D.4: Induction (Formative)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
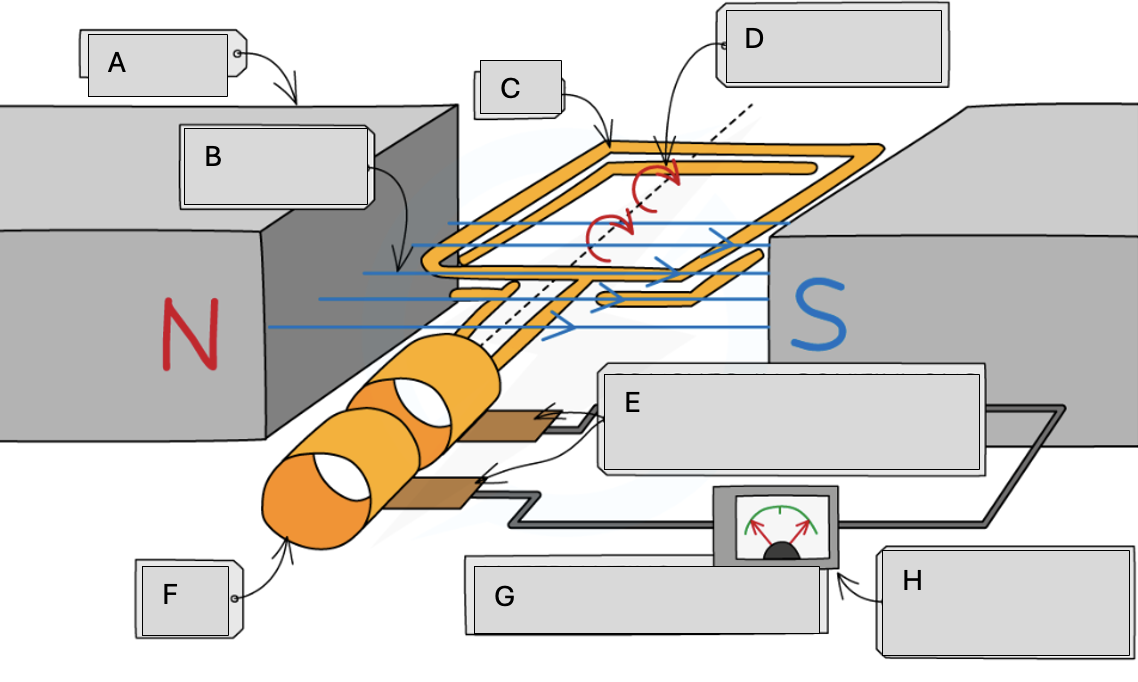
A
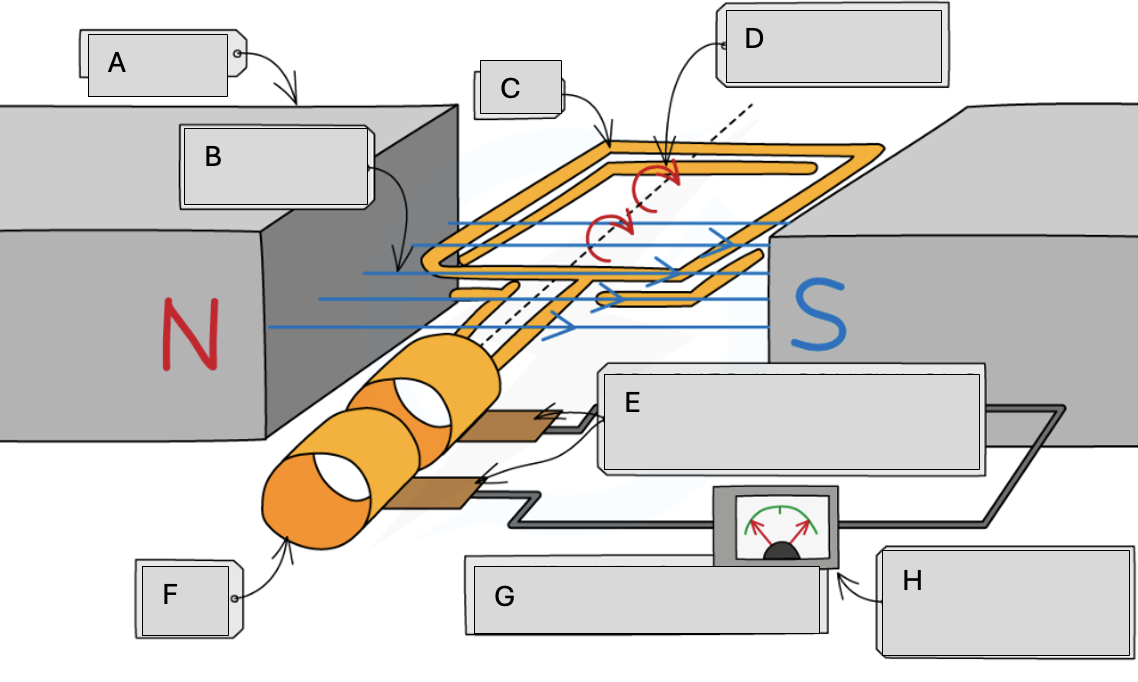
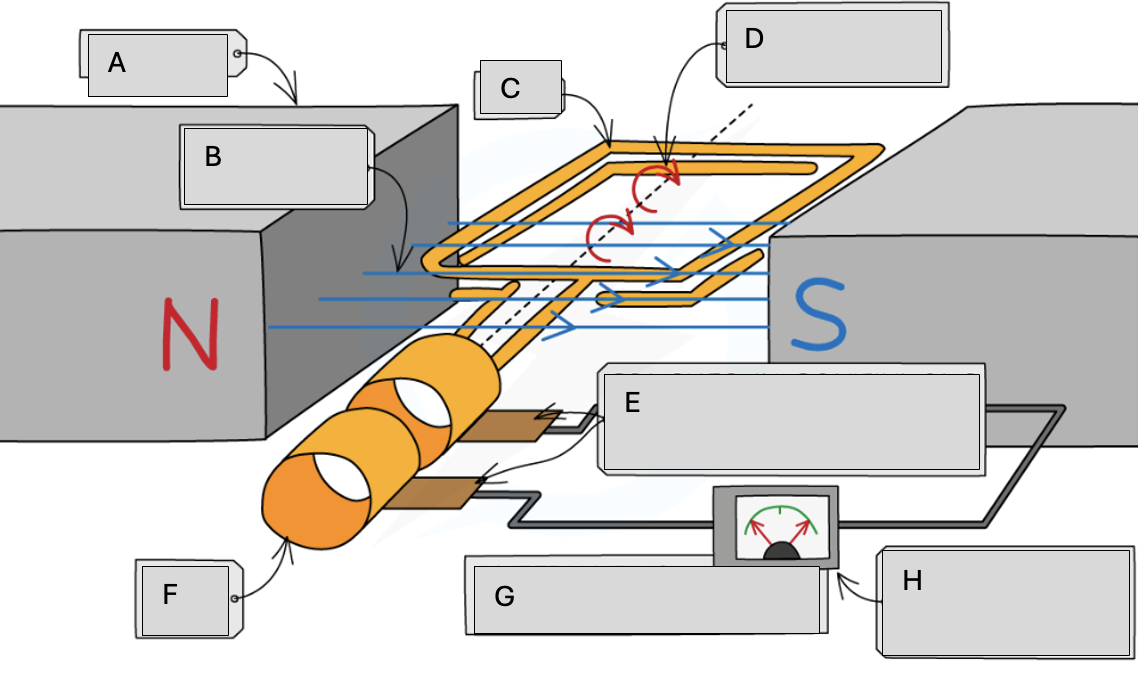
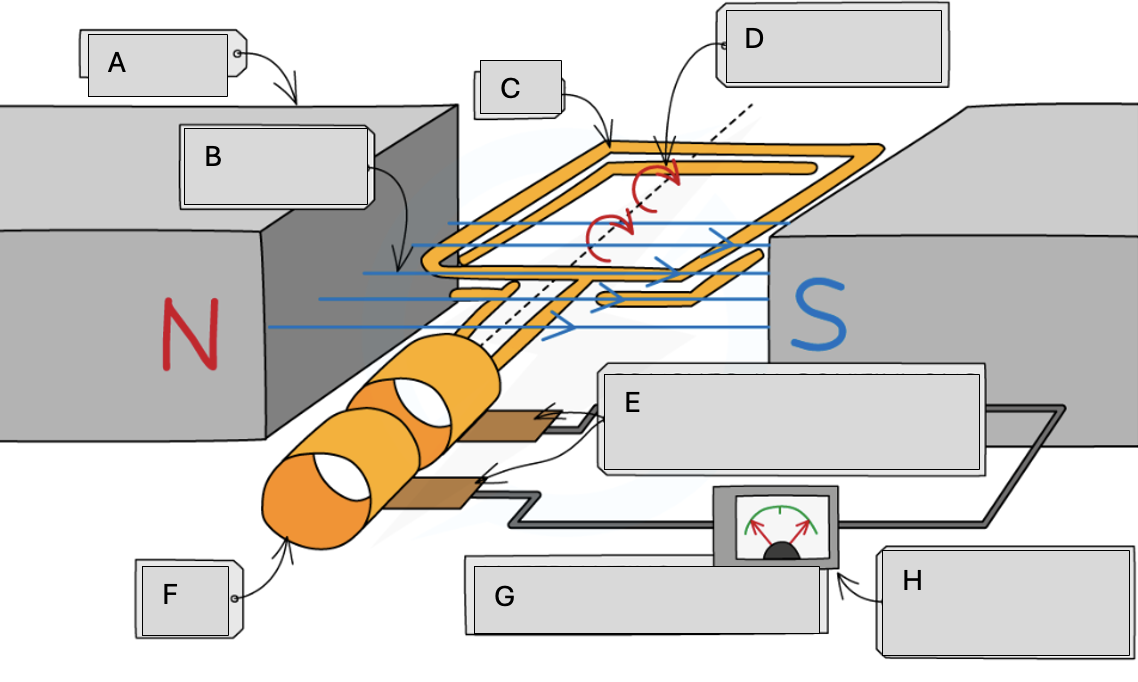
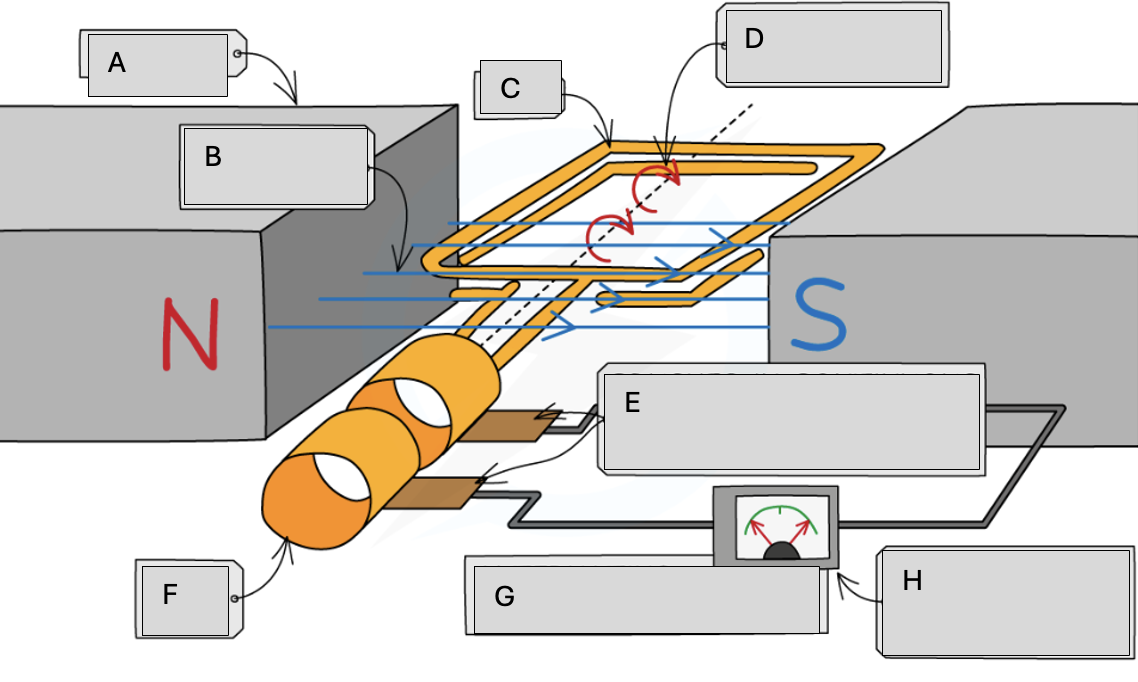
Magnets
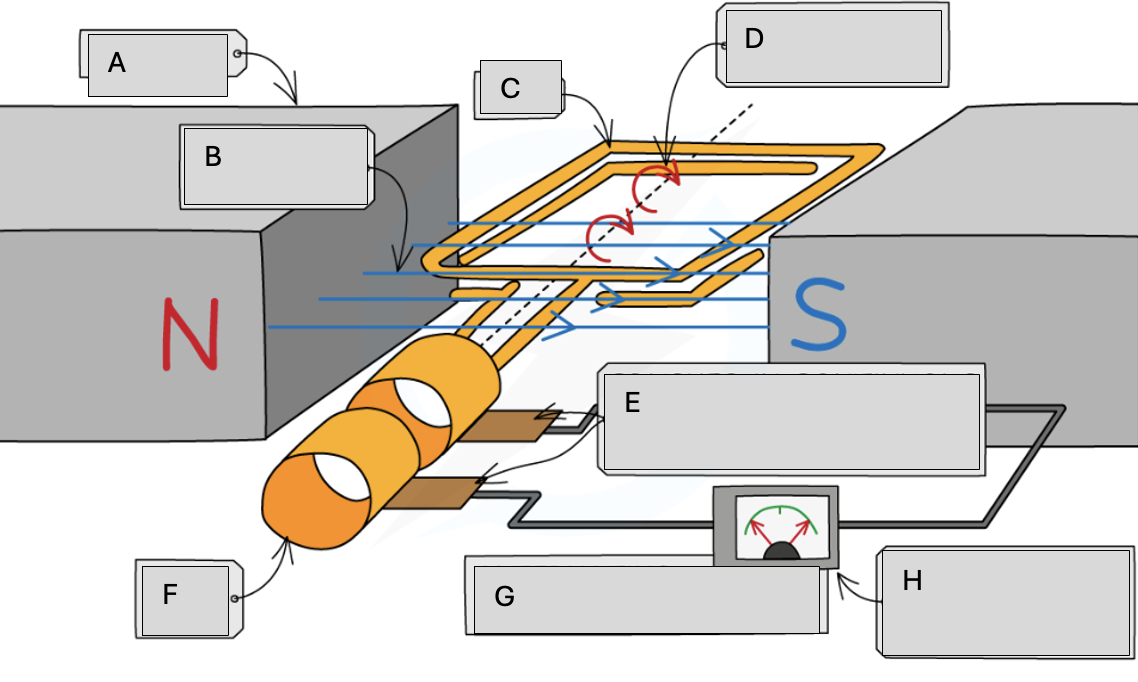
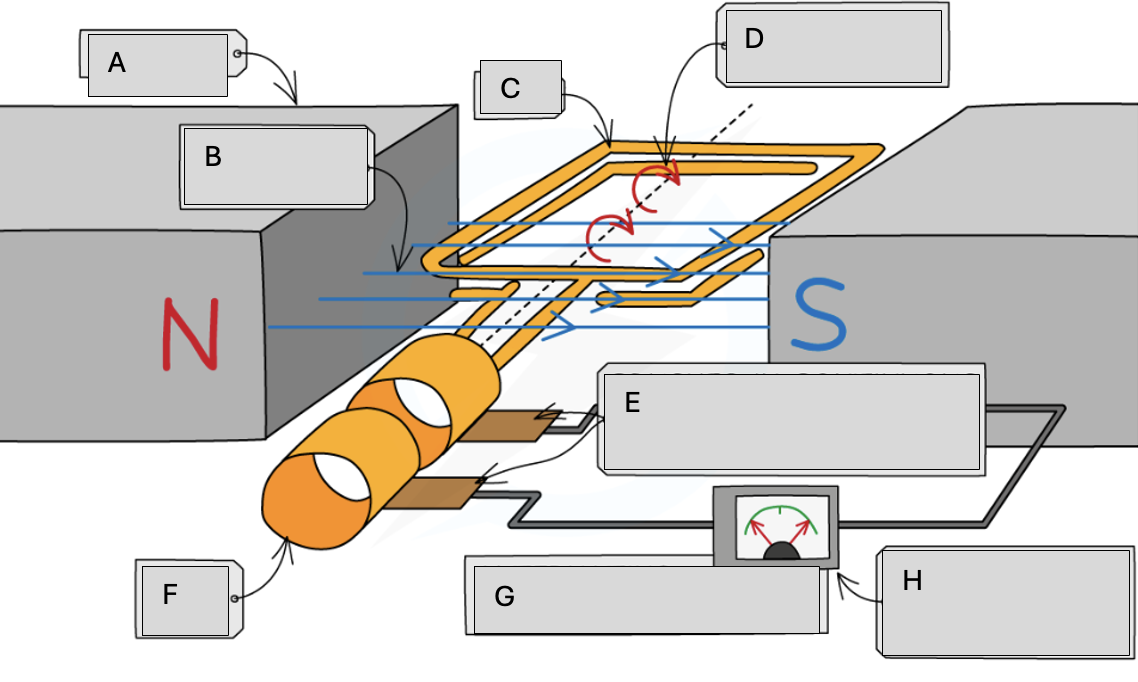
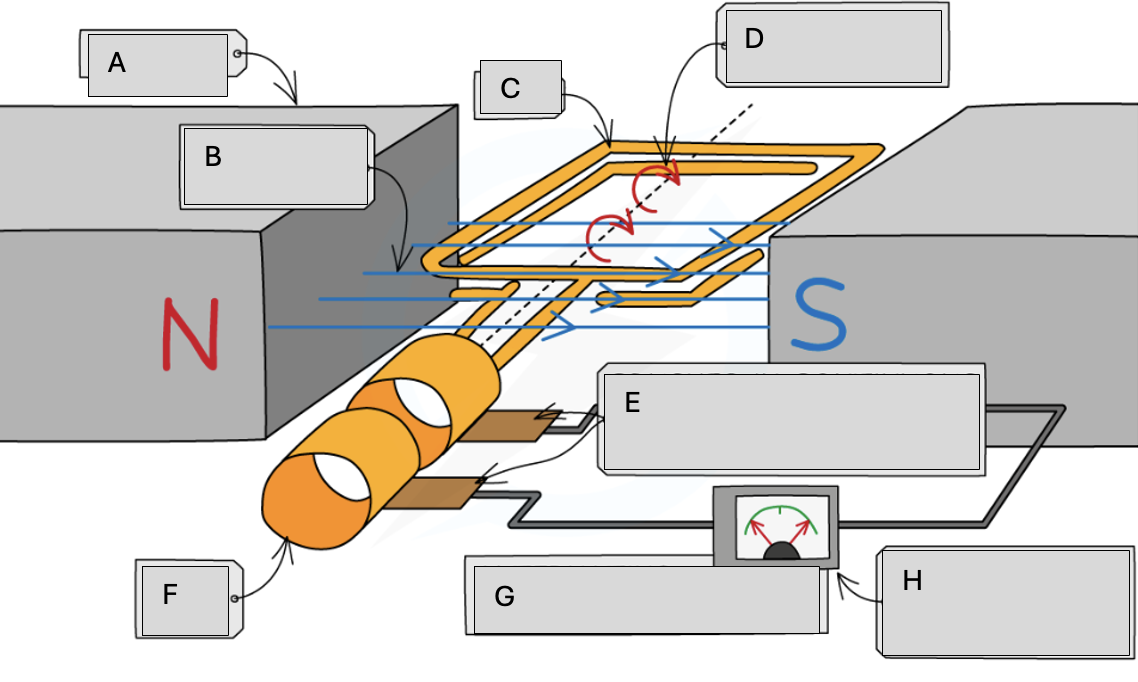
B
Magnetic field lines
C
Coil

D
Steady rate of rotation

E
Brushes in contact with the commutator rings

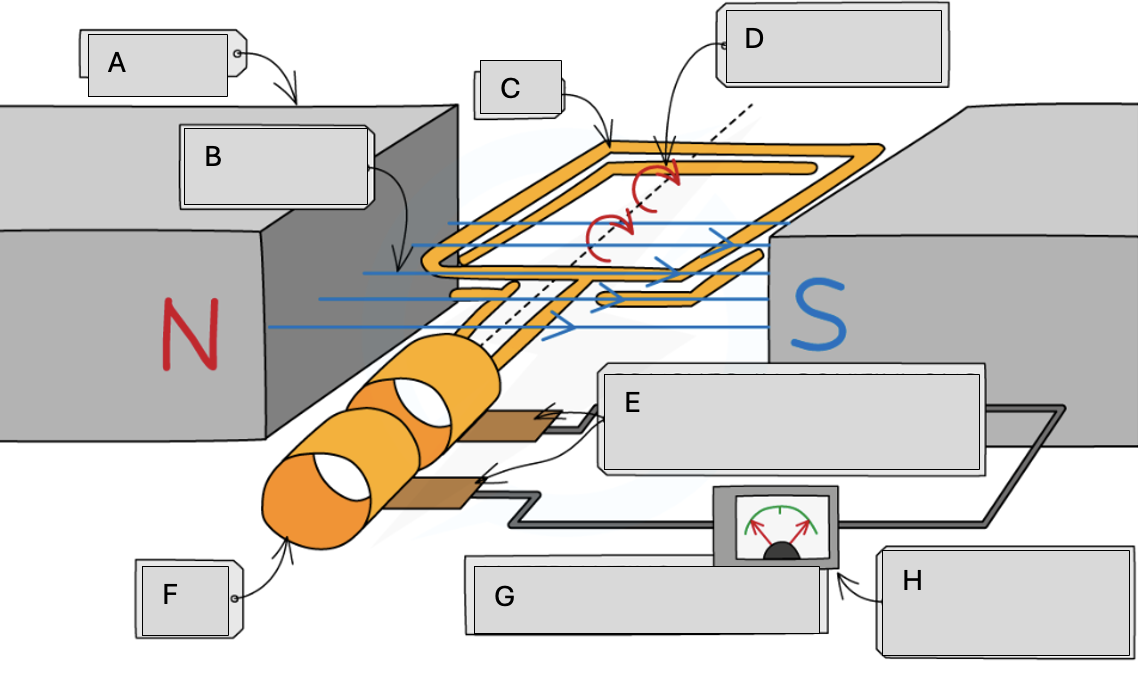
F
Slip rings

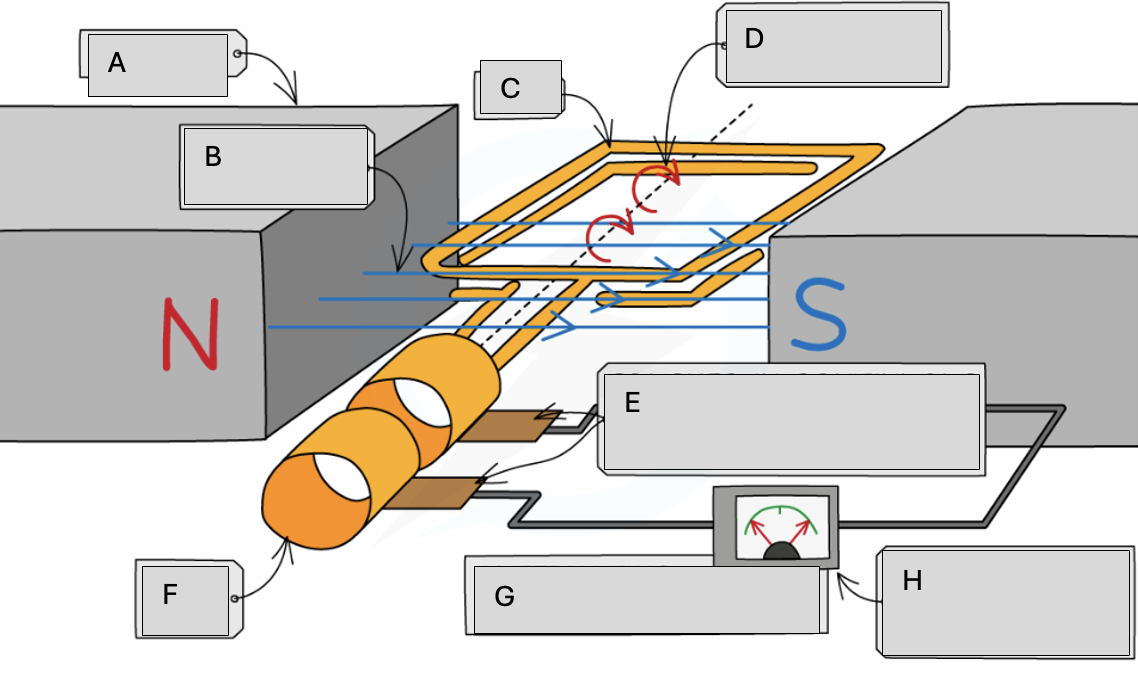
G
Alternating potential difference

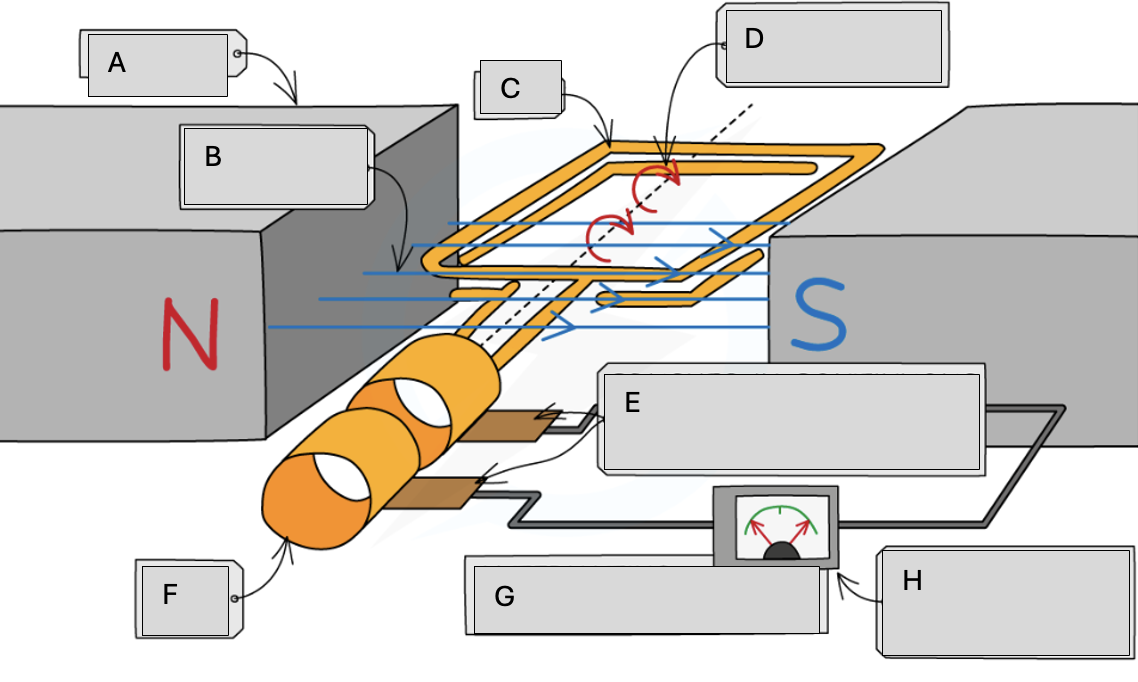
H
Meter pointer swings from side to side

Explain the sinusoidal shape of magnetic flux and emf against time graphs for a coil rotating in a constant magnetic field
bgjnofakmpwdel,fkijon
Identify and explain the changes in induced emf when the frequency of rotation changes in a constant magnetic field.
If the speed of rotation is increased, the graph of emf against time will change in two ways: ____ and _____ because_____.
Time between the peaks will be shorter and the peaks will be higher because the coil moves faster, then the rate of change of flux will be higher and hence the emf will be greater.
Lenz’s Law
An induced current (and emf) will always act to oppose the change that caused it.
Methods to induce magnetic field flux
Change magnetic field strength/magnetic flux density, change the area, change the relative angle.
Magnetic flux linkage
The product of magnetic flux and the number of turns in the coil (MFL=Nφ)
Faraday’s Law
The magnitude of the induced emf is equal to the rate of change of flux [ε=-N(Δφ/Δt)].
Emf
Mechanical energy transferred to electrical energy per unit charge in a circuit, same as potential difference
Induced emf
The amount ofwork done per unit charge in moving the charges to the ends of the conductor
Electromagnetic induction
Occurs due to relative motion b/w a conductor and a magnetic field, inducing emf.
Magnetic flux density
describes how many field lines pass perpendicularly per unit area.
Magnetic flux
a quantity which signifies how much of a magnetic field passes perpendicularly through an area. the force acting per unit current per unit length on a wire placed at right angles to the magnetic field