Galvanic Cells
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Electrochemical Cell
A cell that converts chemical energy to electrical energy (or vice versa)
Galvanic Cell
A cell which converts chemical energy into electrical energy (used in mobile phones and laptops)
Battery
Combination Of Cells
Used to describe cells as well in common day language
External Cicrcuit
Wire that flows outside of the circuit connecting the electrodes
Why The Electrolyte In The Salt Bridge Is Unreactive
If it were reactive, it could participate in chemical reactions, form precipitates, alter cell potential
As it is unreactive, it is only a spectator ion
Spontaneous Reaction
No need for external energy
The reaction happens naturally, and by itself
Primary Cells
Cells that are used once, and cannot be recharged
Alkaline Cells
Cells that are non-rechargeable, once the equilibrium has been reached
Equilibrium (Within cells)
When there is a large chemical potential difference (EMF) between the anode and cathode
anode (has a large driving force to donate electrons)(
cathode (has a large driving force to obtain electrons)
The force slowly depletes as the battery discharges, and charges balance out
Potential Difference/Electromotive Force
In reference to the disparity between anode and cathode
One has a higher tendency to attract electrons, whilst one has tendency to donate
The force is referenced as voltage
Standard Electrode Potential
A standard E value for each half cell - how good a substance is at being reduced
Higher E value = greater tendency to gain electrons (undergoes oxidation)
Lower E value = greater tendency to loose electrons (undergoes oxidation)
Tendency to gain electrons at the cathode (reduction) is greater than the tendency to lose electrons at the anode (oxidation).
E Cathode - E Anode = positive/negative value
If positive - then tendency to gain electrons outweighs the tendency to loose electrons
Standard Hydrogen Half Cell (SHE)
Is the hydrogen half cell
Has a value of 0
Is considered a baseline
EMF
Electrode of high potential - Electrode Of Lower Potential
Limitations On The Predictions Of Redox Equations
In different conditions other than SLC - order in electrochemical series may be different
Does not indicate rate of reaction (can be very quick, or barely anything)
Direct Redox Equations (Reactants mixed together - not seperated through a wire)
Heat energy is released
Products are made almost instantaneously
Rule For Predicting Whether Redox Reaction Will Take Place
Top left to bottom right
e.g. bromine solution is added to a solution
containing chloride ions
Find reduction potential - then u know whats on top and bottom
Whatever’s higher is on top
Whatever’s lower is below
Then establish top left bottom right - if not then no reaction
Fuel Cells
Type of galvanic cell that produces electricity from chemical energy
Are very efficient - create electricity with the by-product of only heat and water
Electricity is made for as long as fuel is supplied
Hydrogen Economy
A society where hydrogen is used as a primary source of fuel, as opposed to non-renewable fossil fuels
Used as a major carrier source - perhaps replacing fossil fuels entirely
Fuel Cell
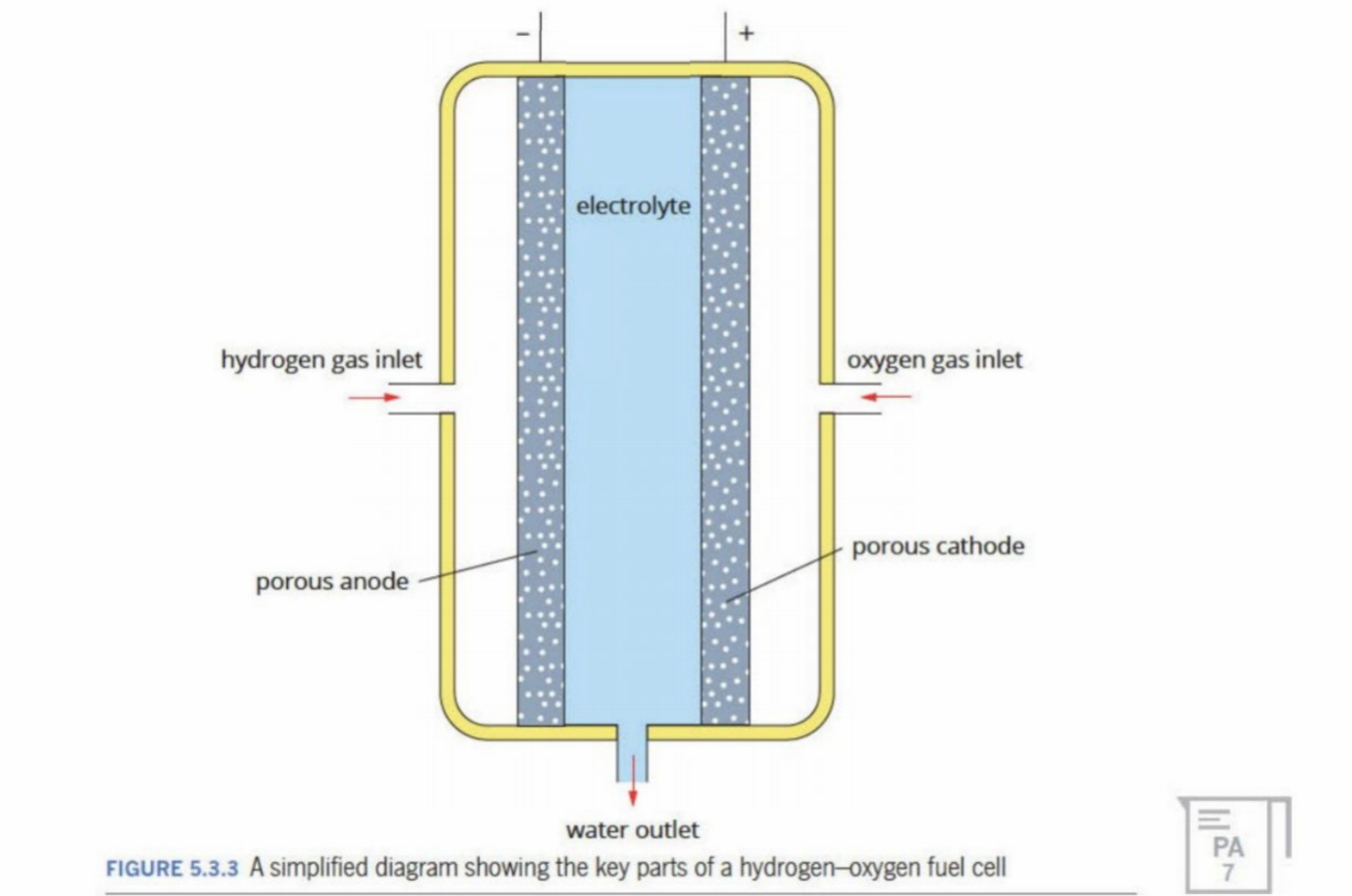
Electrolyte In The Middle
Depending on medium, can have H+ ions or OH- ions
Electrodes
Are porous (have little holes in them)
Greater porosity leads to maximising the reaction
The reaction occurs in the small holes in the electrode itself - where the reactants interact with the electrolyte
So more holes = more sites of reaction
What happens at electrode
For oxidation, protons and electrons split - electrons go through external wire
protons travel through electrolyte to cathode
By products are heat and water
How It Works (Acidic)
At anode, oxdiation occurs (electrons and protons are split)
The protons go through the electrolyte to the cathode
The electrons go through the external circuit to the cathode (because there is a potential difference) - there is a high concentration of negative charge at the anode and a lower concentration of charge at the cathode - electrons are drawn to the region with lower charge
The hydrogen and oxygen react at the cathode, forming water - water is produced in Cathode

Fuel Cell Annotated
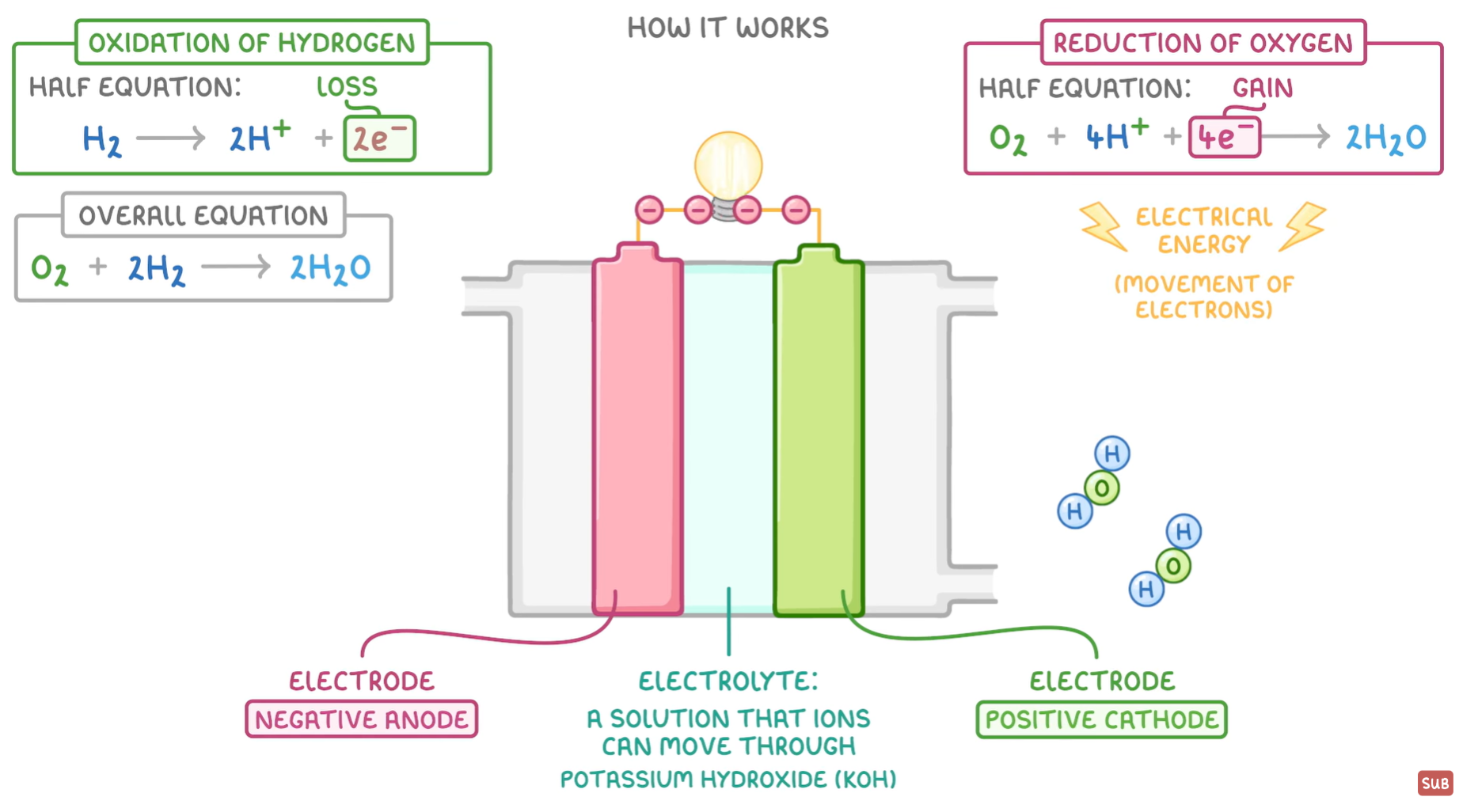
Alkaline Fuel Cells
Instead of H+ ions, OH- ions are used
They go from Anode to Cathode
Water is produced at Anode - cathode produces OH- and it travels through electrolyte to react with hydrogen gas - water moves through electrolyte back to cathode
There is not that muich emission of water as it is continually used by the cell
Key Parts in Alkaline Cell
Water is both used and made - less total output of water
Water is made at anode - back to where it started
Water moves through the electrolyte (though OH- goes the other way), and then reacts with cathode
Electrolyte In Half Equations
Appear in half equations, but not full equations
Efficiency Of Fuel Cells
More efficient (40-60%) than thermal energy (30-40%), and combustion engines (20-25%)
Waste product of steam (water) can be used to push turbines - electricity (efficiency is raised to 85%)
List Of Fuel Cells
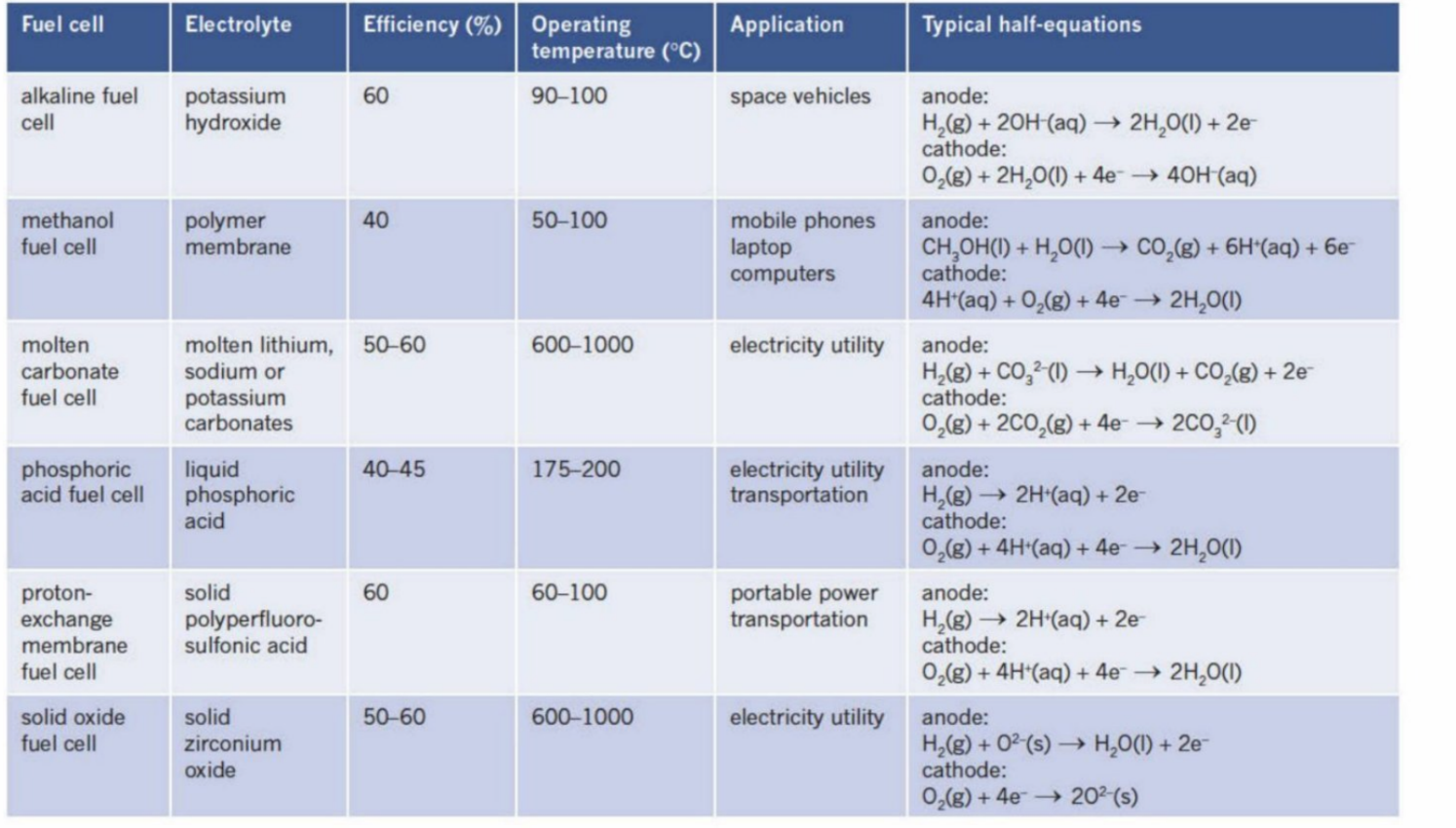
Electrode Surface Area
Surface Area Of Electrode = current that can be drawn
More surface area - more reaction sites - more oxidation can occur - more electrons - more current
Catalysts
Typically Platinum - increases oxidation and reduction
Speeds up reaction

Common Electrolytes

Applications Of Fuel Cells
Making hydrogen-cell fueled vehicles
Will play a key role in transitioning from fossil fuels to sustainable energy sources
Adv vs Disadv of fuel cells

Limitations of usage of biofuels
Biodiesel and bioethanol - require food sources to produce enough energy
Supplying 10% of energy required = sacrificing 30% of agricultural land for energy purposes
Biogas - Not enough energy content (low energy density)
Hydrogen Production
Can be renewable or non-renewable
Steam Reforming
95% of Hydrogen is made this way
Methane is reacted with very hot steam to produce Carbon moxoide and hydrogen
Is done again to produce H2 gas
Steam Forming Image
Steam Reforming Products
Hydrogen produced has lower energy content than normal hydrogen (some energy is lost as heat)
CO2 emissions can be stored underground - geosequestration
Other Forms Of Hydrogen Production
Using electrical energy to sperate the Hydrogen from water
Using biomass from landfill - turning that into biogas and doing steam reforming (preferable to do sustainably)
Storing Hydrogen
Liquid Hydrogen, Compressed Hydrogen, Material Based Storage
Liquid Hydorgen
Hydrogen is liquefied and is used as a liquid fuel - vehicles need larger fuel tank for satisfactory usage
Is less energy dense
Material Based Storage
Hydrogen adsorbs onto a metal, and desorbs when required
Can release hydrogen when required
Can store hydrogen at lower pressure and smaller volumes
Compressed Hydrogen
Keeping hydrogen in its gas form
Must be large in size - as energy density is low
Designing Better Fuel Cells
Avoiding electrode materials posign environmental and humanitarian risks - e.g. not using nickel or cobalt (are being mined by those in extreme labour conditions)
Moving from linear economy - circular economy
Linear Economy - Circular Economy
Optimal use and reuse of resources (fuel cells are on-par with this idealogy)
Green Principles In Relation To Sustainable Fuel Production
design for energy efficiency
use of renewable feedstocks
Caveats of a fuel cell
Membrane Degradation: The internal polymer membrane must stay hydrated to function; if it dries out during storage, it becomes brittle and cracks, losing its ability to conduct protons.
Fuel Storage Density & Leaks: Hydrogen gas is extremely difficult to contain because it is low-density (requiring high-pressure tanks) and its tiny molecules can leak through seals or cause "hydrogen embrittlement" in metal tanks.
Catalyst Poisoning: The platinum catalyst is highly sensitive to impurities in the air; storage in environments with sulfur or carbon monoxide can permanently bond to the platinum, "deactivating" the cell's power-generating ability.
How Fuel Cells Can Be Made In Accordance With A Circular Economy
2. Material Innovation and Substitution
The "circularity" of a fuel cell is often dictated by its rarest ingredients—specifically Platinum Group Metals (PGMs) and perfluorinated polymers (PFAS).
PGM Reduction and Recovery: Platinum is highly circular if it can be recovered. Designing electrodes where the catalyst can be chemically leached or mechanically vibrated off the substrate increases recovery rates.
Bio-based Membranes: Current Proton Exchange Membranes (PEM) often use Nafion, which is difficult to recycle. Research into bio-derived or hydrocarbon-based membranes aims to create materials that are biodegradable or easier to reprocess.
Cradle-to-Cradle Sourcing: Prioritize components made from recycled scrap (e.g., recycled aluminum for bipolar plates) rather than virgin ores.
Overall Summation Of Advancements That Can Be Done To Align With Circular Economy

Finding Equations To A Fuel Cell Reaction - Cathode
Oxygen always reduces at cathode and creates water (H2O) - balance hydrogens and then electrons to get cathode equation
Anode Reaction - acidic
The fuel is always reduced
If the fuel has Carbon, then it always produces CO2 - balance equation through adding hydrogens and electrons
Overall Equation
Add both anode and cathode equation together
Alkaline Conditions Reaction
Do the same balancing, but add OH after the acidic balancing
Microbial Fuel Cell
Using wastewater and waste water sources to create energy through bacteria
Microbial Fuel Cell
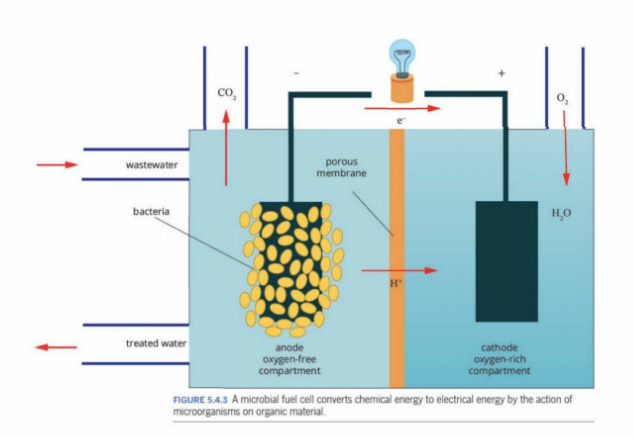
At anode
The microbial bacteria eat the bacteria in the waste supply
The bacteria release electrons during metabolism.
These electrons are transferred to the anode through direct contact, conductive biofilms, or nanowires produced by the bacteria.
Example: glucose → CO₂ + electrons (e⁻) + protons (H⁺)
Reaction at anode:
C6H12O6+H2O→CO2+H++e−\text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_6 + H_2O \rightarrow CO_2 + H^+ + e^-C6H12O6+H2O→CO2+H++e
At Cathode
Step 5: Reaction at the Cathode
At the cathode, electrons meet the protons and oxygen (from air or water).
They combine to form water:
O2+4e−+4H+→2H2OO_2 + 4e^- + 4H^+ \rightarrow 2H_2OO2+4e−+4H+→2H2O
How electrons are forced out
Step 2: Electrons Go to the Anode
The bacteria release electrons during metabolism.
These electrons are transferred to the anode through direct contact, conductive biofilms, or nanowires produced by the bacteria.
Step 3: Electrons Flow Through an External Circuit
Electrons travel through a wire from the anode to the cathode, creating a current (electricity).
Step 4: Protons Move Through the Membrane
The protons generated at the anode move through the PEM to the cathode chamber.
How Microbial Fuel Cells Are Renewable
Generates clean energy from organic waste without burning fossil fuels → reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Treats wastewater naturally → decreases chemical pollution and protects ecosystems.
Uses organic waste efficiently → turns food/agricultural/wastewater into electricity instead of letting it decay.
Supports renewable energy innovation → sustainable electricity production aligns with low-carbon goals.
Potential for community benefit → can provide power in remote or low-resource areas using local waste.