Week 5: Day 1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What did Freud believe shaped development?
Sexual drives shaped development through stages; unresolved conflicts can cause fixation
What are Freud’s psychosexual stages of development?
Oral (0–1), Anal (1–3), Phallic (3–6), Latency (6–11), Genital (Adolescence–Adulthood)
What are the three parts of Freud's structure of the mind?
Id (pleasure), Ego (self-control), Superego (conscience/guilt)
What is Hunger/Id?
“I want it now”, pleasure principle immediate gratification (Baby Stage, 0-1)
what is restraints/ego?
Learning self-control, sense of self in conflict with id (1-3)
What is sexual desire/superego?
Drive in guilt and conscience (3-6)
What is Latency?
Relative calm (6-12 year)
What is Genital?
Sexual maturationand adult sexual relationships (adolescence)
How did Erikson expand Freud’s theory?
Added social and cultural factors; created 8 psychosocial stages across the lifespan
What are Erikson’s first 5 psychosocial stages?
Trust vs. Mistrust, Autonomy vs. Shame, Initiative vs. Guilt, Industry vs. Inferiority, Identity vs. Role Confusion.
What is Trust V Mistrust (0-1)
Can baby trust caregiver, intimate relationship difficulties
What is Autonomy vs Shame (1-3)?
“No! Stage, self doubt
What is Initiative vs Guilt (3-6)?
learning to take lead, lack of conscience
What is Industry vs Inferiority (9-11)?
School age competence, excessive inadequacy and inferiority
Identity vs Role Confusion (teen)?
Who am I? Who are really? Or live in a state of role confusion as an adult
What impact did Freud and Erikson have on psychology?
Freud emphasized the unconscious and early relationships; Erikson emphasized social crises and identity.
What are common criticisms of Freud and Erikson’s theories?
Too vague, not easily testable, and some ideas are questionable.
What does Watson’s Behaviorism say about development?
Environment and conditioning shape behavior; famously did the Little Albert experiment, “I can train any child to be anything”
What is Skinner’s Operant Conditioning?
Learning through reinforcement and punishment; behaviors are shaped by consequences.
What did Bandura contribute to learning theory?
Social Learning—children learn by watching others (BOBO doll); introduced reciprocal determinism. (See what other do)
What is reciprocal determinism?
Children influence their environment and are influenced by it.
What are the four steps of observational learning?
Attention, Encoding, Storing, Retrieving (A child environment influences operate both direction)
What is Selman’s theory?
Role-taking stages—children develop empathy by learning to take others' perspectives, (Young kids are egocentric but as they grow they can see from otehr perspective/develop empathy)
What is Dodge’s theory of aggression?
Hostile attribution bias—children assume others are being hostile, which leads to aggression.
What is Dweck’s Motivation Theory?
Growth mindset (can improve) vs Fixed mindset (I suck); effort-based praise is better than intelligence praise.
What do Social Cognitive Theories emphasize?
Children are active thinkers; they self-socialize and interpret social experiences.
What is Lorenz’s ethological theory about?
Imprinting in animals as a survival mechanism; inspired Bowlby’s attachment theory.
What is Bronfenbrenner’s Bioecological Model?
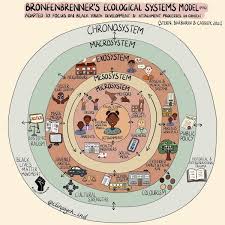
Microsystem: Immediate surroundings (family, school)
Mesosystem: Interactions between microsystems
Exosystem: Indirect environments (e.g. parent’s work)
Macrosystem: Culture and society
What is a Microsystem?
Immediate surroundings (family, school)
What is a mesosytem?
Interactions between microsystems
What is a Exosystem?
Indirect environments (e.g. parent’s work)
What is a Macrosystem?
Culture and society