Antiarrhythmics
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
How is cardiac muscle different to other types of muscle?
Relaxation must occur between contractions → exhibit tetany → contract and hold contraction for certain length of time
Where is the SA node located and what does it do?
Inferior to the superior vena cava
Pacemaker of the heart → sets sinus rhythm (60-80bpm)
Where is the AV node located and what does it do?
Inferior to the pulmonary trunk
Gives time for atria to contract so the ventricles can fill
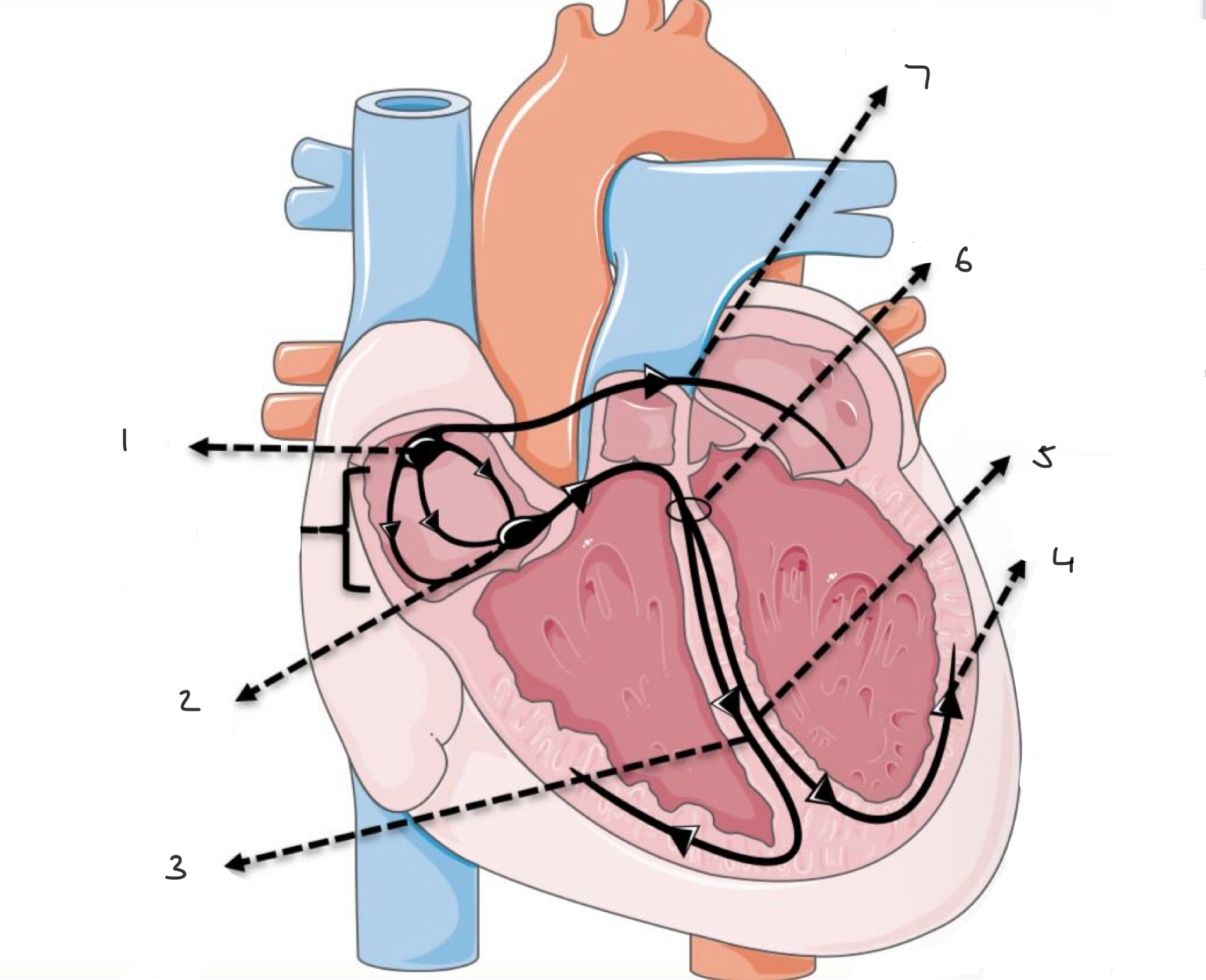
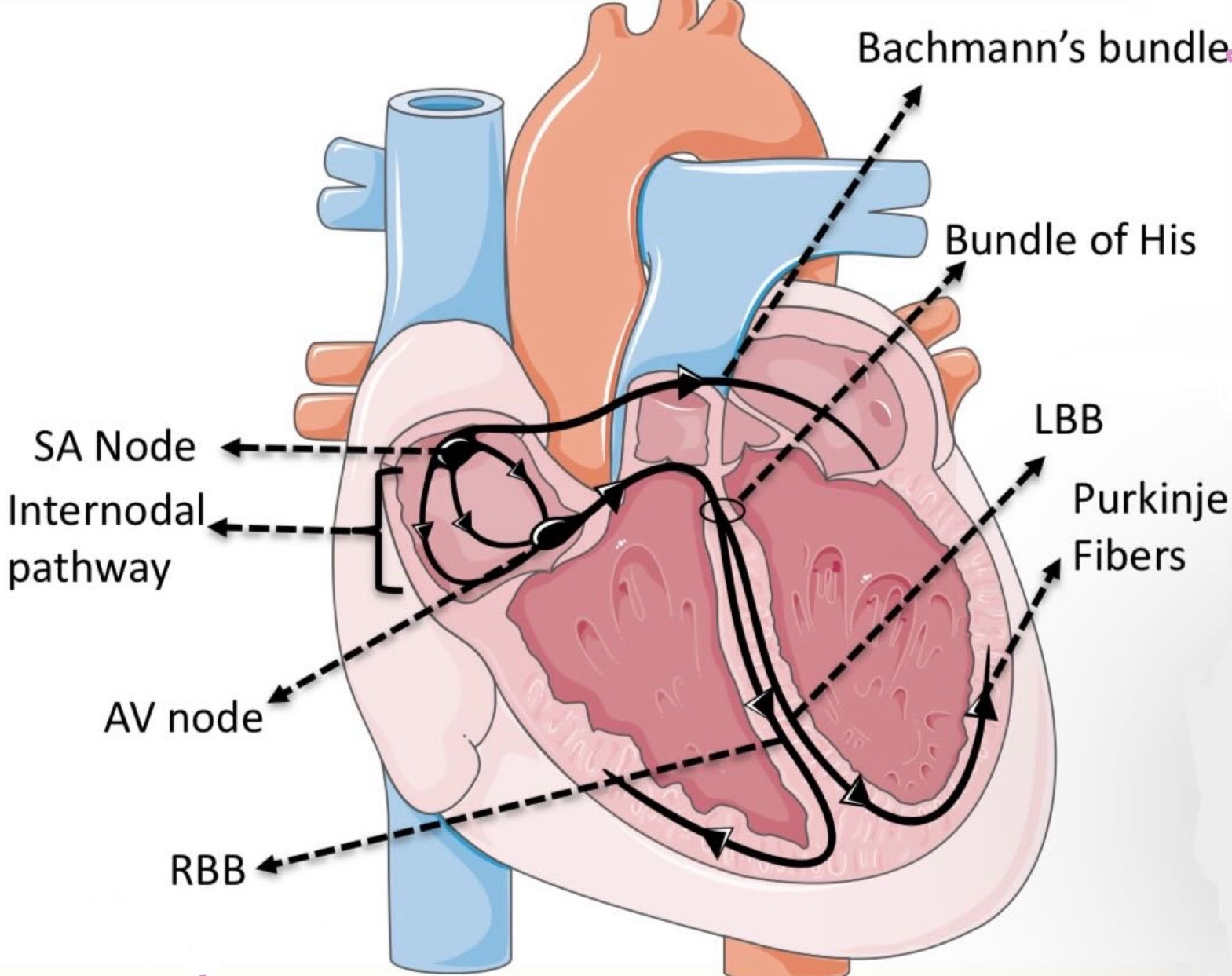
What is the order of conduction in the heart?
SA node
AV node
Common bundle
Bundle (bundle of his)
Purkinje fibres → contraction from apex to base
What causes the P wave?
Atrial depolarisation
What causes the QRS complex?
Ventricular depolarisation
** atrial depolarisation is hidden
What causes the T wave?
Ventricular repolarisation
** repolarisation starts at the base
What forms the U wave on the ECG?
Delayed depolarisation from ventricles
What are the 2 subsets of tachyarrhythmias?
Supraventricular (involve atria or AV node)
Ventricular
what is Wolff-Parkinson-white syndrome?
Current goes down an accessory pathway (bundle of kent) and cause extra contractions in the ventricles → can lead to re-entry circuits
** AVRT
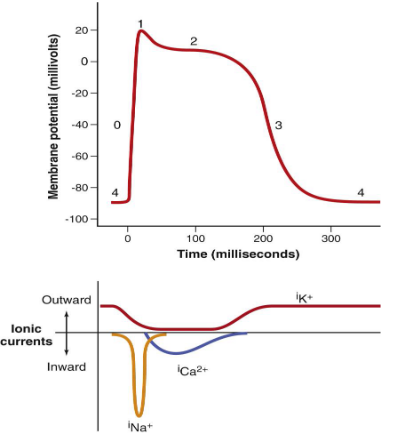
How do contractile cells generate an action potential?
Phase O (upstroke/ deplorasitaion): voltage gated (fast( Na+ channels open: -70 → +20
Phase 1 (initial repolarisation): Fast Na+ channels close. K+ channels open → K+ moves out → 0mV
Phase 2 (plateau): K+ moves out and Ca2+ moves in
Phase 3 (final repolarisation): L-type Ca2+ channels close. Ca2+ is taken back to SR by sodium-calcium exchanger and calcium proton ATPase pumps. Slow K+ channels open and K+ exits the cell
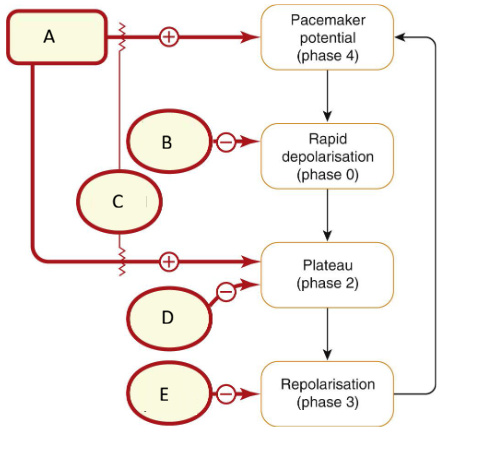
What are the different classes of antiarrhythmics?
Class I: Na channel blocker
Class II: beta blocker
Class III: k channel blocker
Class IV: Ca channel blocker
Name the sodium channel blockers
1a: Quinidine, Procainamide
1b: Lidocaine
1c: Flecainide
Ic > Ia > Ib
Name some beta blockers
Propranolol, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol
** class II
Name some potassium channel blockers
Amiodarone, Sotalol (also beta blcoker)
** class III
Name some calcium channel blockers
Verapamil, Diltiazem
** class IV
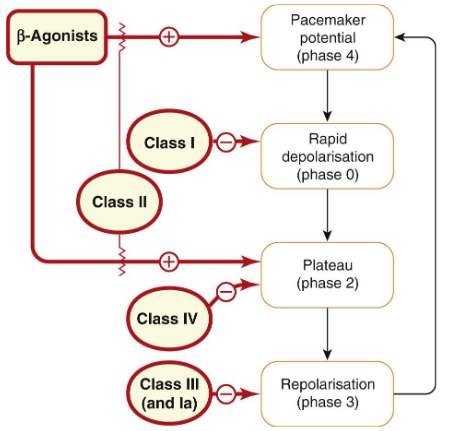
How do sodium channel blockers work?
Blocks Sodium Channels – affects the Rapid Depolarisation (Phase 0) →slowing of conduction within the cardiac muscle
Ia agents are midway, but also prolongs repolarisation (quinidine, procainamide)
Ib agents associate and dissociate rapidly (lidocaine) → binds in Phase 0 but dissociates in time for the next action potential
Ic agents associate and dissociate much more slowly (flecainide)
ECG effects of class Ia Na+ blockers and their side effects
** oral/ IV
↑ QRS, ± PR, ↑QT
side effects:
Hypotension, reduced cardiac output
GI symptoms
** pro-arythmic drugs → Torsades de pointes
ECG effects of class Ib Na+ blockers and their side effects
** oral/ IV
↑ QRS
Side effects:
Dizziness
Drowsiness
GI upset
ECG effects of class Ic Na+ blockers and their side effects
** oral/ IV
↑ QRS, ↑ PR, ↑ QT
side effects:
Proarrhythmic → sudden death especially with chronic use and in structural heart disease
GI symptoms
When do you use each Na+ channel blocker?
Ia: not used often
Quinidine: AF/Flutter, Brugada Syndrome
Procainamide: supraventricular and ventricular tachycardias
Ib: Acute Ventricular Tachycardias
Ic:
AF & Flutter
Premature Ventricular contractions
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
ECG effects of beta blockers and side effects
↑ PR, ↓ Heart Rate
Side effects:
bronchospasm
hypotension
don’t use in partial AV block or acute heart failure (are used in stable heart failure)
When do you use beta blockers?
Sinus and Catecholamine dependent tachycardia
Re-entrant arrhythmias at AVN
Protecting Ventricles from High Atrial Rates
How do beta blockers work?
Work by activating adenylyl cyclase→ produces cAMP → causes phosphorylation of Protein Kinase A (PKA) → acts on multiple downstream targets to produce r esponses
→ Positive Inotropy (predominantly in ventricular myocytes)
→ Positive Chronotropy (predominantly at SAN)
** block the effects of sympathetic activity on the SAN and AVN
How do potassium channel blockers work?
They prolong the plateau phase & repolarisation due to K+ channel blockade
Leads to:
↑ Action Potential Duration (APD)
↑ Refractory period
ECG effects of potassium channel blockers and side effects
Amiodarone (PO/ IV):
↑ QRS, ↑ PR, ↑ QT, ↓ Heart Rate
Side effects: Pulmonary Fibrosis, Liver Disease, Thyroid Disease, Photosensitivity, Optic Neuritis
Sotolol (PO):
↑ QT, ↓ Heart Rate
Side effects: Proarrhythmia, Fatigue, Insomnia
** solotol is also a beta blocker antagonist but has more of an effect on k+ channels
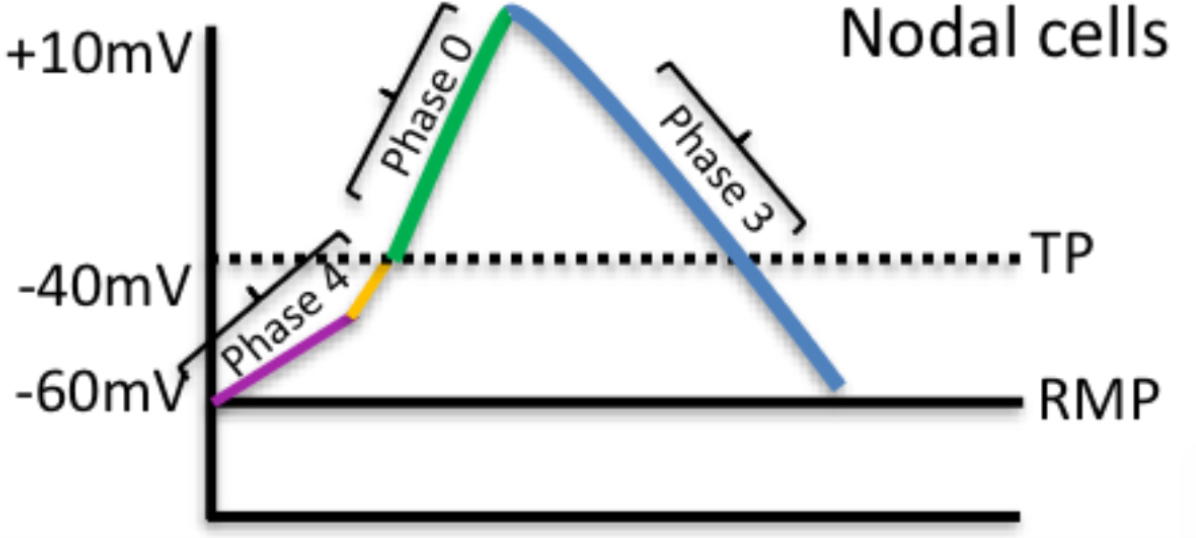
What happens in nodal cells?
Phase 4(diastole): funny Na+ channels open + T type Ca2+ channels open → reaches threshold (-40mV)
Phase 0 (upstroke): L-type Ca2+ channels open → +10mV → Ions move to contractile cells via gap junctions
Phase 3 (final repolarisation): L-type Ca2+ channels inactivate. K
+ channels activate and K+ leaves the cell → cell depolarises
Difference between rate control and rhythm control drugs
Rate: increased heart rate due to increased automaticity of the AV node → Class II + Class IV + class V
** Adenosine, Beta blocker, Calcium channel blocker, Digoxin (ABCD)
Rhythm: due to increased automaticity within the contractile cells (atria/ventricles) → Class I + Class III
Why should class Ic not be given to people with ischaemic or structural heart conditions?
Can be pro arrhythmic for those patients
Ischaemic/sacr tissue conduct in a different way
How do you treat tosades’s the pointes
Magnesium sulphate → decreases QT
ECG effects of calcium channel blockers and side effects
↑ PR, ↑↓ Heart Rate
Side effects:
Asystole in presence of β-blocker
Caution in hypotension and reduced cardiac output
GI upset (constipation)
How do calcium channel blockers work?
Results in delayed depolarisation of SAN
Reduction in conduction velocity (and slight increase to refractory period)
When do you use calcium channel blockers?
Supraventricular tachycardia
When do you use potassium channel blockers?
Most Arrhythmias including supraventricular & ventricular tachycardias
How does adenosine work?
Nucleoside binds to A1 receptors and activates K+ channels in SAN and AVN
→ leads to hyperpolarisation → reduced HR
→ refractory period increase due to decreased calcium activity
→ Slows AV conduction
** given IV
When would you use adenosine?
Convert re-entrant supraventricular arrhythmias
Coronary Artery Disease investigations
How do Cardiac Glycosides (Digoxin) work?
Inhibits 3Na+/2K+ ATPase
Enhances Vagal activity & causes direct AVN block
Slows AV conduction and slows heart rate
Side effects if digoxin?
Confusion, dizziness
GI Upset
Blurred Vision
Photosensitity
Skins Rashes
Arrhythymia (palpitations)
When would you use digoxin?
Reduce Ventricular rates in AF/Flutter
How does Ivabridine work?
Blocks funny ion current highly expressed in sinus node
Slows impulse generation at SA Node
** given orally
Side effects of Ivabridine
Flashing Lights
Teratogenicity → avoid in Pregnancy
When would you use Ivabridine?
↓ Heart Rate in HFrEF / Ischaemic heart disease
** has no effect on bp/ contractility
How does atropine work and when can we use it?
Selective muscarinic antagonist → blocks vagal activity to speed AV conduction and increase heart rate
Vagal Bradycardias