Module 8 - Leading Change
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is organizational change?
Periods of transition that require employee adaptation, resulting from a misalignment between organizations' goals and current results.
Some organizations have shared social knowledge that can transcend change
What is change readiness?
Employees' attitudes about:
The extent to which organizational changes are needed
Their organizations' abilities to successfully undertake changes.
What are typical sources of organizational change?
Changes in leadership
mergers, and acquisitions.
How does restructuring affect Job Performance

Restructuring --> WEAK NEGATIVE --> Job Performance
Task Performance tends to be lower, not much is known about the impact on Citizenship Behavior or Counterproductive Behavior
How does restructuring affect Organizational Commitment

Restructuring --> MODERATE NEGATIVE --> Organizational Commitment
Affective Commitment tends to be lower. Not much is known about the impact on Continuance Commitment or Normative Commitment
What is a negative aspect of organizational change?
Organizational change creates uncertainty, which is stressful and challenges shared social knowledge and expectations.
What is trust in an organizational context?
The willingness to be vulnerable to an authority based on positive expectations about the authority's actions and intentions.
What are the three types of trust?
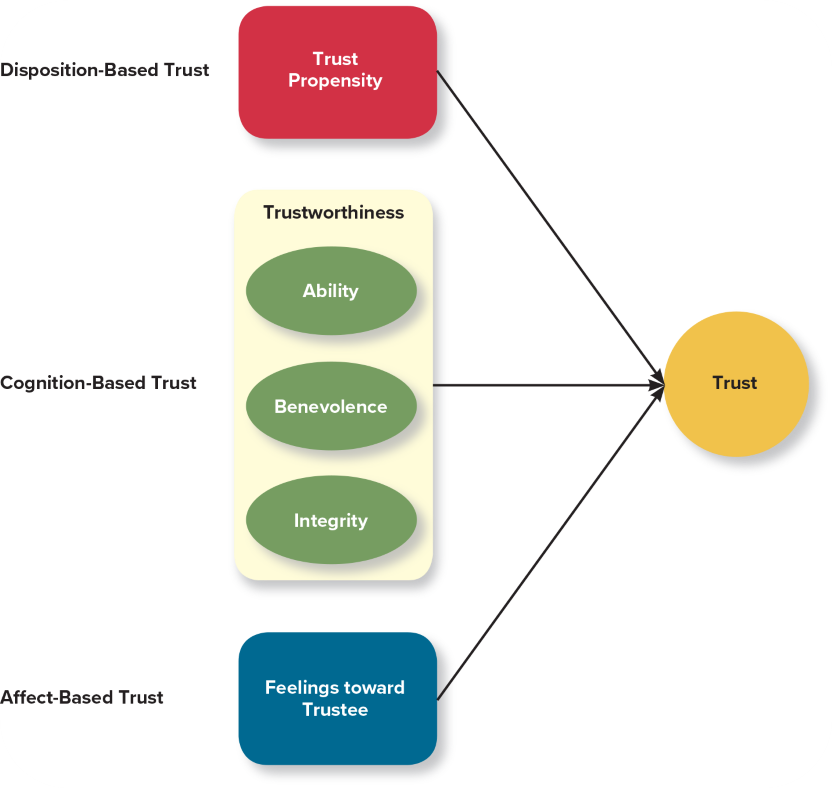
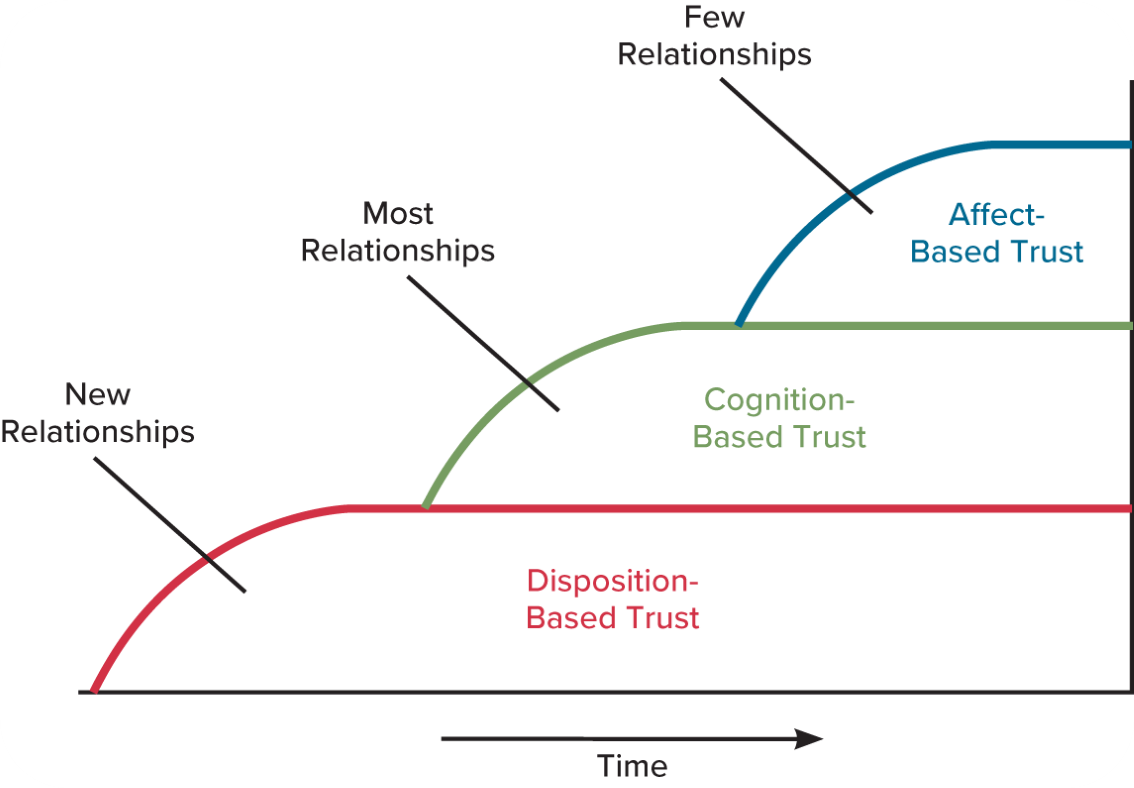
Disposition-based - rooted in personality; new relationships. early in time when we first meet somebody
Cognition-based - rooted in rational assessment; most relationships are in the phase. This is when we gather information
Affect-based - rooted in feelings. few relationships. takes more time. Close friends and family members
What is justice in an organizational context?
The perceived fairness of an authority's decision-making.
What are the four types of justice?
Distributive justice - fairness of decision-making outcomes;
if you get a promotion, you dont really ask questions because you like the outcome
Procedural justice - fairness of decision-making processes;
if you miss a promotion to somebody who deserved it, you might ask some questions about the process and why you got passed. if you miss a promotion to somebody who did not deserve it, you will question the fairness of the process
Interpersonal justice - fairness of interpersonal treatment;
The treatment we receive. How much information is shared, “Quantity”
Informational justice - fairness of communications.
How we receive the information, “Quality”
How are the reactions to authority based off high or low procedural justice?
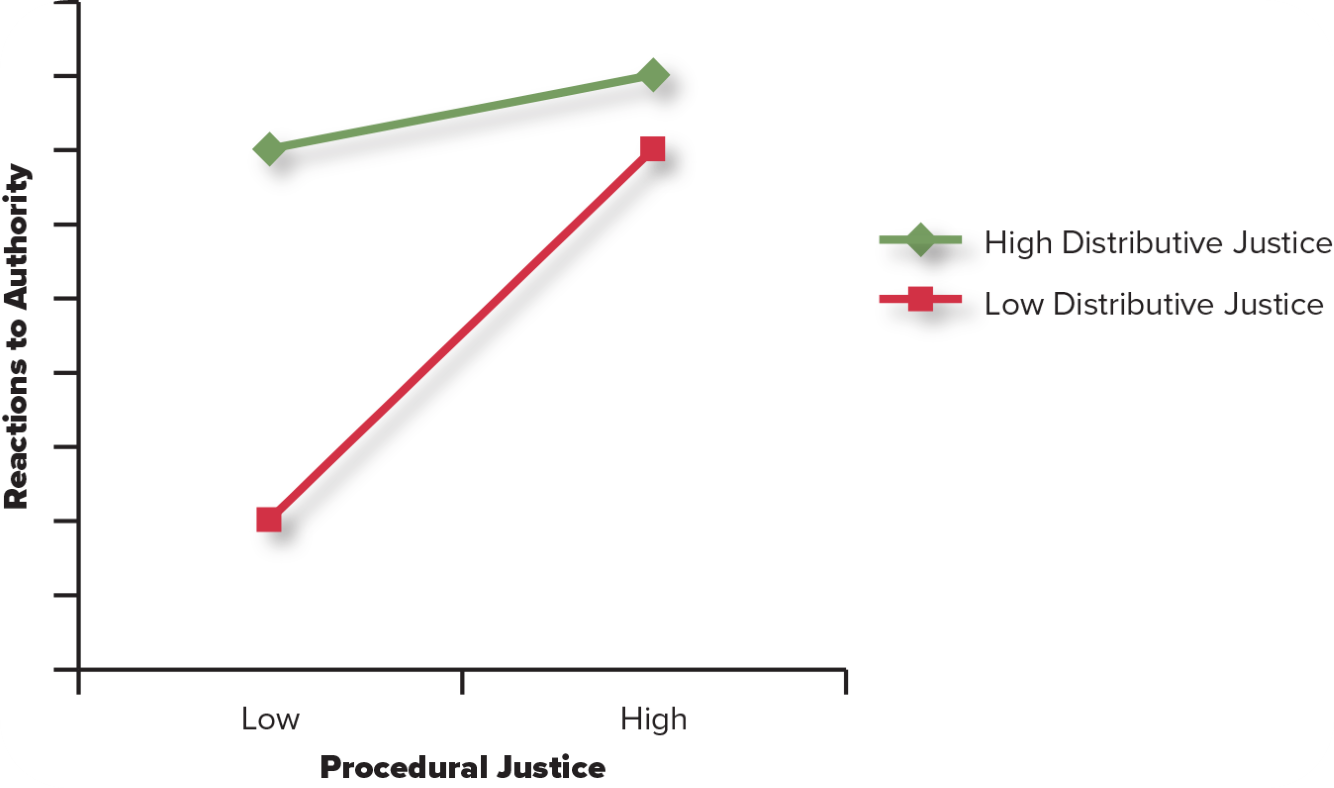
When there is High Distributive Justice (we like the outcome). We are not as focused on the Procedural Justice. When there is Low Distributive Justice (we dont like the outcome) we focus on Procedural Justice.
When Distributive Justice is High and Procedural Justice is High, we have the same high reaction to authority as when Distributive Justice is Low and Procedural Justice is High.
This means if we are passed on a promotion, but the leader speaks to us with respect and explains the decision we accept and respect the decision.
When Distributive Justice is Low and Procedural Justice is Low, we have an extreme negative reaction to authority
This means if we are passed on a promotion, and the leader speaks to us with disrespect, we get very upset.
What is Organizational Politics?
Individual actions directed toward the goal of furthering a person's own self-interests.
What is Political Skill?
The ability to understand others and influence them to further personal and/or organizational objectives. This is like a personality trait, but
This is a trainable skill.
What are the components of political skill?
Networking ability; Can you be comfortable in a room of people and build meaningful relationships?
Social astuteness; Can you pickup on nonverbal cues?
Interpersonal influence; Can you help guide other people’s attitudes and behaviors.
Apparent sincerity. Do you appear to be genuine?
What is Political Will?
The motivation to engage in strategic, goal-directed behavior that advances employees' personal and/or organizational objectives.
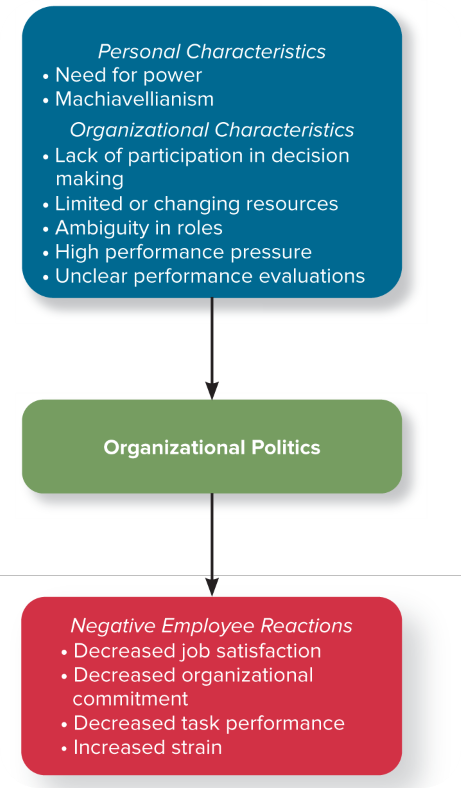
How can Personal Characteristics and Organizational Characteristics negatively affect Employee Reactions in regards to Organizational Politics?
What is Organizational Culture?
The shared social knowledge within an organization regarding the rules, norms, and values that shape its employees' attitudes and behaviors.
This can transcend organizational change if strong enough
What are the three components of organizational culture?
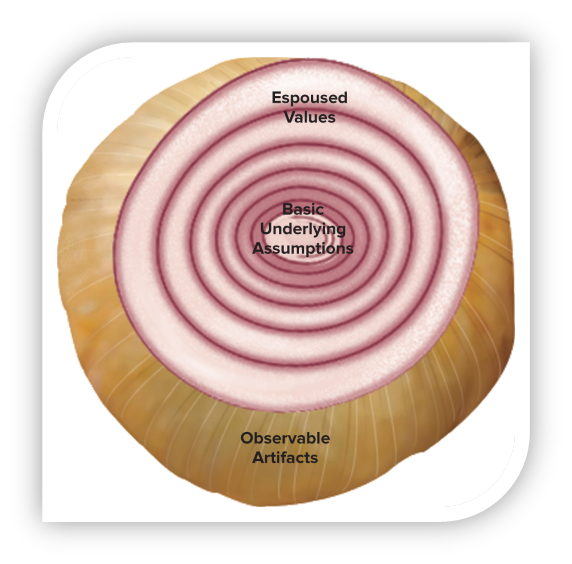
Observable artifacts; - the outer layer of an organization
Espoused values; - the inner layer of an organization
Basic underlying assumptions. - the core of an organization
What are Observable Artifacts in organizational culture?
Aspects of an organization's culture that employees and outsiders can easily see or talk about. - like a mascot, landmark or logo
What are Espoused Values?
The beliefs, philosophies, and norms that an organization explicitly states.
What are Basic Underlying Assumptions?
Employees' ingrained beliefs and philosophies.
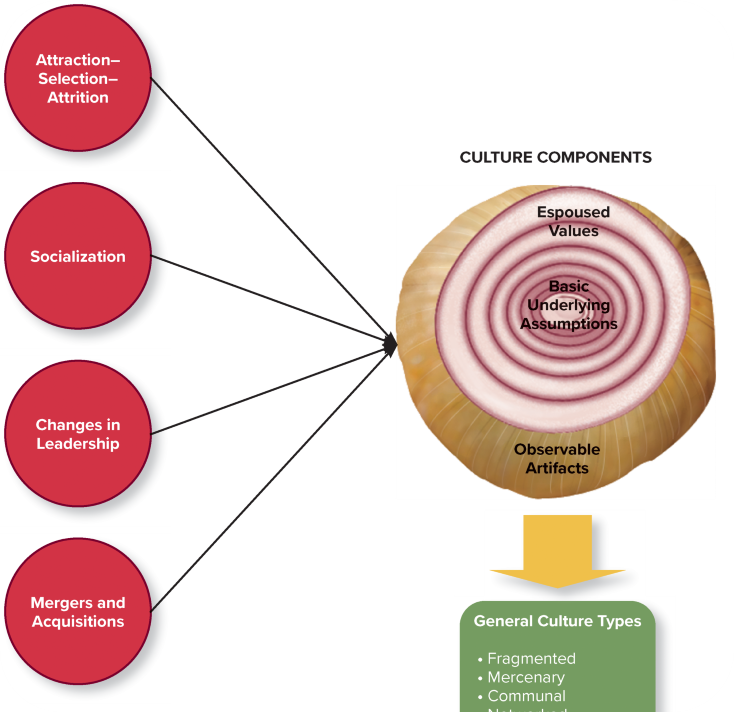
What goes into the 3 Culture Components, and what are the General Culture Types?
What goes in to Organizational Socialization?
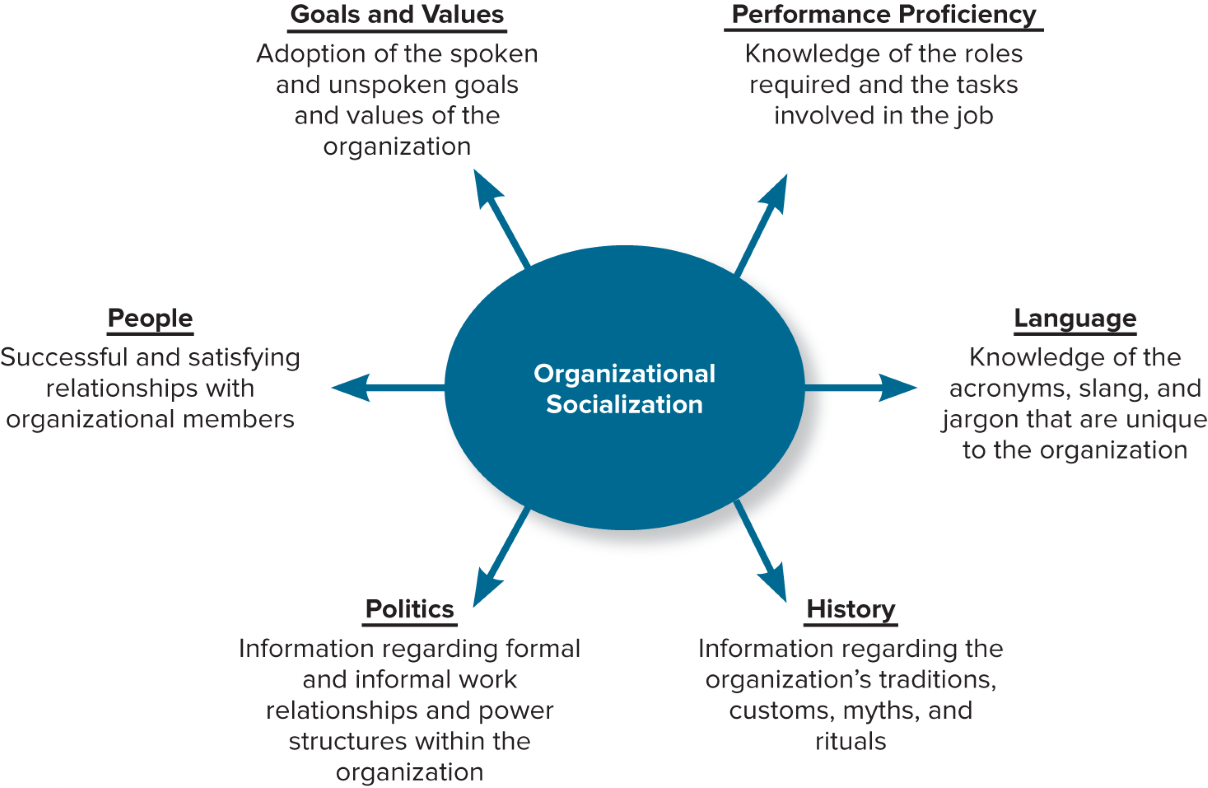
This is how we learn about the organizations rules and norms. What it is like to work for an organization.
Book Club The Infinite Game - Simon Sinek, What is the difference between finite and infinite thinking?
Finite Thinking involves playing to win a game with fixed rules and a clear endpoint
Infinite Thinking involves playing in a game with flexible rules and no defined endpoint.
Some leaders us finite thinking, some use infinite. With an infinite mindset, the goal is to just keep playing, not to “beat somebody”. Just plan for what’s next and how can we grow.
Microsoft vs Apple - Microsoft was “Finite”, they just wanted to beat Apple, and Apple just focused on what to do next, “Infinite”
How can an infinite mindset be fostered?
Advance a just cause;
what do you stand for?
Build trusting teams;
so people can share information and rally to your side
Study your worthy rivals;
find a comparison other to build up your weaknesses
Prepare for existential flexibility;
don’t get too stuck in your ways
Demonstrate the courage to lead.
don’t be afraid to take risks. advocate for yourself and your team.
What is Ethical Fading?
A process that occurs over time when short-term finite achievements are valued more than ethical decision-making.
When you slowly push your ethical limits little-by-little your benchmark ethics get worse and worse. focusing on the bottom line at all costs
What is a key takeaway for leaders regarding goals?
Leaders have to balance short-term (finite) and long-term (infinite) goals effectively.
What is the difference between a 'why' and a just cause?
A 'why' identifies our values, whereas a just cause is a vision for our future.