AP Psych
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
comprised of brain and spinal chord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
comprises all nerves in the body (excluding those in brain and spinal chord)
can be subdivided into somatic and autonomic nervous systems
Somatic nervous systems
responsible for voluntary movement of large skeletal muscles
Autonomic nervous system
control nonskeletal or smooth muscles (like heart and digestive track)
can be divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
Sympathetic nervous system
Associated with processes that burn energy. Heightened state of psychological arousal (e.g. fight-or-flight response)
Reactions of sympathetic nervous system
• increased heart reate
• increased respiration rate
• decrease in digestion
• decrease in salivation
• blood transfer to skeletal muscles
Parasympathetic nervous system
complementary system responsible for conserving energy
Reactions of parasympathetic nervous system
• digestion continues
• decreased heart rate
• decreased breathing rate
(body returns to homeostasis)
Hindbrain
Oldest part of the brain to develop (evolutionary terms)
components of the hindbrain
• cerebellum
• medulla oblongata
• reticular activating system (RAS)
• pons
Cerebellum
controls muscle tone and balance
Medulla oblongata
Control involuntary actions; basic life functions (e.g. breathing, heart rate, digestion, swallowing)
Reticular activating system (RAS)
controls arousal (a.k.a. reticular formation)
Arousal
wakefulness and alertness
Pons
(latin for bridge) way station, passes neural information from one brain region to another
Components of midbrain
• Colliculus (superior and inferior colliculi)
• tectum
• tegmentum
Midbrain
the topmost part of the brainstem, the connection central between the brain and the spinal cord
Superior colliculi
(a.k.a. optic tectum) control head, neck, and eye movements
Midbrain functions
involved in several functions, including motor control (particularly eye movements) and processing of vision and hearing
Inferior colliculi
main part of the midbrain's auditory pathway. Help with sound localization, startle responses, and discriminating pitch and rhythm
Tegmentum
region in the brainstem that controls movement coordination, sensory processing, and alertness (arousal)
Forebrain
brain structure responsible for higher-order mental processes such as memory and decision-making
Components of forebrain
• limbic system
• cerebral cortex
Limbic system
emotional center of brain
Components of limbic system
• Thalamus
• Hippocampus
• Amygdala
• Hypothalamus
Cerebral cortex
involved in higher cognitive functions (thinking, planning, language use, fine motor control)
Sensory cortex
Area of cerebral cortex that receives sensory input
Motor cortex
Area of cerebral cortex that sends out motor information
Corpus callosum
band of connective nerve fibers that join left and right cerebral hemispheres
Left hemisphere
typically specialized for language processing
Broca’s area
in charge of speaking ability
Expressive aphasia
loss of the ability to speak
Wernicke’s area
in charge of comprehending speech
Receptive aphasia
inability to comprehend speech
Right hemisphere
processes visual and spatial information
where right visual field is processed
left, more verbal side of brain
where left visual field is processed
right, more visual side of brain
Contralateral processing
ability of (non-split) brains to use both hemispheres and integrate information between them via corpus callosum
Components of cortex
• 4 lobes:
• frontal lobe
• parietal lobe
• temporal lobe
• occipital lobe
• association areas
Frontal lobe
responsible for higher-level thought and reasoning (e.g. accessing working memory, attention, problem solving, planning, performing movement)
Parietal lobe
handles somatosensory information & home of somatosensory cortex (receives info about temp, pressure, texture, and pain)
Temporal lobe
handles auditory input (critical for processing speech and appreciating music)
Occipital lobe
processes visual input (this input crosses optic chasm)
Optic chiasm
part of the brain where the optic nerves from each eye cross over
Association areas
responsible for associating information in the sensory and motor cortices
Dysfunctions due to damage to association areas
• apraxia
• agnosia
• alexia
• agraphia
Apraxia
inability to organize movement
agnosia
difficulty processing sensory input
Alexia
inability to read
Agraphia
inability to write
Nerves
bundles of neurons, basic unit of nervous system. Cells with clearly defined soma
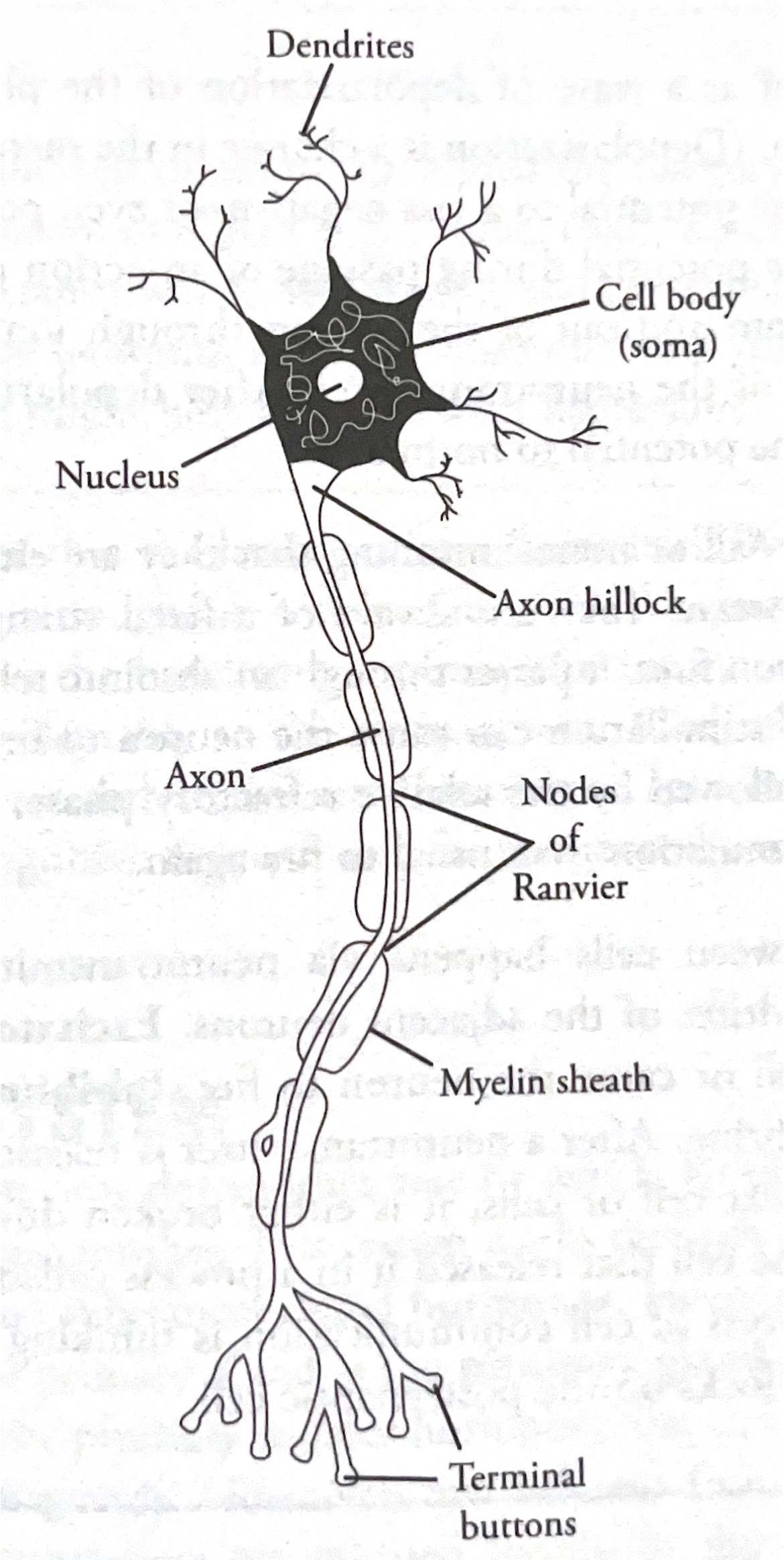
Soma
nucleated cell body
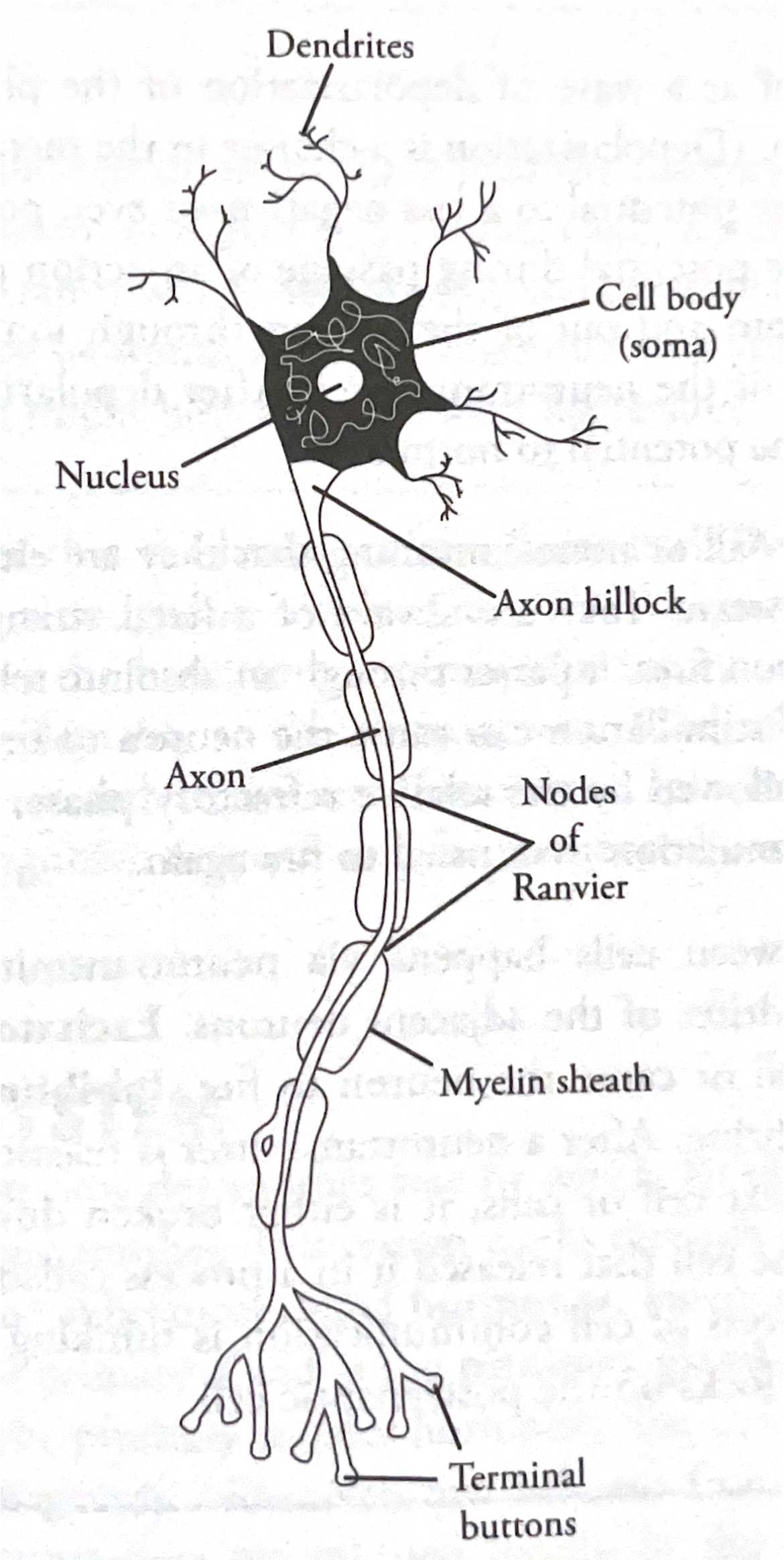
Dendrites
receivers of input from other neurons (through receptors on surface) that branch out from soma
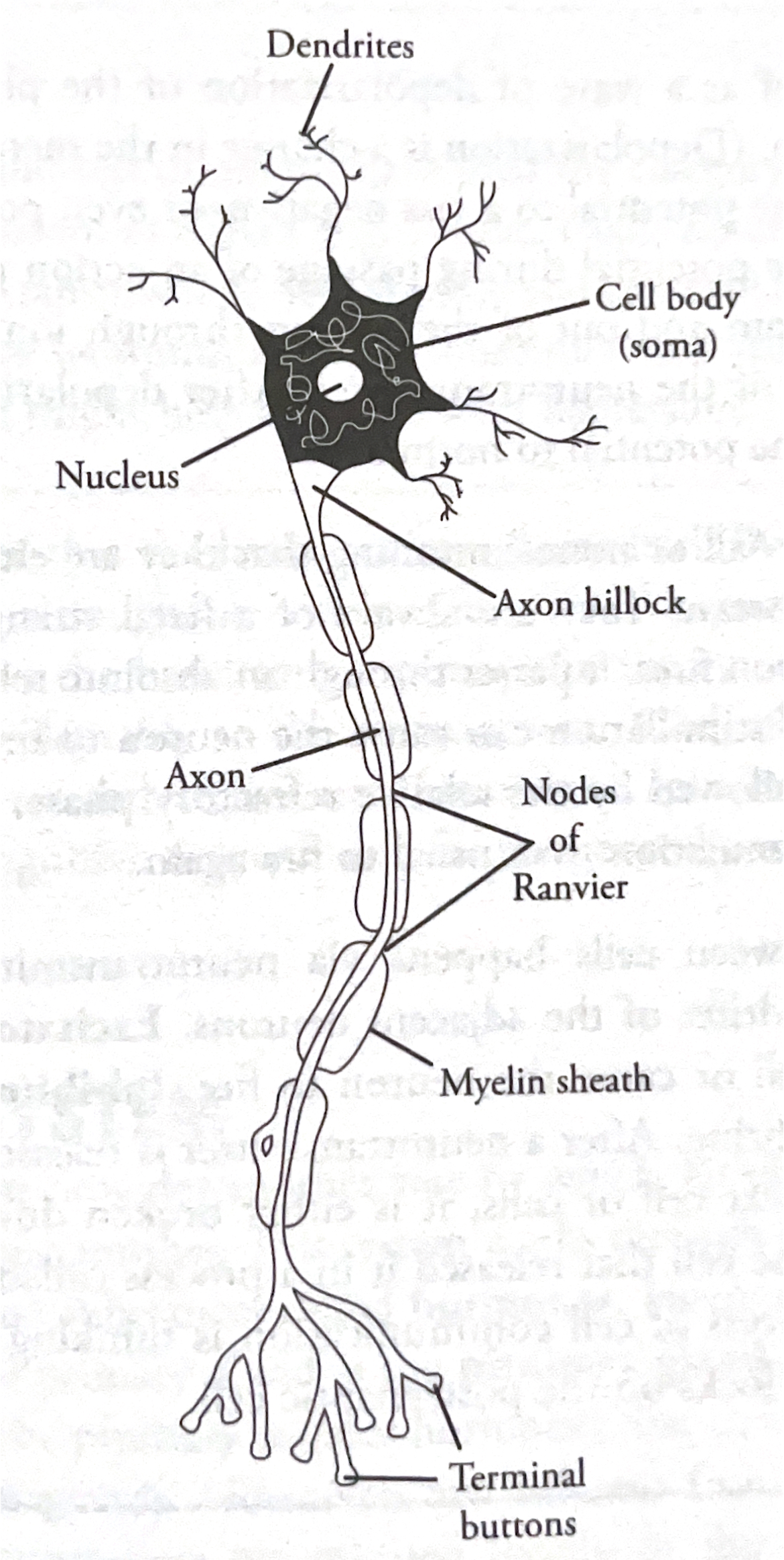
Axon
long, tubelike structure that responds to input from dendrites and some