ECHO 1
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
what views do you see in parasternal?
long axis
short axis
what views do you see in apical?
4CH
5CH
2CH
3CH (long axis)
what view do you see in subcostal?
4CH
short axis (not in every protocol)
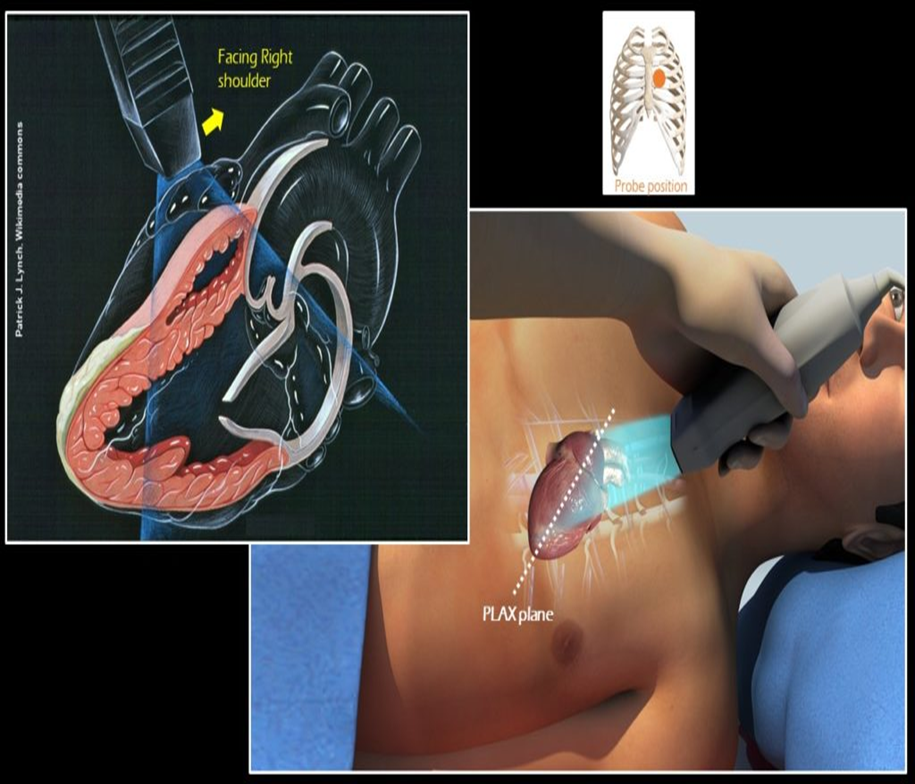
where should the probe be placed for PLAX?
between 3rd and 4th intercostal spaces, adjacent to the sternum
where is the notch pointed in PLAX? patient position?
10 o clock ; LLD
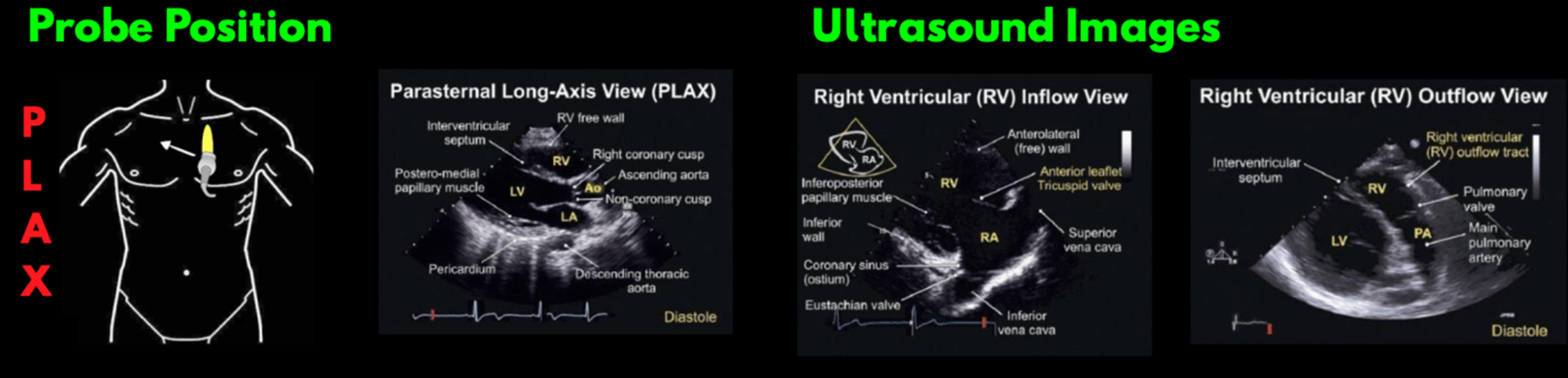
what views are obtained in the PLAX view?
LV (standard view)
RVIT
RVOT
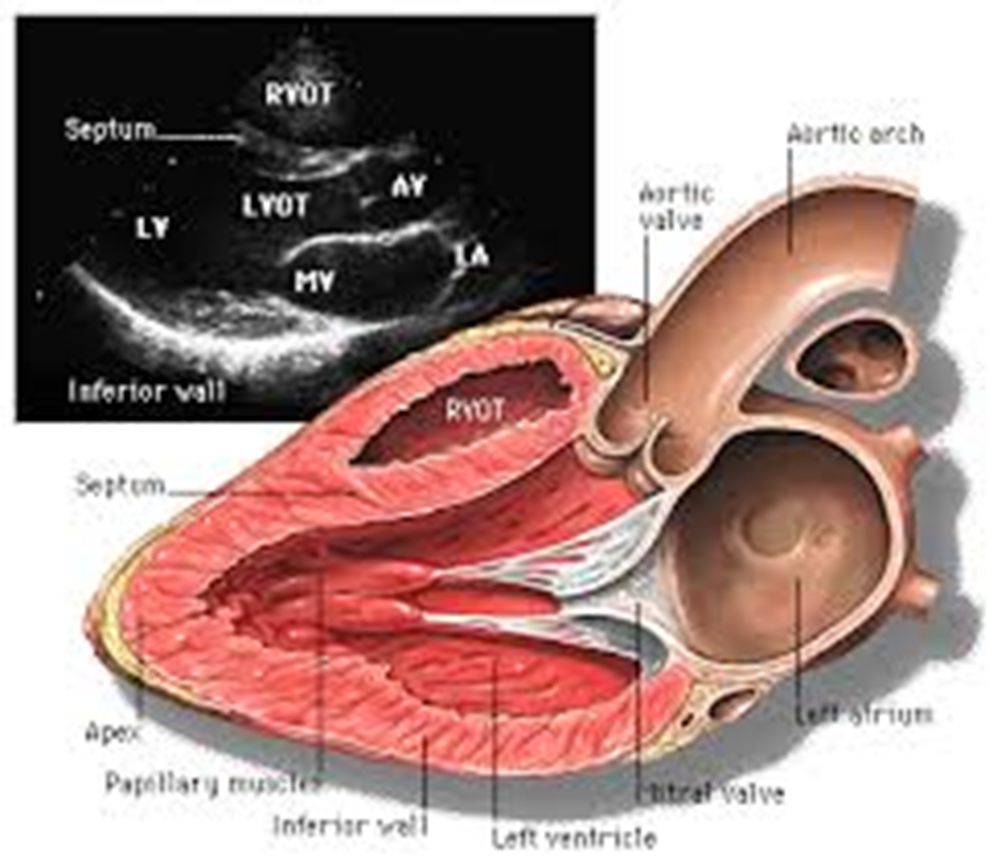
what are the standard landmarks for PLAX?
RV
LV
aortic valve & prox asc aorta
mitral valve
LA
descending ao
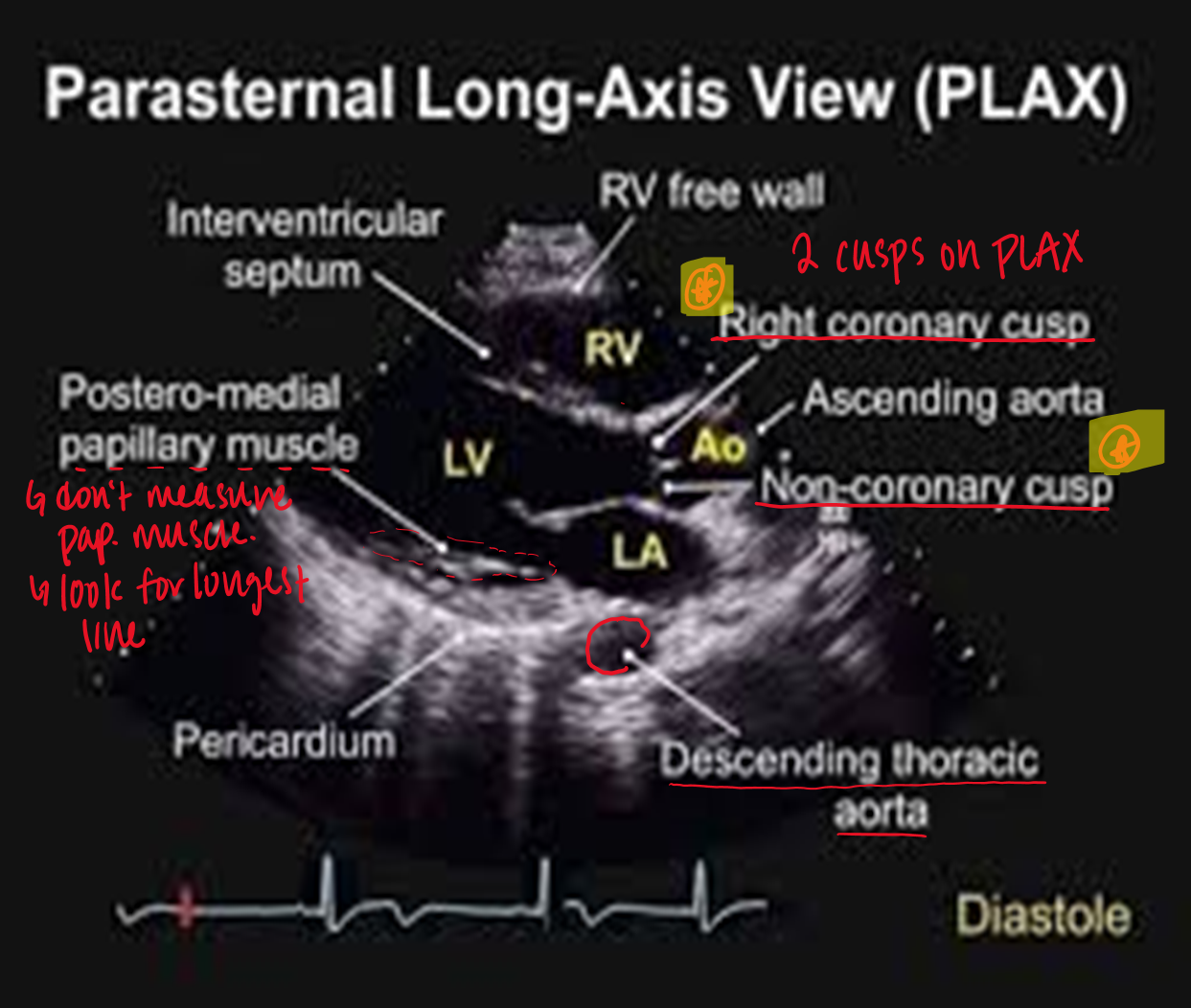
what are you assessing when looking at the
pericardium
LV
aorta
ao valve
mitral valve
RV
pericardium : fluids
LV : wall thickness, size, function
aorta : size
ao valve : motion, openng, calcifications, hemodynamics
mitral valve : motion, opening, calcification, hemodynamics
RV : size
know this
is the apex visualized in PLAX?
no
does breathing help PLAX visualization?
yes
what end diastolic measurements are taken in PLAX?
RV outflow (optional)
LVID
IVS
LVPW
aortic root
how and where is LVID measured?
measured immediately below level of mitral valve leaflet tips
calipers placed on interface between myocardial wall and cavity & interface between wall and pericardium
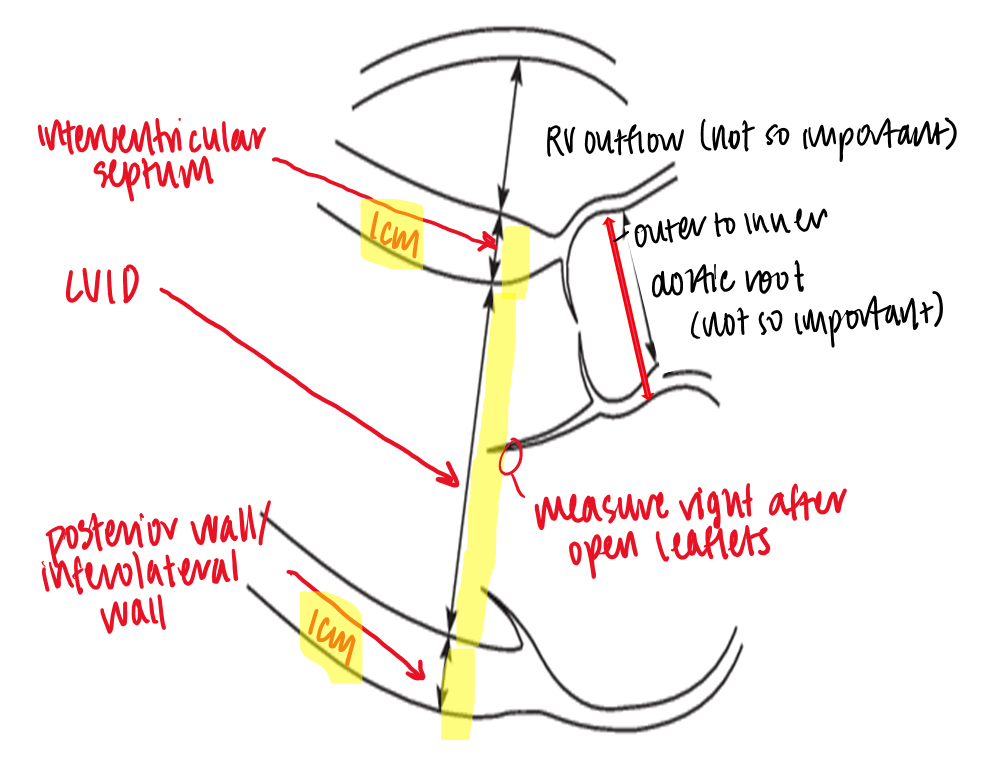
how is the aortic root measured?
max diamter of sinus of valsalva
leading edge to leading edge
what measurements are taken in PLAX systole?
LVID systole
left atrium
how is LVID systole measured?
at the smallest LV dimension, place calipers on interface between myocardial wall and cavity & interface between wall and pericardium
how and where is LA measured in PLAX systole?
meaured from directly under midpoint of sinus of valsalva, perpendicular to the aortic root axis
dont measure these
what is considered a dilated LV in males? females?
males : >5.8
females : >5.2
what is considered abnormal LV thickness in males? females?
male : >1
female : >.9
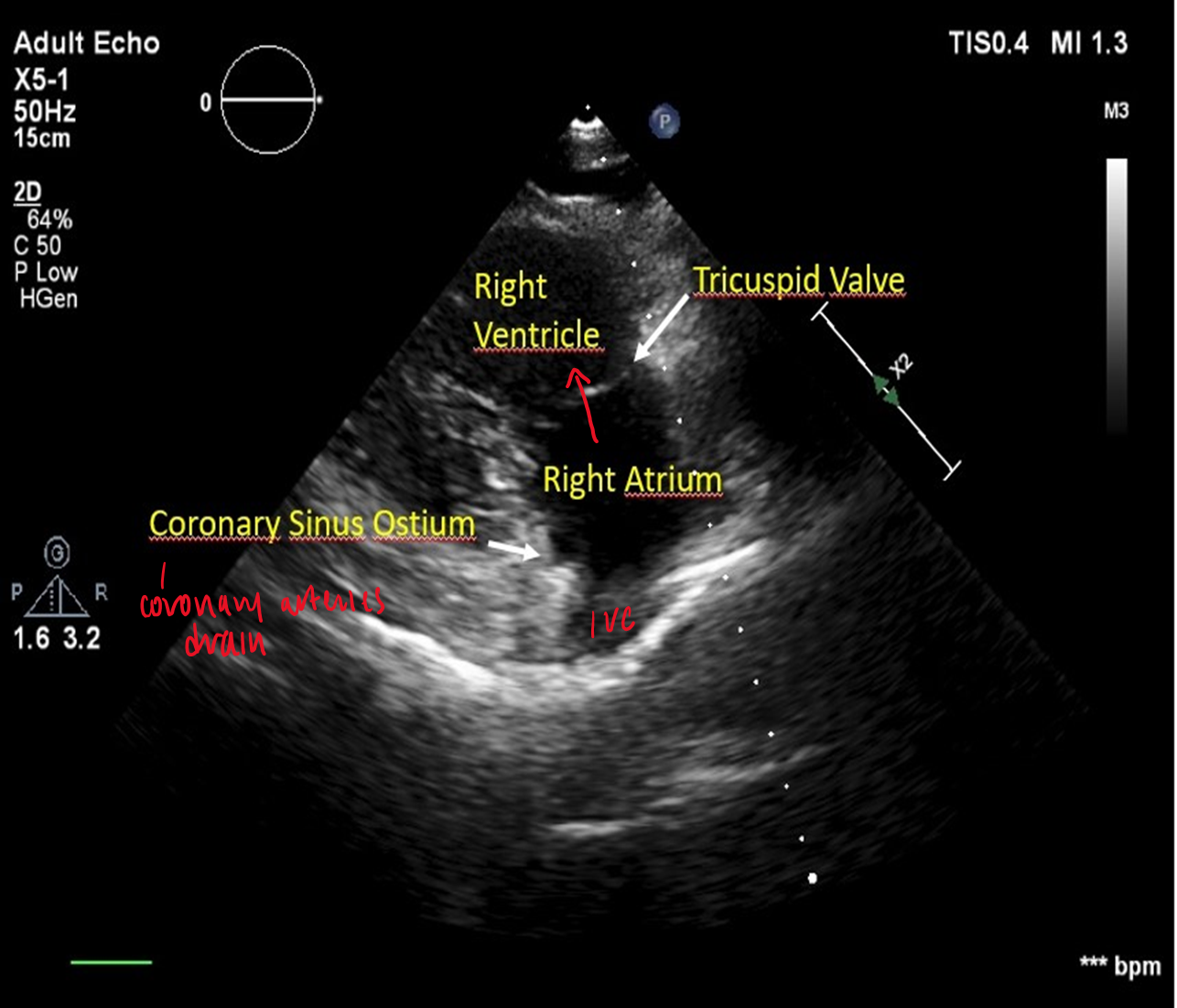
how do you obtain the RVIT from standard LV PLAX view?
angle transducer infero-medially towards patient’s right hip
what can you see in PLAX RVIT view?
RV
tricuspid valve
RA
IVC/SVC
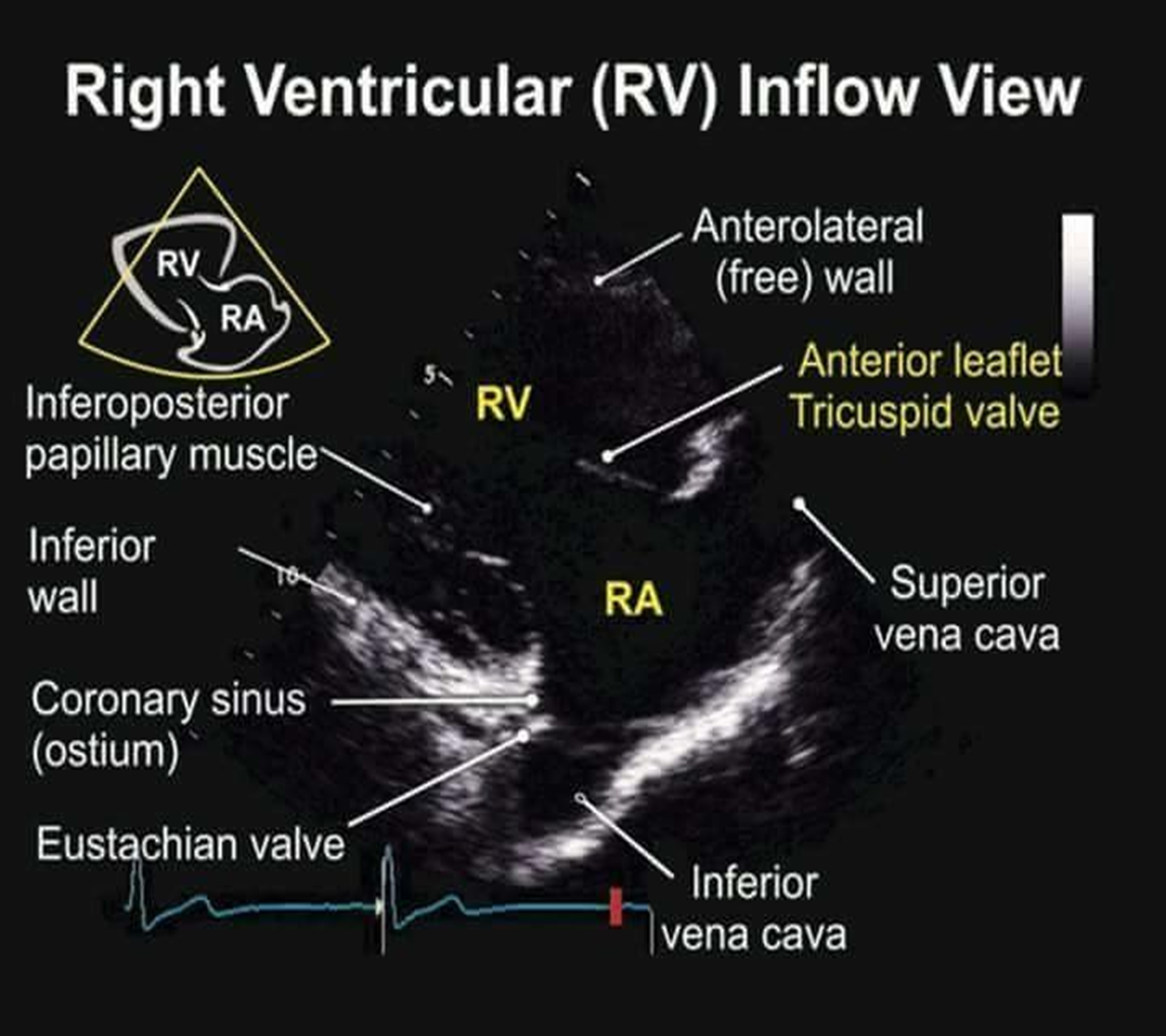
how do you obtain RVOT from standard LV PLAX?
angle transducer superiolaterally towards patient’s left shoulder
what structures do you see in RVOT view?
RV outflow tract
PV
PA
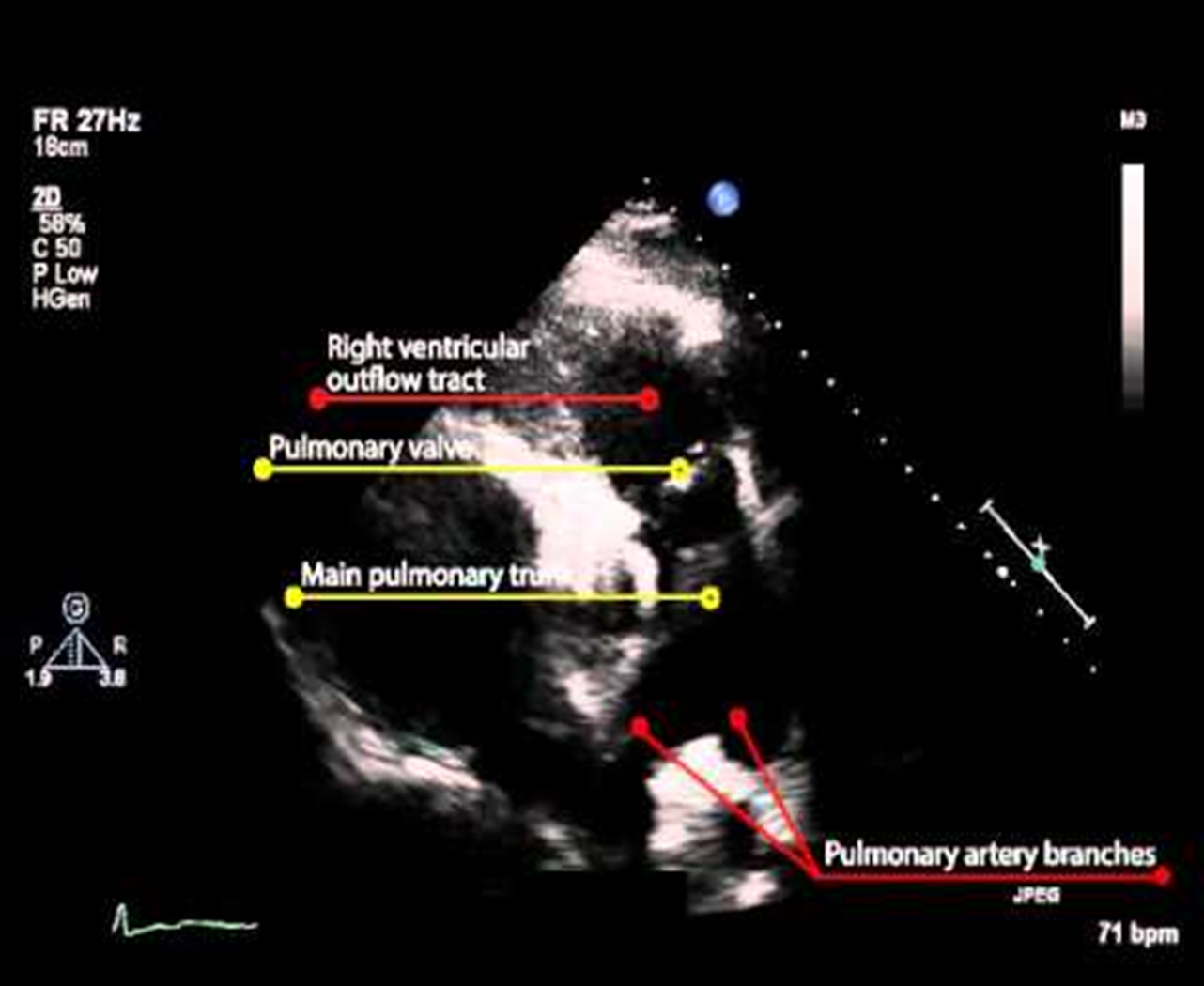
how do you obtain PSAX from PLAX? time position?
rotate notch of transducer 90 degrees CW towards the patient’s left shoulder ; 2 oclock
what are the different views to obtain in PSAX?
aortic valve
mitral valve
papillary muscle
apex
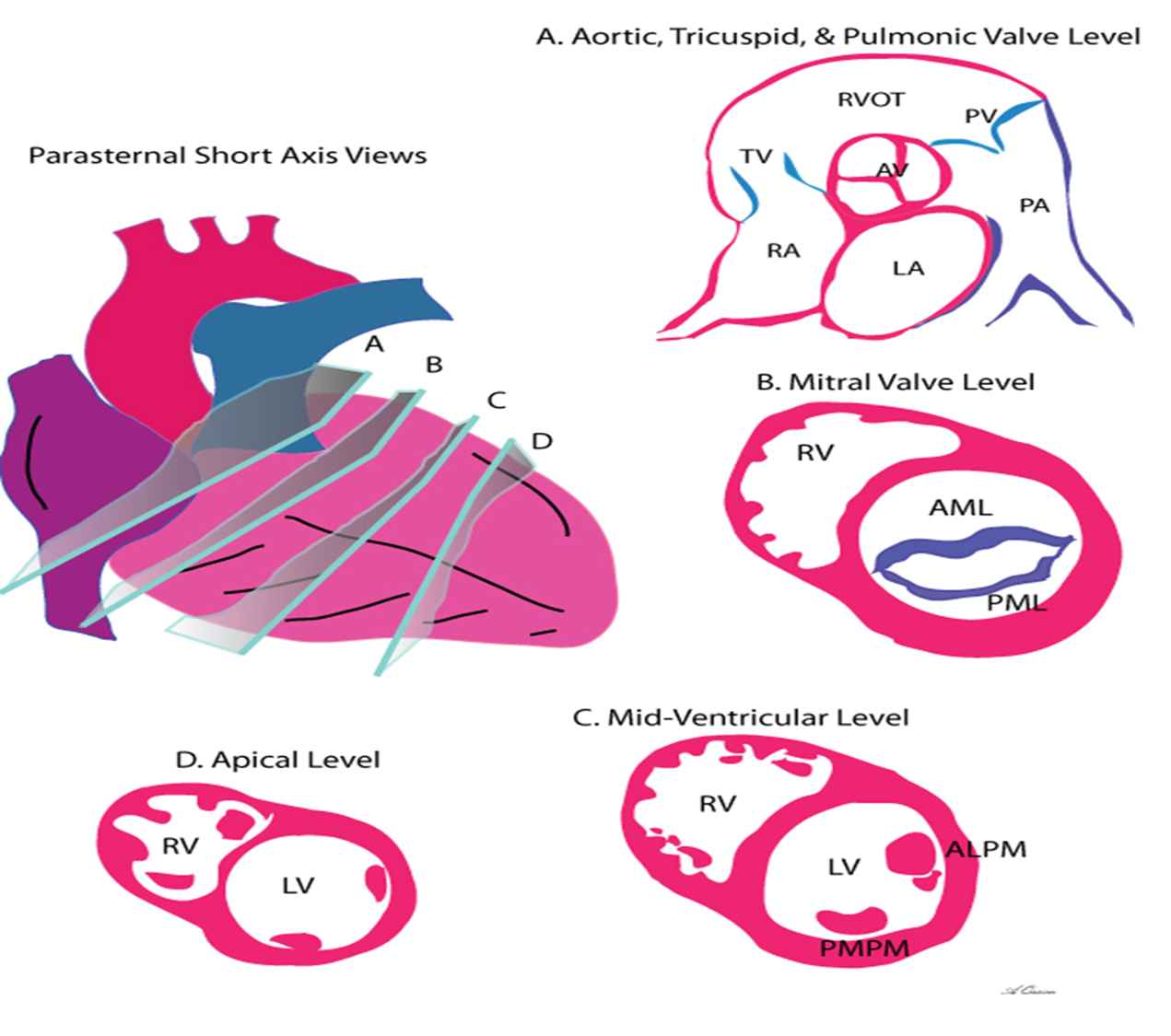
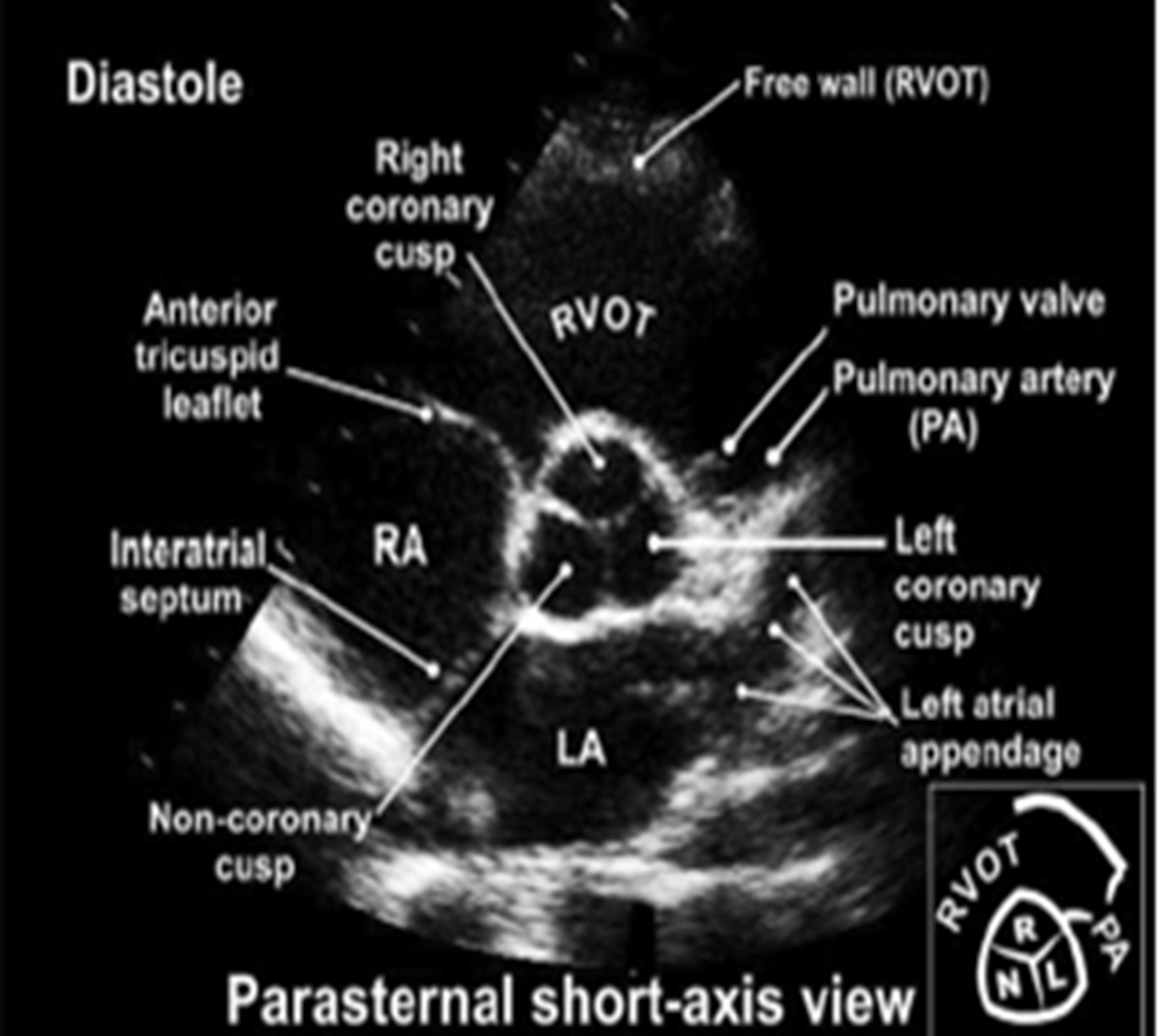
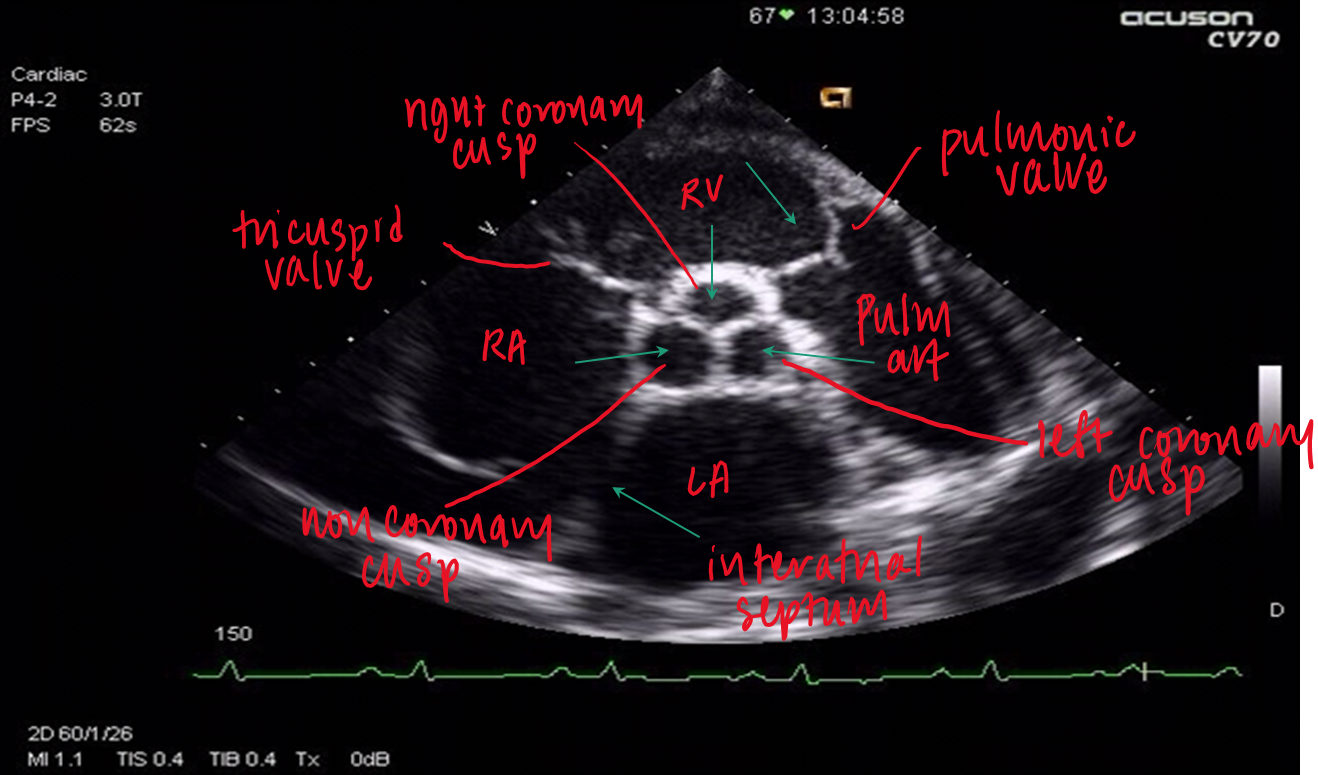
how do you obtain the PSAX at the aortic level?
tilt superior/ superiomedially from PSAX
what structures can you see in PSAX aortic level?
3 leaflets (right, left and non coronary cusps)
RVOT
RA
LA
PA (left and right)
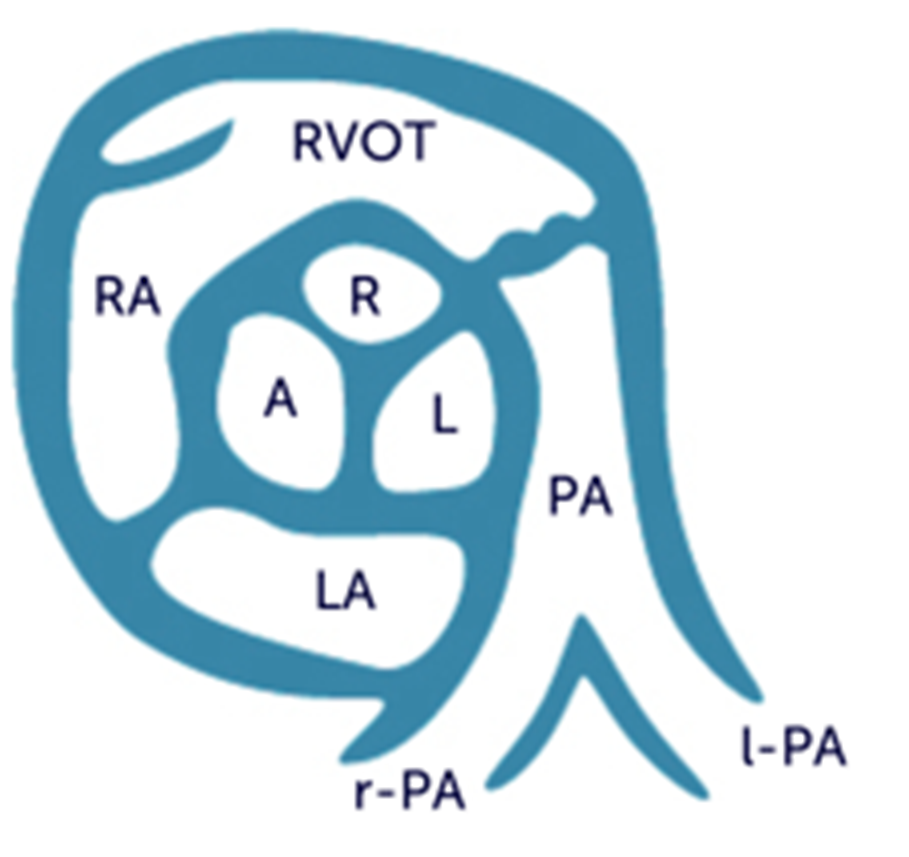
where does the right coronary cusp lie? left? non?
right : adjacent to RVOT
non : adjacent to interatrial septum (between RA/LA)
left : adjacent to LA
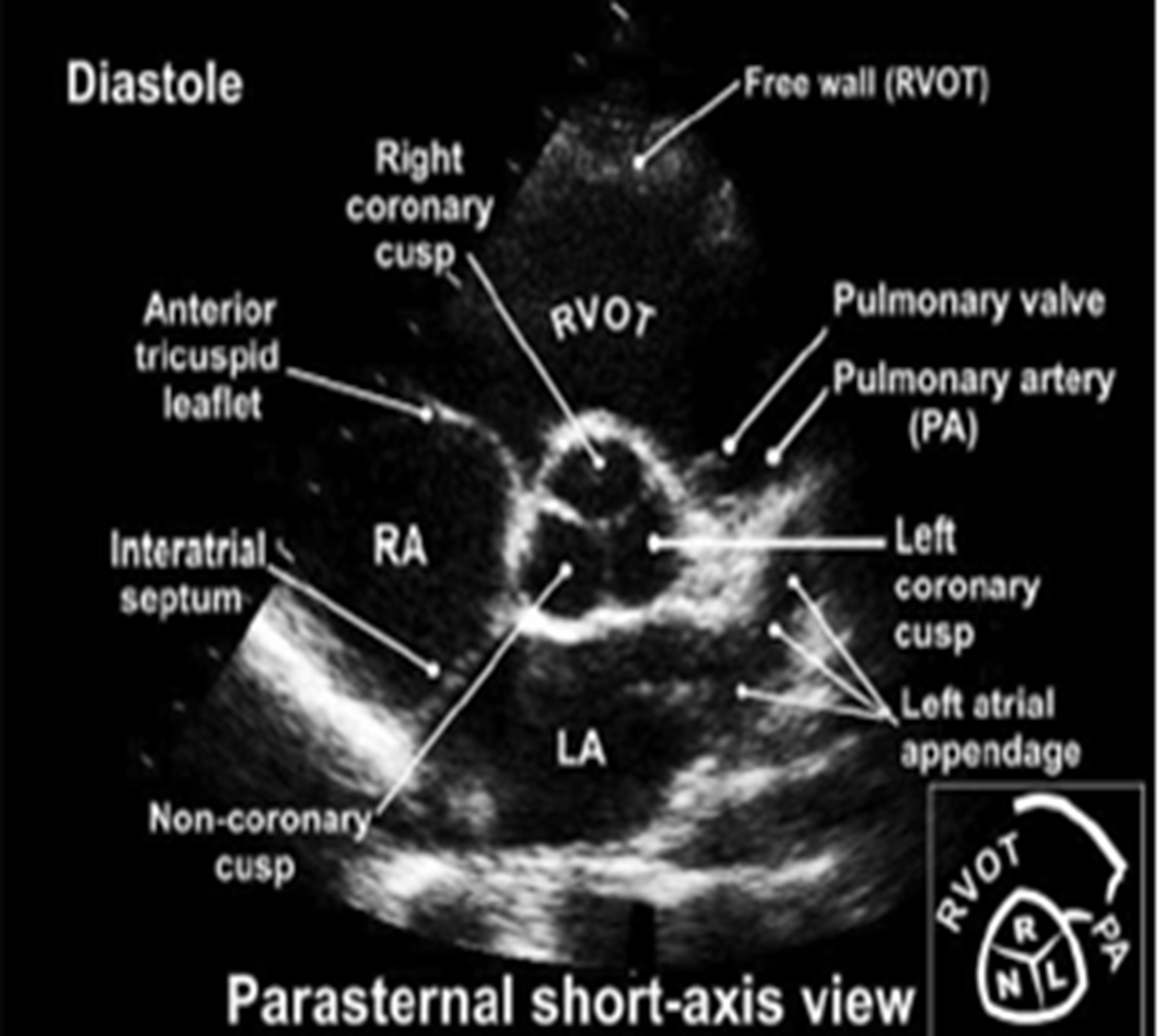
when should the 3 aortic leaflets be identified and why?*
must be seen in systole when the valve is open ;
this is because a bicuspid valve may appear tri-leaflet in diastole as a result of raphe
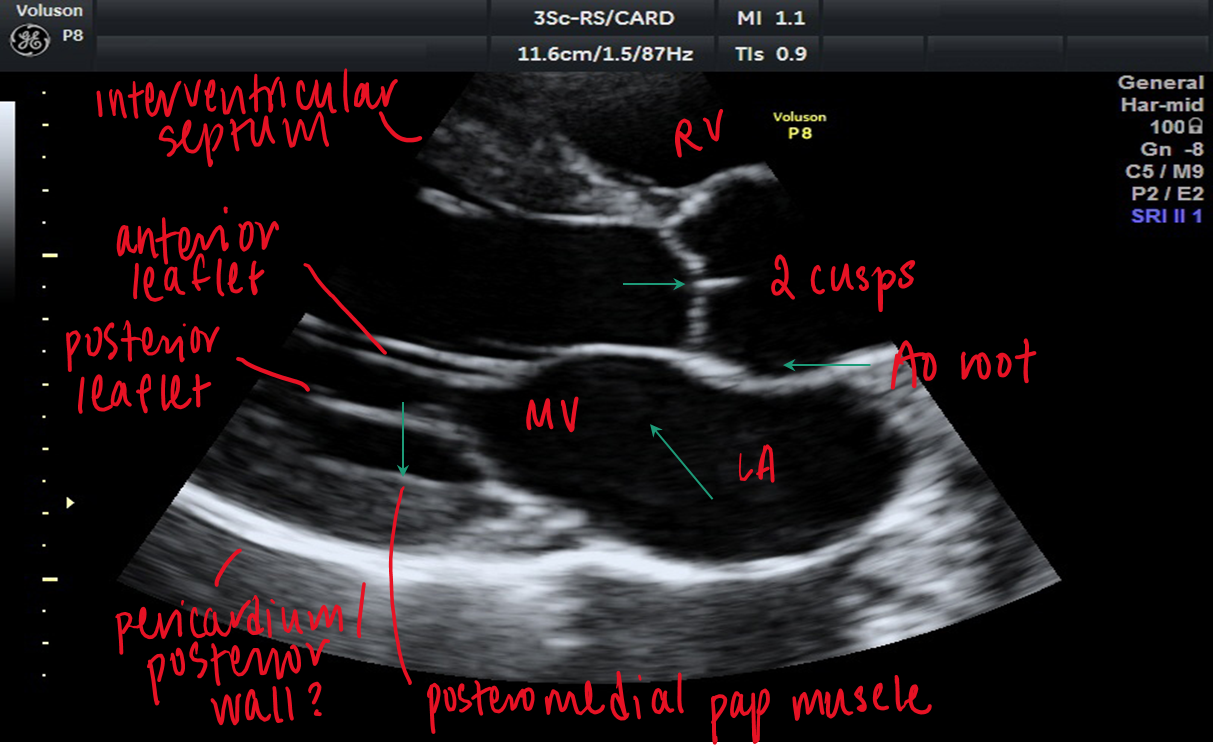
how do you obtain the PSAX mitral (aka?) view from aortic PSAX level?
aka fishmouth
tilt inferiolaterally towards patient’s left hip
(may have to move one intercostal spaces down (no angling) or move 2 intercostal spaces down and angle superiomedially)
which leaflets are visible in PSAX mitral valve view and where are they located?
anterior and posterior mitral valve leaflet
anterior closer to LV/IVS in PSAX mitral valve view
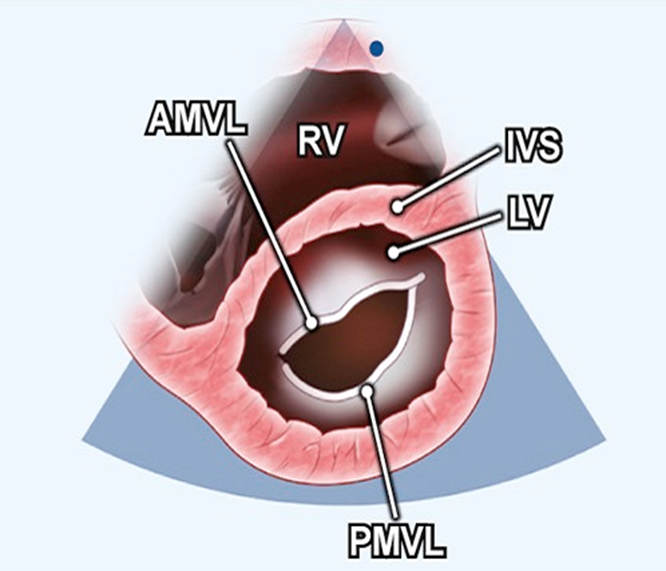
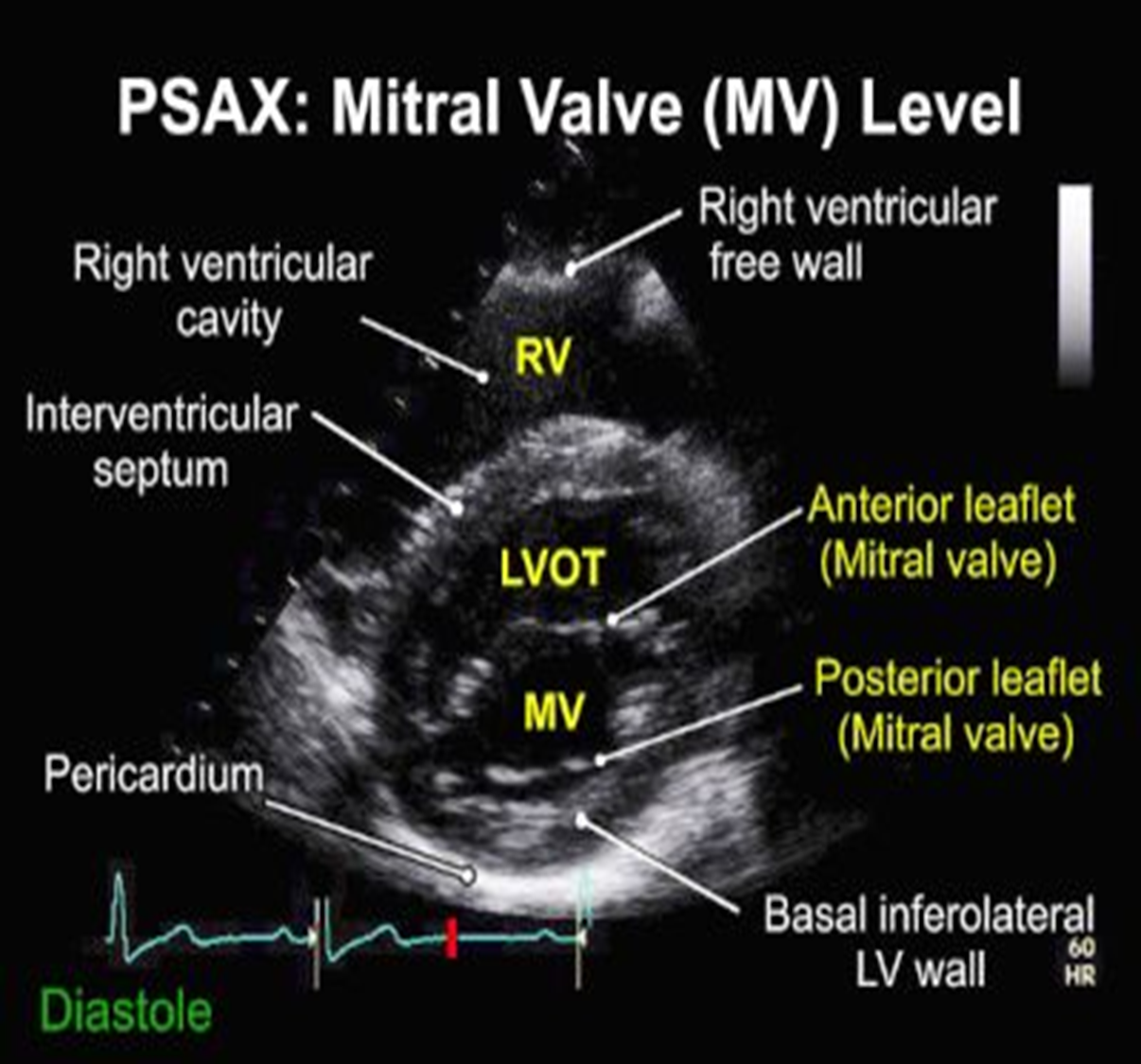
what can be assessed on the PSAX mitral valve level?
calcification, rheumatic disease, regurg, stenosis, IVS defects
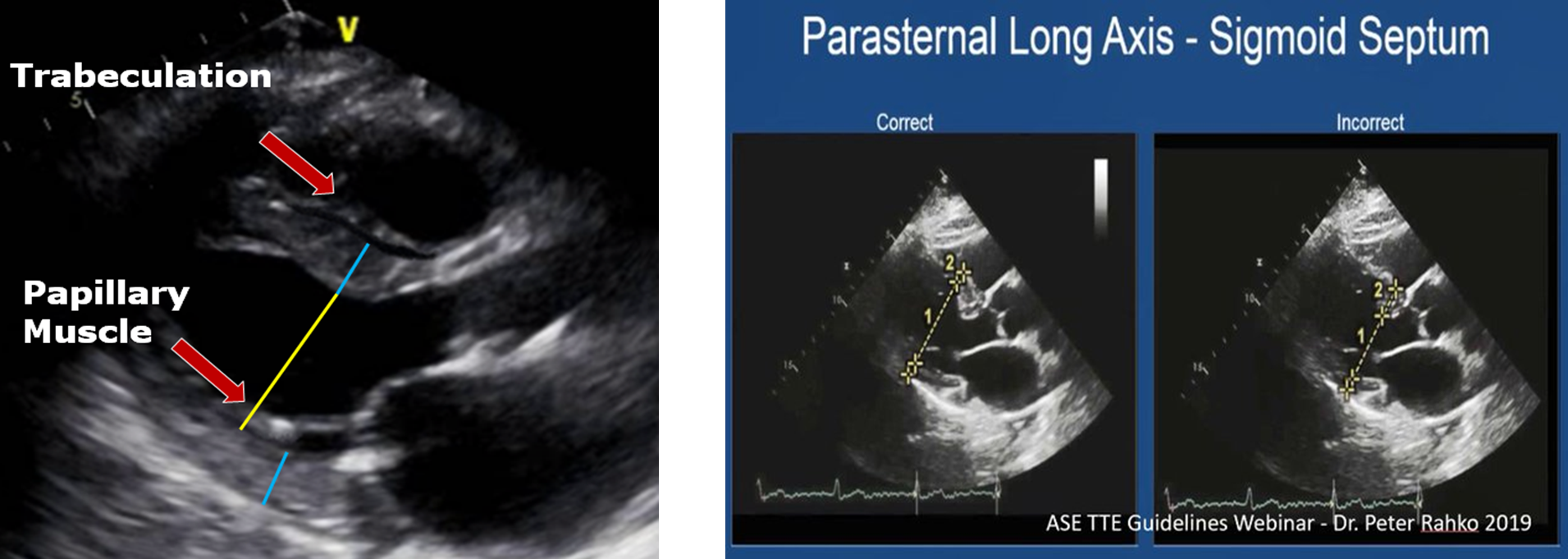
how can you obtain the PSAX view at the papillary muscle level?
tilt/slide more inferior in relation to heart (inferiolaterally)
what landmarks are seen in PSAX at level of pap muscle?
both pap muscles
LV cavity
pericardium
RV cavity
NO mitral valve
what are the pap muscles and where are they located?
posteromedial (left side of screen) and anterolateral (right side of screen) pap muscle
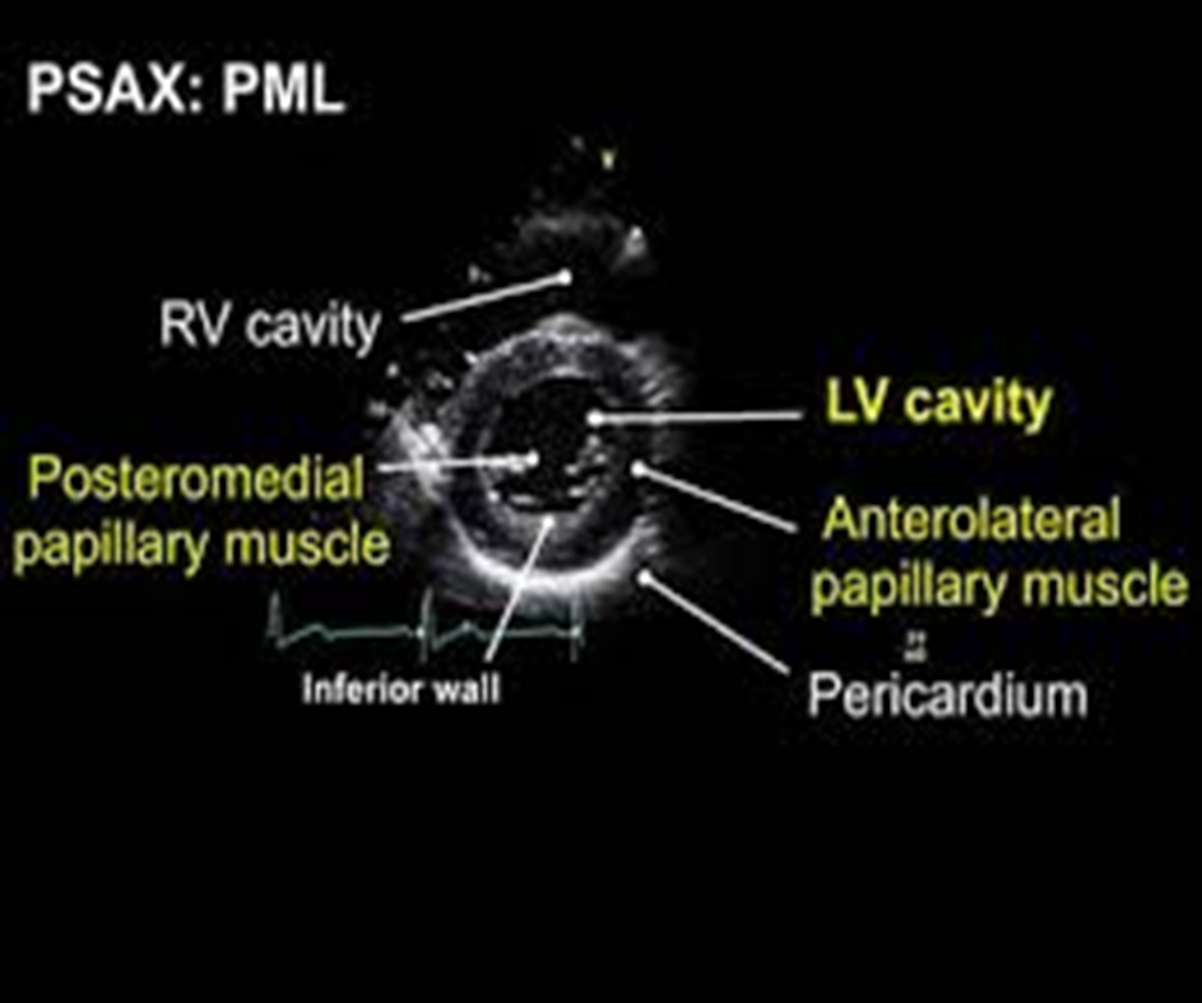
how do you obtain PSAX at the apical view?
tilt/slide more inferolaterally
what is visualized in PSAX apical view?
only myocardium/endocardium
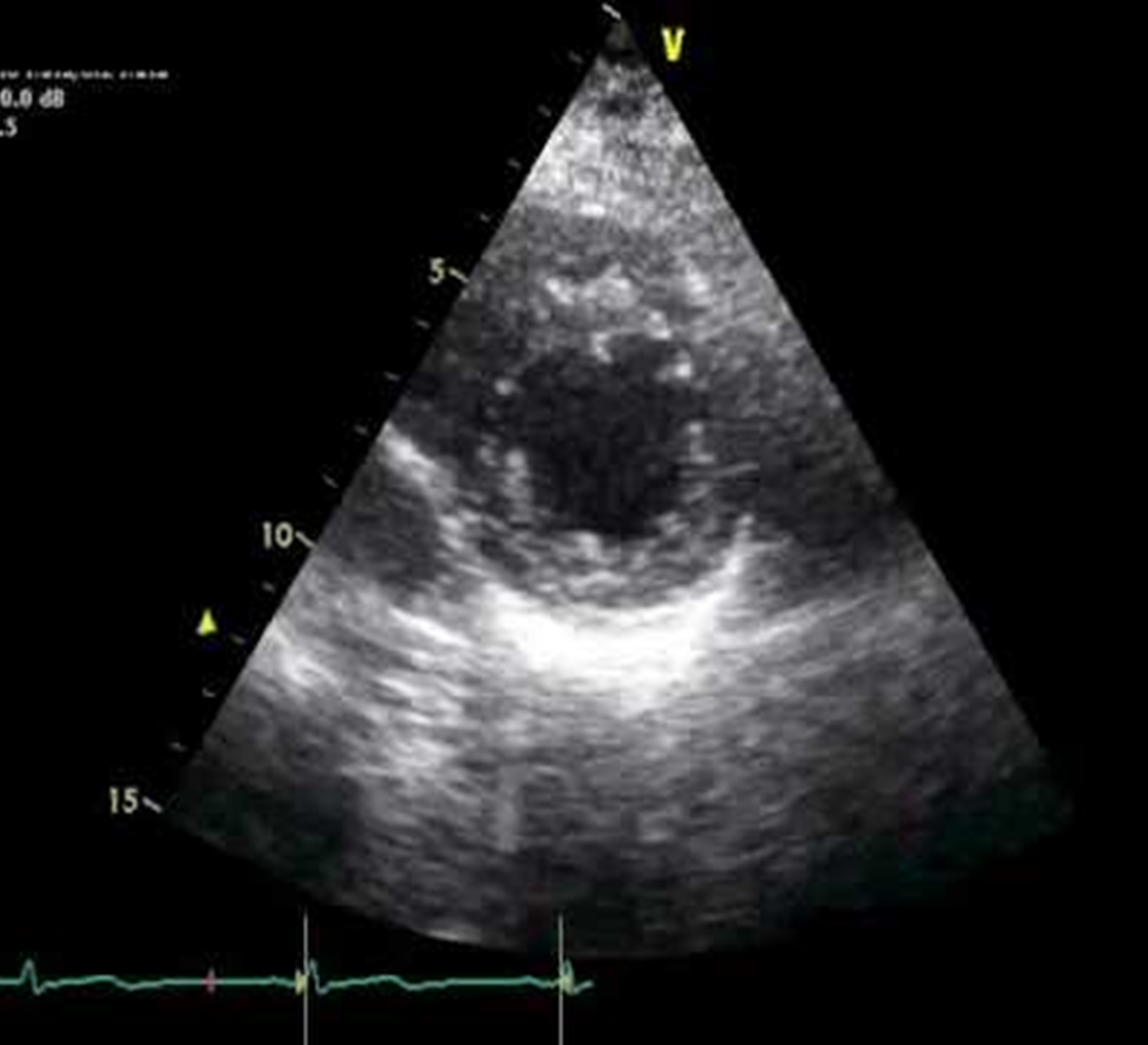
what are the apical views?
4CH, 2CH, 3CH(long axis)
where should the transducer be placed to find the apical 4CH view?notch?time?
by the 5th intercostal rib on the anterior axillary line with the notch pointed towards pt’s left at around 2-3 oclock (can be pinpoint apex by feeling for apical pulse)
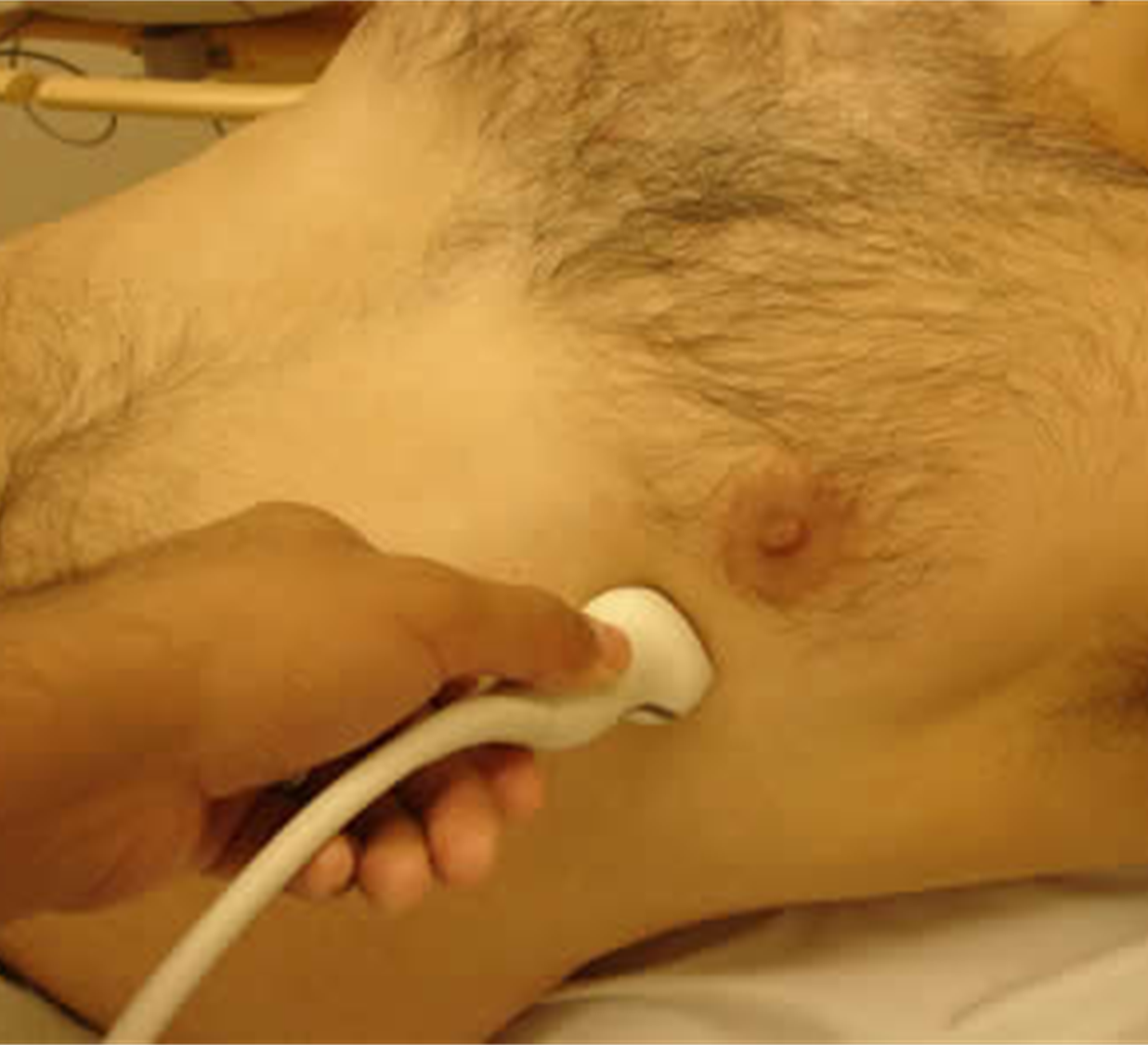
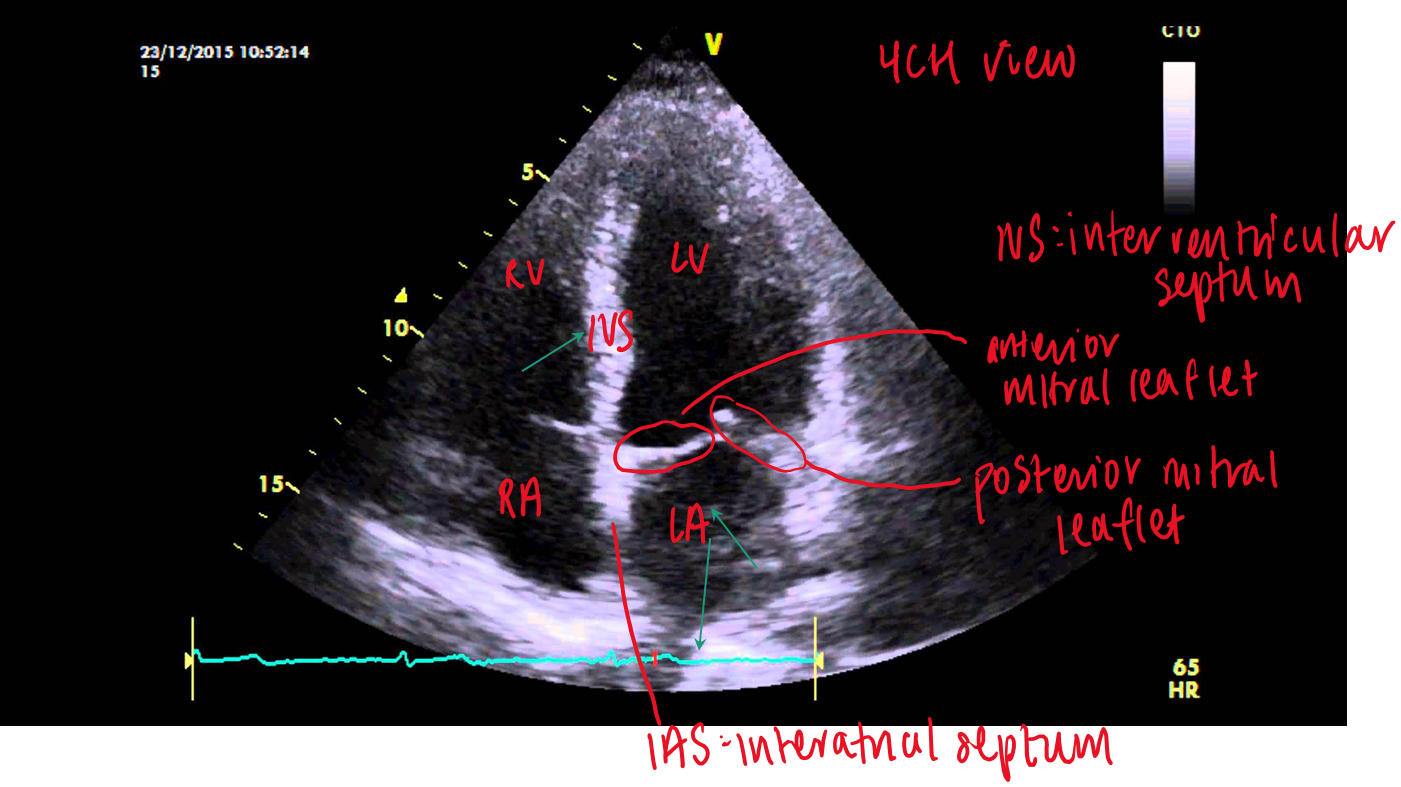
what structures are visualized in apical 4CH?
RV/ LV
TV / MV
RA/LA
IVS
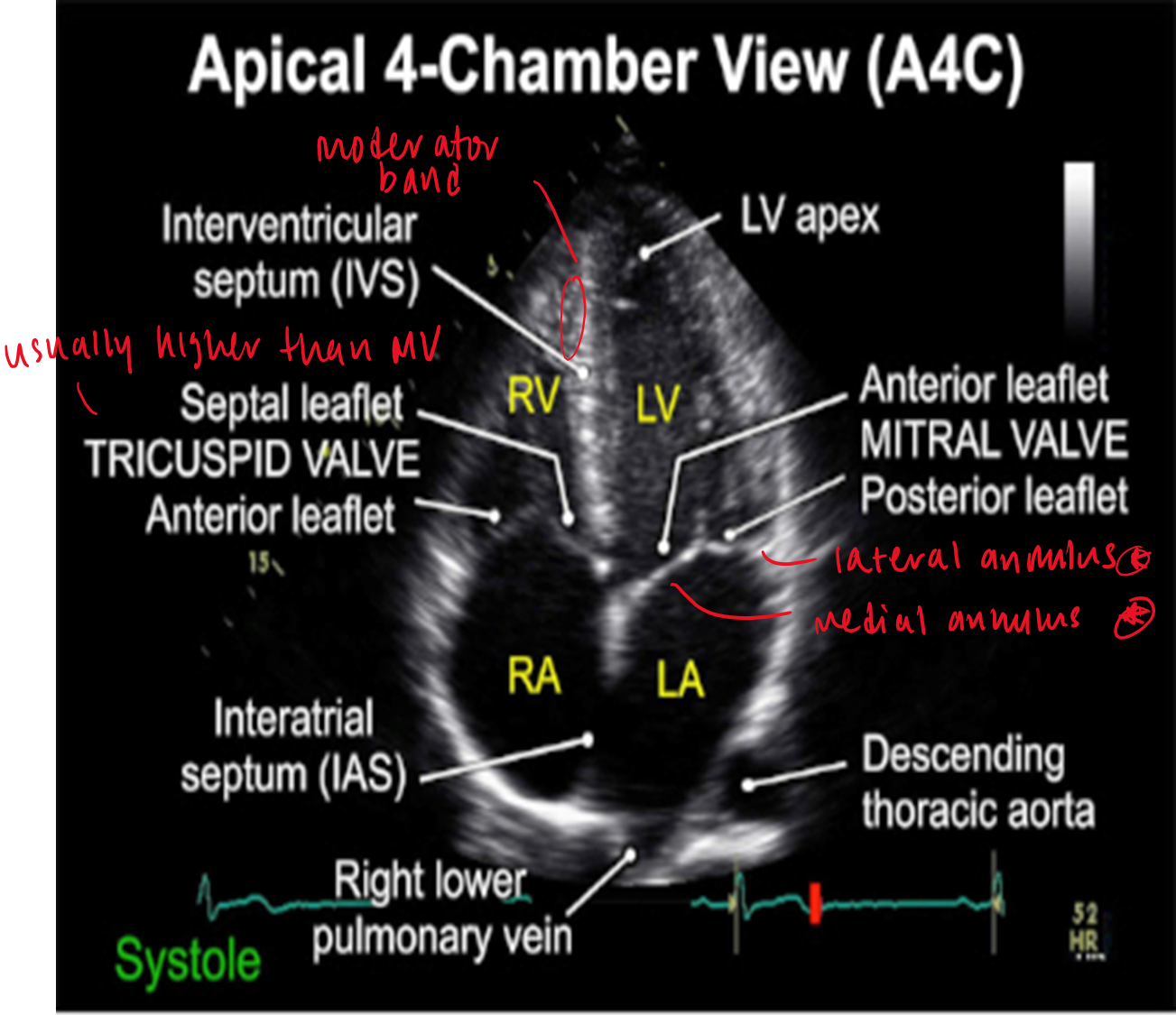
where do the tricuspid and mitral annulus lie relative to eachother?
tricuspid annulus lies slightly higher (1cm) than mitral
how do you obtain the apical 5 chamber view?
tilt transducer superiorly from apical 4 chamber view
what is the difference between apical 4CH and 5CH?
in 5CH you now see LVOT and aorta
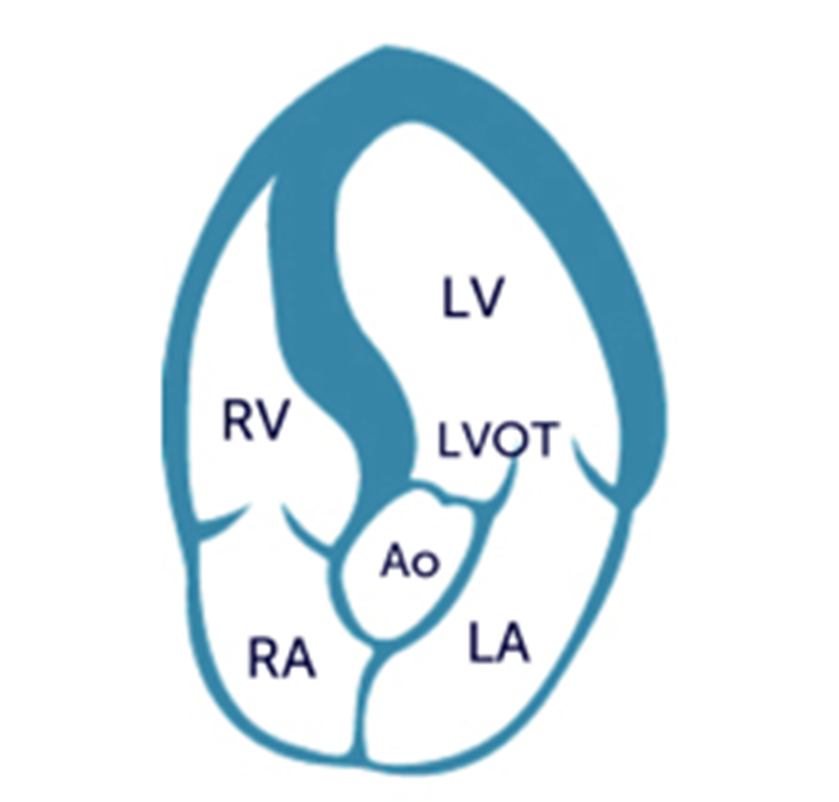
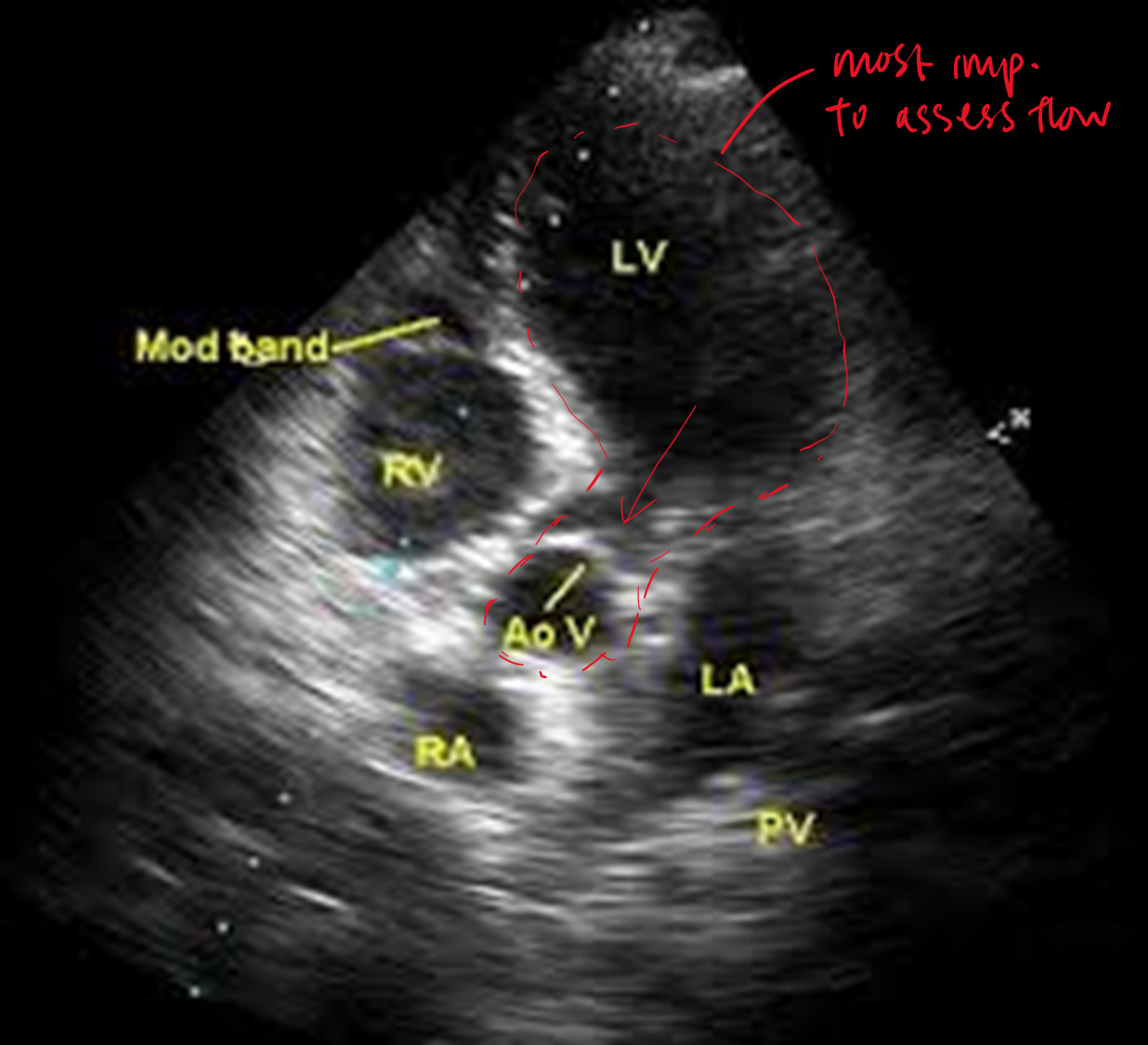
another view of apical 5CH
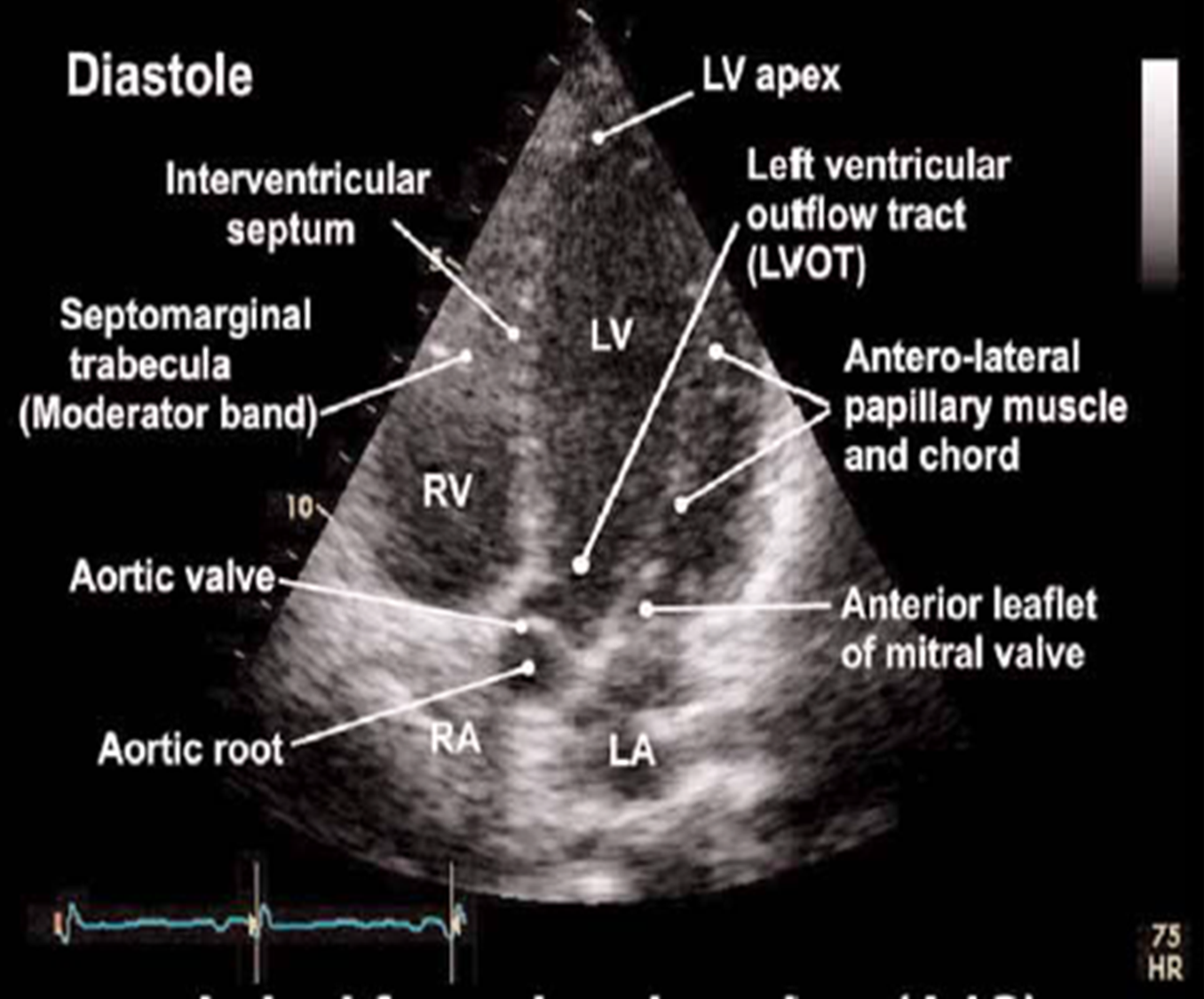
how do you obtain the apical 2CH view?
from the apical 4CH view rotate transducer 60 degrees counterclockwise
what is 2CH view mostly used to asses?
wall motion of anterior and inferior walls
what structures are visualized in apical 2CH view?*
LV
LA
(LA appendage and coronary sinus may be seen)
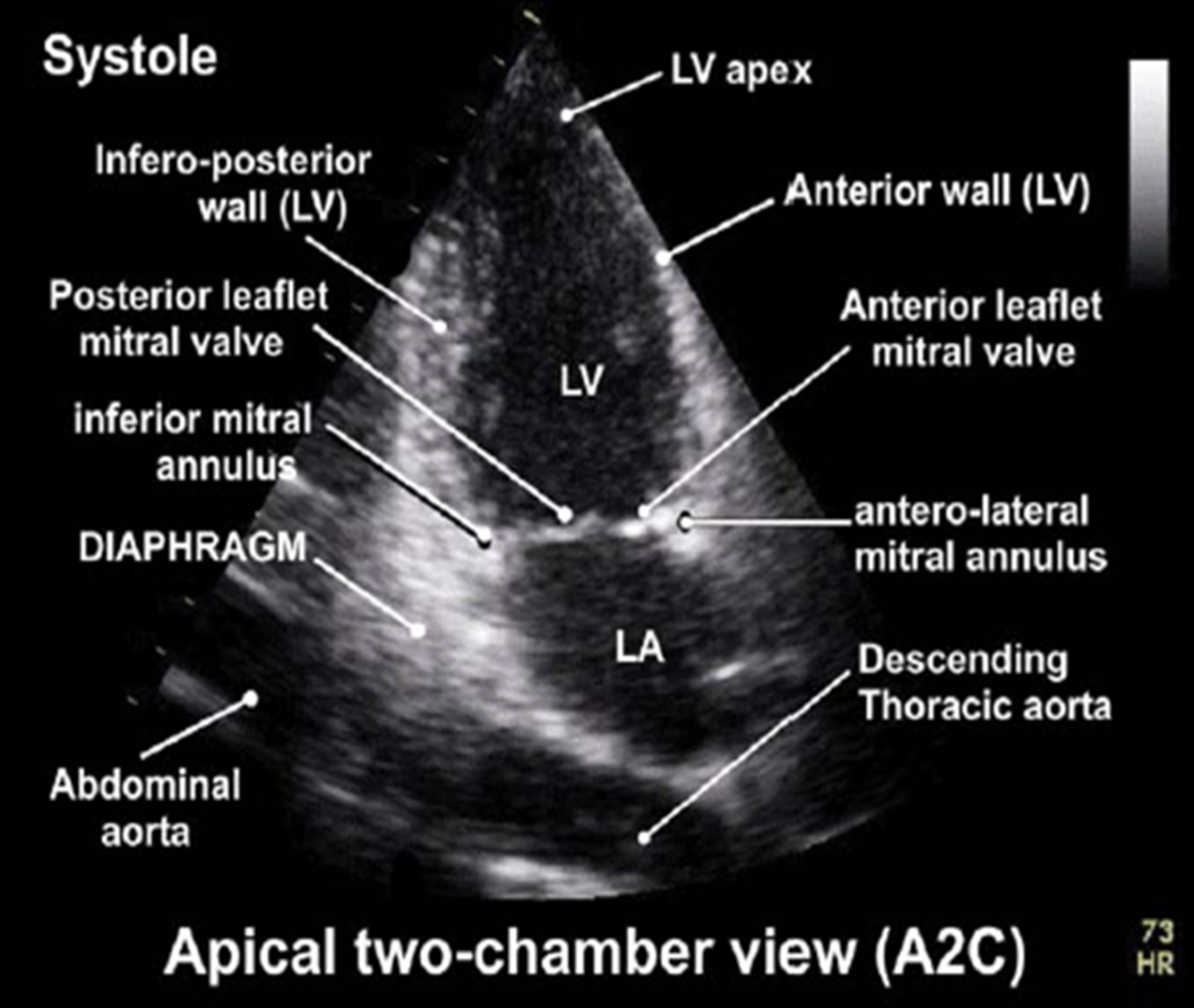
how do you obtain the apical 3CH view
from the 2CH view rotate the transducer an additional 60 degrees CCW
what structures are visualized in apical 3CH view?
LV
IVS
MV (anterior and posterior leaflet)
LA
Ao
right coronary cusp
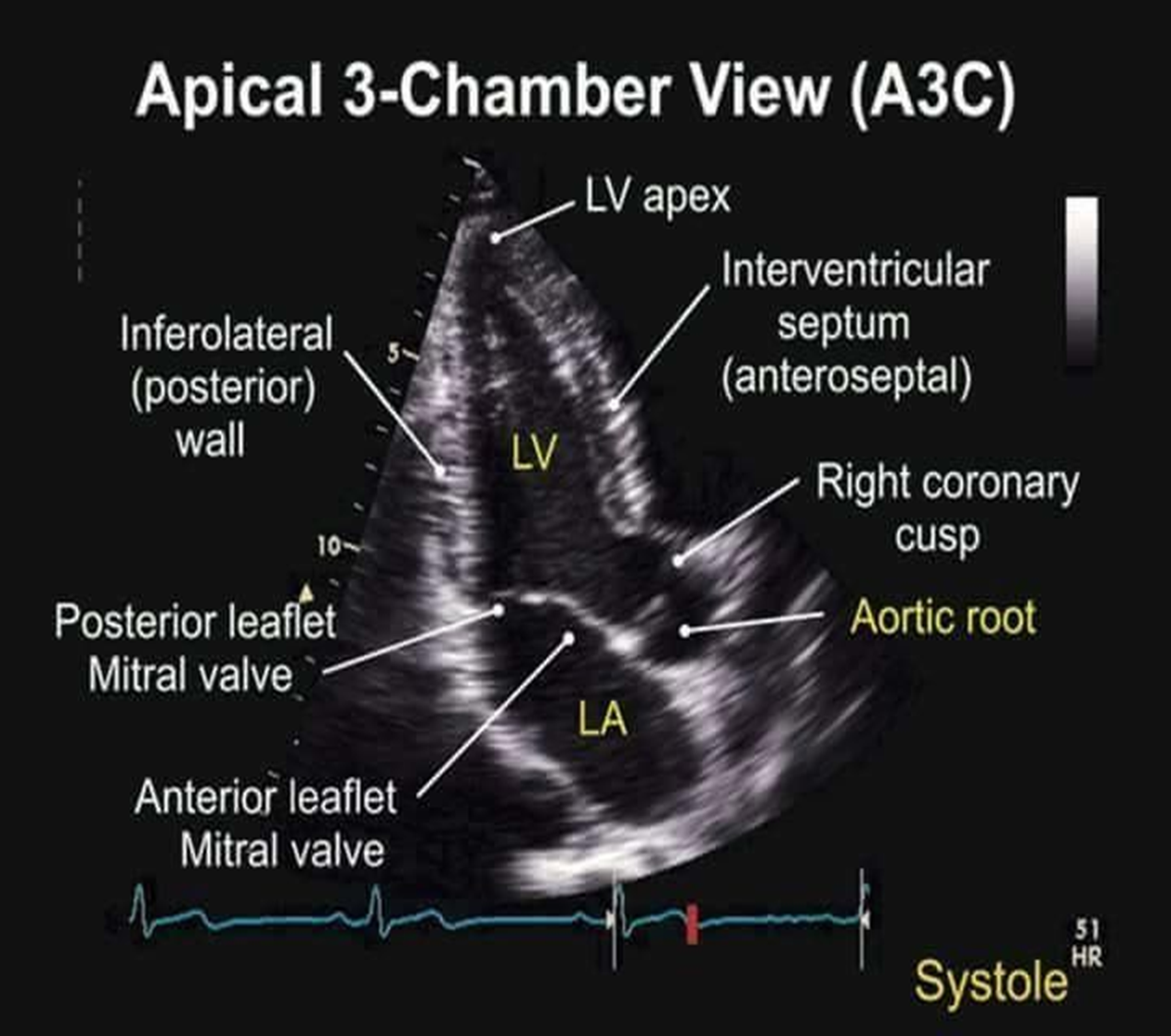
3Ch view is aka?
apical long axis view (PLAX from apex)
how does apical 3CH compare to PLAX?
in apical 3CH you can see the LV apex
however, aortic and mitral valve are at greater depth → poorer resolution
how do you obtain the subcostal view? time? notch?
place transducer directly below the xiphoid process with notch towards pt’s left at 3 oclock (opposite of scanning abdomen)
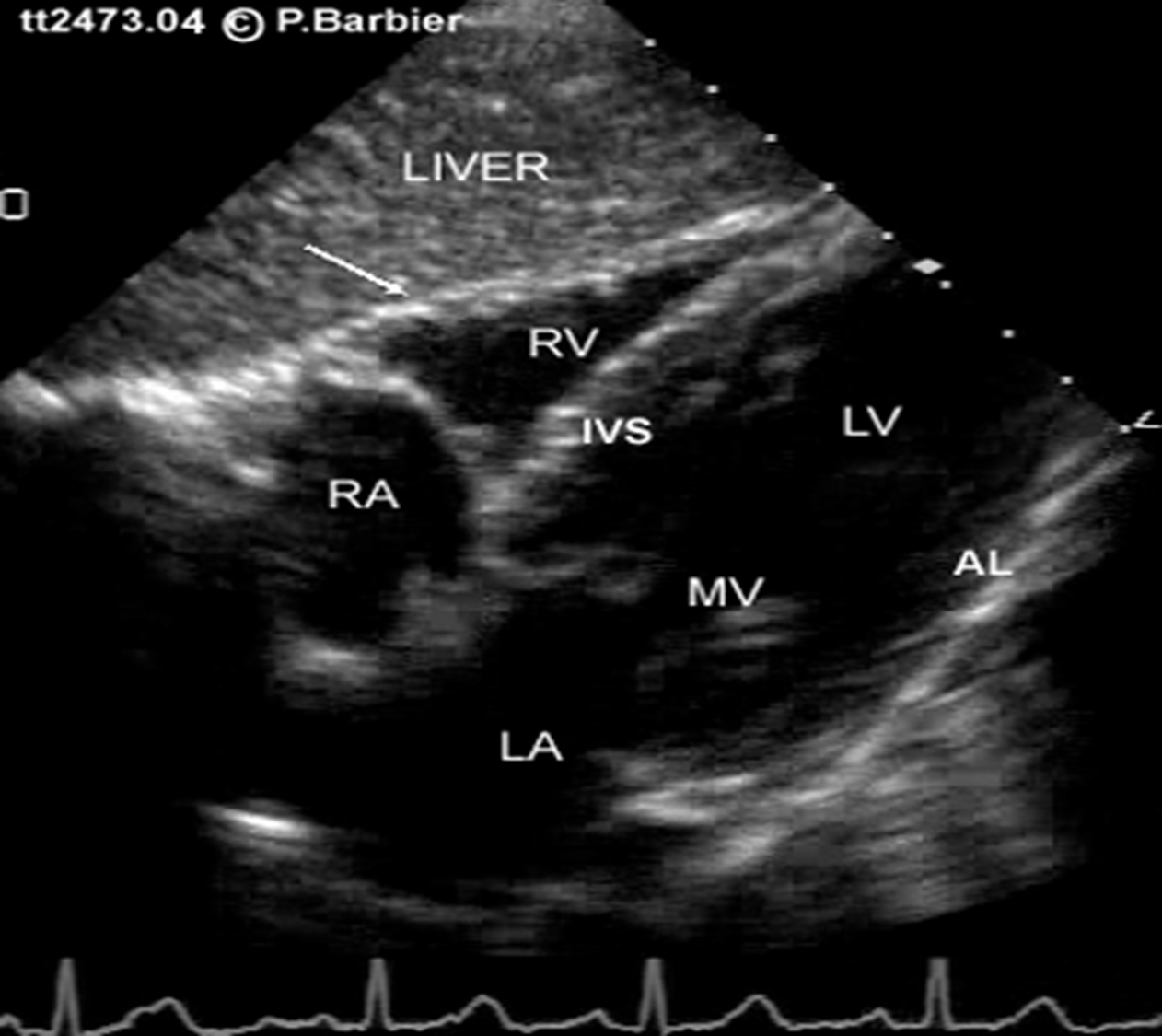
what is the best pt position for optimizing subcostal view?
pt supine with legs bent (deep breaths help lower heart for better optimization)
what structures do you see in subcostal view?
RV/LV
RA/LA
IVS
interatrial septum
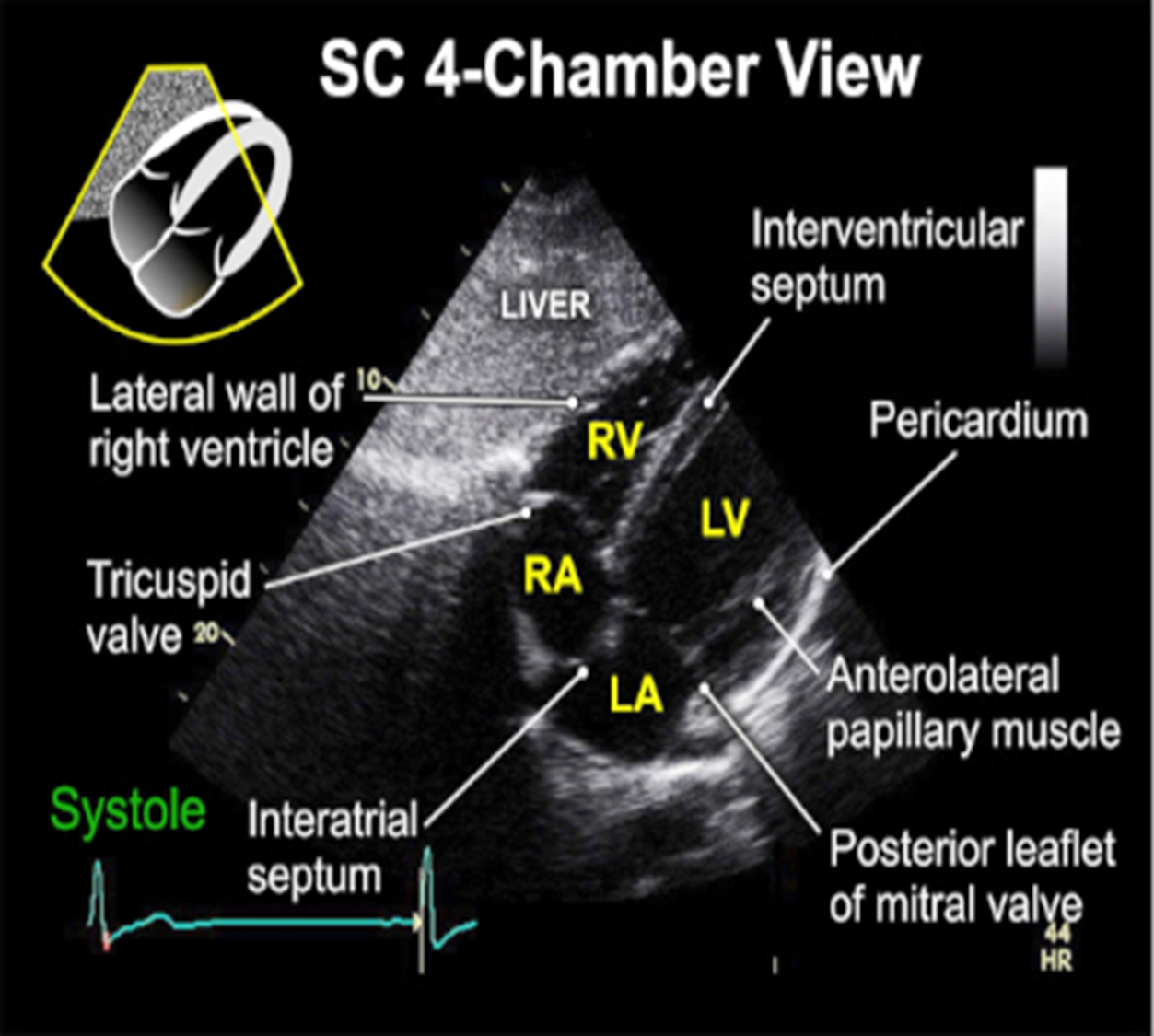
what view is best for assessing ASD? why
subcostal because interatrial septum is perpendicule to ultrasound beam
how do you assess IVC from subcostal view?
rotate notch to 12 oclock to see IVC entering RA
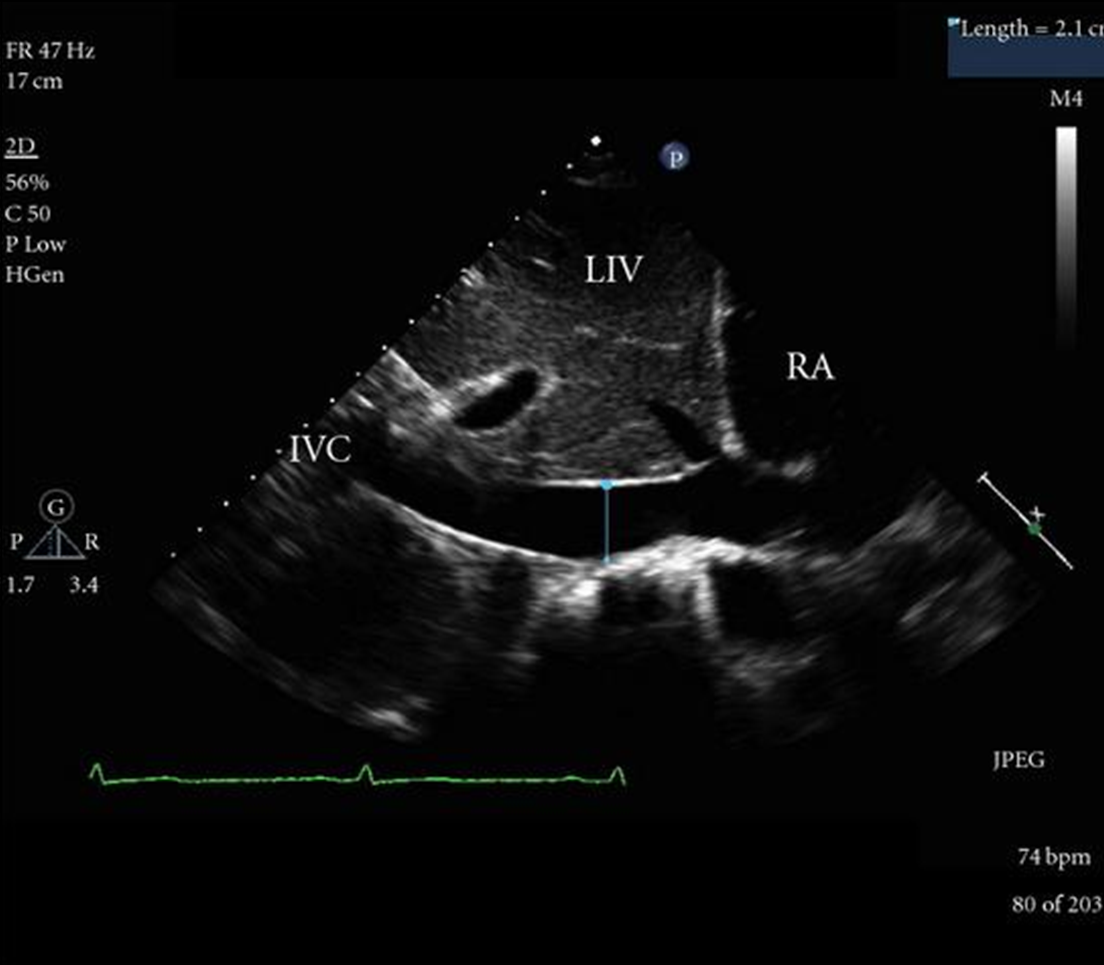
what is the normal change of the IVC from rest and respiration?
IVC should collapse at least 50% with respiration
subcostal view is a good view to assess
pericardial effusion. septal defects, venous return
when is subcostal SAX used and how does it compare to PSAX from parasternal window?
short axis view from the subcostal area
looks the same as PSAX but includes liver
subcostal SAX has decreased frame rate because of increased depth
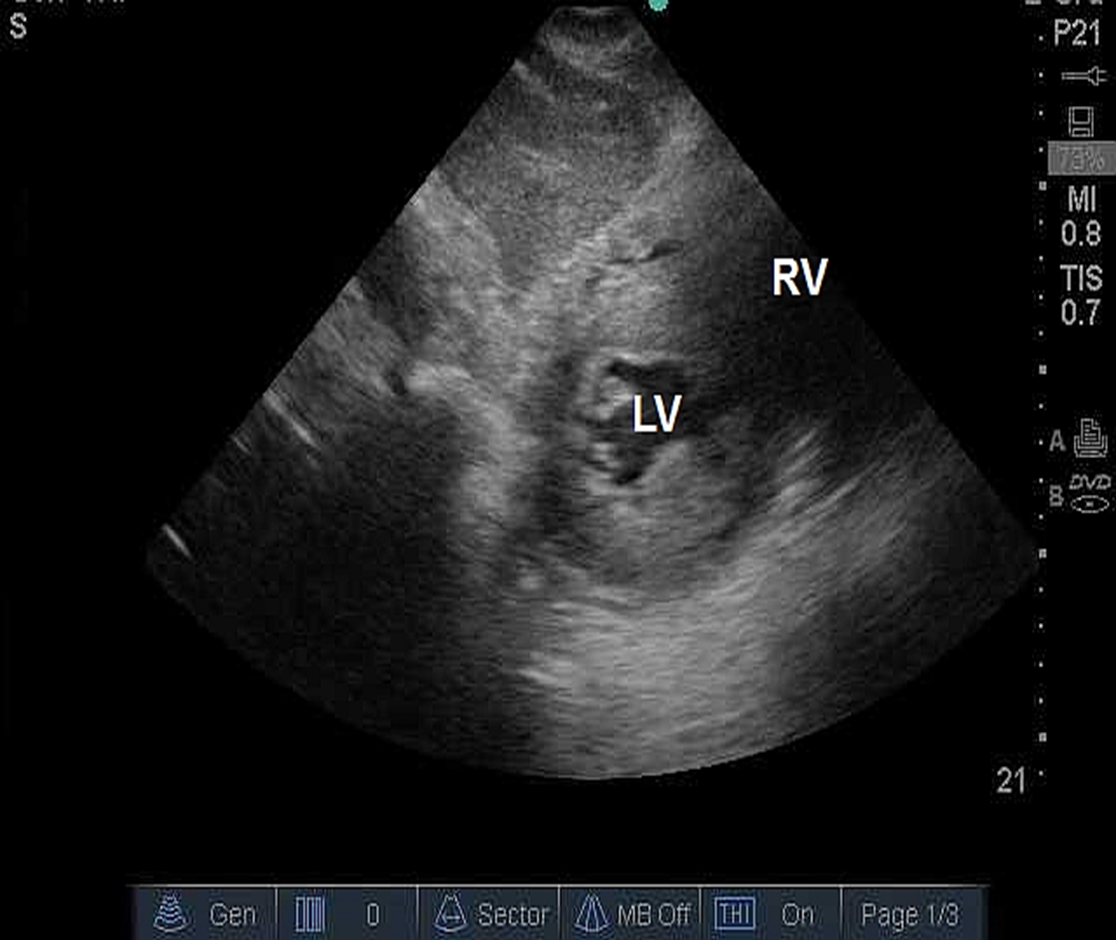
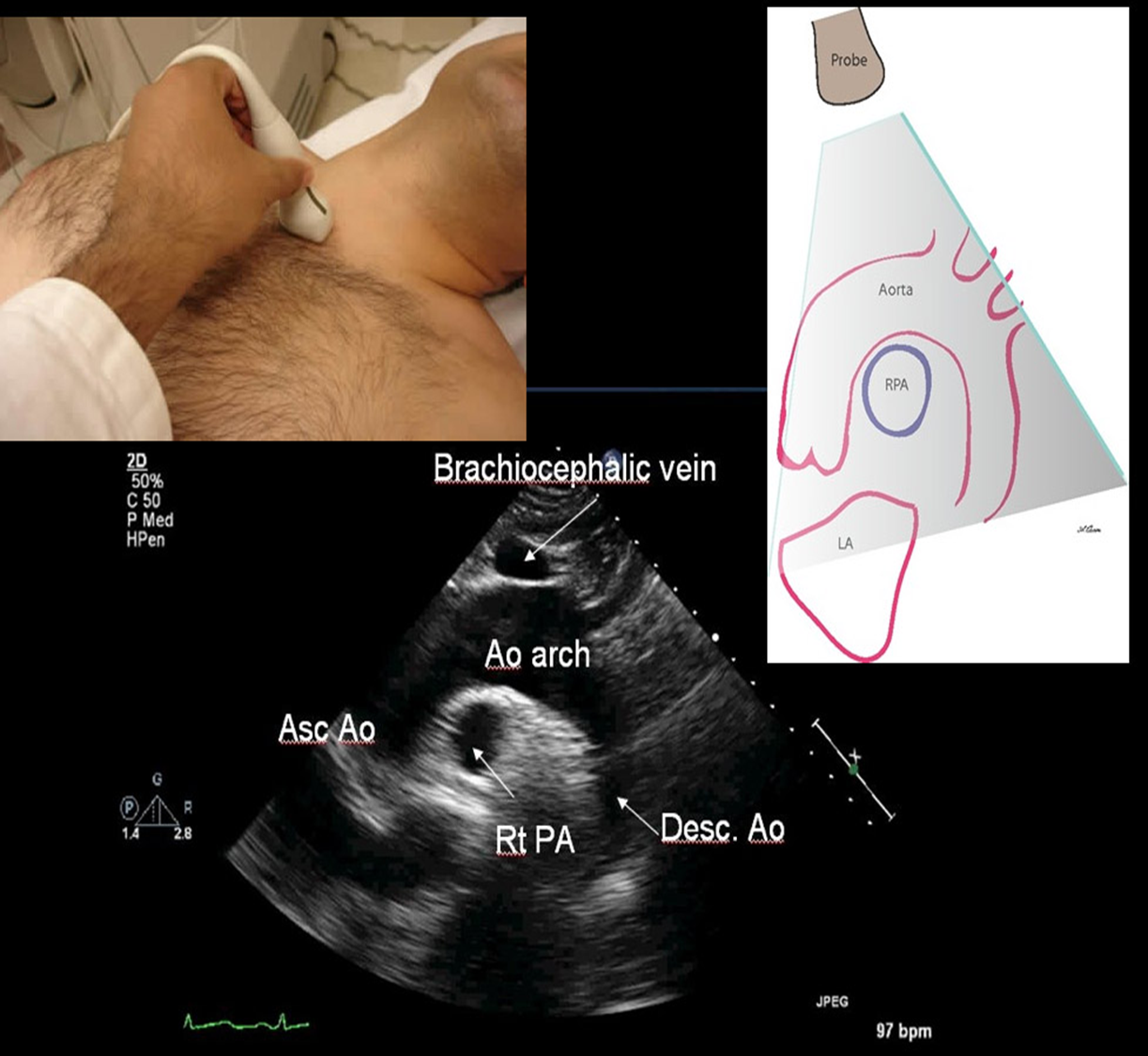
what position should the pt be in for SSN view?
pt should be supine with neck extended
what structures are seen in SSN?
aortic arch / ascending / descending
RPA
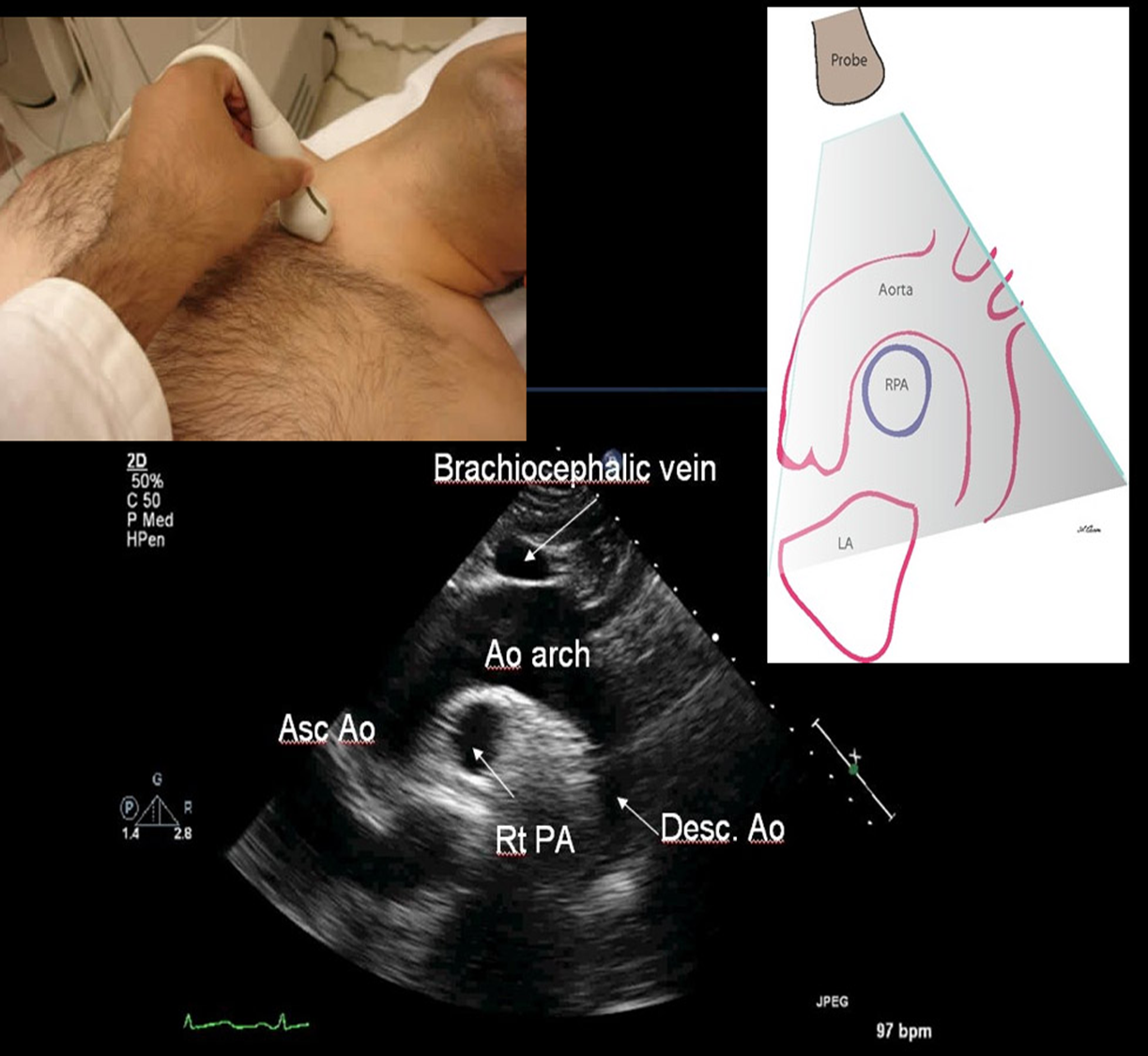
SSN is used for
aortic stenosis
aortic dissection
aortic aneurysm
measure the aorta
aortic regurg
what is the right parasternal view used for?
demonstrate flow in the ascending aorta
review Qs
name all the windows used in echo
parasternal
apical
subcostal
suprasternal
review Q
in what views do we see the pulm art?
PSAX (aortic level)
parasternal RVOT
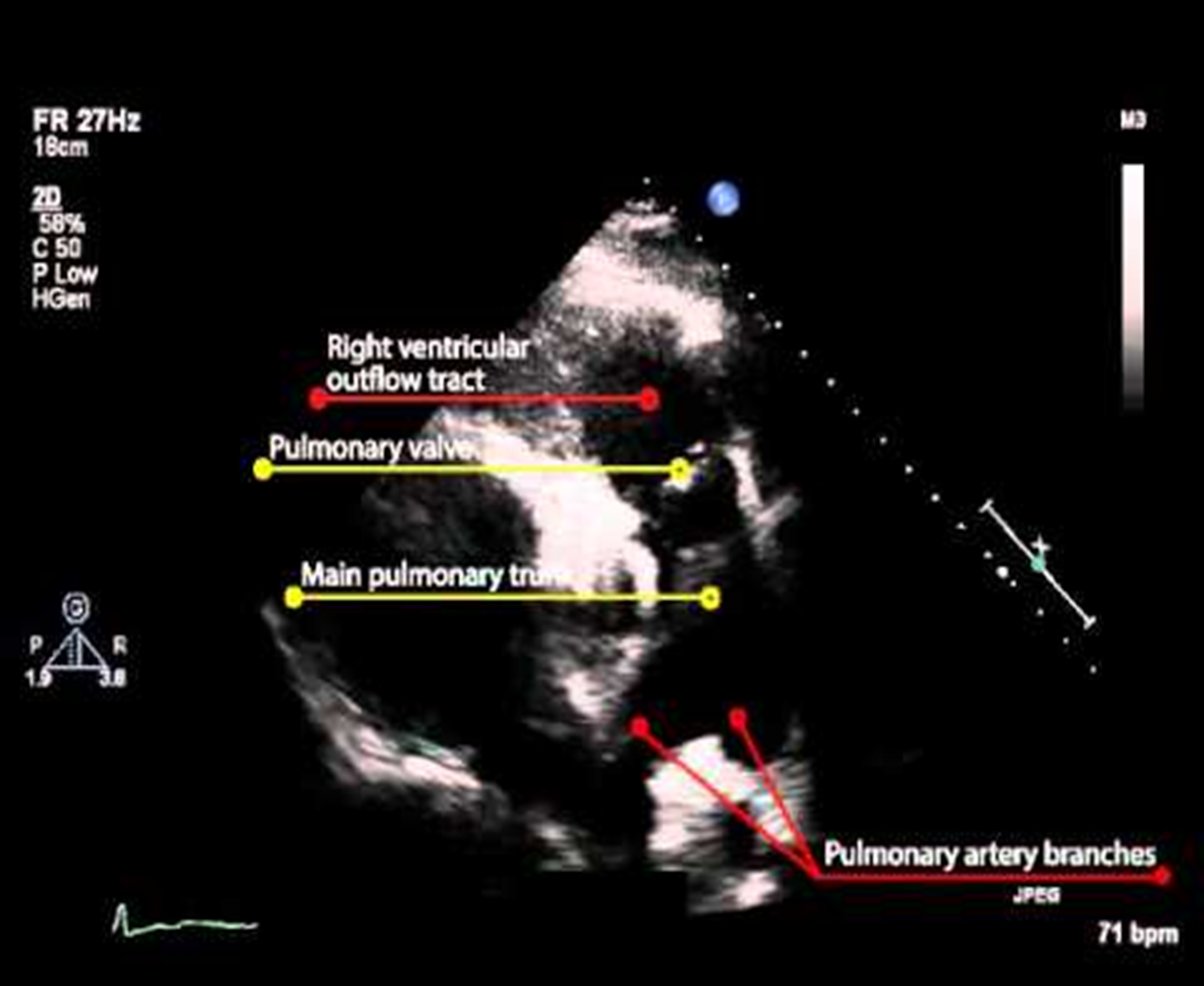
suprasternal
review Q
what views do we see the RA?
parasternal RVIT
PSAX aortic level
apical 4ch, 5ch
subcostal 4ch
review Q
what position should notch be in to obtain apical 2CH?
60 degrees counterclockwise from 4ch (notch towards 12 o clock)
review Q
what view do we measure the wall thickness of LV? what about aortic root?
measure LV wall thickness : PLAX, (potentially PSAX at pap muscle level)
aortic root : PLAX
**know which phases of cardiac cycle you measure all plax structures**
review
review
review
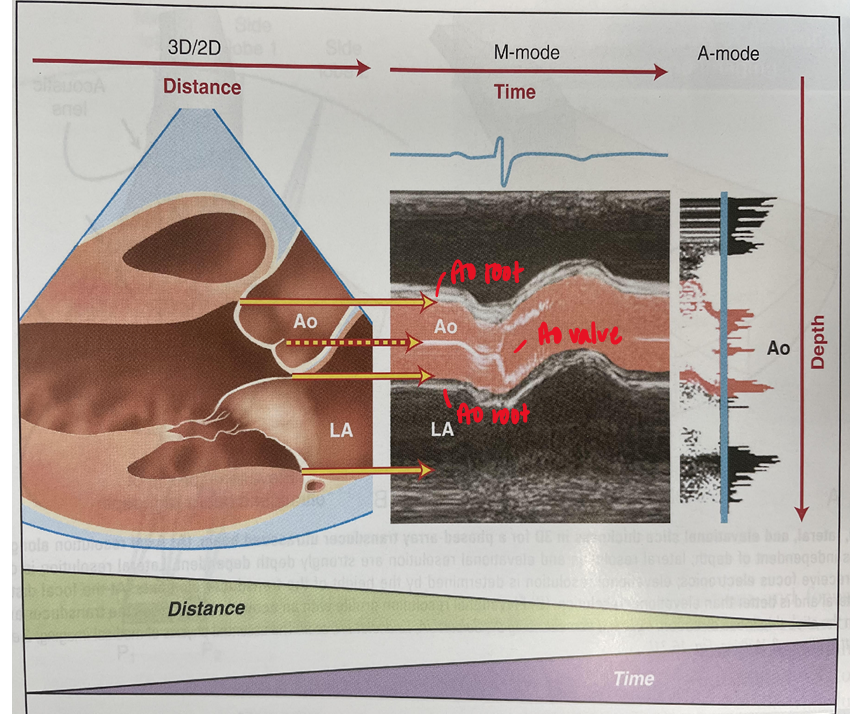
what does the x and y axis of m mode depict?
x axis : time
y axis : depth
review
m mode has superior - resolution which makes identification of what more accurate and reproducible?
temporal resolution; thin moving structures such as LV endocardium
m mode guided by 2d imaging is most helpful and used for
assessing fast moving structures
very rapid motions
precide measurements of cardiac dimensions
aids in diagnosing conditions such as cardiac tamponade, MVP, paradoxical septal motion
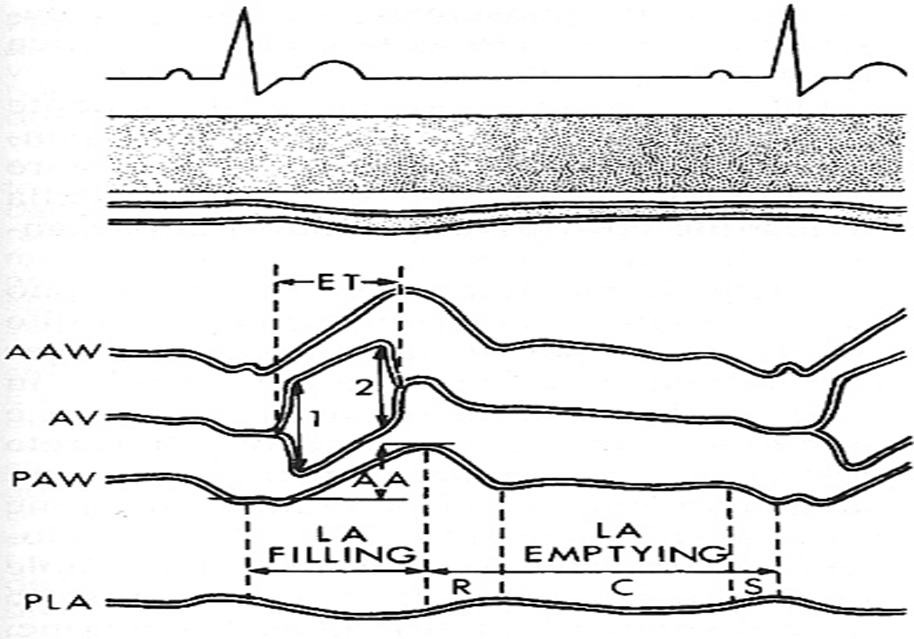
what do the two peaks represent?
what does this show?
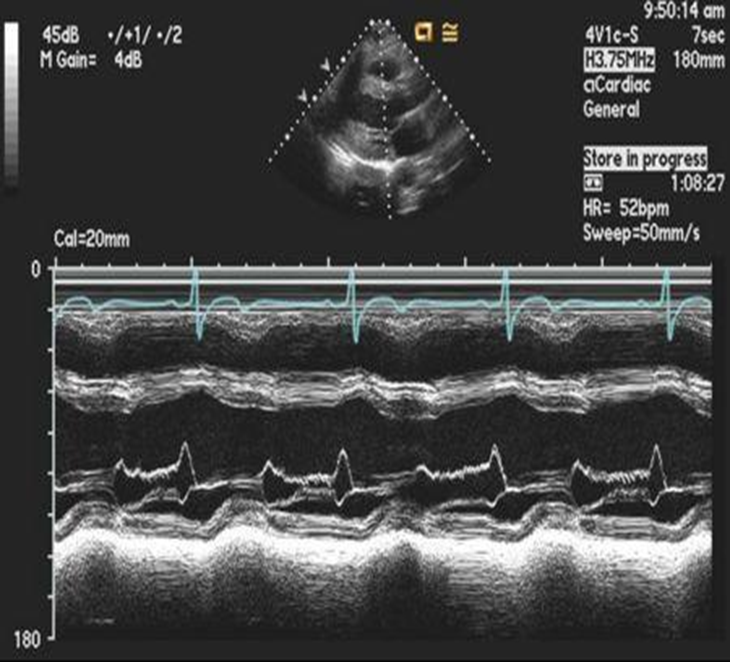
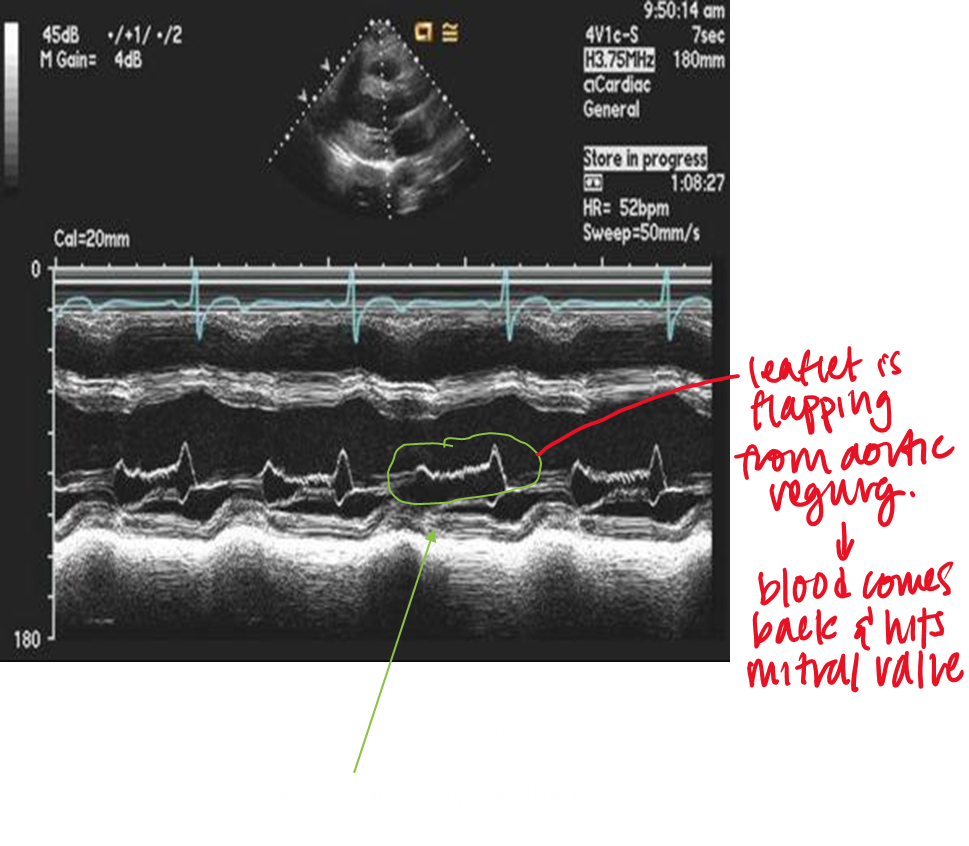
not normal m mode
what is anatomical m mode?
cursor placement must always be perpendicular to structure; anatomical m mode is a post processing function circumvents limitation → but reduces temporal resolution
review
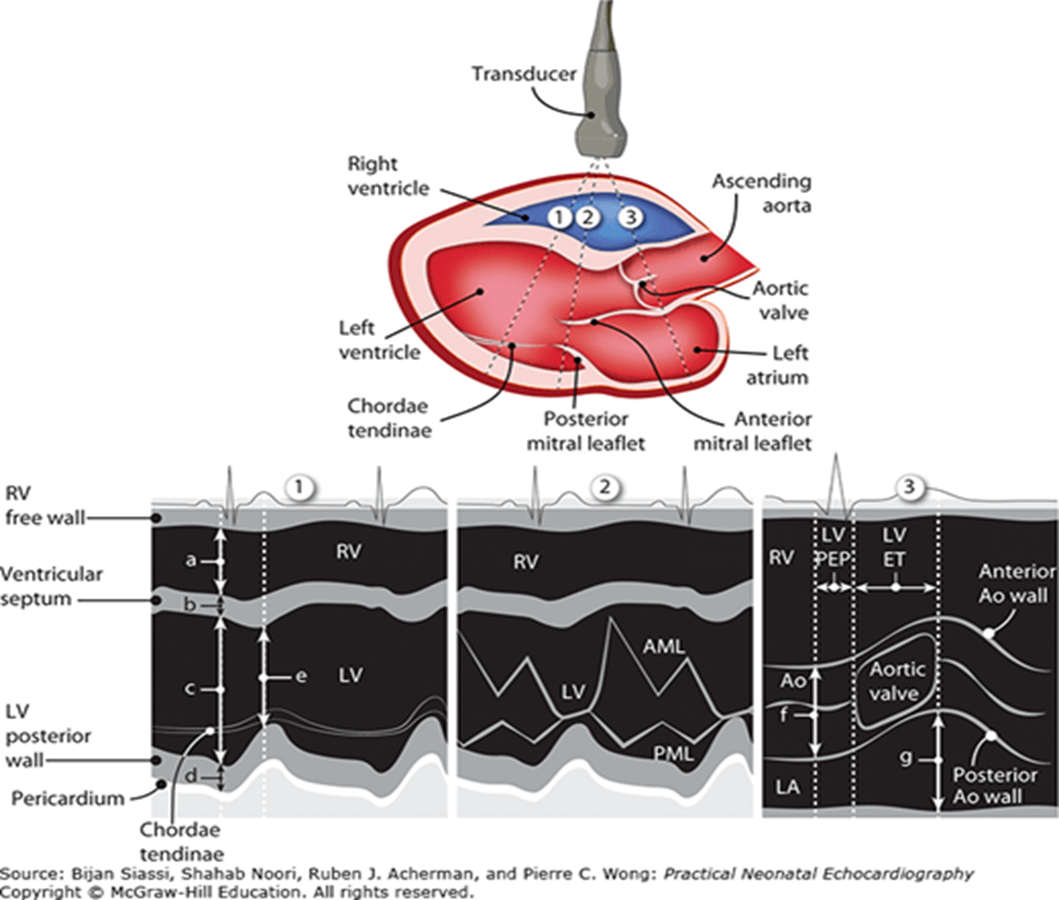
review
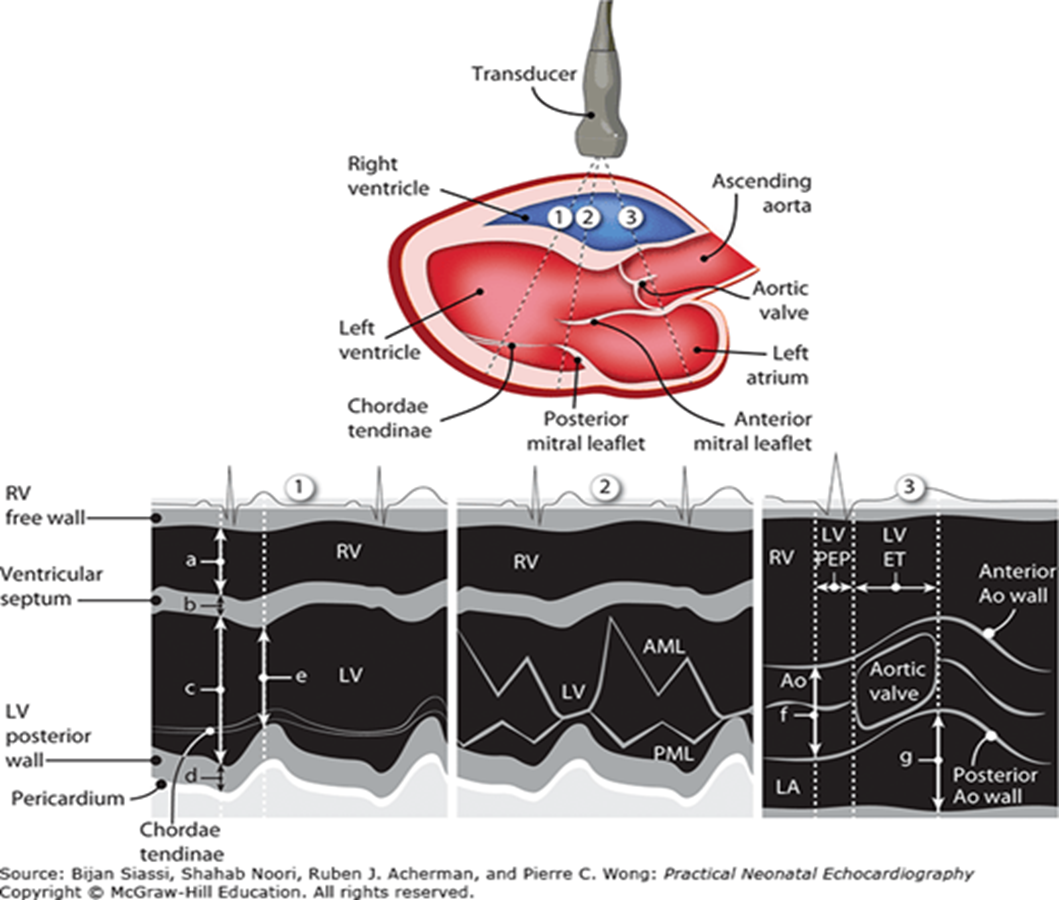
what structures are visualized in m mode aortic root diameter/LA/cusp separation
RV free wall
aortic root
RCC
NCC
left atrium
fibrous pericardium
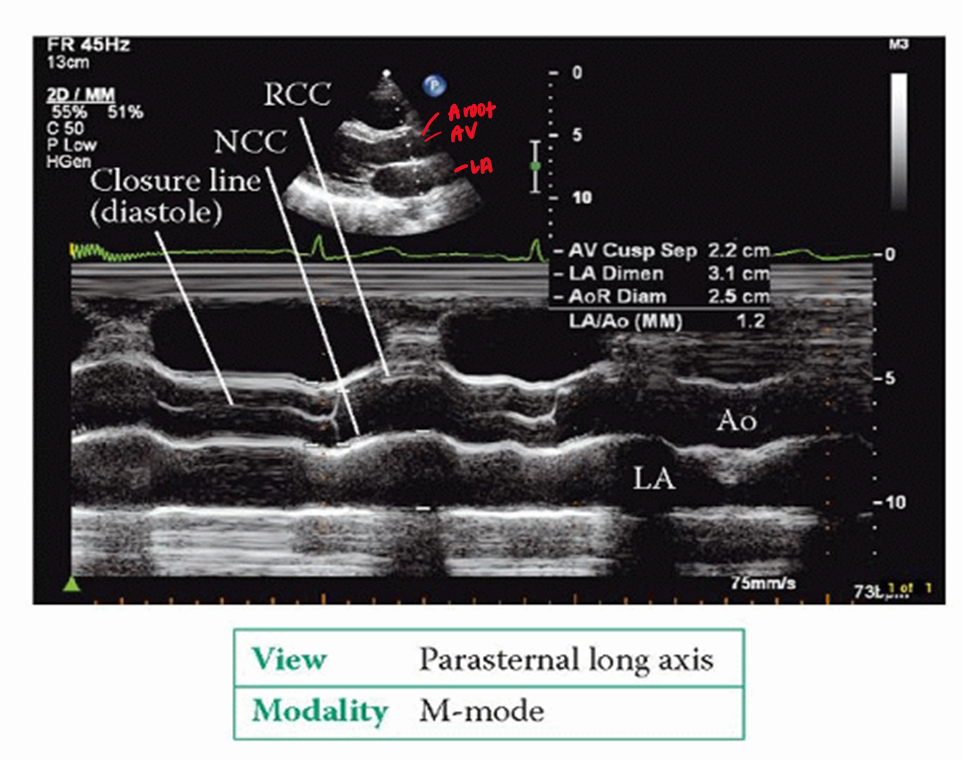
**all measurements in m mode should be
leading edge to leading edge (outer to inner)
what are the three measurements taken in m mode:aortic root diameter/LA/cusp separation
ao root diameter
acs (aortic cusp separation)
LA
when is the aortic root measured?
at the onset of ventricular systole or end diastole
when is the ACS (aortic cusp sep) measured?
onset of ventricular ejection when cusps first open
when is LA measured?
closure of ACS (end of systole) - t wave
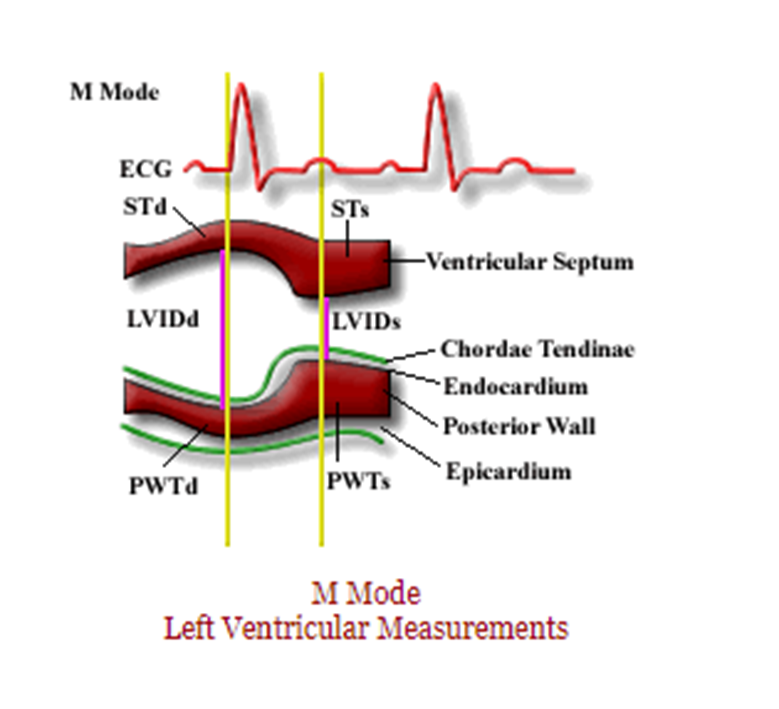
what structures are visualized in m mode through LV?
RV anterior wall
RV
IVS
LV (LVIDd & LVIDs)
LV posterior wall
fibrous pericardium
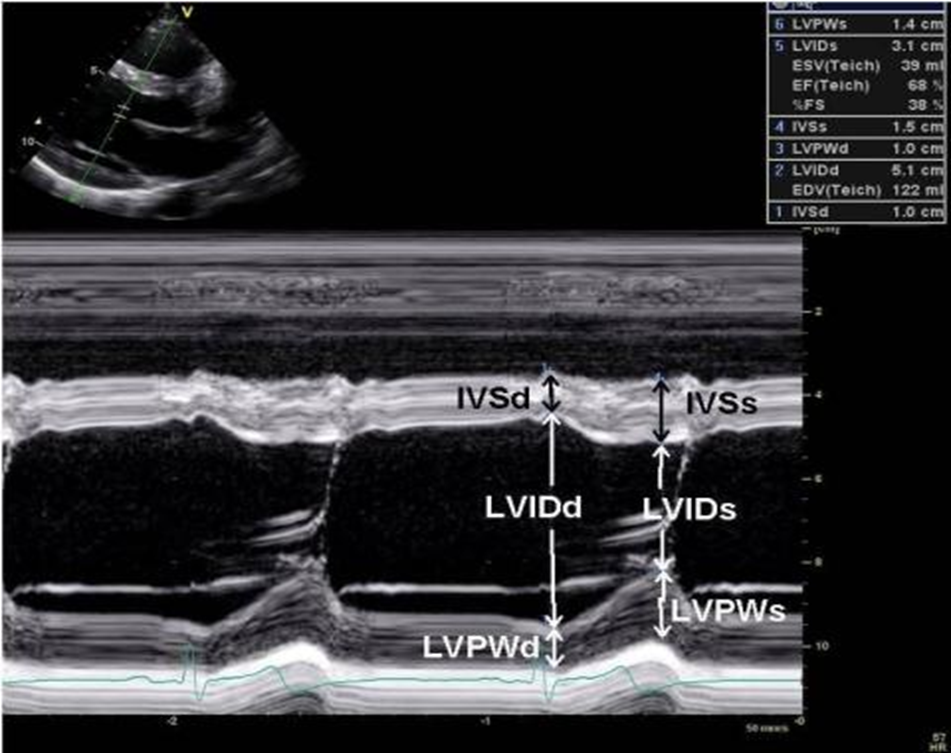
how do you calc ejection fraction?
measure LV in end diastole (QRS) and systole (T wave)
IVS and PW greater than what indicates LVH?
1.1cm
what is measured in end diastole?
RV
IVS
LV
PW
PW
Aortic root
if your PLAX image is not perpendicular what can you do?
use anatomical m mode
why is EF% produced via m mode only reliable with symmetric left ventricular systolic function?
it is only showing the movement through the one like on the cursor and therefore may not show abnormalities not on the line
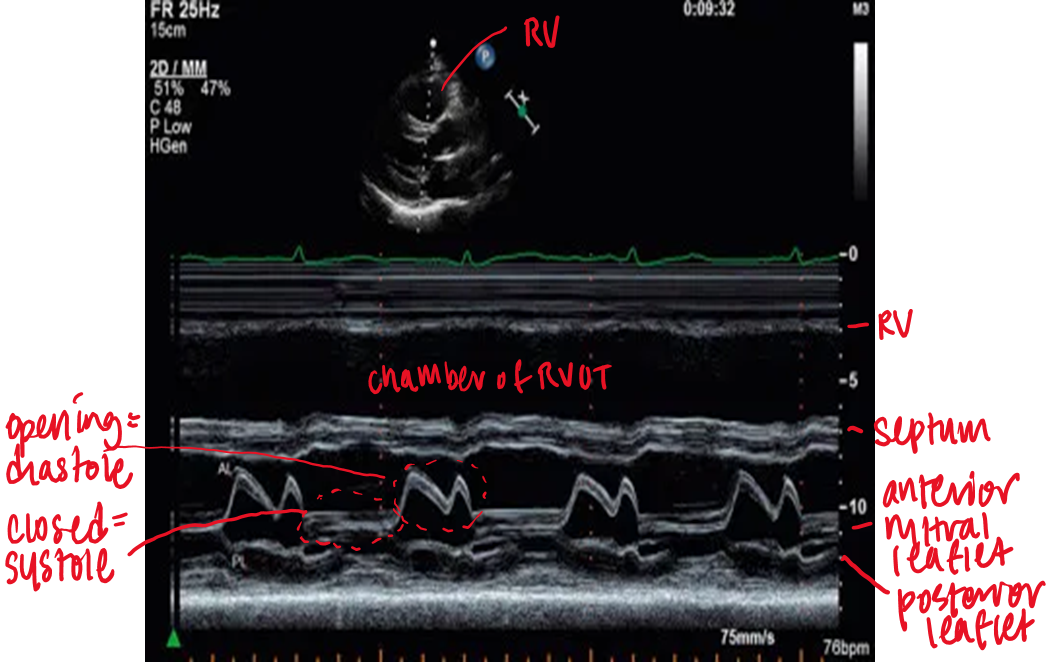
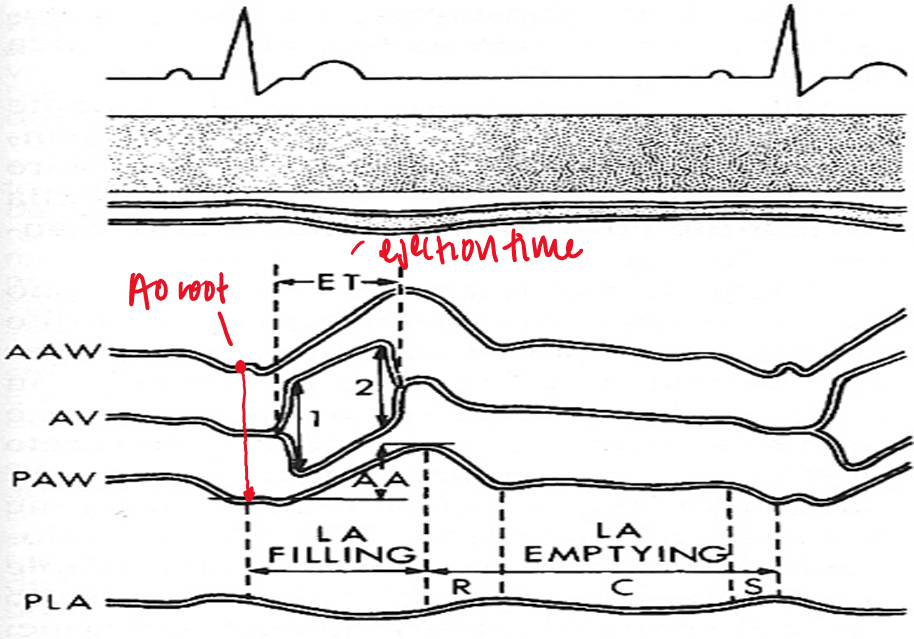
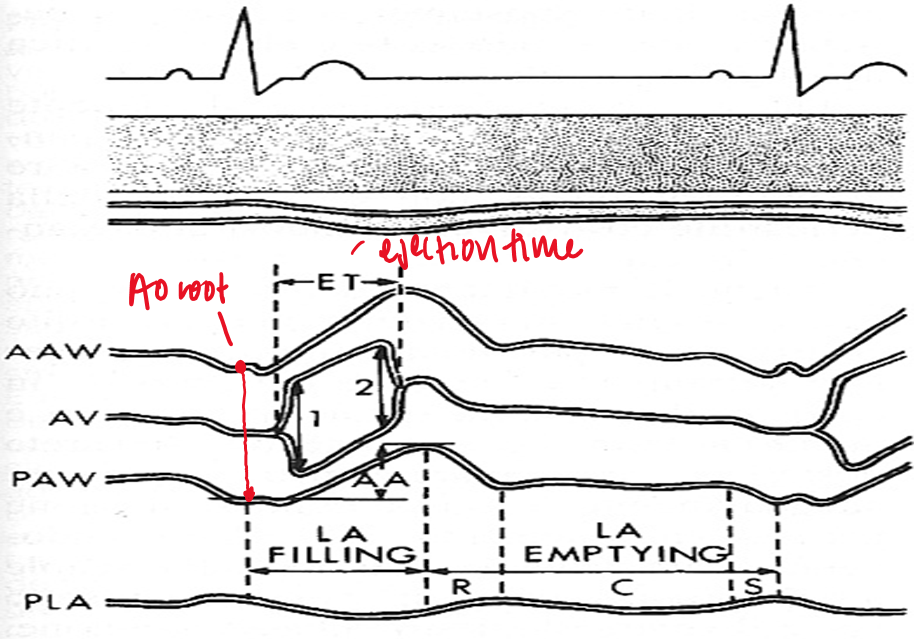
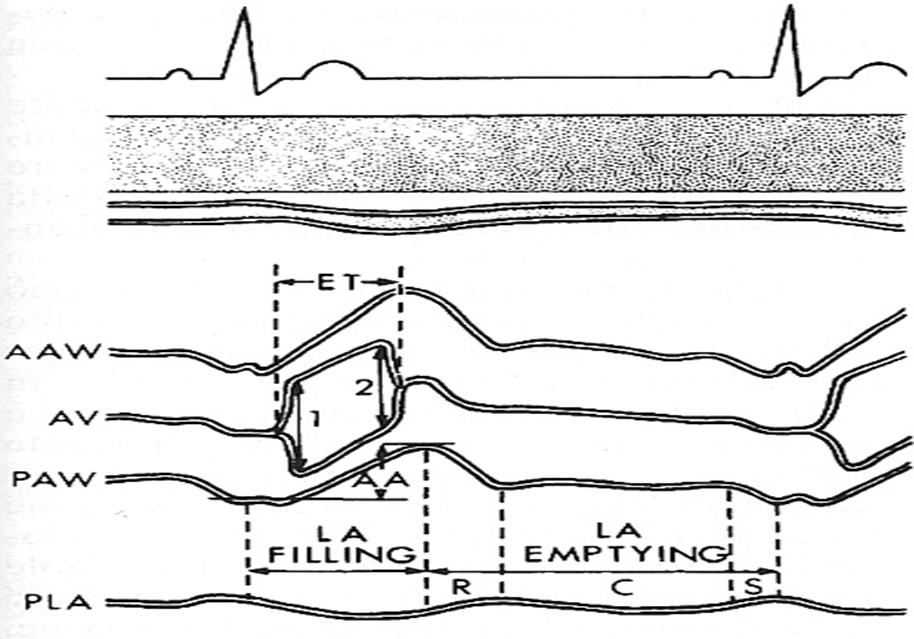
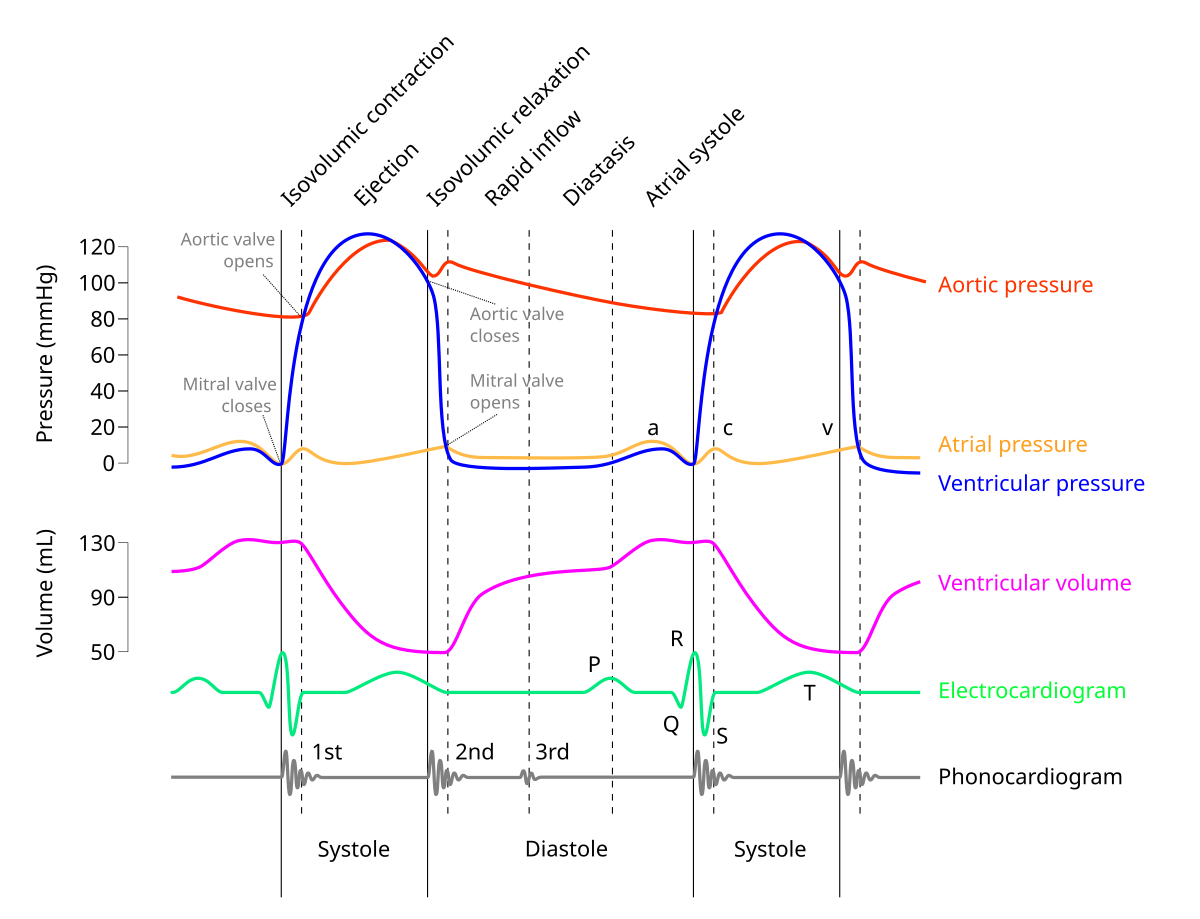
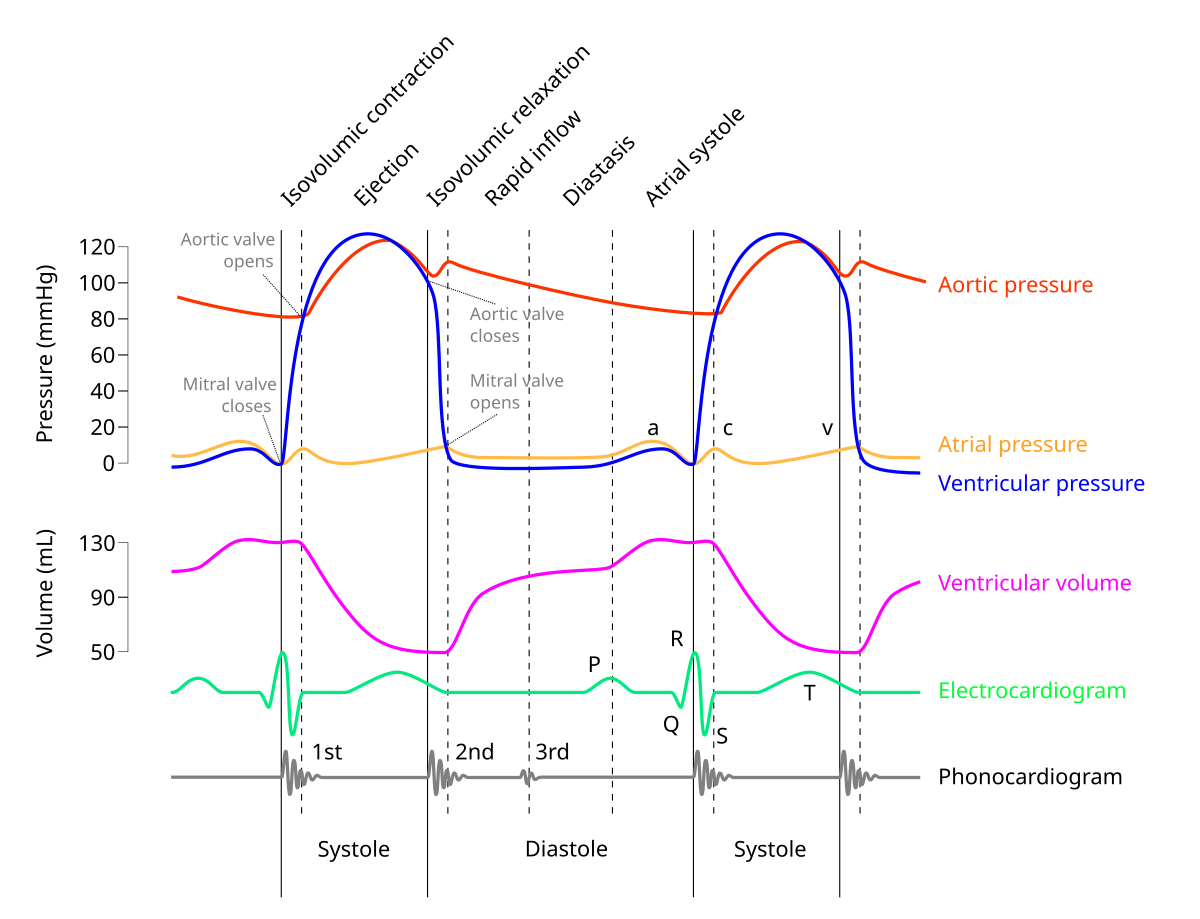
in M mode mitral valve, what does D represent?
end of isovolumetric relaxation (shortly after t wave)
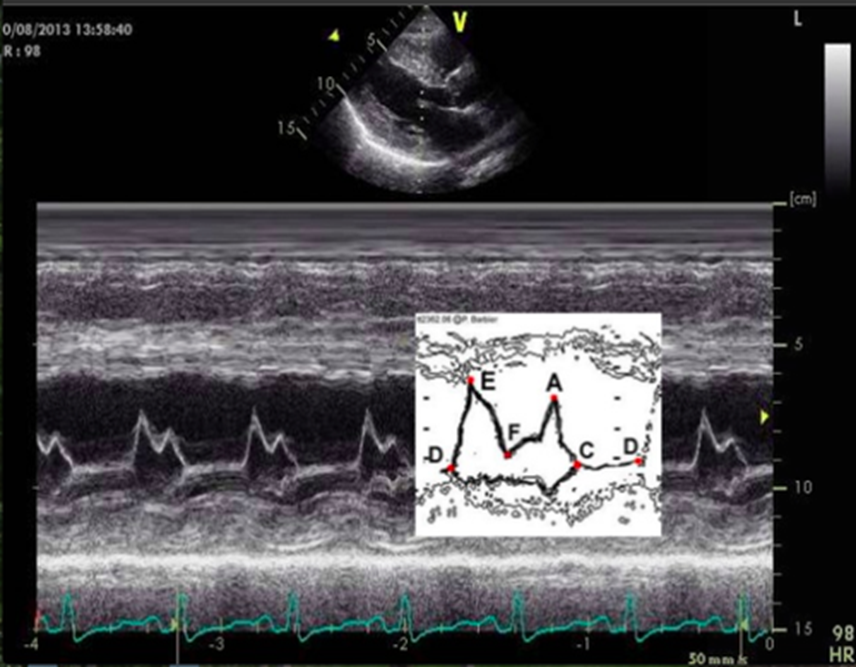
in M mode mitral valve, what does E represent?
early ventricular diastole (mitral valve opens)
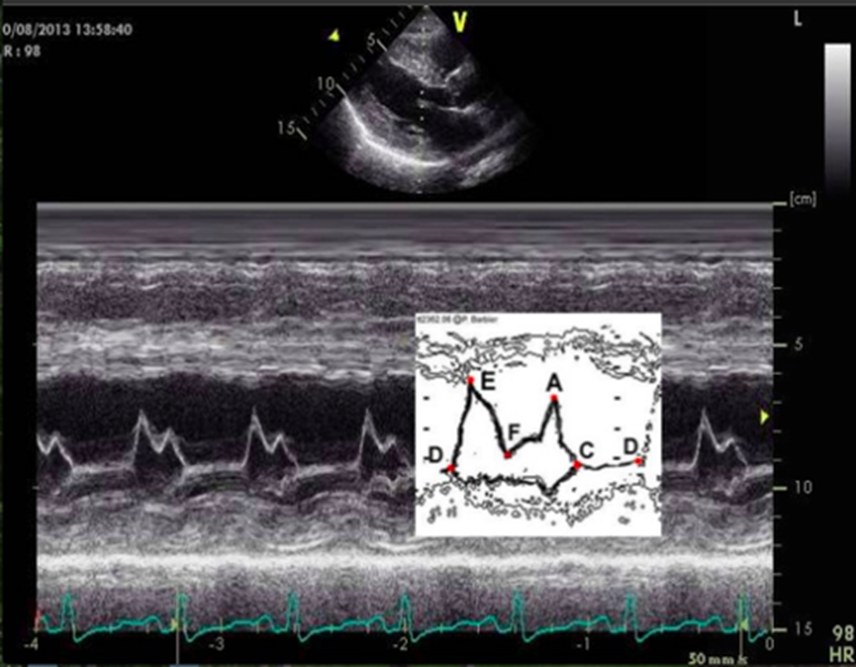
in M mode mitral valve, what does F represent?
mid diastolic partial closure

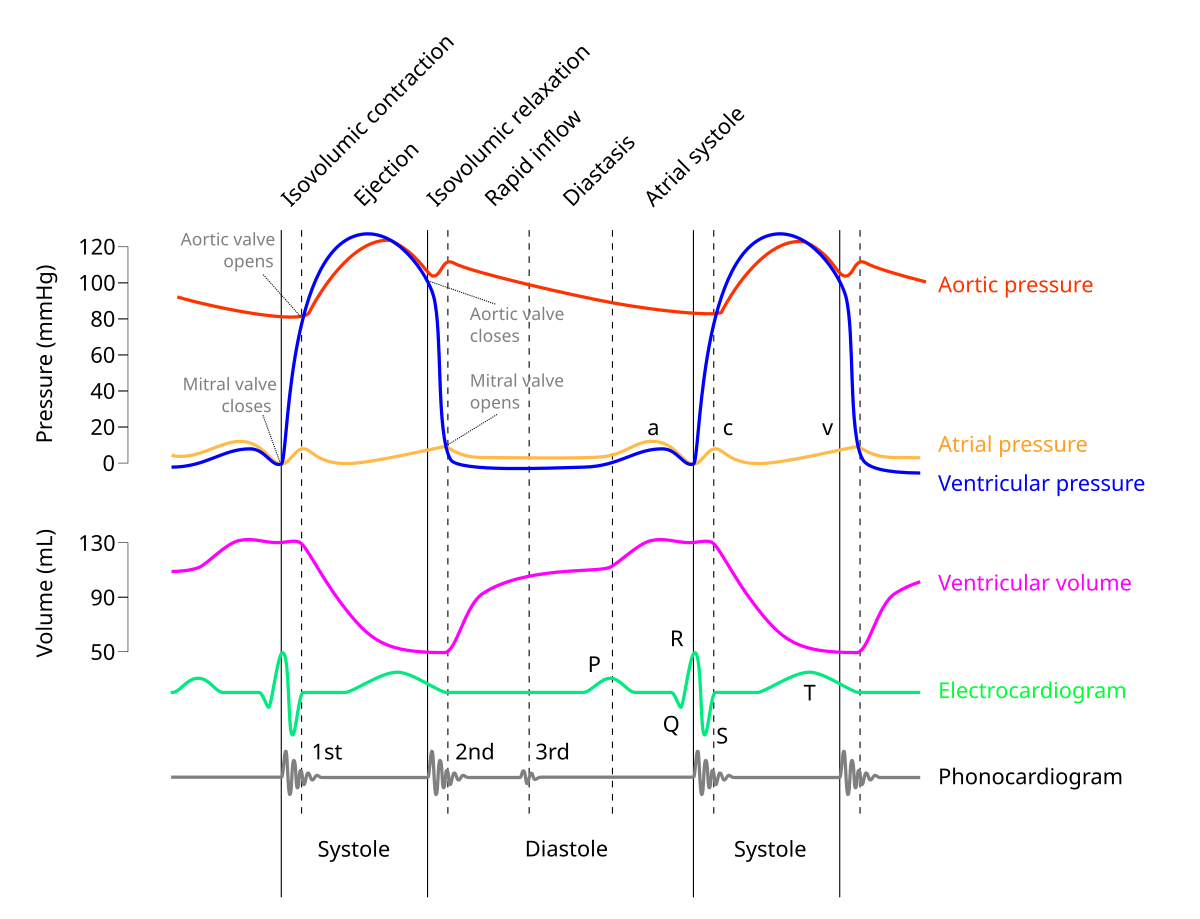
in M mode mitral valve, what does A represent?

late ventricular diastole (atrial kick) - mitral valve opens again
seen after P wave or on QRS
in M mode mitral valve, what does C represent?
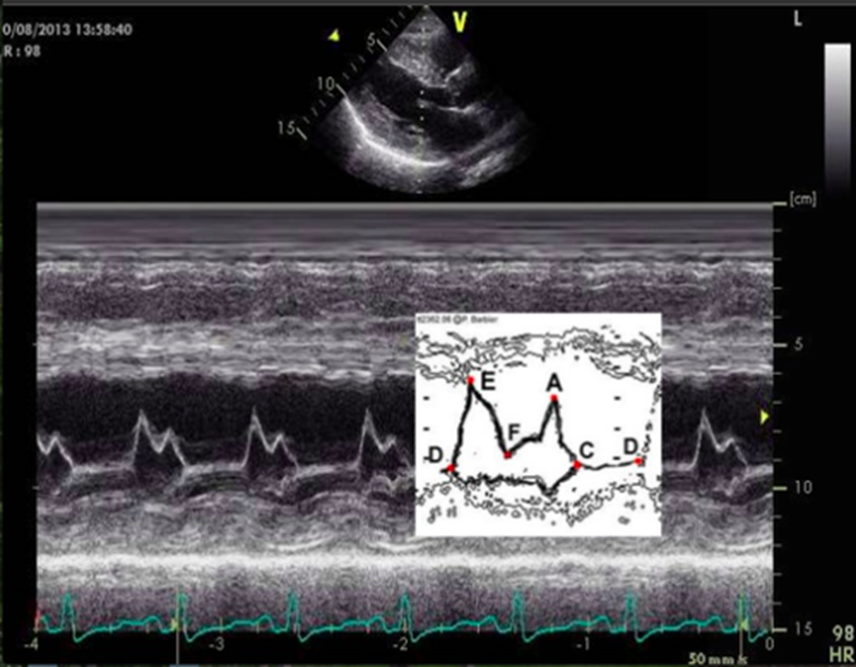
onset of isovolumetric contraction
normally appears near R wave
ventricular filling is described as
biphasic (e and a wave)