Sinusitis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
4 stages of sinusitis
Acute sinusitis which lasts 2 to 4 weeks. It usually begins with cold-like symptoms such as runny nose and facial pain that may last up to 10 days.
Sub-Acute Sinusitis which usually lasts 4 to 12 weeks commonly occurs with seasonal allergies or bacterial infections.
Recurrent Sinusitis occurs when an individual has at least 4 episodes of acute sinusitis over the course of 1 year where each episode lasts at least 7 days.
Chronic Sinusitis lasts 12 weeks or longer and the symptoms are often less severe than acute sinusitis symptoms. It can be caused by bacterial infection and commonly occurs alongside persistent allergies or structural nasal issues.
Etiology
allergens
Irritants
Viruses
Fungi
Bacteria
- Popular irritants are animal dander, polluted air, smoke, and dust.

clinical presentation
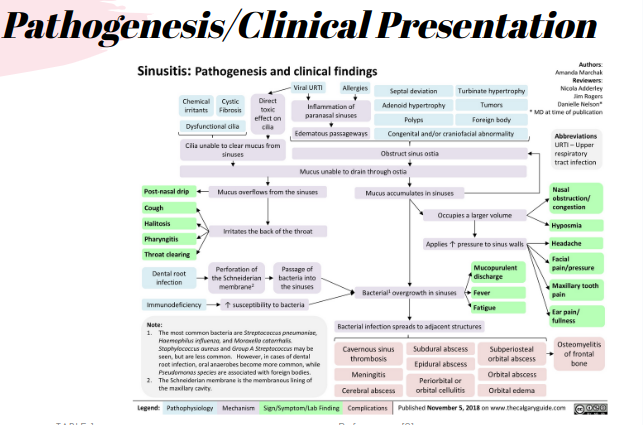
There are different types of sinusitis however they all have similar symptoms even if the duration and severity differs.
Acute sinusitis has the shortest duration and may last up to 4 weeks. It is caused via viral infection and it may present with symptoms of the common cold that may last up to 10 days.
Subacute sinusitis can last up to 12 weeks and commonly occurs with seasonal allergies or bacterial infections.
Recurrent acute sinusitis occurs when an individual has at least 4 episodes of acute sinusitis over the course of 1 year where each episode lasts at least 7 days.
Chronic Sinusitis can last for more than 12 weeks and the symptoms are often less severe than acute sinusitis symptoms. It can be caused by bacterial infection and commonly occurs alongside persistent allergies or structural nasal issues.
Risk factors
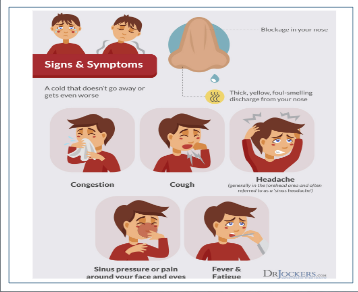
- Impaired mucous transport from diseases
- Immunodeficiency from chemotherapy, HIV, diabetes mellitus, etc.
- Rhinitis medicamentosa, toxic rhinitis
- Prolonged oxygen
- nasogastric or nasotracheal tubes
- Nasal allergies.
- Asthma
- Growth of nasal polyps
- Deviated septum; in which the tissue that divides the nose isn’t straight and causes one passage of the nose to be wider than the other leading to blockage.
- Taking drugs that weaken the immune system or having a compromised immune system i.e. HIV
- Smoking and exposure to second hand smoke
- Previous cold
- Seasonal allergies
- Dental Infection
- Airplane travel (exposure to high germ concentration)
what are the 3 types of sinusitis
Bacterial, Virus,fungi
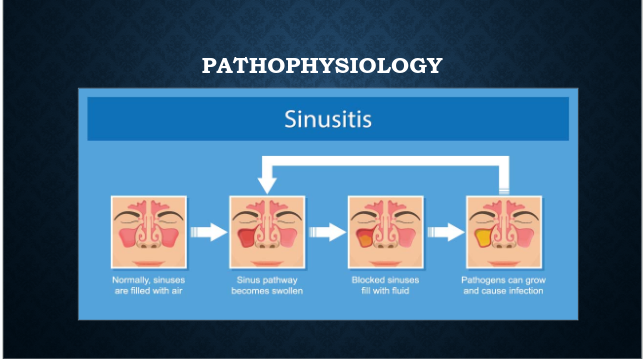
Pathophysiology
Differential Diagnosis
Sinusitis may be mistaken with rhinitis or an upper respiratory infection.
maxillary toothache can mimic pain caused by maxillary sinusitis.
Tension headaches and vascular headaches
foreign bodies
brain and epidural abscesses
meningitis
Diagnosis
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): An elevated ESR may signify a systemic illness or osteomyelitis complicated sinusitis.
Complete blood count
Serum immunoglobulin
HIV test
Allergy test as needed to identify triggers.
IMAGING:
x-ray
CT scan
MRI
NASAL ENDOSCOPY:
Visual
sampling
TESTING:
Blood
Allergy
Management:
say what is recommended for the specific duration of symptoms .
Sinusitis is treated both pharmacologically and non-pharmacologically
Symptoms <10 days (antibiotics not recommended)
Symptoms lasting 2-3 weeks without bacterial symptoms (oral/nasal decongestants)
Symptoms >10 days without improvement,no signs of recovery, adults and children over the age of 12 should consider a high-dose nasal corticosteroid for 14 days.
Goals of treatment
Eradicate the infection
Decrease the severity and duration of symptoms
Prevent complications.
Non pharmacological treatment
Humidification/vaporizer
Warm compresses
Adequate hydration
Smoking cessation
Balanced nutrition
Properly clean hands
Taking the Flu Vaccine and Pneumococcal Vaccine
Avoid Close Contact with individuals who have colds and Upper respiratory Infections
Avoid Smoke (Including Second hand smoke)
Keep Hydrated (Drink Clear Fluids)
Steam (Inhalation of steam from a bowl of warm water).
Eating spicy foods (Helps drain passages)
Nasal rinse with salt water
First line treatment
Co-amoxiclav 500/125mg T.I.D for 5 days
(combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid) destroys bacteria by disrupting their ability to form cell walls.
500mg/125mg three times daily for 5 days (children and adults 12 years and older).
0.25ml/kg of 125/31 suspension three times daily for 5 days (children 1 to 11 months).
5ml of 125/31 or 0.25ml/kg of 125/31 suspension three times daily for 5 days (children 1 to 5 years).
5ml of 250/62 suspension or 0.15ml/kg of 250/62 suspension three times daily for 5 days (children 6 to 11 years).Side effects : hepatitis, dizziness, cholestatic jaundice, vasculitis, exfoliative dermatitis.
Phenoxymethylpenicillin 500mg Q.I.D. for 5 days.
inhibits the biosynthesis of cell wall.
500mg four times daily for 5 days (children and adults 12 years and older).
62.5mg four times daily for 5 days (children 1 to 11 months)
125mg four times daily for 5 days (children 1 to 5 years)
250mg four times daily for 5 days (children 6 to 11 years)Side effects : nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, skin rash
what are the alternatives (pharmacological treatment)
Doxycycline 200mg on day 1 followed by 100mg OD for 4 days.
inhibit translation by binding to the 16S rRNA portion of the ribosome. , stops the replication of bacteria and produces a bacteriostatic effect.
200mg stat dose
then 100 mg daily for four days (children and adults 12 years and older).Side effects : dizziness, bloating, constipation, dark urine, headache, fever, increased heart rate, itching and/ swelling of the eyelids, face, lips, or tongue.
Clarithromycin 500mg B.I.D. for 5 days
Under 8kg; 7.5mg / kg B.I.D for 5 Days.
8 to 11 kg, 62.5mg B.I.D for 5 Days.
12 to 19 kg, 125mg B.I.D for 5 Days20 to 29 kg, 187.5mg B.I.D for 5 Days.
30 to 40 kg, 250mg B.I.D for 5 Days.
12 to 17 years; 250 mg B.I.D or 500mg B.I.D for 5 Days.Erythromycin 250mg - 500 mg Q.I.D a day or 500mg – 1000mg B.I.D. for 5 days. (Pregnancy)
Oral Alpha-adrenergic agents and the Adverse effects
Pseudoephedrine oral:
▪ Immediate release: 60mg po Q6h prn for no more than 14 days.
Extended release: 120mg Q12h
Phenylephrine oral:
▪ Immediate Release: 10mg po Q6h (Not to exceed 60mg in 24 hr)
ADVERSE EFFECTS:
▪ Tachycardia
▪ Insomnia
▪ Palpitations
Topical Vasoconstriction and their adverse effects
Oxymetazoline: 2 sprays per nostril q12hr for no more than 3 Days.
Xylometazoline: 2 Sprays per nostril q12hr for no more than 3 days.
Adverse Effects:
▪ Burning
▪ Stinging
▪ Dryness
▪ Rebound congestion
Nasal Polyps and their adverse effects
Intranasal fluticasone: 1 Spray in each nostril B.I.D (100mcg)
Adverse Effects:
▪ Headache
▪ Upper Respiratory Infection
▪ Nasal congestion
▪ Epistaxis (Hemorrhage from the nasal cavity)
Prognosis
Sinusitis does not cause any significant mortality by itself
complicated and chronic (especially bacterial), sinusitis may lead to morbidity , in rare cases mortality.
Patients with acute sinusitis, when treated with appropriate antibiotics, usually show prompt improvement.
Most cases of uncomplicated acute bacterial sinusitis can be treated as an outpatient with a favorable outcome. Frontal or sphenoid sinusitis with high amounts of air-fluid may necessitate hospitalization and intravenous (IV) antibiotics. Patients who look to be immunocompromised or toxic require admission. Fungal sinusitis has a significant morbidity and mortality rate.
Follow up
report after treatment duration
to report on symptoms
to evaluate the success of treatment
Patients should return to the pharmacy/doctor after the duration of treatment (non-pharmacological or pharmacological) to report if there is change in symptoms and to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment.
when to refer to a doctor
experiencing severe symptoms (severe headache or facial pain)
symptoms get worse after improving,
lasts more than 10 days without getting better
fever lasting longer than 3-4 days