Unit 9: Cell Energy
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/188
Last updated 4:20 AM on 6/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
1
New cards
Cellular respiration
Burning glucose using oxygen to make ATP
2
New cards
What uses cellular respiration?
Almost everything (animals, plants, bacteria, ect.)
3
New cards
Energy molecules
Glucose & ATP
4
New cards
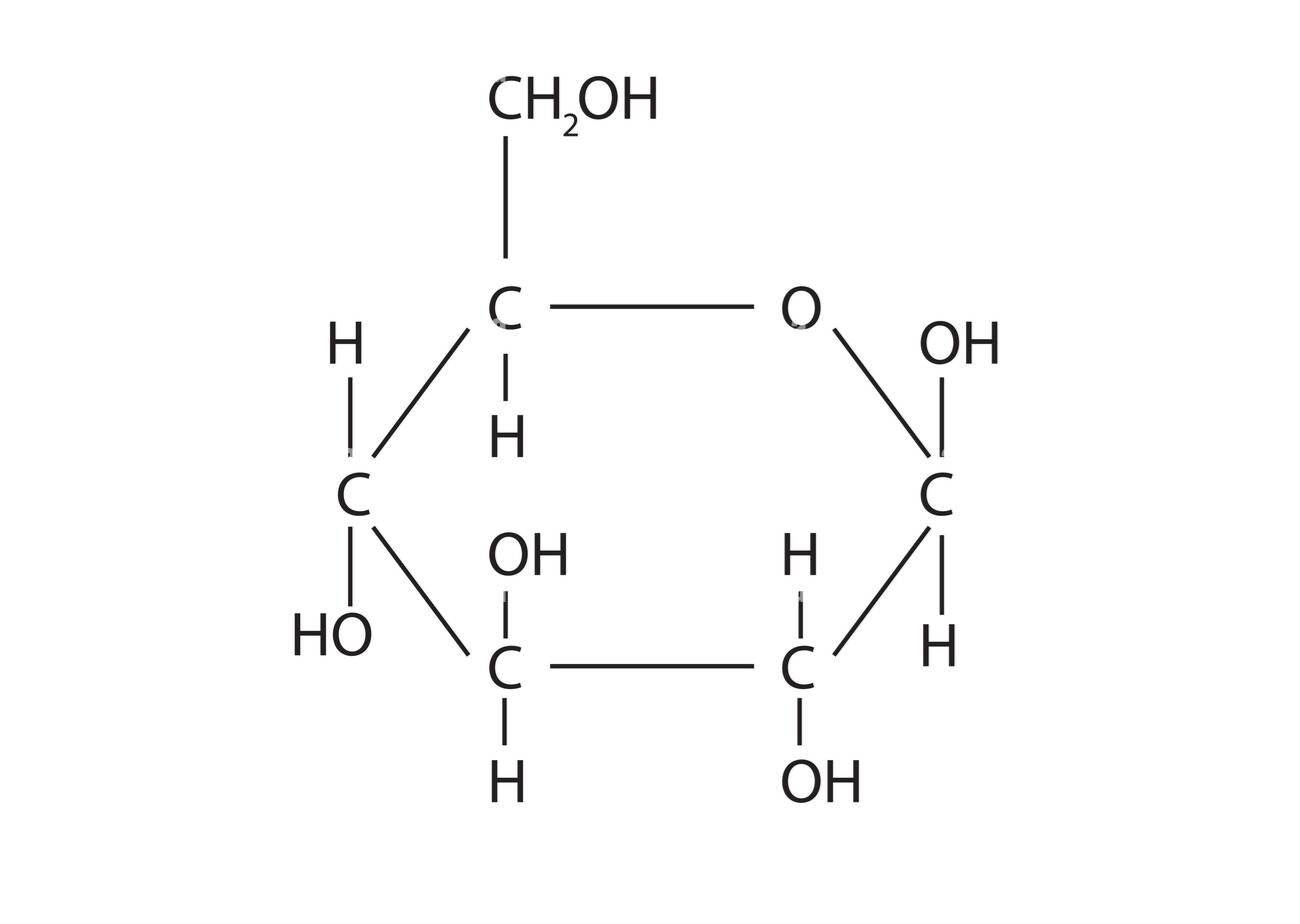
Glucose formula
C₆H₁₂O₆
5
New cards
Glucose purpose
The saving account of energy (bank account when out of cash; cash = energy)
6
New cards
ATP
Adenine triphospate
7
New cards
What organic moluecle is ATP?
RNA Nucleotide
8
New cards
What makes up ATP (RNA Nucleotide)?
3 phospate groups, 1 ribose sugar, & adenine base
9
New cards
What base does ATP use?
Adenine
10
New cards
What is the cash molecule for ALL cells?
ATP
11
New cards
How can ATP be drawn as?
A - P \~ P \~ P
12
New cards
What do the “\~” represent when drawing ATP?
Breakable bonds
13
New cards
How to spend ATP?
Break off 1-2 phosphates
14
New cards
How much energy is released when breaking a phosphate bond?
7 kcal/mol
15
New cards
How much energy is needed to reattach a phosphate bond?
7 kcal/mol
16
New cards
Is 7 kcal/mol enough energy to do most jobs?
No
17
New cards
What are you left with after breaking off 1 phosphate?
ADP + Pi
18
New cards
What is ADP?
Adenosine diphosphate
19
New cards
How is ATP drawn with 1 phosphate broken off?
A - P \~ P
20
New cards
What are you left with after breaking off 2 phosphates?
AMP + Pi + Pi
21
New cards
What is AMP?
Adenosine monophosphate
22
New cards
How is ATP drawn with 2 phosphates broken off?
A - P
23
New cards
What is Pi?
Inorganic phosphate, what’s broken off of ATP, waiting to be reattached to rebuild ATP
24
New cards
Does cellular respiration turn glucose straight into ATP?
No
25
New cards
Spending ATP gives cells energy to…
* Active transport
* Building/breaking molecules
* Cellular respiration
* Movement
* Building/breaking molecules
* Cellular respiration
* Movement
26
New cards
What does a cell do after spending most of its ATP?
Rebuilds it by burning glucose
27
New cards
Does ATP get spent super quickly?
Yes
28
New cards
What does broken down glucose recombine into?
CO2 and H2O
29
New cards
How much energy does glucose have?
676 - 686 kcal/mol
30
New cards
How many phosphates can be reattached to rebuild how many ATP using glucose energy?
38 phosphates, 38 ATP
31
New cards
How efficient is converting glucose energy into ATP energy?
40% efficient
32
New cards
What is the remaining 60% of energy when converting glucose energy into ATP energy lost as?
Heat
33
New cards
How is the 60% of energy lost as heat used?
To keep the body warm
34
New cards
What is the general equation for cellular respiration?
C6 H12 O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38 ATP
35
New cards
Why do we break little energy of glucose bonds at a time?
Breaking all bonds of glucose at once would release everything in only heat
36
New cards
How many stages are there of cellular respiration?
3 1/2 stages
37
New cards
What is the first stage of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis
38
New cards
What is the first and a half stage of cellular respiration?
Oxidation of pyruvate acid
39
New cards
What is the second stage of cellular respiration?
Kerb’s cycle
40
New cards
What is the last stage of cellular respiration?
Electron transport chain (ETC)
41
New cards
What is the purpose of glycolysis?
To break glucose in half
42
New cards
What is the starting molecule of glycolysis?
Glucose
43
New cards
What is the final product of glycolysis?
Pyruvic acid or pyruvate
44
New cards
What is pyruvic acid or pyruvate?
Half of a glucose (3-C each)
45
New cards
What is the difference between pyruvic acid or pyruvate?
A single proton difference, otherwise same molecule
46
New cards
Where does glycolysis take place?
In the cytoplasm (ONLY stage here)
47
New cards
Is glycoysis aerobic or anaerobic?
Anaerobic
48
New cards
Which stages are anaerobic?
One, only glycoysis
49
New cards
What controls chemical reactions in all the stages of cellular respiration?
Enzymes
50
New cards
Can the chemical reactions in the stages of cellular respiration be controled by one enzyme?
No, each reaction needs a different enzyme
51
New cards
What is NAD+?
Vitamine, co-enzyme
52
New cards
What does NAD+ do?
Helps break down glucose, steals 2 p+ and 2 e- from glucose
53
New cards
What does NAD+ convert to after taking 2 high energy e- from glucose?
NADH
54
New cards
What does NADH do?
Stores e- temporarily to be used in last stage to make ATP
55
New cards
How much ATP is made in glycolysis?
2
56
New cards
What is the equation that summarizes glycolysis?
C6 H12 O6 + 2 ATP + 2 NAD+ → 2 pyruvic acid 4 ATP + 2 NADH
57
New cards
What is the total net energy yield gained from glycolysis?
2 ATP + 2 NADH
58
New cards
Why is only 2 ATP gained from glycolysis?
Makes 4 ATP, spends 2 to build
59
New cards
What is the starting molecule of oxidation of pyruvic acid?
Pyruvic acid (product from previous stage glycolysis)
60
New cards
Where does oxidation of pyruvic acid take place?
Matrix (inside center part of mitocondria)
61
New cards
Is oxidation of pyruvic acid aerobic or anaerobic?
Aerobic
62
New cards
How is oxygen used in oxidation of pyruvic acid?
It doesn’t use, but needs to be present
63
New cards
What is the final product of oxidation of pyruvic acid?
2 acetyl groups
64
New cards
What is the equation glycolysis?
2 pyruvic acid + 2 COA + 2 NAD+ → 2 CO2 + 2 acetyl COA + 2 NADH
65
New cards
How many carbon does an acetyl group have?
2-C
66
New cards
What is COA?
Enzyme, vitamin B
67
New cards
What does COA do?
Leads 2 acetyl like crossing gaurd
68
New cards
What is the total net energy yield per glucose in oxidation of pyruvic acid?
2 NADH
69
New cards
How many chemical reactions make up the oxidation of pyruvic acid stage?
1
70
New cards
What is the purpose of Kreb’s cycle?
To completely break down acetyl groups (glucose)
71
New cards
What is the starting molecule of Kreb’s cycle?
2 acetyl groups
72
New cards
How many times is Kreb’s cycle done?
Twice
73
New cards
Why does Kreb’s cycle have to be done more than once?
For every acetyl group, a single cycle does 1 group
74
New cards
Where does glycolysis take place?
Matrix of mitocondria
75
New cards
Is Kreb’s cycle aerobic or anaerobic?
Aerobic
76
New cards
How is oxygen used in Kreb’s cycle?
It doesn’t use, but needs to be present
77
New cards
What is the final product of Kreb’s cycle?
Carbon dioxide gas
78
New cards
What does FAD do?
Picks up 2 H (like NAD+) in Kreb’s cycle
79
New cards
What does FAD convert into after picking up 2 H?
FADH2
80
New cards
Where can FADH2 be made?
ONLY Kreb’s cycle
81
New cards
How are the acetyl groups completely broken down?
4 CO2 is made in Kreb’s cycle
82
New cards
What is the total net energy yield gained from Kreb’s cycle (per glucose)?
2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 FADH2
83
New cards
What is a ETC made of?
Chain of 9 proteins
84
New cards
Where does ETC take place?
Inner membrane of mitochondria
85
New cards
What is the starting molecule of ETC?
All NADH and FADH2 from previous stages (10 NADH, 2 FADH2)
86
New cards
What does NADH do in ETC?
Gives 2 H to 1st protein, recycled into NAD+ to get more H
87
New cards
What does the 1st protein of ETC do?
Seperates H atom into H+ and e-
88
New cards
What are H+?
Protons (p+)
89
New cards
What happens when e- pass through a protein in ETC?
Drops slightly in energy
90
New cards
When do e- have big drops in energy levels during ETC?
Beginning, middle, and end
91
New cards
Why does e- have big drops in energy when going through ETC?
Energy used in active transport to move 2 H+ through protein door into intermembrane
92
New cards
Is ETC aerobic or anaerobic?
Aerobic
93
New cards
How is oxygen used in ETC?
Accepts final e-, makes water
94
New cards
What is the final e- accepter in ETC?
Oxygen
95
New cards
How is water made in ETC?
* Oxygen binds final 2 e- at ETC end to itself
* Finds 2 p+
* Reunites 2 e- and 2 p+ = 2 H
* Makes H2O
* Finds 2 p+
* Reunites 2 e- and 2 p+ = 2 H
* Makes H2O
96
New cards
What is the final product of ETC?
H20 (water)
97
New cards
What is ATP synthase?
Protien acting like enyzme
98
New cards
What does ATP synthase do?
Makes ATP
99
New cards
How does ATP synthase make ATP?
* H+ leaks (without energy) through ATP synthase using facilitated diffusion from intermembrane space to matrix
* H+ leaks when 2 H+ goes through protein during ETC active transport
* Every time H+ leaks, ADP reunites with Pi to make ATP
* H+ leaks when 2 H+ goes through protein during ETC active transport
* Every time H+ leaks, ADP reunites with Pi to make ATP
100
New cards
How much ATP is made per NADH?
3