenosum
>> Erythema nodosum
>> OA
>> Anemias
>> Uveitis
>> Renalithiasis
>> Gallstones
-Dx:
> Endoscopy =
>> Fibrosis --> Strictures
>> SKIP LESIONS
>> Aphthous ulcers
>> Large ulcers interspersed
>> Cobblestone appearance (nodular thickening + linear/serpiginous ulcers)
> Lab = CBC, CMP, CRP/ESR
> Stool Analysis = CALPROTECTIN
>> Elevated
>> To r/o infex
> Imaging (MRE/CTE)
> Histology
Ulcerative Colitis
Define Condition:
Recurring episodes of inflammation limited to the mucosal layer of the colon
-Path: Involves RECTUM (extends in proximal and CONTINUOUS fashion)
-Sx/PE:
> Diarrhea (+/- blood)
> Frequent but small (volume) BMs
> Colicky Abd Pain
> Urgency
> Tenesmus (needing to have a bowel movement, even when your colon is empty)
> Incontinence
> Extraintestinal
>> Large Joint arthritis
>> Pyoderma Gangrenosum
>> Erythema nodosum
>> OA
>> Anemias
>> Uveitis
>> Renalithiasis
>> Gallstones
>> PSC
-Dx:
> Endoscopy =
>> Extensive ulceration of mucosa
>> Irregular, friable surgace
>> Erythematous + Loss of vascular markings
>> Pseudopolyps (rxn of inflammation)
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Define Condition:
Ulcerative colitis (colon) + Crohn's Disease (anywhere in GI tract)
-Tx:
> Steroids
> Budesonide
> 5-ASA
> Immunomodulators
> Biologics
> Surgery
Microscopic Colitis
Define Condition:
Chronic inflammatory disease of the colon that is characterized by chronic, watery, non-bloody diarrhea
-Hx: NSAIDs!
-Path:
> Collagenous vs Lymphocytic
-Dx:
> Colonoscopy = Normal or almost normal
-Tx:
> Loperamide
> Budesonide
Causes ENS issues --> disordered motility of the small bowel and the colon
How might Diabetes cause Dysmotility GI issues?
Hyperthyroidism increases GI motility and often chronic diarrhea noted
How might Thyroid Issues cause Dysmotility GI issues?
Deposition in small bowel can cause dysmotility and lead to diarrhea or constipation
How might Amyloidosis cause Dysmotility GI issues?
Factitial Diarrhea
Define Condition:
Multiple loose BMs despite negative stool studies, endoscopic evaluations, and lack of labs findings
-Dx:
> Stool Osmolar Gap
>> > 75 = laxatives containing magnesium, sorbitol, lactose, lactulose, or polyethylene glycol as the active ingredients
>> < 75 = secretory laxative (e.g., senna, bisacodyl) or osmotic diarrhea caused by a sodium-containing laxative
> Stool Mg > 90 = Magnesium Induced
> Stool Phos > 33 = Phosphate-Induced
-Metformin
-Chemo
-Colchicine
-ARBs
What medications' S/Es can MIMIC medications that cause acute diarrhea (but cause IATROGENIC diarrhea)?
-Radiation
-Post-surgical
-Vagotomy
-Post cholecystectomy (BAM)
What procedures can cause IATROGENIC diarrhea?
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Define Condition:
A functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract characterized by chronic abdominal pain and altered bowel habits (recurrent abdominal at least once per week in 3 mos)
> Related to Defecation
> A/w change in stool frequency
> A/w change in stool form (appearance)
-Types:
> IBS-D (Diarrhea predominant)
> IBS-C (Constipation-predominant)
> IBS-Mixed (both)
-Hx:
> FHx of IBD/Colorectal cancer/Celiac Disease
-Tx:
> Diet Change
> Anti-Spasmodic Meds
> Immunomodulators
> Tx Stress
VIPoma
Define Condition:
Excessive, unregulated secretion of VIP by tumor --> More fluid in GI Tract
-Sx/PE:
> Watery diarrhea persisting w/ fasting (Secretory darrhea w/ OG < 50)
Gastrinomas
Define Condition:
Secretion of gastrin by duodenal or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
-Path: Excessive gastrin secretion --> in high gastric acid output ==> inhibit the absorption of sodium and water by the small intestine, thereby adding a secretory component to the diarrhеа
-Sx/PE:
> SECRETORY (Watery) Diarrhea
Carcinoid Syndrome
Define Condition:
Neuroendocrine tumor which synthesize, stores and release a variety of polypeptides, biogenic amines, and prostaglandins
-Sx/PE:
> Abd Pain
> Flushing
> Diarrhea
> Pulmonic/Tricuspid Valve Disease
-Tx:
> Surgical excision
> Hepatic resection
> Octreotide