AST201 week 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:55 PM on 2/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
gravitational contraction
the sun generates energy by slowly contracting in size, a gradually shrinking sun would always have some gas moving inward converting gravitation potential energy into thermal energy
2
New cards
sun has 2 kinds of balance that keep its size and energy output stable
gravitational equilibrium and energy balance
3
New cards
gravitational equilibrium
between outward push of internal gas pressure and the inward pull of gravity
4
New cards
energy balance
between the rate of which fusion releases energy in the sun’s core and the rate at which the sun’s surface radiates this energy into space
5
New cards
in about 5 billion years…
the sun will finally exhaust its nuclear fuel and gravitational contraction will begin once again
6
New cards
sunspots
visible splotches that appear darker than the surrounding surface (larger in life than earth)
7
New cards
power
the rate at which energy is used or released
8
New cards
luminosity
a stars total power output
9
New cards
solar wind
stream of charged particles continually blown outward in all directions from the sun
10
New cards
corona
outermost layer of the atmosphere, temp is astonishingly high, density is very low
11
New cards
cromosphere
middle layer of the solar atmosphere and the region that radiates most of the sun’s UV light
12
New cards
photosphere
lowest layer of the atmosphere, visible surface of the earth
13
New cards
convection zone
where energy generated in the solar core travels upward, transported by the rising of hot gas and falling of cool gas called convection
14
New cards
radiation zone
where energy moves outward primarily in the form of photons of light, turbulence of convection zone gives way to the calmer plasma
15
New cards
core
source of suns energy, density is more than 100 times that of water, extreme pressure
16
New cards
radiative energy
the energy that light carries
17
New cards
joules
the unit we measure energy in
18
New cards
power
the rate of energy flow, measured in units called watts
19
New cards
spectrum
a prism split light into the rainbows of light
20
New cards
white light
a mix of all these colours in roughly equal proportions
21
New cards
black light
when we perceive no light and hence no colour
22
New cards
primary colours of vision
red, green, blue (RGB)
23
New cards
how do light and matter interact
emission, absorption, reflection
24
New cards
transparent
materials which transmit light
25
New cards
opaque
materials that absorb light
26
New cards
particle
can sit still or move from one place to another
27
New cards
waves
consist of peaks
28
New cards
wavelength
distance from one peak to the next
29
New cards
frequency
number of peaks passing by any point each second
30
New cards
hertz
another name for cycles per second
31
New cards
field
describe the strength of force that a particle would experience at any point in space
32
New cards
electromagnetic waves
light waves are traveling vibrations of both electric and magnetic fields
33
New cards
photons
light comes in individual “pieces” that have properties of both particles and waves
34
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum
light that we can see
35
New cards
electromagnetic radiation
light itself
36
New cards
visible light
light that we can see with the naked eye
37
New cards
infared
light with wavelengths somewhat longer than those of red light
38
New cards
Ultraviolet
lies between blue and end of the rainbow in wavelengths
39
New cards
atoms
all ordinary matter is composed of atoms
40
New cards
element
atoms come in different types and each type corresponds to a different chemical element
41
New cards
atoms are made up off:
* protons
* neutrons
* electrons
* nucleus
* neutrons
* electrons
* nucleus
42
New cards
attraction and repulsion
oppositely charged particles attract and similarly charged particles repel
43
New cards
molecules
number of different material substances is far greater than the number of chemical elements because atoms can combine to form molecules
44
New cards
chemical bond
interactions between electrons that hold the atoms in a molecule together
45
New cards
molecular dissociation
high enough temp, the collisions become so violent they break chemical bonds
46
New cards
pressure
force per unit area pushing on an objects surface
47
New cards
energy levels
the possible energy of an atom
48
New cards
energy level transitions
an electron can rise from a low energy level to a higher one, or fall from a high level to a lower level
49
New cards
spectroscopy
the process of obtaining a spectrum and reading the info it contains
50
New cards
three basic types of spectra
1. continuous spectrum
2. emission line spectrum
3. absorption line spectrum
51
New cards
continuous spectrum
the spectrum of a traditional, or incandescent, light bulb is a rainbow of colour, because the rainbow spans a brand range of wavelengths without interruption
52
New cards
emission line spectrum
a thin or low density cloud of gas emits light only at a specific wavelengths that depend on its composition and temp, the spectrum consists of bright emission lines against a black background
53
New cards
absorption line spectrum
cloud of gas lies between us and a lightbulb, still see most of the continuous spectrum of the light bulb, but the cloud absorbs light of specific wavelengths, so the spectrum shows dark absorption lines over the background rainbow
54
New cards
two laws of thermal radiation
1. each square metre of a hotters object surface emits more light at all wavelengths
2. hotter objects emit photons with a higher average energy
55
New cards
doppler effect
if an object is moving toward us the light waves bunch up and its entire spectrum is shifted shorter wavelengths
56
New cards
sun’s size
diameter is 100 times Earth’s diameter
57
New cards
sun’s distance
8 light minutes from Earth
58
New cards
Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin
showed that the sun was made mostly of hydrogen, a little helium, and tiny amounts of other elements
59
New cards
colour and wavelength
the wavelength of light determines its colour and energy
60
New cards
short wavelengths
bluer (and more energetic)
61
New cards
red light
low energy (700 nm)
62
New cards
blue light
high energy (400 nm)
63
New cards
the sun appears to have
a continuous spectrum: it has some of every colour of light
64
New cards
opaque objects
emit a special kind of continuous spectrum
65
New cards
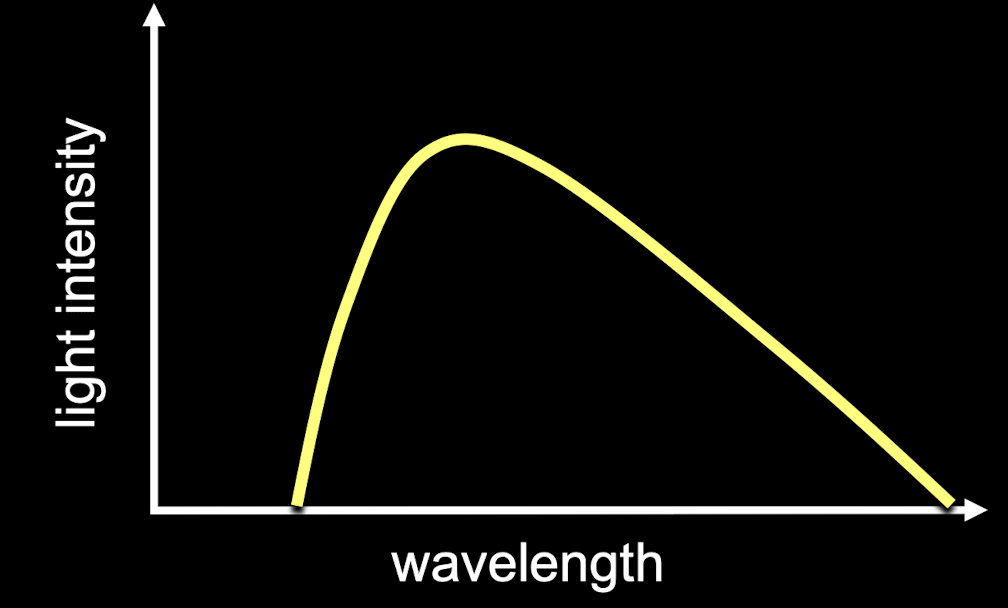
blackbody spectrum
the amount of light given off by a blackbody and the wavelength where it emits the most light set by the temp of the blackbody
66
New cards
as you heat an opaque object
it emits more light
67
New cards
as you heat a blackbody
the wavelength at which it emits the most light shifts to shorter wavelengths
68
New cards
spectral lines
tell us what the sun and other stars are made of
69
New cards
electrons can be forced to jump to a higher-energy orbital by
absorbing light
70
New cards
different chemical elements have
different sets of orbitals
71
New cards
electrons can spontaneously drop to a lower-energy orbital by
emitting light
72
New cards
orbitals do not have colours but
transitions between orbitals do
73
New cards
stars are
blackbodies or “thermal emitters”
74
New cards
sun is not
on fire, it is mainly made of hydrogen
75
New cards
plasma
a gas that is so hot, the electrons break free from the atoms
76
New cards
hydrostatic equilibrium
the sun is in this, the pressure pushing outwards and the gravity pulling inwards is balanced
77
New cards
sun’s surface temperature
5800 K
78
New cards
sun's core temperature
15 million K
79
New cards
E = mc^2
the reaction between energy and mass
80
New cards
nuclear reactions can
convert matter to energy (or the reverse)
81
New cards
in the centre of the sun,
hydrogen is being converted into helium via nuclear fusion
82
New cards
nuclear fusion
providing enough outward pressure necessary to support stars against collapse
83
New cards
neutrinos
only interact with other matter via the weak nuclear force and gravity, can pass through objects that are very large and dense
84
New cards
neutrinos dont
respond to the electromagnetic force, so they dont interact with most matter