Unit 1 Knowledge (Biology 1-2 H)
- be able to define:
---Monomer: a molecule that can be bonded w. other molecules to form polymer
---Polymer: a substance that is a long chain of bonded monomers
---mono, di, and poly saccharide: monosaccharide=1 saccharide, disaccharide=2 saccharide, polysaccharide=many/more then 2 saccharide
---substrate: the substance that enzymes alter.
---Active Site: The site of the enzyme that catches/temporarily bonds with the substrate in order to speed up the chemical reaction.
---Denature: when an enzyme is altered due to high/low temperature, and low/high pH levels, causing it to have difficulty bonding with substrates. In other words it becomes deformed.
- Know the function of:
---lipids: they store energy, control hormones, and cushion vital organs.
---nucleic acids: they store and express genetic information.
---carbohydrates: used to provide and store energy, and is part of the cell membrane.
---proteins: They store energy, repair and build tissues, helps structure, function, and regulation of the body’s organs, and it copies and stores DNA.
- Know the monomers of:
---nucleic acid: nucleotide
---carbohydrate: monosaccharide
---protein: amino acids
Identify the shape of:
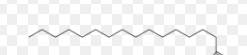
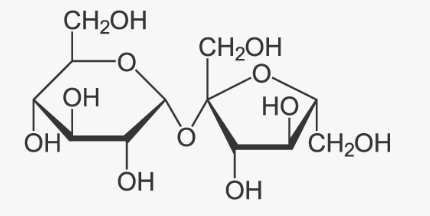
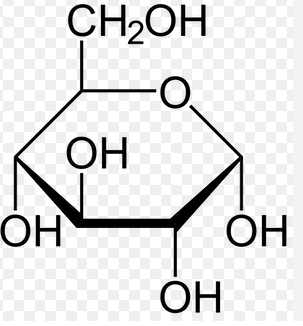
Know which foods contain:
---Lipid: meat, poultry, fish, seeds, nuts, plant oils
---Nucleic Acid: Every living thing has these.
---Carbohydrate: grains, vegetables, fruit, and dairy.
---Protein: poultry, fish, seafood, and dairy.
- Know the function of an enzyme:
---Enzyme: An enzyme’s function is to speed up chemical reaction in substrate.
- Know how the function of an enzyme is effected by:
---temperature: Raising the temperature generally speeds up the chemical reaction, and lower temperature generally slows down the reaction. Above the specific temperature range, the enzymes begin to denature, resulting in less collisions with substrate.
---pH: When the charges of amino acids change, the enzyme changes shape due to it, though this shape may not be effective.
Criteria of living things:
- needs and has the ability to take in some form of nutrients
- ability to take in water
- is capable of growing/developing
- ability to exchange gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc)
- capable of reproducing
- made of cells
- maintain homeostasis
- use energy
- adaptability
- made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphate
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
Cells
What is a cell?
Cells are the basic building blocks of many living things. There are many different types, so none of them are the same. They’ve adapted over many years in order to fulfill different roles and environment needs
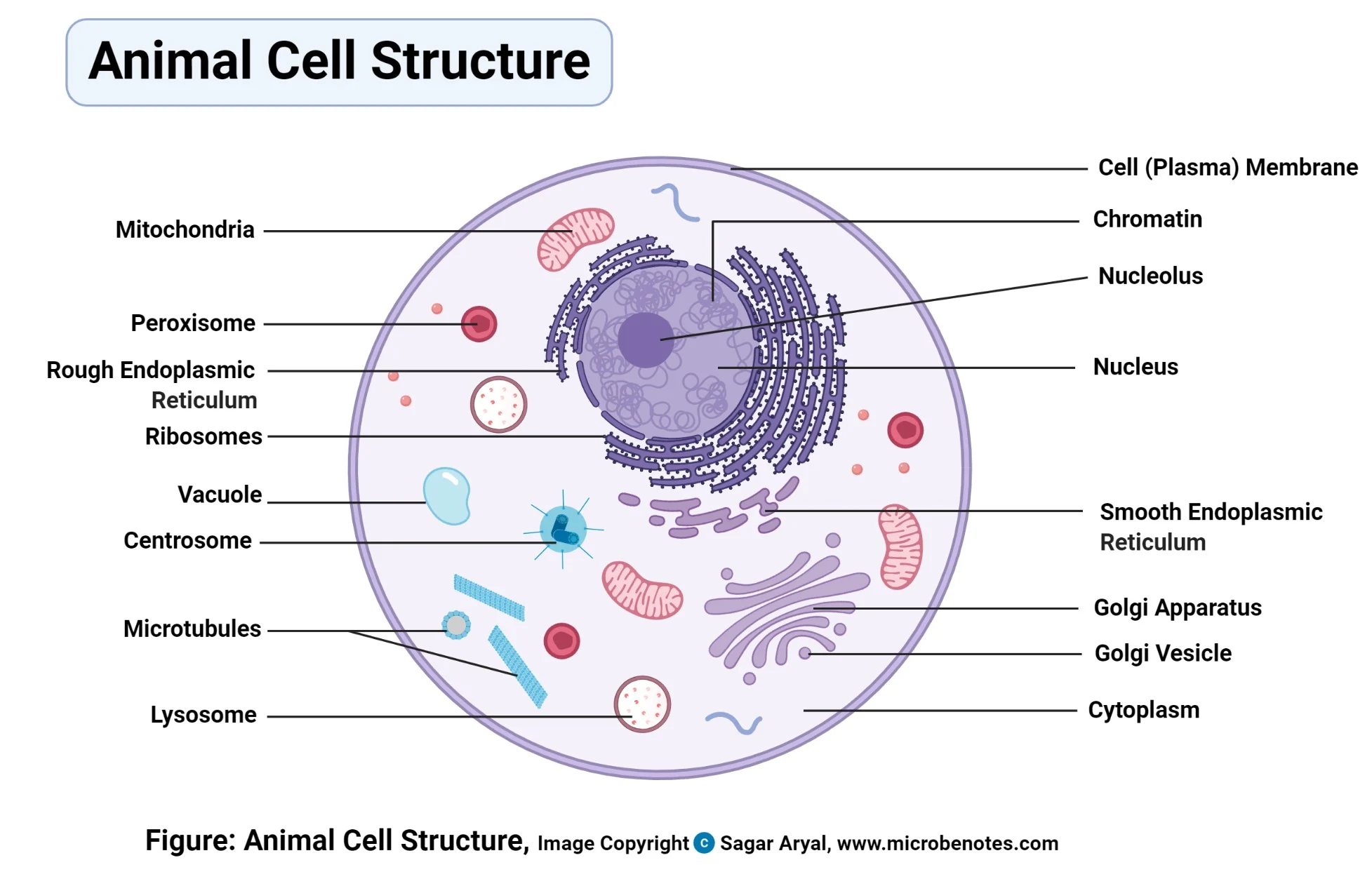
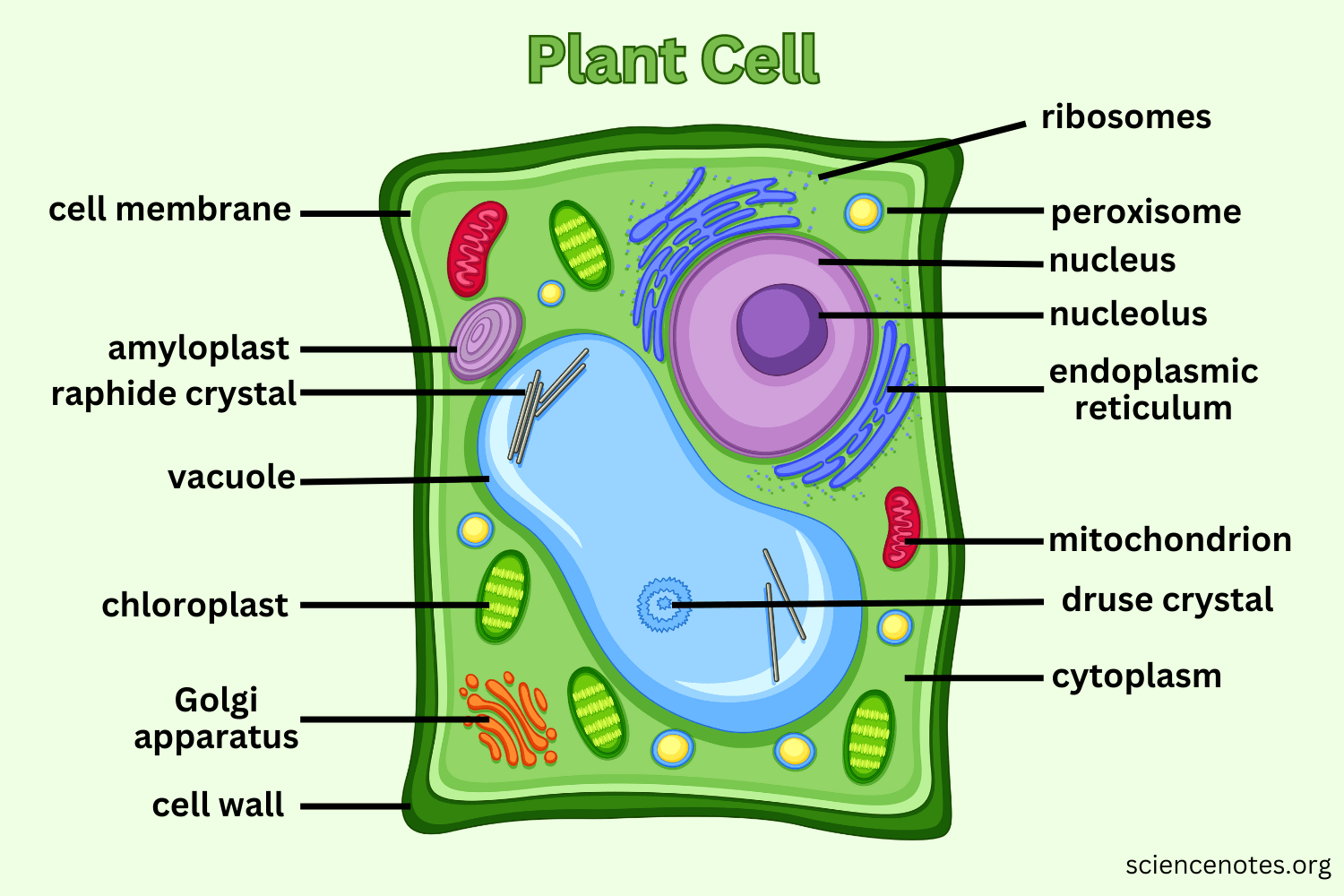
| Celular Structure | Placement and Description in your model | justification |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | A recipe card drawn in the center of the cell. | The nucleus contains DNA, which stores directions or ‘recipes’ for making proteins. The nucleus can be thought of as the central command center at the of the cell. |
| Cytoskeleton | This could be seen as an organizer. | They organize cell parts and provide structure to the cell, similar to organizers. |
| Cytoplasm | This could be seen as a water balloon. | The inner fluid of this cell contains water, ions, and organic molecules, similar to water balloons. |
| Flagellum | ||
| Plasma Membrane | This could be seen as security. | Plasma membrane’s purpose is to control the movements of substances in and out of the cell, which is what security does. |
| Cell Wall | ||
| Mitochondria | ||
| Chloroplast | This could be thought of as a solar panel. | Chloroplast turns solar energy into chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates, which is of similar use to a solar panel. |
| Lysosome | This could be seen as stomach acid. | This breaks down proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Stomach acid breaks down food. |
| Golgi Body/Apparatus | This could be seen as a packer from amazon or another company of the sort. | The Golgo Apparatus’s purpose is to sort, modify, and package proteins and lipids to be exported from the cell, which is exactly the job of packers in real life (just with objects, not proteins and lipids). |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | This could be thought of as a builder. | Endoplasmic reticulum synthesizes lipids and protein, which is essential for the membrane. A builder builds things. |
| Vacuole | ||
| Vesicle | This could be seen as one of the subway or transportation systems of the cell | The vesicle’s purpose is to assist in cell transportation, much as what a subway does for humans. Therefore, the vesicle could be seen as one of the subway or transportation systems in the cell. |
| Ribosomes | This could be thought of as a welder. | Because it links amino acids together by messenger RNA, which a chain needs a welder to be linked. |
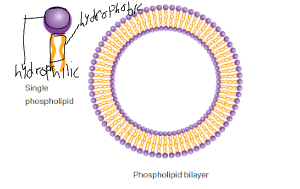
Hydrophobic: repels against water
Hydrophilic: Attracts water
Where would you be likely to find water?
You’d be likely to find water in the hydrophilic part of the phospholipid bilayer.
Why would a phospholipid bilayer self-assemble when phospholipids are surrounded by water?
A phopholipid bilayer would self assemble when surrounded by water due to the ends of the single phospholipids being hydrophobic and the middle of the single phospholipid being hydrophilic.
Cell Membranes: Cell membranes can flex without breaking, much like a bubble. The membrane of the cell can also spontaneously repair any small tears in the lipid bilayers. There can be multiple layers to a singular cell membrane. A tunnel can be created in order to transfer molecules from one cell to another. The cell membranes can effectively divide, allowing for molecules to be transferred to other cell membranes.
Properties of Water
- Made of 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen
- A fundamental need for organisms
- Has a solid, liquid, and gas form
- Is inside the cell memory
- Density of 1
Water Droplet Experiment
We could move around the water droplet and put the toothpick inside the water drop, but it would not pop due to the toothpicks not being hydrophobic. Because the toothpicks were made of wood and not hydrophobic, they would have the ability to absorb the water. When we tried to move the water droplets we were then able to split the water droplet into smaller water droplets. When we coated the toothpicks in dish soap, it popped the water droplets, resulting in a small puddle of water instead of a droplet. After the dish soap was put on the toothpick, we lost the ability to move the water droplets. The dishwasher popped the water droplet because the dish soap may have hydrophobic properties.
Information on Water
Water is an extremely important need for organisms. Up to 90% of the body weight of some organisms comes from water. Cells of living organisms are, overall, mostly water. Water’s ability to dissolve so many substances allows our body to valuable nutrients, minerals, and chemicals in biological processes. Adhesion and cohesion are properties of every water molecule on earth. (Eg: water on the window of a car and not moving despite gravity and the car moving) It will also clump into drops because of these two properties. These two properties happen because water molecules have positive and negative poles, much like a magnet. When the negative pole of another water molecule nears the positive pole of a different molecule, they stick together to form a droplet. The two hydrogen’s are the positive pole of the molecule, while the oxygen molecule is the negative pole of the molecule. Due to this science, there is a slight negative and positive charge in a water molecule. Water molecules are excellent solvents, being attracted to polar compounds; such as salt, which is also polar. Nonpolar compounds are repellent towards water, therefore hydrophobic. Capillary action moves water (and all the things that are dissolved in it) around. It is defined as the movement of water within the spaces of a porous material due to the forces of adhesion, cohesion, and surface tension. (Surface tension is the property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force, due to the cohesive nature of its molecules.) An example of this would be water being drawn up by a paper towel.
Movement of Water in Plants.
The plant draws water up through the roots by using capillary action. The water will also break down the nutrients, minerals, and chemicals in the soil, allowing the plant to draw that up with the water and gain valuable nutrients.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
flashcards for these notes ↓
https://knowt.io/flashcards/42494a35-0976-4293-a1ae-de3e8354b936