Lecture 26: Principles of Minimally Invasive Sx
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is endoscopy?
Use of instrument (i.e., an endoscope) to visualize interior of organ or body cavity that cannot be examined w/o surgery
What are the components of flexible endoscopes?
• Handle- Where scope held by operator
• Insertion tube- Part inserted into patient
• Umbilical cord- Part attaches scope to light source & video processor
• Biopsy channel- Allows instrument placement through scope (Biopsy forceps, FB retrieval forceps, aspiration tubes, cytology brushes)
What type of flexible endoscopes can have handles placed in water without risk of damage
immersible scopes
What are the three portions of a flexible gastroduodenoscope?
umbilical cord: attaches scopes to light source
handle
insertion tube: introduced into patient
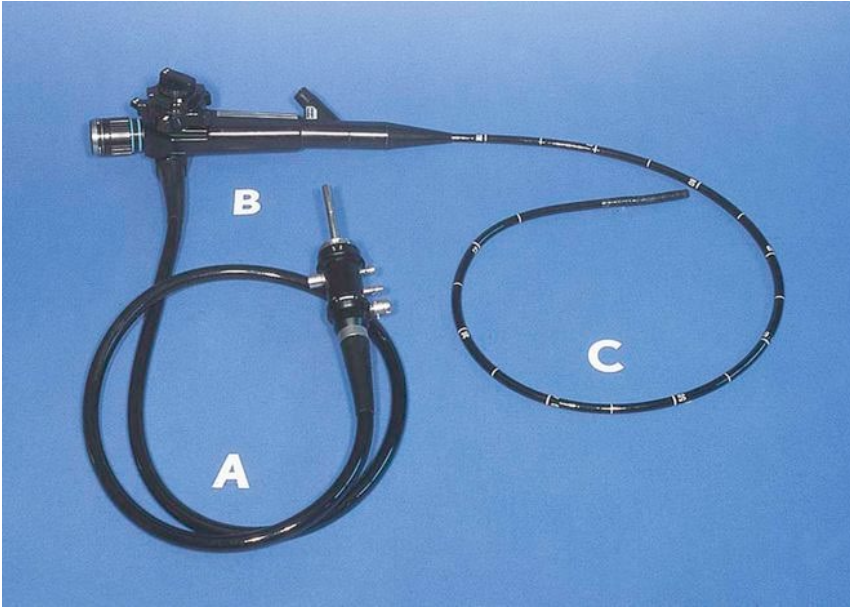
What is this tool?
flexible gastroduodenoscope
What are the portions of a rigid endoscope?
lens: at scope tip, allows looking at various angles - even 180 degrees backwards
obturator: device placed into hollow endoscope to aid insertion of scope into organ
trocar: obturator with sharp point to aid penetration through tissue
How is a rigid endoscope inserted into the body?
through skin (portals) and soft tissue or a natural orifice
How are endoscopy portals defined?
by use:
• Scope inserted thru scope or camera portal
• Power & hand tools inserted thru instrument portal
What is a cannula?
metal tube that maintains portals and protects instruments
What is triangulation in rigid endoscopy?
Visualization of instruments through scope to perform biopsies or therapeutic procedures w/in body cavity
What is a retrograde cystoscopy?
advancing scope through urethra into bladder
What is a transabdominal cystoscopy?
placing scope through cannula through abdominal wall and bladder wall
What is an endoscopy of the peritoneal cavity?
laparoscopy
What minimally invasive surgeries are performed through laparoscopy in small animals?
gastropexy and jejunostomy tube placement
What are the general uses for endoscopy?
• Used to biopsy organs, remove foreign objects, examine inside hollow structures
• Perform procedures done by more invasive surgery
When is endoscopy NOT useful?
• If tissue samples inadequate for dx
• Unacceptable trauma occurs during endoscopic removal of foreign objects
• Mucosal surfaces cannot be adequately examined
What are the indications for a gastroduodenoscopy?
• Gastric & intestinal biopsy/cytology for dx of infiltrative & lymphatic disorders
• ID of mass, ulceration, erosion, lymphangiectasia, or Physaloptera infestation
• ID & removal of FBs
• Placement of G-tube
• Location of lesions (e.g., ulcer, site of bleeding) before/during surgery
• Removal of gastric polyps w/ clinical signs
What are the indications for a esophagoscopy?
• ID & removal of foreign objects (FBs)
• Dx & dilation of strictures
• Aid in stent placement
• Dx of esophagitis
• Biopsy of tumors
What are the indications for a proctoscopy & colonoileoscopy?
• Biopsy (Bx): Colon, rectum, ileum, or cecum for infiltrative disorders
• ID of occult whipworm infestation
• Dx/removal of polyps
• Dx of cecocolic intussusception
What are the indications for a laryngoscopy?
• ID of laryngeal paralysis
• ID of elongated soft palate and/or everted laryngeal saccules
• Location & removal of FBs
• Bx mass or other infiltrative lesions
What are the indications for a cystoscopy?
• Dx of ectopic ureters
• Biopsy proliferative lesions in urethra & bladder, esp. carcinomas
• Injection of collagen in urethra for incontinence
What are the indications for a thoracoscopy?
• ID/bx of masses & other infiltrative lesions (Lung biopsy)
• Placing chest tubes in animals w/ pyothorax
• Determine if thoracotomy is indicated and the best open approach
• Performance of minimally invasive surgery: Pericardiectomy, Ligation/resection of PRAA
What are the indications for a broncoscopy?
• ID of lesions (Collapsed trachea, Oslerus osleri infestation)
• Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) or brushing of trachea/bronchus for cytology/culture
• ID & removal of FBs
• ID of lung lobe torsion
• Biopsy of mucosa (Chronic bronchitis)
• Placement of stents/evaluation of stents previously placed
What are the indications for a rhinoscopy?
• ID & removal of foreign objects
• Biopsy/cytology of mass lesions & mucosa for infiltrative disorders
• ID & bx of aspergillomas
• ID of source of epistaxis or chronic nasal discharge
What are the indications for a posterior nares (choanal) examination?
• ID & removal of FBs
• Cytology/culture of the caudal nares
• ID of & bx of proliferative disorders
• ID, dilation, & stenting of nasopharyngeal stenosis
• ID of nasal mites
What are the indications for a laparoscopy?
• Exam & bx of abdominal viscera
• Determine if celiotomy indicated (Evidence of metastasis where surgery can’t be curative?)
• Minimally invasive interventional surgery: Gastropexy, placement of J-tube, OHE, cryptorchid removal
What are the indications for a arthroscopy?
• ID & bx of lesions
• Removal of loose bodies (cartilage fragments, bone fragments, torn meniscus)
• Topical management of osteoarthritis—abrasion arthroplasty, microfracture
• Joint lavage for sepsis
• Arthroscopic assisted fracture repair
• Arthroscopic assisted joint stabilization
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a flexible endoscope?
advantages:
greater access to more sites in viscous organs
more expensive than rigid scopes
disadvantages:
easier to damage, requires training to assemble and clean w/o damaging
requires substantial training to use properly
What are the advantages of a rigid endoscope?
• Less expensive than flexible scopes
• Usually more durable
• Easier to learn to use
• Capable of larger biopsies than w/ flexible scopes
What is a rigid endoscope usually used for?
• Excellent for simultaneous removal of foreign objects & protecting mucosa
• For viscous organs: Only access esophagus, descending colon, larynx, nose, & trachea
• Used in peritoneal, pleural, & joint spaces
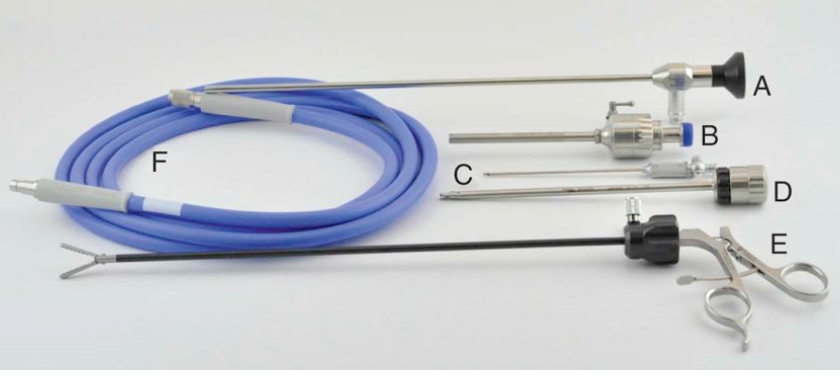
What are the parts of this rigid laparoscope?
A. Autoclavable laparoscope
B. Laparoscope sheath w/ automatic valve & manual valve lever
C. Insufflation Veress needle
D. Locking shielded trocar
E. Rotatable grasper w/ locking handle
F. Fiberoptic light cable
What are the three commonly used foreign body retrieval forceps?
shark’s tooth forceps
rat’s tooth forceps
coin retrieval forceps
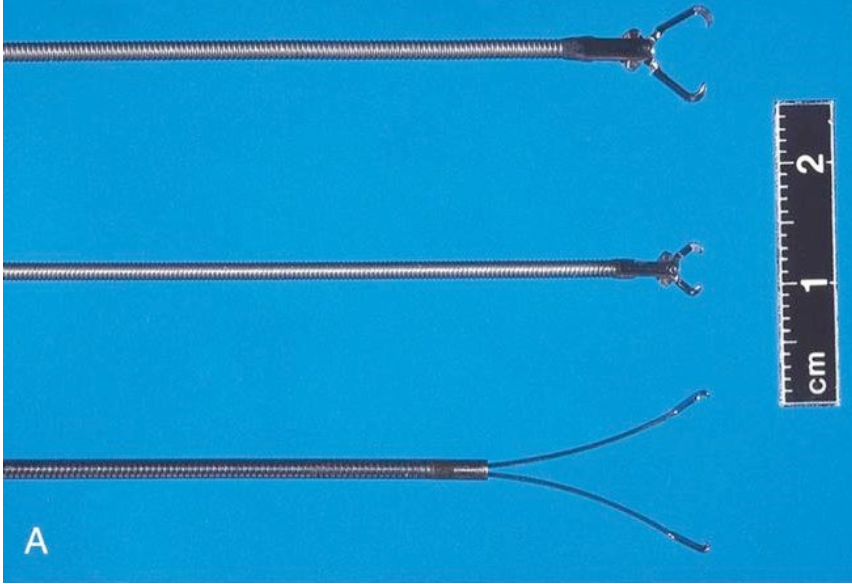
What are these three commonly used foreign body retrieval forceps?
Top to bottom:
• Shark's tooth forceps
• Rat's tooth forceps
• Coin retrieval forceps
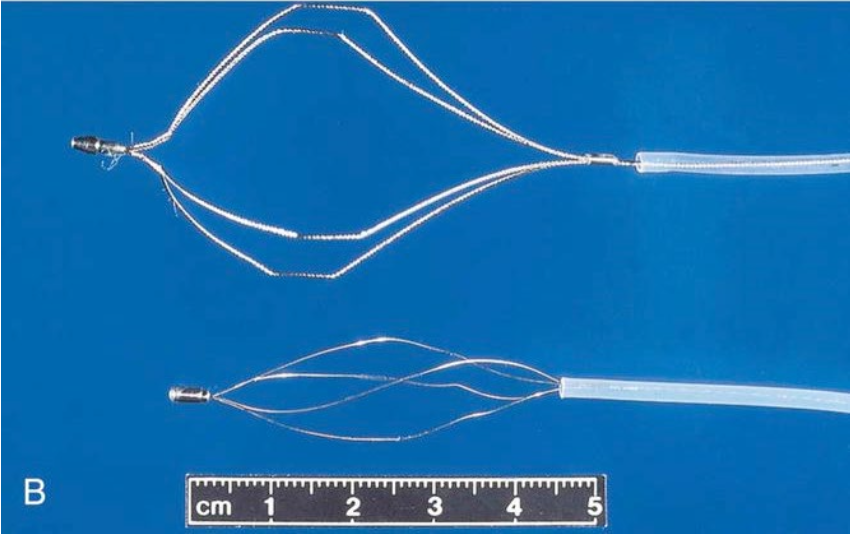
What are these retrieval forceps?
top: four-wire basket with flexible wires
bottom: four-wire basket with firm wires that do not open as widely
NEVER introduce insertion tube into mouth of an unanesthetized animal during and endoscopy and always use a _________.
mouth gag
What should flexible scopes never be subjected to?
heat, especially autoclaving
What are the four basic principles that apply to most endoscopic procedures?
1. Advance scope only if you can see where you are going!
2. If you cannot see what is happening (i.e., a condition known as a “red out”)
Back scope out a little rather than advancing it
Or insufflate a little air/infuse some fluid into lumen (or do both)
3. Aim scope toward center of lumen (Unless looking at specific lesion)
4. Do not insert endoscope into patient any harder than you would want a physician to insert it into you!
What are the advantages of endoscopic removal of foreign objects?
• Faster than surgery
• Less stressful to patient
• Reduced tissue trauma, morbidity & recovery time
• Reduced cost to client
What are the disadvantages of endoscopic removal of foreign objects?
• Cannot remove all objects
• Can hurt patient w/ careless technique
• Requires assortment of expensive foreign body retrieval devices
What is the most commonly performed arthroscopic procedure?
fragment removal:
osteochondritis dessicans (OCD)
fragmented coronoid process (FCP)
Why is arthroscopy superior to radiography in dx of joint disease>
• Allows direct visualization of cartilage & soft tissue structures
• Provides magnification
• Enables biopsy of virtually all structures w/in joint
What is the most significant diagnostic advantage of arthroscopy?
ability to assess condition of cartilage surface
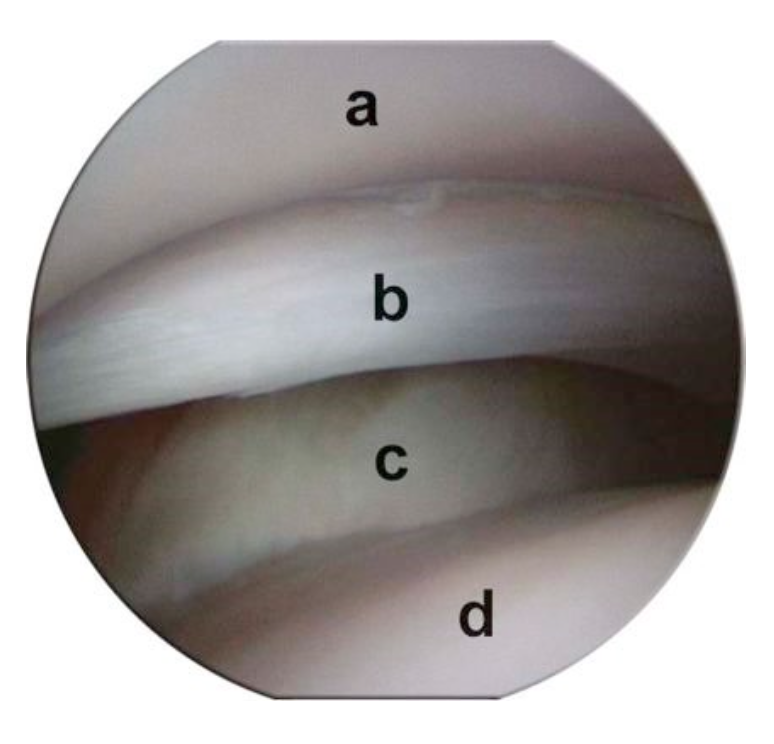
What is being seen in this arthroscopic view?
a. Glenoid cavity
b. Medial collateral ligament
c. Subscapularis ligament
d. Humeral head
What are the common shoulder diagnoses with arthroscopy?
• OCD
• OA
• Biceps disease
• MCL tearing
• LCL tearing
What are the common elbow diagnoses with arthroscopy?
• FCP
• OCD
• Ununited Anconeal Process (UAP)
• OA of medial compartment
• Incomplete ossification of humeral condyle (IOHC)
What are the common carpus diagnoses with arthroscopy?
OA
chip fractures
What are the common hip diagnoses with arthroscopy?
• OA
• Labral tearing & avulsion
• Tearing of ligament of femoral head
• Neoplasia
What are the common stifle diagnoses with arthroscopy?
• OCD
• Cruciate disease/damage
• OA
• Meniscal disease/damage
What are the common tarsus diagnoses with arthroscopy?
• OCD
• Chip fractures
What are the common shoulder arthroscopic procedures?
• Fragment removal - OCD
• Osteoarthritis treatment: Microfracture, Abrasion
• Biceps tenotomy
What are the common elbow arthroscopic procedures?
• Fragment removal: OCD, FCP
• Osteoarthritis treatment: Microfracture, Abrasion
What are the common carpus arthroscopic procedures?
• Fragment removal: Chip fractures
• Osteoarthritis treatment: Microfracture, Abrasion
What are the common hip arthroscopic procedures?
OA assessment
biopsy
What are the common stifle arthroscopic procedures?
• Fragment removal: OCD
• OA treatment: Microfracture, Abrasion
• Meniscal tear treatment
• Cruciate ligament debridement
What are the common tarsus arthroscopic procedures?
• Fragment removal: OCD
• OA treatment: Microfracture, Abrasion
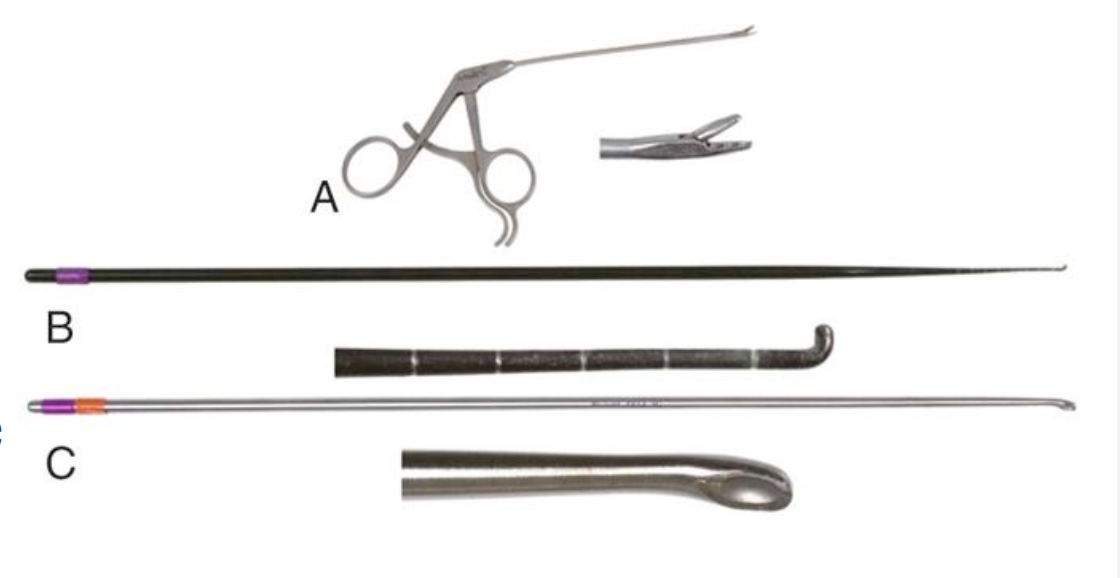
What are these hand instruments for SA arthroscopy?
A. Grasping forceps
B. Right angle probe
C. Microcurette