medical planes and terminology
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
prone position
lying facedown
supine position
lying face-up
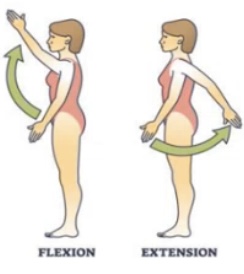
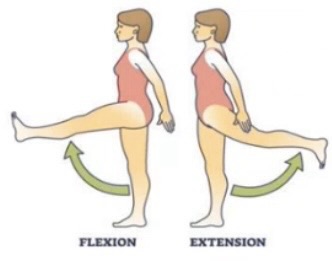
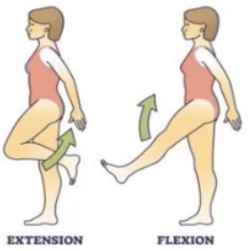
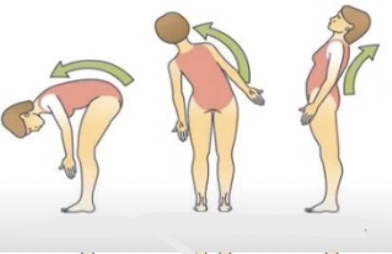
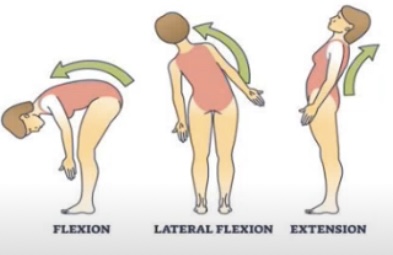
Flexion meaning
Bending a joint in a way which decreases the angle between body parts (like bending your elbow)
Extension meaning
Straightening a joint which increases the angle between body parts (like straightening your elbow)
Dorsi- prefix meaning
the back of
Palmar-
Relating to the palm of the hand
Plantar- meaning
Relating to the sole of the foot
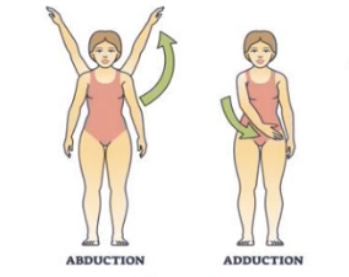
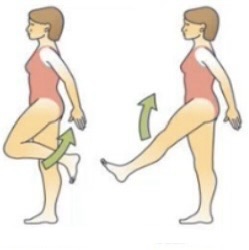
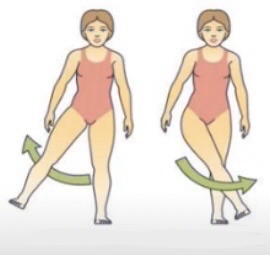
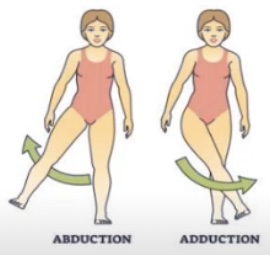
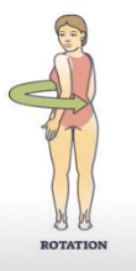
Abduction and adduction are relative to the ___
Midline
Abduction meaning
Moving away from the midline
Adduction meaning
Moving towards the midline
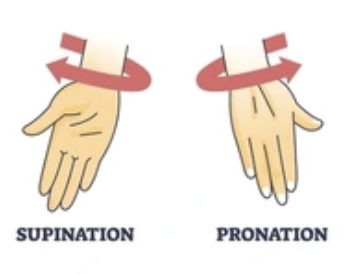
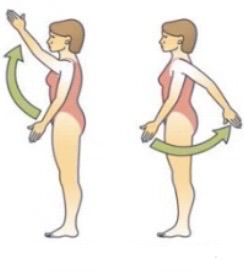
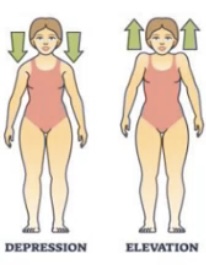
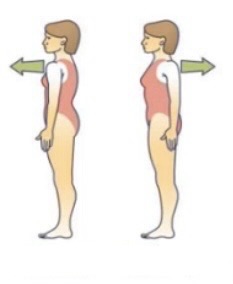
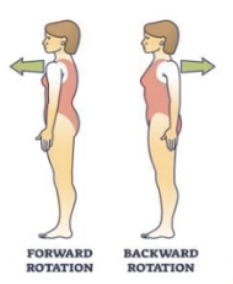
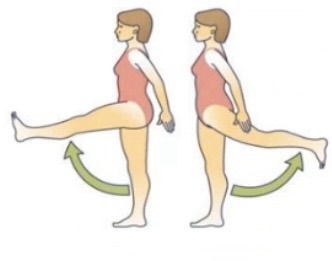
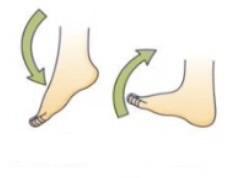
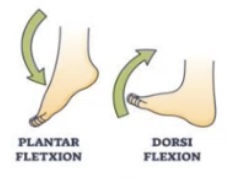
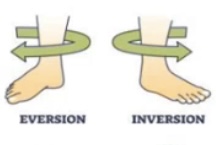
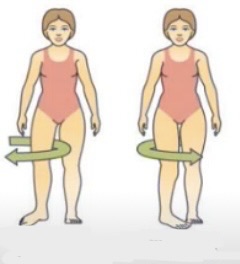
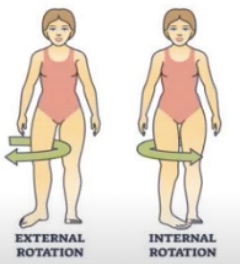
Plantar flexion = toes pointing down
Plantar flexion is like pressing a gas pedal
Dorsi flexion = toes up towards the shin
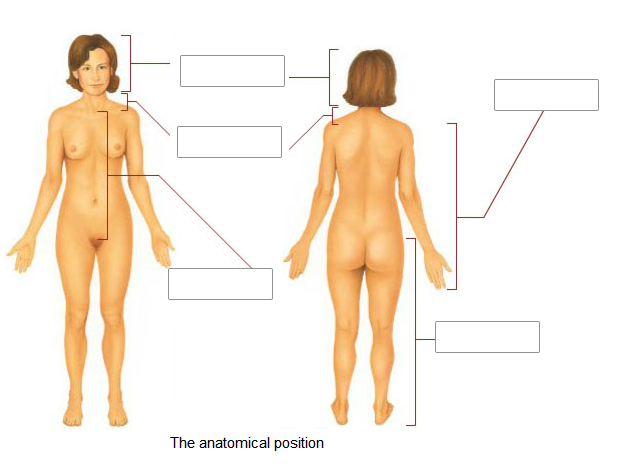
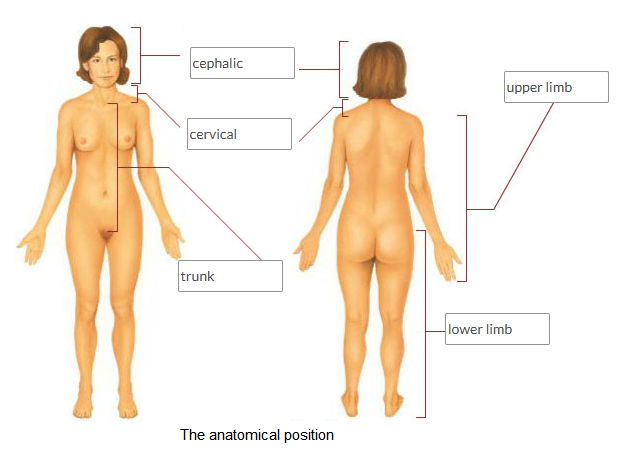
1)anterior
2)posterior
3)superior
4)inferior
1)nearer to the front of body
2)nearer to the back of the body
3)above
4)below
fill in the gaps
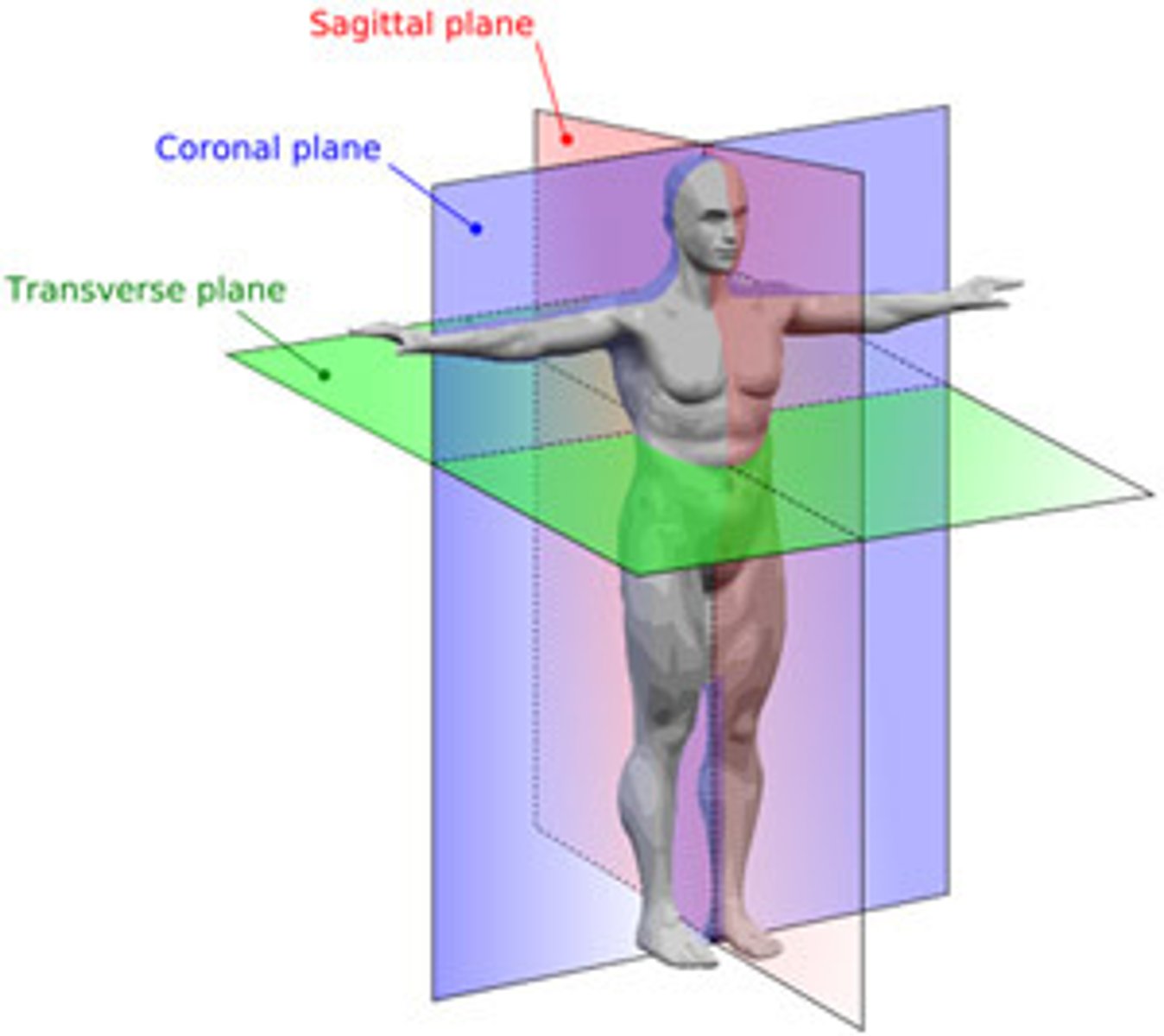
3 main planes of the body
transverse, frontal, sagittal
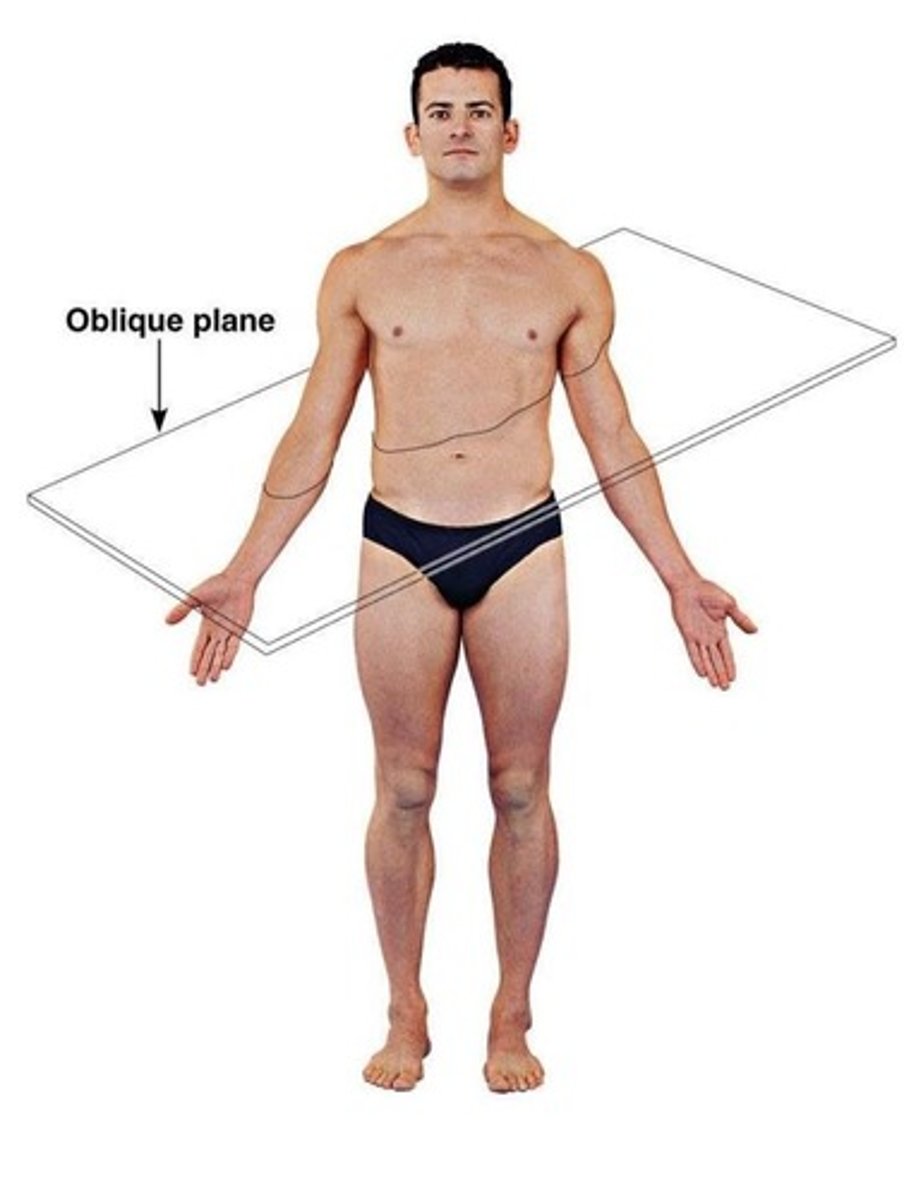
What is an oblique plane?
An oblique plane passes through the body/organ at any angle other than a 90 degree angle.
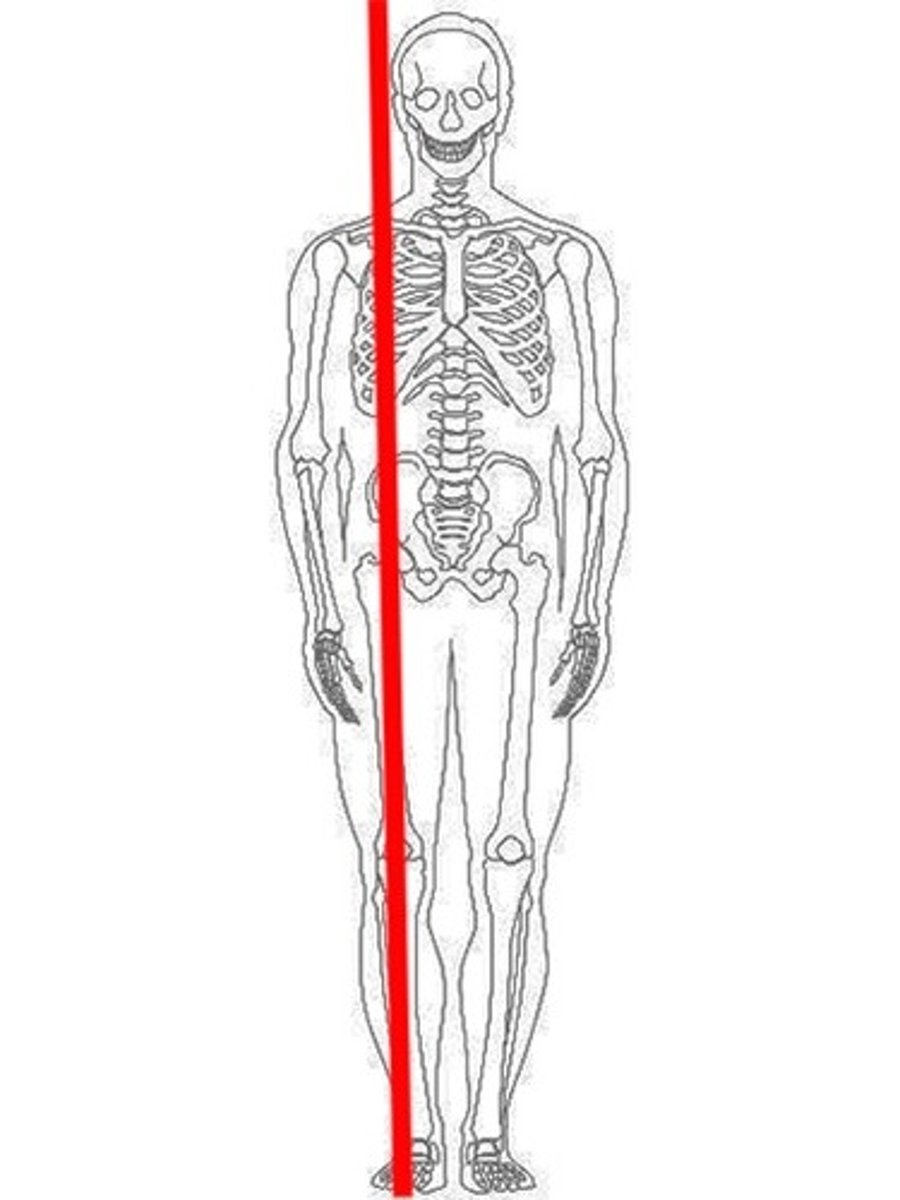
What is a parasagittal plane?
A parasagittal plane divides the body/organ into left and right unequally.
medial vs lateral
Medial= towards the midline
Lateral= away from the midline
proximal vs distal
Proximal = closer to trunk
Distal = farther from trunk.
Superficial vs. Deep
Superficial = toward surface
Deep = away from surface (deeper into the body)
Ipsilateral vs. Contralateral
ipsilateral = on the same side of the body
contralateral = on the opposite side
intermediate meaning
inbetween 2 structures
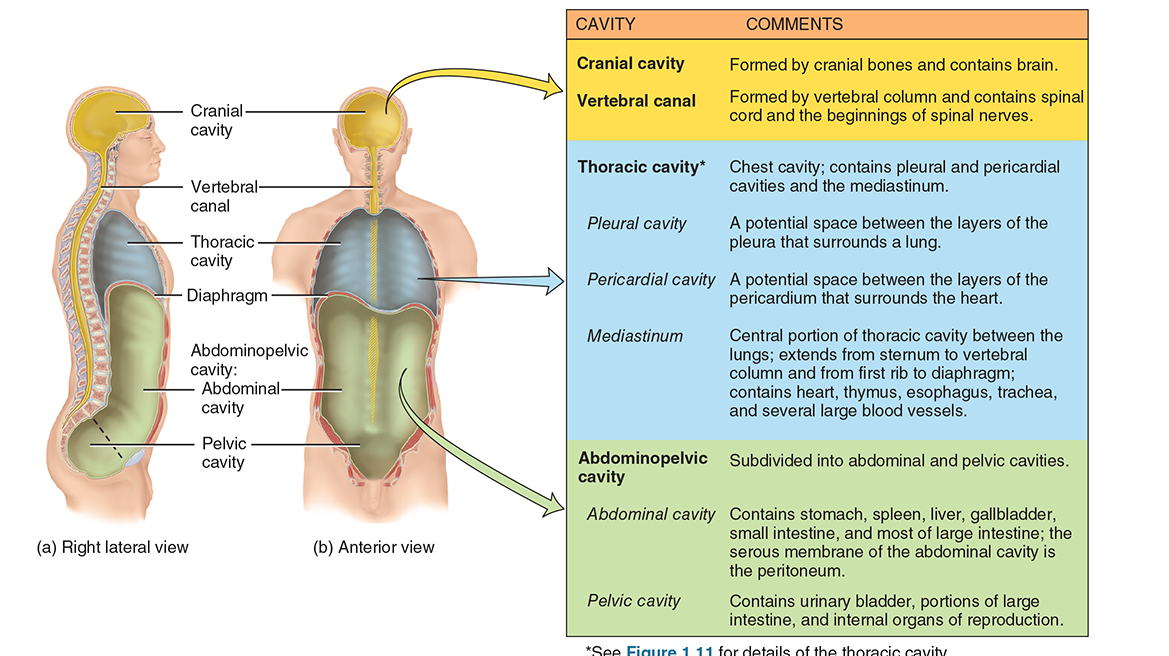
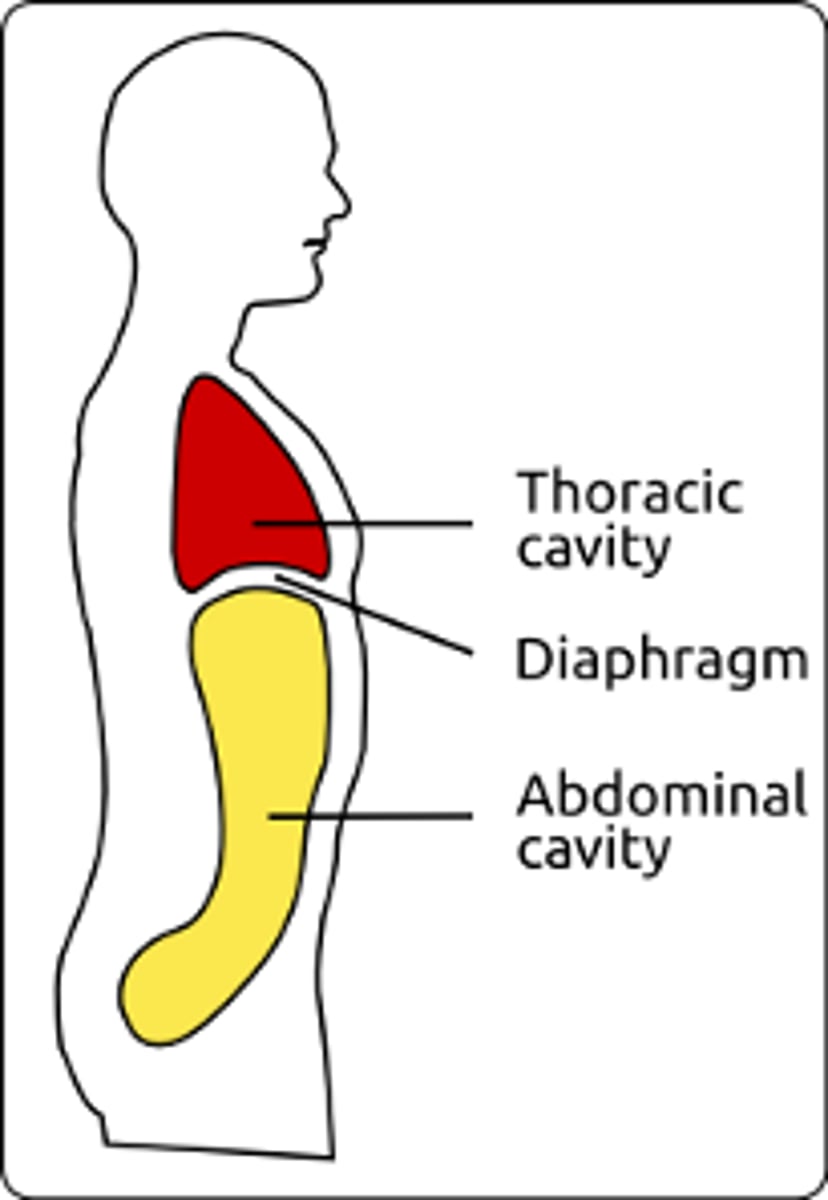
the area of the abdominopelvic cabity
from diaphragm to groin
abdominal cavity contains the...
stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder, small intestine, and most of the large intestine
the pelvic cavity contains the...
urinary bladder, portions of the large intestine, and most of the internal organs of the genital systems.
organs inside the abdominopelvic cavity are called...
viscera
serous membrane definition and function
the double-layered membrane which covers the viscera. it does not open directly to the exterior
layers of the serous membrane.
outer - parietal layer
inner - visceral layer
what is in between the layers of the serous membrane?
some fluid which allows the layers to slide somewhat during movement
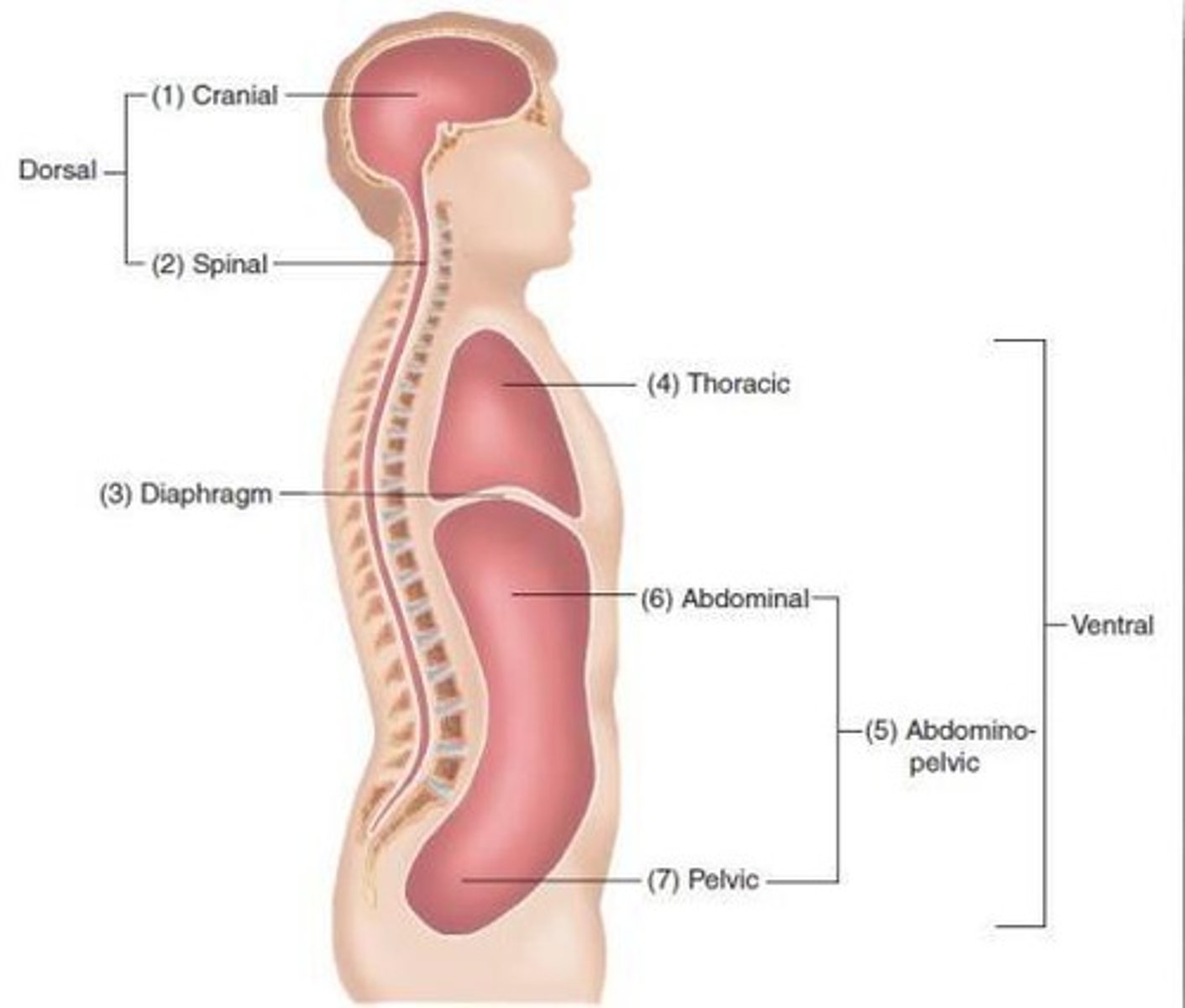
cavities in the head and trunk
cranial + vertebral (forms the dorsal cavity)
thoracic cavity
abdominal + pelvic (forms abdominopelvic cavity)
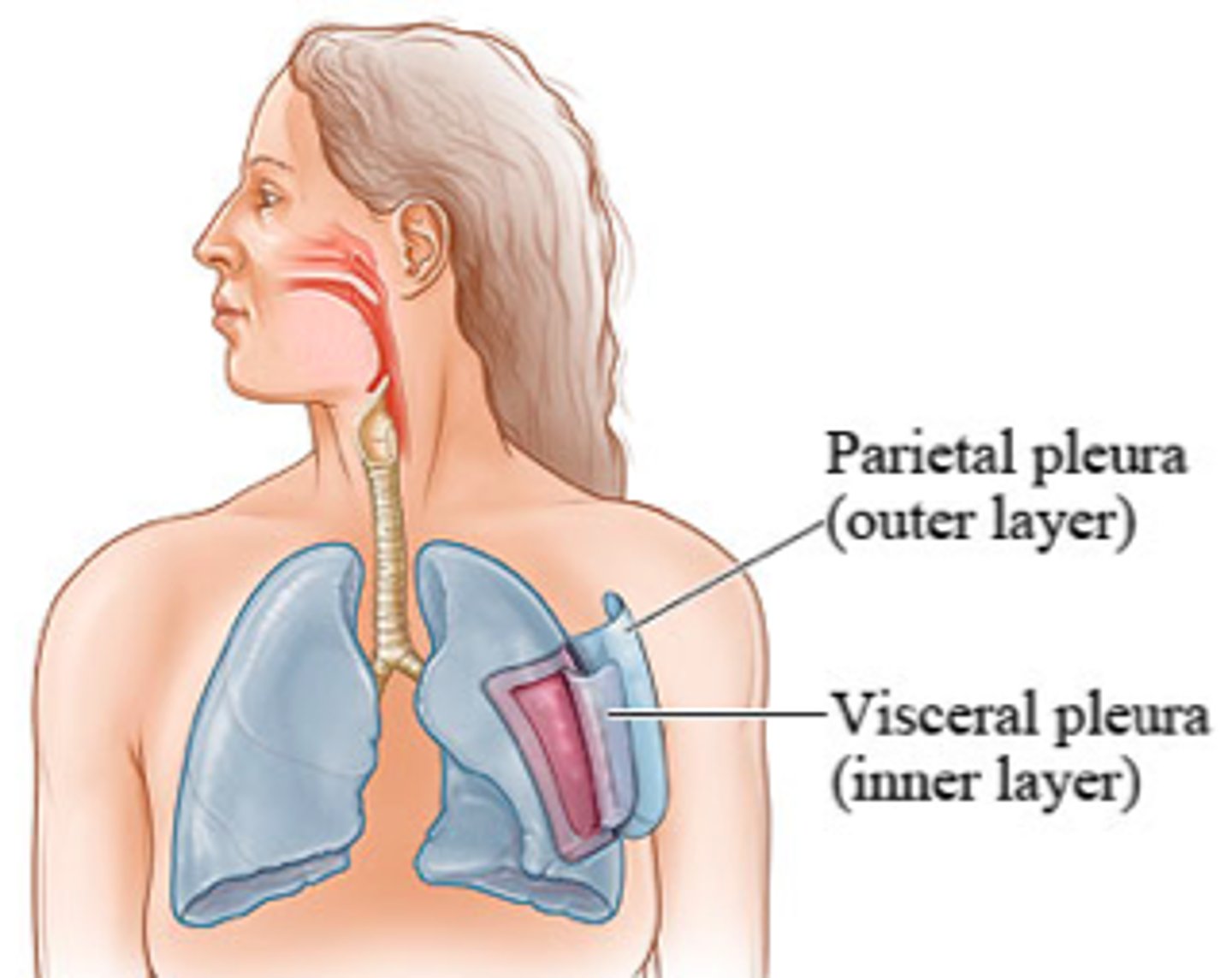
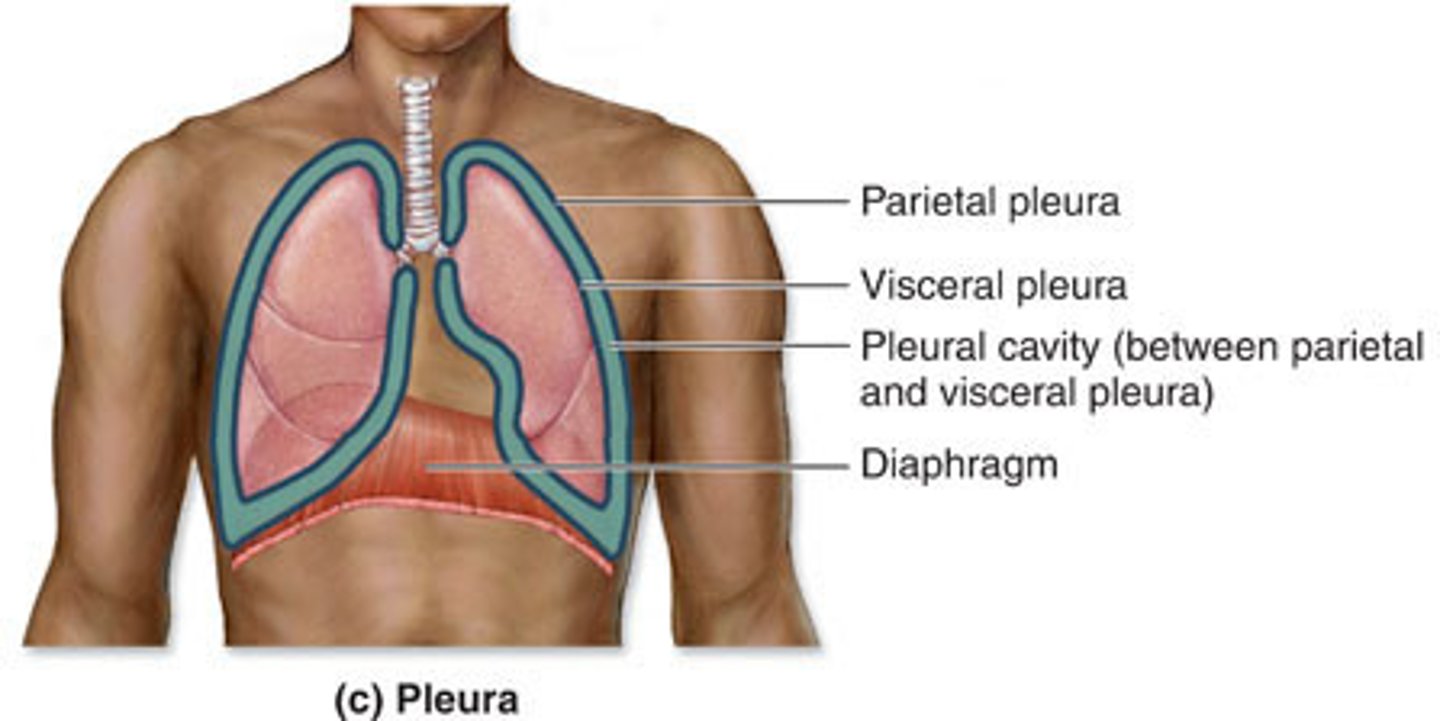
membranes of the pleural cavity (in order out to in)
parietal pleura
↓
pleural cavity (fluid filled gap)
↓
visceral pleura
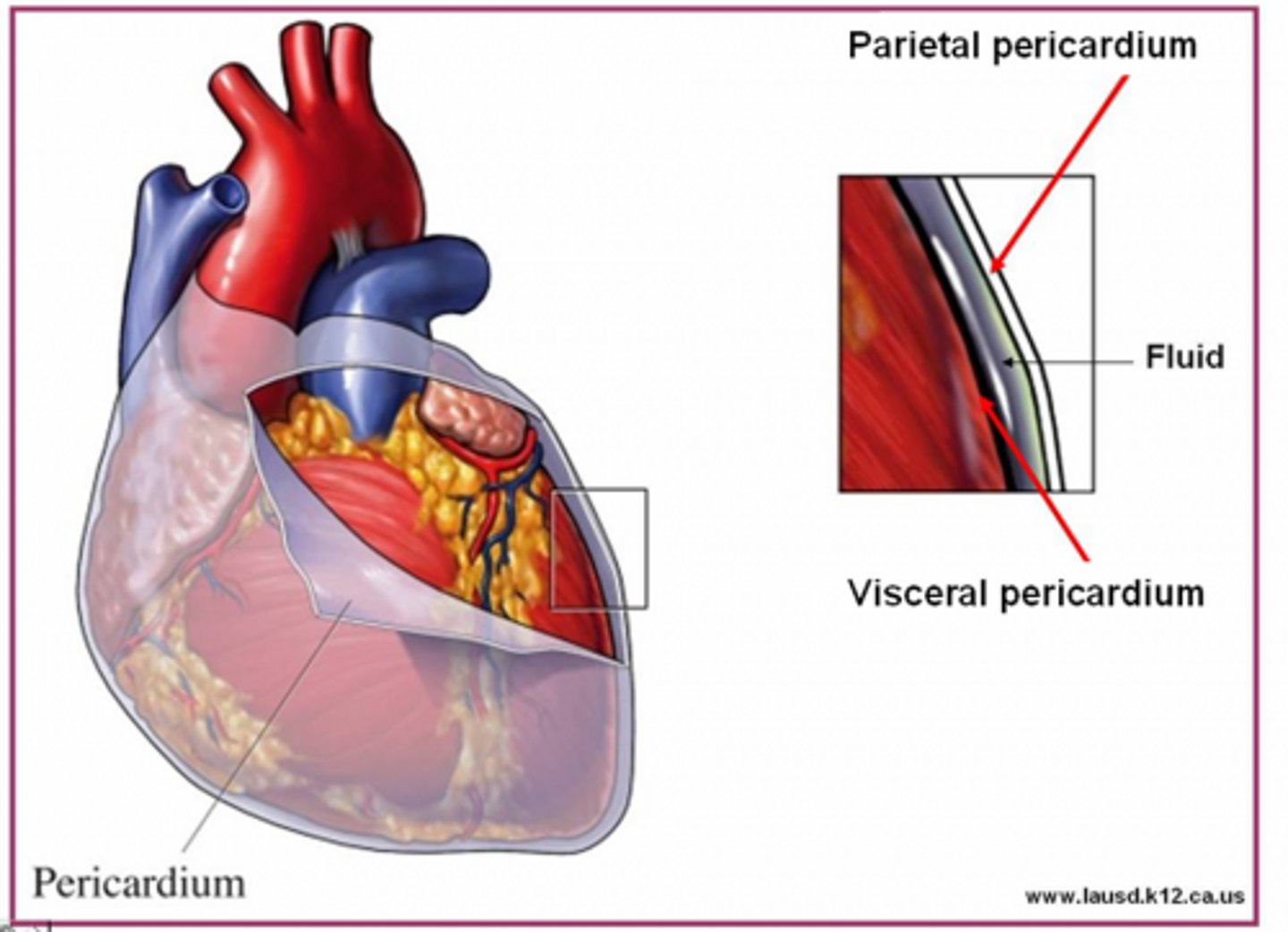
membranes of the pericardial cavity (in order from out to in)
parietal pericardium
↓
pericardial cavity (fluid filled gap)
↓
visceral pericardium
membranes of the abdominal (peritoneum) cavity (in order from out to in)
parietal peritoneum
↓
peritoneal cavity (fluid filled gap)
↓
visceral peritoneum
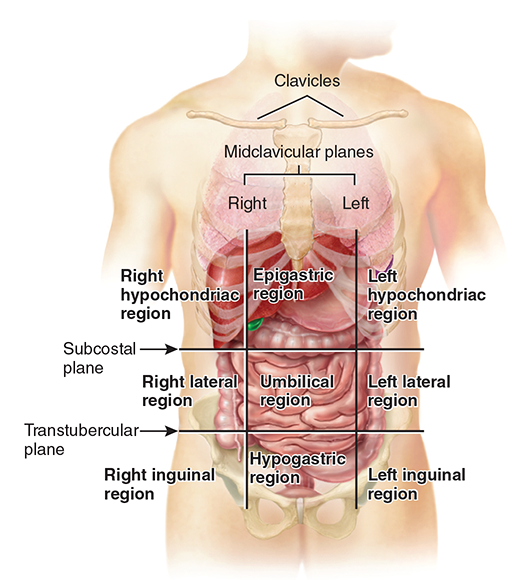
abdominopelvic regions
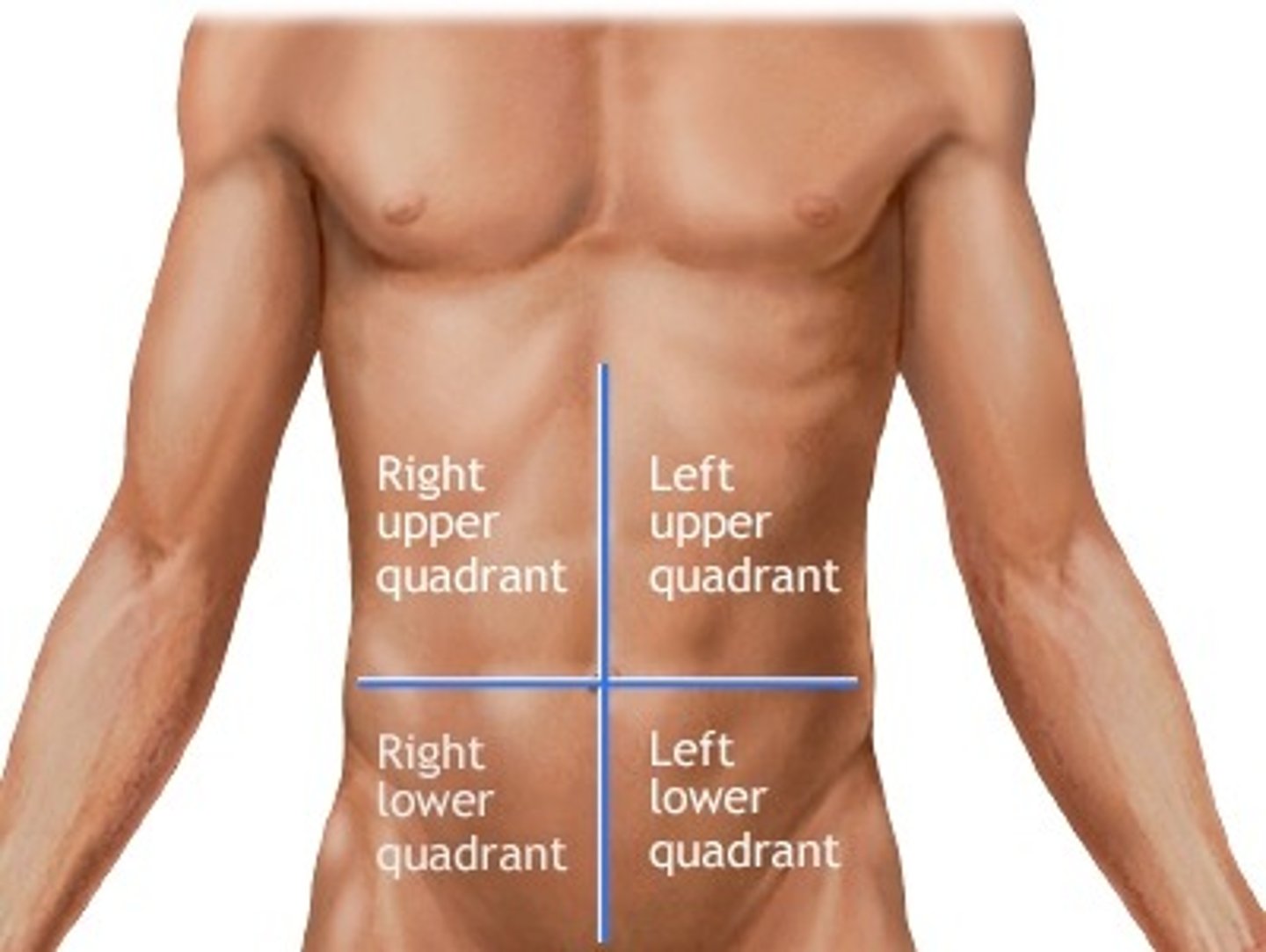
abdominopelvic quadrants
RUQ
RLQ
LUQ
LLQ
select all the correct list of structures which are retroperitoneal
major body cavities
the cranial cavity, vertebral cavity, thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, and pelvic cavity (pelvic + abdominal=abdominopelvic cavity)