Chemical Compounds in Plant Cells and Their Functions
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
Element
Substance that cannot be chemically broken down.
Compound
Substance of at least two different elements combined.
25
How many essential elements are necessary for life in general?
Oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen
What 4 elements make up around 96 to 99.5% of living matter?
70%
Water is ____ of the entire plant body
Inorganic Molecules
A group of molecules/compounds that have no carbon. Includes water, inorganic salts, and ions.
Water
Most abundant substance in living organisms. Universal Solvent
Hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-)
What is produced when water dissociates?
Organic compounds
These are molecules that contain a carbon
Hydrogen Bond
_____________ form when a covalently-bonded H is attracted to a negatively-charged atom in a neighboring molecule
Are all compounds with carbons organic? What are examples of such?
No, not all carbon compounds are organic. Some examples are:
CO2, CO (carbon oxides)
CO3, HCO3 (carbonates/bicarbonates)
HCN (cyanides)
Compounds with one C and usually with no H
What are the four basic types of organic molecules?
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Carbon Compounds
Includes all organic molecules and some inorganic.
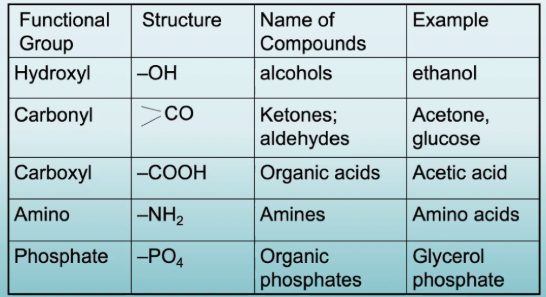
Functional Groups
Clusters of atoms that define molecular behavior and perform a useful function
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds made of sugars and starches.
the word comes from a ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen to form C6H12O6
used for energy production, storage, and structure
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars, the building blocks of carbohydrates.
Disaccharides
condensation synthesis required to link two monosaccharides with each other through glycosidic bonds
Polysaccharides
bound together through polymerization of covalent bonds of 3 or more monosaccharides
can be classified into: structural and storage
Hydrocarbons
Non-polar compounds like oils and waxes that only contain carbon and hydrogen
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
Structural Isomers
Same atoms, different bonding patterns.
Stereoisomers
same molecular formula and sequence but differ in 3D (geometric isomers and enantiomers)
Cis-Trans Isomers
Stereoisomers differing in arrangement around a double bond.
Cis - same molecules on the same side; Trans - same molecules on opposite sides
Enantiomers
Molecules that are mirror images of each other.
Glycogen
Storage polysaccharide in animals, primarily in liver.
Cellulose
Structural polysaccharide in plant cell walls.
Also known as fibers
Most abundant organic compound on Earth; Toughest organic compound to digest
Chitin
Polysaccharide forming exoskeletons in insects, spiders, and crustaceans
Leathery texture but hardens when encrusted with calcium carbonate
found in cell walls in fungi
Starch
Energy storage polysaccharide in plants.
Alpha configuration of glucose that is a storage polysaccharide
Inulin
Fructose polymer found in some plants.
Lipids
Non-polar macromolecules, mainly for energy storage.
mostly hydrocarbons that share one common trait: little to no affinity for water and do not contain monomers
Triglycerides
Fats composed of glycerol and three fatty acids.
Saturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids with single bond between carbons; more stable
solid at room temp
examples: coconut oil, palm oil, and animal fat (lard)
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acids with double bonds; weaker due to low melting point and sensitivity to oxidation
liquid at room temp
examples: corn oil, soybean oil, olive oil, and canola oil
Phospholipids
Major components of cell membranes.
Lipids that deal with cell membranes
Waxes
Lipids used for waterproofing surfaces.
functions as retard water loss from plants
Steroids
Lipids that function as hormones.
Hydrocarbon with four linked carbon rings.
Fatty Acid
Hydrocarbon chain with carboxylic acid group.
Trans-Fatty Acids
Formed from partially hydrogenated oils, unhealthy for consumption.
Phospholipid
Glycerol with two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Two layers of phospholipids forming cell membranes.
Hydrophilic Head
Water-attracting part of a phospholipid.
Hydrophobic Tail
Water-repelling fatty acid chains in phospholipids.
Atherosclerosis
Plaque buildup in arteries due to excess cholesterol.
Epidermis
Thin layer on plants that reduces water loss.
Hydrogenation
Process of adding hydrogen to oils, creating trans fats.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins, 20 types exist.
contains amino group, carboxyl group, and an R group
Peptide Bonds
Covalent bonds linking amino acids together.
Dipeptide
Two amino acids linked by a peptide bond.
Lectins
Plant proteins that agglutinate cells and induce division.
Primary Structure of a plant cell
Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Secondary Structure of a plant cell
Local folded structures in polypeptides, e.g., alpha-helix.
Tertiary Structure of a plant cell
3D folding pattern of a protein, with 3.6 amino acids at every turn that has h-bonds stabilizing the structure between NH and CO groups
considered a functional protein
Quaternary Structure of a plant cell
Protein has more than one amino acid chain
Protein Denaturation
When proteins at their more functional, complex forms (tertiary or quaternary), revert to their simpler, non-functional forms (primary or secondary)
denatures via Heat, organic solvents, or physical agitation
16
How many of the essential elements for life are essential to plants?
Matter
All organisms are composed of _____
G. Tin
Plants have trace elements of the following EXCEPT:
A. Boron
B. Iron
C. Manganese
D. Zinc
E. Copper
F. Molybdenum
G. Tin
Being attracted to a lot more compounds
Involved in more reactions
Benefits of being polar
Liquid at room temperature
Universal solvent for polar molecules
Water molecules are cohesive, which means they really stick together
Slow temperature change
Characteristics of water that benefit living things
Glycerol and fatty acids
What are the building blocks of lipids?
Nucleotides
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids?
1:2:1 respectively
What is the ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in carbohydrates?
Alcohol (-OH) groups attached
What makes most carbohydrates water-soluble?
Number of sugar molecules
Location of carbonyl group
Size of carbon skeleton
How can carbohydrates be classified?
Glucose: This is the main food molecule used by most living things that is produced through photosynthesis
What is this molecule?
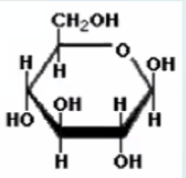
True
[T/F] Glucose can be assembled into starch and cellulose
Fructose: Fruit sugar used to sweeten food products
What is this molecule?
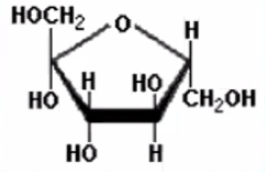
Their structure, specifically ISOMERS
If monosaccharides have the same chemical formula, what differentiates them from each other?
Galactose
What is this molecule
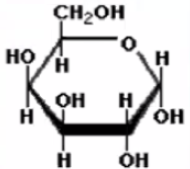
Geometric isomers
different spatial arrangements using the cis-trans
When we work, even when we sleep, all our cells are working
Cells use up energy when they work
Immediate source of energy are: carbohydrates
So if we want to lose weight, we go on carb-free diets
If we consume our carbs already, the stored carbs are the one that is lost
If we are active and we don’t eat carbs, the next source of energy are the lipids
Lipids provide us energy
Hence, we don't see the results of our diet immediatel
Carbohydrates as quick sources of energy
Glucose, fructose, galactose
What are the monomers of carbohydrates?
Process of condensation synthesis or dehydration synthesis, where two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water
How do two monosaccharides link together to form disaccharides?
Through hydrolysis, where a larger molecule forms two (or more) smaller molecules and water is consumed as a reactant. Water is introduced to break up the bond
How do you break up disaccharides?
Lactose
What is this molecule?
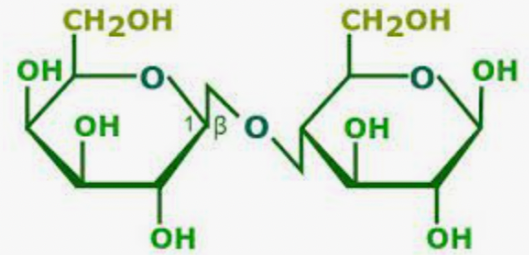
Maltose: malt sugar; glucose + glucose
Sucrose: common table sugar; glucose + fructose
Lactose: milk sugar; glucose + galactose
Most common disaccharides are:
Glucose
Fructose
Ribose, Deoxyribose
Vitamin C
What are examples of monosaccharides?
Sucrose
What is this molecule?
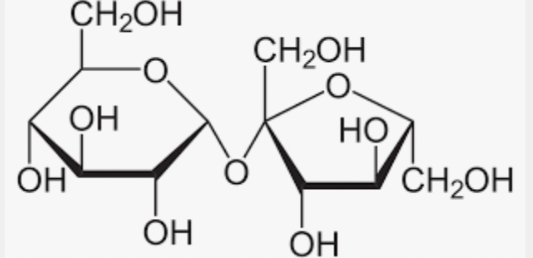
Maltose
What is this molecule
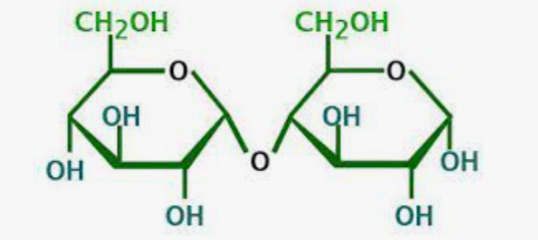
Cellulose
Starch
Most important polysaccharides for plants are
Cellulose
Chitin
Pectin
Examples of structural polysaccharides
100 billion tons
How much cellulose do plants produce per year?
Pectin
Found in cell walls and mid-lamella, as well as fruits especially citrus
Starch
Inulin
Gums
3 Storage Polysaccharides
Amylose; Amylopectin
Unbranched (simple) and branched (complex) starches are:
Glycogen
Starch is stored as ________ by animals in their liver and muscle cells
Gum
White sap in plants that are food reserve in seeds; serves as protection of plants when damaged
Oligosaccharides
What do you call 3 to 12 monosaccharides connected together, but also contains proteins?
Aldose (terminal)
Ketose (inner)
What are the two terms for the differing carbonyl groups of carbohydrates?
Ribulose, fructose
Examples of ketose carbohydrates
3 | triose |
4 | tetrose |
5 | pentose |
6 | hexose |
7 | heptose |
8 | octose |
9 | nonose |
What do you call different aldoses with 3 to 9 carbons?
3 | triulose |
4 | tetrulose |
5 | pentulose |
6 | hexulose |
7 | heptulose |
8 | octulose |
9 | nonul |
What do you call different ketoses with 3 to 9 carbons?
Miraculin (glycoprotein)
Steveoside (diterpine glycoside) or stevia
Clycyrrhizin (triterpine glycoside) or licorice
Give 3 sugar substitutes
All living organisms are made up of organic molecules and use organic molecules to function
Carbon can form a great variety of organic compound
Why is carbon so important to life?
List the different functional groups
Some lipids are amphipathic—part of their structure is hydrophilic and another part, usually a larger section, is hydrophobic. This means that lipids “fear” water
What does “affinity for water” mean?
Fats/oils
Phospholipids
Waxes
Steroids
What are the 4 types of lipids?
Fats/oils
Lipids that deal with energy storage
Tetrahedron
Triangular pyramid
Long chains and rings
Carbon’s bonding patterns
They are easier to break up since they have weaker bonds
Why are unsaturated fats “healthier”?