AP pre-calculus review
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
an=ak+d(n-k) or a n=a0+dn
Arithmetic sequences
gn=g0(r)^n or gn=gk(r)^(n-k)
Geometric sequence
r=an/an-1
Common ratio
a(b)^(x-1)+k
Exponential
logb(MN)=logbM+logbN
Product property
Logb(M/N)=logbM-logbN
Quotient Property
LogbNp=p(logbN)
Power Property
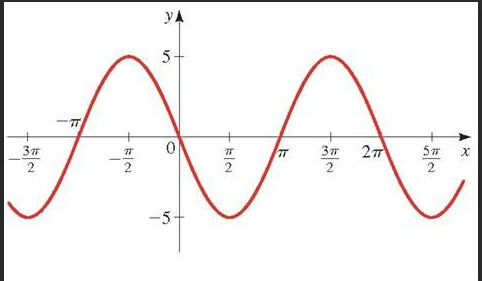
y=sinx
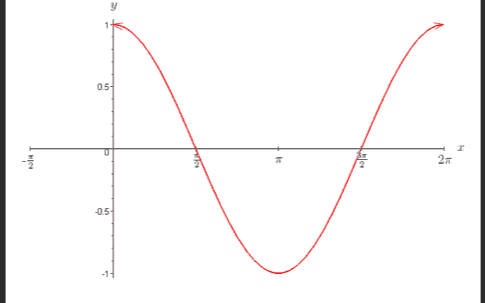
y=cosx
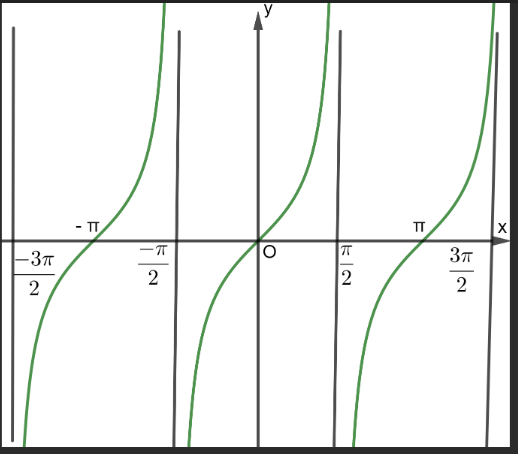
y=tanx
y=cscx
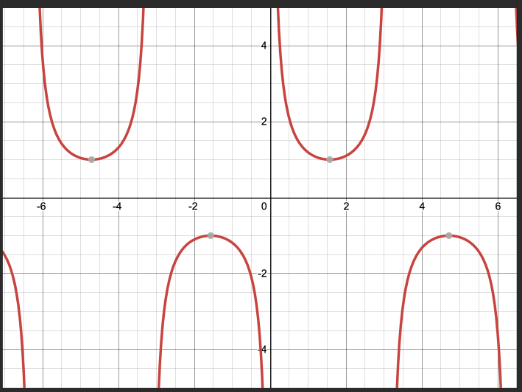
y=secx
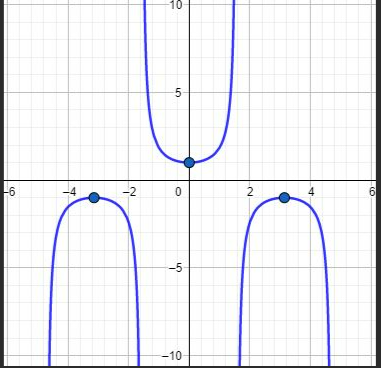
y=cotx
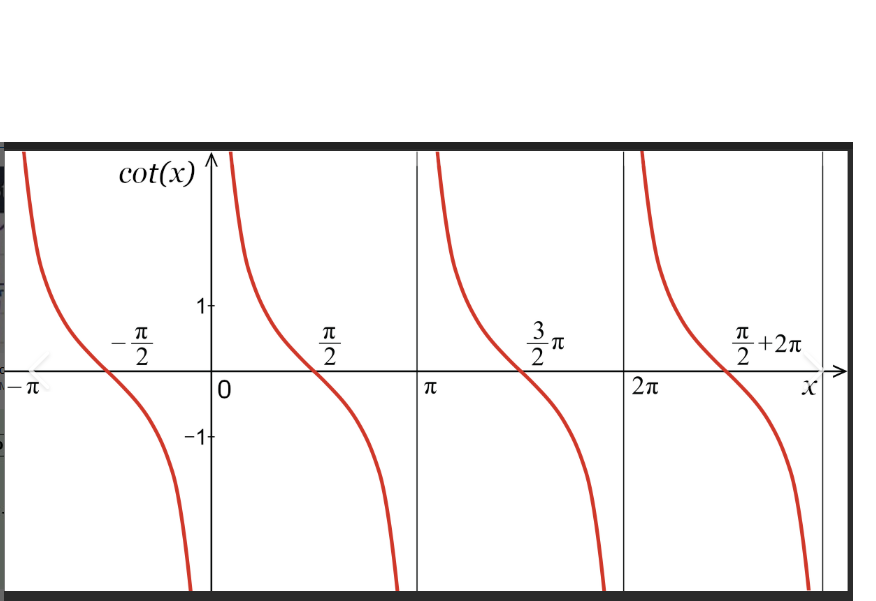
sin2x+cos2x=1
1+tan2x=sec2x
cot2x+1=csc2x
Pythagorean Theorom
2sinxcosx
sin(2x)=
cos^2x-sin^2x
2cos^2x-1
1-2sin^2x
cos(2x)=
sinAcosB+cosAsinB
sin(A+B)=
cosAcosB-sinAsinB
cos(A+B)=
sinAcosB-cosAsinB
sin(A-B)=
cosAcosB+sinAsinB
cos(A-B)=
The amplitude, A=(max-min)/2
y=Asin[B(x+c)]+D, y=Acos[B(x+c)]+D
A is…
Number cycles in 2π
y=Asin[B(x+c)]+D, y=Acos[B(x+c)]+D
B is…
(2π)/B
Period
B/(2π)
Frequency
Phase shift
y=Asin[B(x+c)]+D, y=Acos[B(x+c)]+D
C is…
Midline (y=D)
D=(max+min)/2
y=Asin[B(x+c)]+D, y=Acos[B(x+c)]+D
D is…
The location for points of inflection on tangent curve
y=Atan[B(x+C)]+D
D is…
Phase shift
y=Atan[B(x+C)]+D
C is…
Period=π/B
y=Atan[B(x+C)]+D
B is…
x=(π/2)+kπ
y=Atan[B(x+C)]+D
Vertical asymptotes
x=rcosθ
X value in a polar coordinate is…
y=rsinθ
Y value in a polar coordinate is…
Distance from the origin is increasing
When r=f(θ) is increasing, and r is positive…
Distance from the origin is decreasing
When r=f(θ) is decreasing, and r is positive
Distance from the origin is decreasing
When r=f(θ) is increasing and r is negative
the distant from the origin is increasing.
When r=f(θ) is decreasing and r is negative
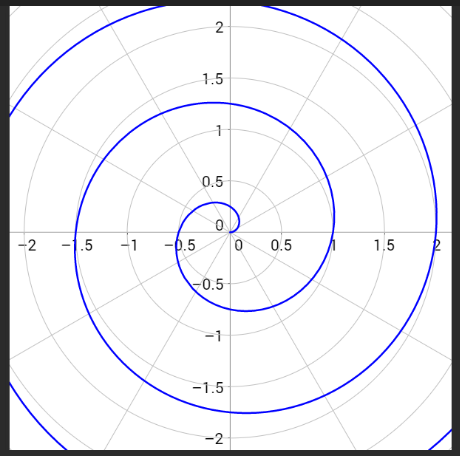
r(θ)=θ
r=acosθ
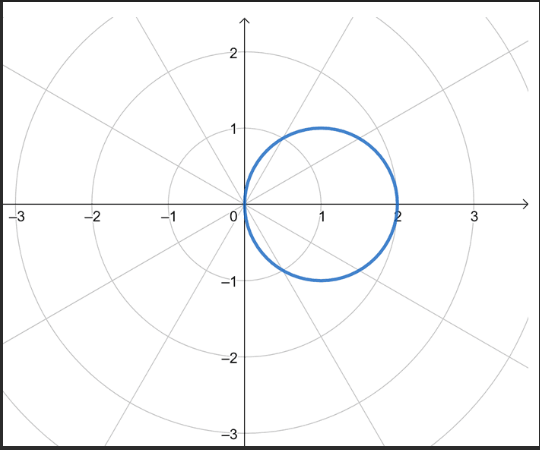
r=asinθ
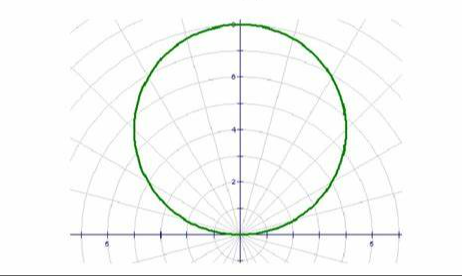
r= a+-bcosθ (a/b =1) Cardioids
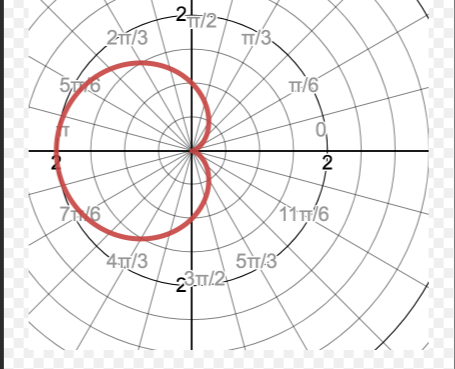
r= a+-bsinθ (a/b =1) Cardioids
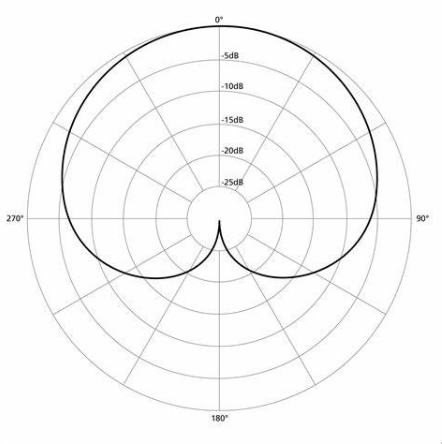
r= a+-bcosθ (a/b >2) Convex Limacon
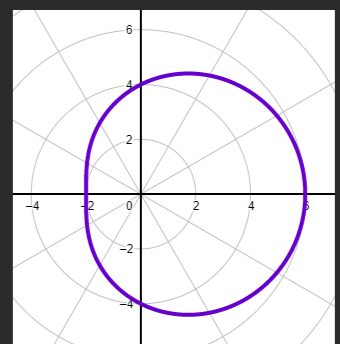
r= a+-bsinθ (a/b >2) Convex Limacon
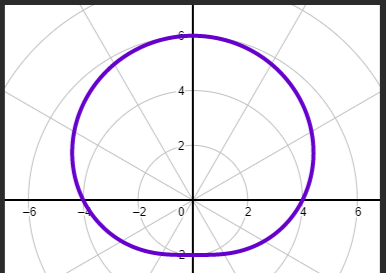
r= a+-bcosθ (a/b <1) Limacon
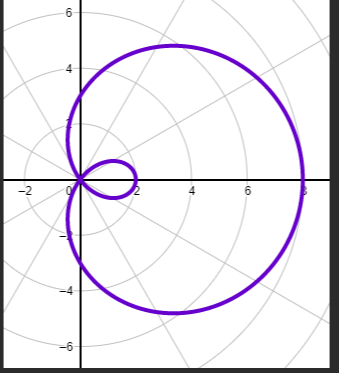
r= a+-bsinθ (a/b <1) Limacon
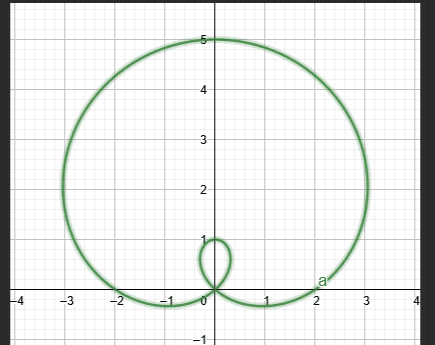
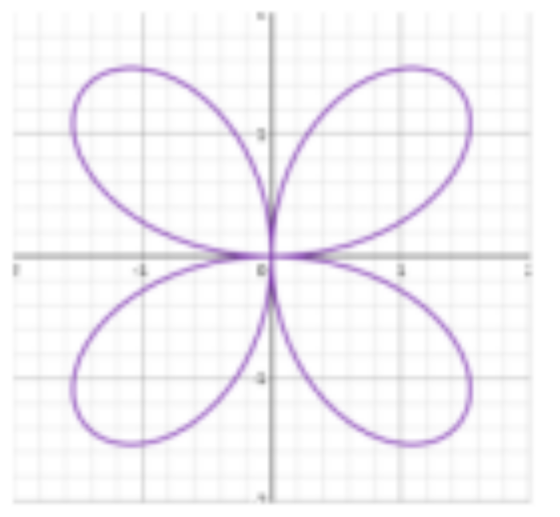
r= acos(nθ)
n=3,odd
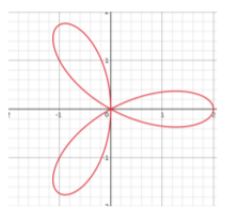
r= asin(nθ)
n=4,even