miya's econ notes
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fuck it we ball
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What’s a business?
A business is an entity that offers goods and/or services to customers
What’s the main characteristic of the economy?
Exchanging goods & services for money or other means of payment (exchange)
How does a business create value?
Businesses createw value by repairing products, making them more accessible, solving a problem, or offering additional services
Key risks & investments of starting a business
Starting a business means working longer hours, investing your own savings, potential risk of failure, and also needing a car/vehicle to transport goods
What does entrepreneurship involve?
Entrepreneurs develop an idea, solve problems, create value for their customers, make sensible economic decisions. Entrepreneurship is riskier than working in a company, and a person considering it should be aware of potential risks & losses
How do people & businesses fulfill their needs in the economy?
Businesses provide goods & services for people who need these goods & services. Businesses also have needs. And individuals might also exchange goods with each other. In the economy, people & businesses exchange goods & services to fulfill their needs & wants
Why do we need to economize?
Exchanging would be much easier if all that we want or need was available in abundance, but that is not the case
Resources are scarce & need to be managed
This is why we all need to economize. No one is able to opt out of making economic decisions
What is the basic economic problem of everyone?
It is a basic economic problem of households, businesses, and the government to decide how to use their limited resources and to make choices when allocating these scarce resources between different options
What’s opportunity cost?
Opportunity cost is the (financial) benefit of the (next best) alternative that was lost or given up in order to choose or achieve something else
What’s economic a study of?
Economics is the study of how individuals (as part of private households) and businesses make decisions to satisfy their needs and wants with limited resources
What’s micro & what does it focus on?
Microeconomics focuses on the behavior and decisions of individual households & businesses and how they interact. A question in micro could focus on the change in demand of electric cars
What’s macro & what does it focus on?
looks at the bigger picture & deals with questions concerning the overall economy (of 1 country, for example) and aggregate quantities. Among other phenomena, it studies economic growth, unemployment, interest rates, price levels, and inflation
who plays an important role in the circular flow of the economy & why?
public authorities, because:
governments collect taxes from households & businesses
taxes are used to finance goods (infrastructure, streets, streetlights) & services (national defense, public security like police)
these goods & services are necessary, but private businesses won’t supply them b.c. of “free riders” - people who use a service w/o paying for it
in many countries, they also provide healthcare & education
three functions of money
medium (flexibility) of exchange
unit of account (express value of things)
store of value
What’s inflation?
the decline in the purchasing power of money due to a general rise in prices of goods & services over time. the european central bank considers an inflation rate of 2% most beneficial to the economy.
how can inflation be fought?
by increasing the price for money, i.e. the interest rates
why is division of labour important?
it allows people to focus on what they are best at, making work more efficient
how does spezialization happen?
it happens when when individuals, businesses, and countries focus on specific tasks or products, improving productivity & efficiency
what are the levels of specialization?
within households: one person shops, another cooks
within businesses: departments focus on different functions like procurement, production, marketing, sales, and finance
between businesses: some produce raw materials, others refine them, etc.
internationally: countries specialize based on climate, resources, labour costs, and legal frameworks
what are the disadvantages of spezialization?
repetitiveness may make work boring
reduced flexibility: workers & businesses struggle to adapt to other tasks
if a specialized industry declines, workers may lose jobs, and businesses may fail
situation in a market economy
individuals & businesses are (more or less) allowed to make many of their own economic decisions
situation in a planned economic system
the government plays a dominant role, (mainly or partly) control the resources & means of production, decide which goods are produced & which services are offered (at what price). People have a limited choice of jobs to do & goods to buy
situation in a free market economy
the government plays a minor role by only providing the legal framework & not influencing the economy much
situation in an eco-social market economy
the government influences the economy more by supporting the poor & protecting the environment
when is a market formed?
when buyers & sellers meet to communicate the conditions of exchanging goods & services in a market economy
what does a type of market depend on?
on what is offered: consumer goods markets, labour markets, housing markets, money markets, capital markets, commodity (raw material) markets
definition of supply?
supply (of a certain good or service) is the quantity of that good/service that is available for purchase
the law of supply?
the higher the price is, the higher the supply will be (ceteris paribus)
main factors influencing supply?
production capacity
available resources
price that can be charged
number of suppliers: more suppliers → more supply
technological changes: can reduce costs → supply increases
changes in resource prices: if resource costs decrease but service prices stay the same, more providers enter the market
price expectatons: if future prices are expected to fall, supply may decrease
what’s marginal cost & how does it affect the shape of the supply curve?
it is the cost of producing an additional unit of a good or by providing an additional unit of a service. Supply curve shape is affected by increasing marginal costs. As production expands, marginal costs rise (need more machines, workers, etc.). Supply increases only if price ≥ marginal cost.
what’s demand?
the quantity of goods and/or services that customers are willing and able to buy
law of demand?
the higher the price is, the lower the demand will be
how does income affect demand?
More income = higher demand for services (demand curve shifts right). Less income = lower demand (demand curve shifts left)
facctors influencing demand?
income: higher income → higher demand
complementary goods; related goods can increase demand
consumer preferences: changes in preferences shift demand
substitute goods: availability of substitutes can reduce demands
what affects market competition?
number of suppliers & availability of substitute goods are the main ones
what’s a monopoly?
market situation, where it’s just 1 supplier. Rare, but possible in local areas
what’s an oligopoly?
market situation with a few suppliers. Competition’s strong → one change = others react
what’s a cartel?
suppliers’ agreement on terms of sale to prevent harsh competition. Illegal, because competition in. the market is concidered beneficial for customers (better prices, innovation)
what’s perfect competition?
so many buyers & suppliers no one can influence the price
what are the (theoretical) prerequisities for perfect competition?
all market players & sellers must have access to all information at all times
there must not be any barriers to enter/exit the market
there must not be aby (personal) preferences - i.e. goods must be replaceable
what are the factors of production?
resources that are used by businesses to make products/offer services:
entrepreneurship:
- labour (all human resources)
- land (all natural resources)
- capital (machinery, plant, vehicles, financial resources)
knowledge & technology
what’s the 3-sector model & which sectors are in it?
Primary sector - extracts raw materials from the earth (farming, fishing, mining, forestry)
Secondary sector - transforms raw materials into goods (manufacturing). Mostly produce cars, ships, machinery, printed circuit boards & IC substrates, computers, clothes, etc.
Tertiary sector - comprises the service industry, like distribution, banking, insurance, coaching etc. in developed countries (like the EU). In wealthy countries with high GDP this sector = 70% of the economy.
what’s GDP?
gross domestic product - the total monetary value of final goods & services produced in a country in a year
what are the pros & cons of gdp?
pros:
is considered to measure the overall economic activity of a country & also as an indicator of economic growth: if GDP (adjusted for inflation) increases over time, the economy is growing
cons:
doesn’t reflect the sustainability of growth, nor it is a perfect indicator of economic well-being in a country. E.g. natural disasters can increase GDP due to rebuttal efforts
why are profits important for everyone involved in a business?
they can be reinvested, enhancing the durability & sustainability. they are also important for the owners & investors b.c. the profits are their reward for the risk they have taken
difference between profit & no-profit organizations?
profit-oriented: aim for profit (revenue>cost)
not-for-profit: focus on covering costs, any profit is reinvested to enhance the service (The Red Cross, WWF)
sizes of a business
.
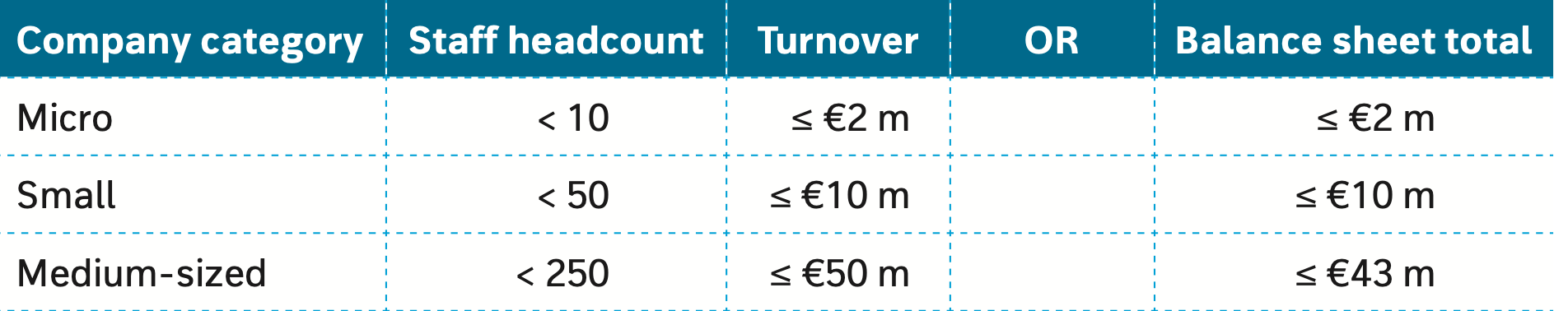
why is definition of an SME important?
for access to finance & EU support programs targeted at these enterprises & for accounting
local business & its properties
they operate in a small area, most customers live nearby, doesn’t serve the national market. Possible challenges: finding customers, undercapitalisation
national business & its properties
serves the whole country. Possible challenges: choosing a suitable location (just like local business), deciding on the delivery. The supply chain is much longer
international business & its properties
sell products in multiple countries. Possible challenges: longer supply chain, different legal & economic systems, different cultures & language, different currencies
what do all businesses have in common?
they are always integrated into an environment they operate in
who’s a stakeholder?
everyone that is (potentially) affected by the activities of a business
who are the main stakeholders & why they matter?
owners - invested money, want profits
managers/employees - jobs=income, want security & purpose
suppliers - provide needed materials, rely on orders
customers - buy the product, want quality & value
communities - affected by business activities (local, national, global)
government - regulates businesses, collects taxes, protects the environment
factors that influence the success of a business?
considering the stakeholders & their (conflicting) interests
having a suitable legal structure
having a solid financial structure
awareness of the market & changes in it
awareness of costs & profitability
what are possible answers to the question “who owns the business?”
The owner and manager can be the same person, but he may also wish to invest his money and own (a part of) the business but want other people to run the business and make the management decisions. A business can also be owned by another business.
why is the legal structure of a business important?
The legal structure of a business has an impact on its financial options. And businesses usually need some additional sources of finance. Therefore, businesses often change their legal structure in order to gain access to further financial options.
what is a sole proprietorship?
Sole proprietorship / sole traders- a business that is owned by one person who also manages and runs the business. Easy to establish. No financial requirements. Is not a legal entity of its own → profits directly reported to owner’s tax statement. Owner is liable for all debts & obligations. If the sole proprietor needs support, he/she can hire personnel and it will become his/her task to make the most important management decisions and take all the risks.
Financial funds for sole proprietors:
External sources of finance:
own savings (own investments)
investors
creditors (all kinds of credit are liabilities):
long-term bank loans (are based on land and property as collateral (mortgage))
short-term credit:
bank overdraft (once the bank account has been opened, the sole proprietor can withdraw money from the account when it is needed. Interest is only paid when the account is overdrawn)
trade credit (based on an agreement with the supplier. Usually a business doesn’t have to pay all purchases immediately but is provided a trade credit period)
Internal sources of finance (no financial charges have to be paid for this sort of funds):
the profit of a business can be retained and reinvested as soon as the business generates revenue (unless the profit is taken by a sole proprietor)
the sale of assets that are not needed
what’s a partnership?
two or more persons jointly found a business. They need a partnership agreement in order to settle the rights & responsibilities as well as the division of profits & loses, it also specifies each partner’s percentage of ownership, the division of profit & loss, terms of partnership, rights & responsibilities, decision making & resolving disputes, and etc.
financial funds for partnerships
similar to those of sole proprietors, but partners should possibly be able to invest more, raise more funds, and offer more collateral for getting a loan
what types of partnerships are there?
a general partnership and a limited partnership
what’s a general partnership?
General partnership - all partners have equal rights, liabilities, and responsibilities. “Offene Gesellschaft”, or “OG” in Austria. In this type of partnership each partner has unlimited liability - each of them is solely liable for all debts of the business
what’s a limited partnership?
Limited partnership - at least 1 partner is not involved in the management of the business. “Kommanditgesellschaft”, or “KG” in Austria. The person who is not involved in the management has limited liability - their liability is limited to the amount of money that they have contributed to the business.
what’s a corporation
a legal entity of its own, meaning it has the same rights & obligations as people (can own property & land, hire people, close contracts, sue, be sued). The owner/shareholders need not to manage the company, and the managers need not own a share of business. The shareholders’ liability is usually limited to the amount of money they invested when buying the shares.
who is a corporation managed by?
by the board of directors, persons who are elected by the shareholders to make all major business decisions and to represent the shareholders. They include: Chief Executive Officer (CEO), Chief Financial Officer (CFO), Chief Operating Officer (COO), Chief Information Officer (CIO) or Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
financial funds for corporations:
Everything in the sole proprietorship
Share capital. It is usually not redeemed by the company. It is long-term capital or even permanent capital.
Bonds - a loan (is a liability for a company) between investors as creditors & a corporation. Usually more attractive than borrowing money from banks. Enables corporations to invest in long-term assets
who’s a stockholder
stockholder or shareholder - a person who buys shares
what’s a stock exchange?
is a financial market, regulated by the authorities, where shares and other securities (e.g. bonds) can be easily bought & sold by other people & businesses
what’s an initial public offering (IPO)?
an introduction of shares on the stock market by the company for a certain price. Then the prices are determined by supply and demand
reasons for why the demand for shares of a corporation can change positively:
people expect that the business is doing well, it will make profits in the future, it will increase market share and/or successfully introduce a new product → demand rises
economic indicators:
economic growth
low interest rates
higher rates of inflation
what does an increase in share prices mean for the company?
it does not have any additional financing effect for the issuing corporation. The beneficiaries of this increase are shareholders only
most important reasons why people invest in shares:
they believe in the business & want to support it financially
annual income: the wish to get dividends in return
capital growth: they hope that the share prices will rise and the shares can be sold at a higher price than they were bought at
the wish to go to the annual stockholders’ meeting and vote & influence business decisions (because common stock includes the right to vote at the meeting). Shareholders of preferred shares do not have this right, but earn a higher dividend
investment in real values that will not lose its price so easily even due to inlation
what’s a public limited company (PLC) and what it’s called in other places?
a corporation that is publicly traded on the stock market. In USA the term “Inc.” for “Incorporated” or “Ltd.” for “Limited” is used. In German-speaking countries the term “Aktiengesellschaft” (AG for short) is used. Minimum capital requirement - 70k€
What’s a European Company (SE)?
it is a corporation that is similar to an AG governed by Community Law applicable in all - and only in - memeber states of the EU
what’s free float?
shares that are available on the stock exchange and are not held by anyone
key figures on shares that are of interest for investors
share price & its development.
market capitalization or “market cap” - total market value of a company’s (outstanding) shares (=shares currently held by all the shareholders multiplied by the current market price). It used to evaluate a corporation's size. Not necessarily a meaningful metric, b.c. there are many reasons why share prices might be low.
dividend yield - expresses the dividend in relation to the share price
price-earnings ratio (P/E ratio) per share - company’s current share price relative to its earnings per share. (p/e ratio of x means you can expect to invest x euros in the company to receive 1 euro of their earnings). Low P/E ratio = shares are undervalued / company is thriving & earnings are high
what are bonds?
a loan between investors as creditors and a corporation. More attractive to corporations that borrowing from banks b.c. the interest rate is lower and it allows the to invest in long-term assets
what’s a private limited company and what is it called in other places?
corporations, whose shares are offered to the other owners of the company instead of a public stock exchange. Limited Liability Company (LLC) in the USA, private company limited by shares in the UK, and “Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung” or GmbH in german-speaking countries. Minimum capital is 35k€
if a business has several sources of finance available that it can choose from, what will it make its decision based on?
costs, the intended use of the financial funds and its current financial situation:
costs comprise interest payments for loans & credit or administration costs for issuing shares/bonds
if financial funds are used for capital expenditures (buying assets that will be used over many years), long-term finance is required. Revenue expenditures (buying material that is used for production) can be financed by short-term finance sources.
a high-geared business (one that has a high proportion of loan capital) might have difficulties obtaining more credit. Lenders are reluctant to offer more funds (only at a higher interest rate) and/if collateral can be offered. Such a business should use internal sources of finance and/or find investors.
why do all loans have to be repaid?
a high proportion of loan capital can be a burden (risk of insolvency)
definition of marketing according to the American Marketing Association?
“the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large’. Market activities intend to “have a market”, know the market, tailor the products to customers’ needs and wishes and continuously improve the product
what does marketing aim at?
identifying the (potential) customers’ needs and wants
developing the product(s) and the product features accordingly
communicating the products and their benefits to the (potential) customers at a price they are willing to pay and made available to them through the distribution network
what’s marketing about?
it’s more than a management process, it is a philosophy that is present in the whole business. It’s about creating value for the customer.
what’s marketing based on?
on the analysis of the strengths of a business and its know-how that is put into the development of its products. It also requires a thorough analysis of the market and the wishes and needs of (potential) customers in order to offer products that solve customers’ problems & fulfill their wishes and needs.
what’s a product in marketing terminology?
every good and/or service that can be exchanged in order to fulfill the wishes and needs of customers
who can be a customer of a business?
either businesses (producer products, B2B) or customers (consumer products, B2C)
marketing objectives:
customer satisfaction: satisfied customers often become loyal customers who will possibly buy the product again.
creating a unique selling proposition (USP): a USP is a product considered to be different from other similar products. This is also called differentiation and can be based on a certain characteristic of the product or how it is promoted. Building a brand supports creating a USP.
gaining and maintaining market share: it indicates their competitiveness.
maintaining or increasing sales: sales are needed to cover production costs and make a profit.
profitability: the higher the sales figures are, the more profit the business will make. Profits are important because they can be retained & reinvested and they also reimburse the owner for the invested money.
product orientation vs market orientation:
product orientation: focus on production & production features → a good product sells itself (advertisement) → sales
market orientation: focus on customers’ needs/wants → producing what customers need/want → sales
what customer relationship management (CRM) aims at?
it aims at creating a long-term relationship with customers. Their data is kept to mail or email newsletters and etc.
what’s market research?
it provides information about existing and prospective customers of a business, the (potential) buyers of its product(s), about the competition, and the industry in general.
what’s market research based on?
It is based on 2 sources:
primary sources: gained by conducting an empirical study on having data collected by a market research institute. a business might be interested in who their customers are, which products they they buy, what they think about these products, if they also buy similar products from other businesses. but conducting a study can be very costly, especially for small businesses
secondary sources: based on existing research. Government agencies, trade and/or industry associations or other businesses often conduct such research free of charge. But, in most cases, this information is very general and not tailored to the specific needs of a business
what are the questions that customer analysis answers?
who its current and potential customers are: B2B, B2C. Also, the buyer and the user might not be the same person (e.g. parents bought a toy for their kid)
what the customers do with the products
where the customers buy the products: helps identify preferred channels of distribution, show weaknesses of some of them and encourage the usage of alternative ones
when the customers buy the products: helps identify seasonal fluctuation, plan production ahead accordingly, and consider price differentiation over the year
why customers choose or don’t choose a product: important for product development and enhancing market share
what’s market size (or market volume)?
the total sales of a product of all the businesses in the market. can be expressed as a value (e.g. in euros) or as a quantity (# of pieces sold)
what’s absolute market share & its formula?
it refers to the proportion (percentage) of a certain market that is held by a busines/its products/brands.
Absolute market share = sales volume of one business (or brand) / market volume
what’s relative market share & its formula?
shows how a business/one of its brands is doing in terms of its largest competitor.
you need to know absolute market share to calculate this one!!!!!!
Relative market share = market share of a business (or brand) / largest competitor’s market share
Market and sales volume versus market and sales potential