PHOrgChem (Lecture) | Module 6 (Part 1: ALIPHATIC, AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS AND ALKYL HALIDES ONLY)
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Hydrocarbons
Fundamental in organic chemistry
Hydrocarbons
● Serves as a base for numerous industrial applications, components to pharmaceuticals
Hydrocarbons
● Organic compounds consisting solely of Carbon and Hydrogen
Hydrocarbons
● Found in fuels, medicines, plastics, etc.
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons, and Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Classified into TWO MAJOR GROUPS of HYDROCARBONS that can be categorized into different types
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
open chain/ straight/branched chains
○ Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
ring base/ contains benzene rings
○ Benzene and its derivatives
Hydrocarbon Derivatives
Derivative of Benzene
Hydrocarbon Derivatives
AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS: compounds which contain Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur or Halogen
Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, or Halogen
Hydrocarbon Derivatives is derivative of Benzene which contains?
Hydrocarbon Derivatives Containing Oxygen
HYDROCARBON DERIVATIVES: Alcohols, Phenols, Ether, Ketone, Aldehyde, Carboxylic Acid, Esther, and Acid Anhydride
Hydrocarbon Derivatives Containing Nitrogen
HYDROCARBON DERIVATIVES: Amine, Imine, Amide, and NItriles
Hydrocarbon Derivatives Containing Phosphorus
HYDROCARBON DERIVATIVES: Organophosphates
Hydrocarbon Derivatives Containing Sulfur
HYDROCARBON DERIVATIVES: Thiols, Sulfides, Disulfides, and Sulfoxides
Hydrocarbon Derivatives Containing Halogens
HYDROCARBON DERIVATIVES: Alkyl Halides
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
HYDROCARBONS: Categorized based on the type of bonding
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
HYDROCARBONS: Widely used in energy industrial applications, and chemical synthesis
Alkanes
Saturated hydrocarbons (single bonds).
Example: Methane (used as fuel and energy source)
CnH2n+2
Chemical Formula of ALKANES
Methane
ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONS: used as fuel and energy source
Alkenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (double bonds).
Example: Ethylene (used in plastic production and plant hormone)
CnH2n
Chemical Formula of ALKENES
Ethylene
ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONS: used in plastic production and plant hormone
Alkynes
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (triple bonds).
Example: Acetylene (used in welding and chemical synthesis)
CnH2n-2
Chemical Formula of ALKYNES
Acetylene
ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONS: used in welding and chemical synthesis
Molecules
The physical state of alkanes depends on their?
Smaller Alkane
PHYSICAL STATE OF ALKANE: they are gases
Larger Alkane
PHYSICAL STATE OF ALKANE: they exists as liquid or solid
Nonpolar
POLAR OR NONPOLAR: Alkane
Insoluble
Alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes are nonpolar, thus the solubility of alkanes to water is?
Soluble
Alkanes alkenes, and alkynes are nonpolar, thus the solubility of alkanes to nonpolar solvents/organic solvents is?
Substitution Reaction
Alkanes undergo what reaction with halogens and other reactive species?
Combustion
It is ia key reaction on Alkanes as it releases energy into the place
Carbon 1 to Carbon 4
LENGTH OF CARBON: Gases, odorless
Carbon 5 to Carbon 17
LENGTH OF CARBON: Liquids
Waxy Solids
Higher alkanes are?
Less
Alkanes are _____ dense than water
Halogenation, Nitration, Sulfonation, and Combustion
Reactions of Alkanes
Halogenation
ALKANES: Reaction with halogens (Cl, Br, I, F).
Nitration
ALKANES: Substitution of hydrogen with nitro (-NO2) group.
Sulfonation
ALKANES: Substitution with sulfonic acid (-SO3H) group
Combustion
ALKANES: Produces CO2 and H2O.
Alkenes
Used in industry applications such as plastics and furniture parts
Alkenes
They are highly reactive due to their double bonds and their reaction forms important industrial compounds like plastics
Alkenes
Boiling points and melting points is lower than alkanes due to their double bonds, increase with molecular weight.
Less
Alkenes are _____ dense than water
Lower Alkenes
PHYSICAL STATE OF ALKANE: they are gases
Higher Alkenes
PHYSICAL STATE OF ALKANE: they are liquids or solids
Hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, and hydration
Addition Reaction of Alkenes
Diols, or Carboxylic Acid
ALKENES: Oxidation, Forms?
Polymerization
ALKENES: Used in plastic production.
Example: Ethylene polymerizes to polyethylene
Alkynes
More reactive than alkenes due to their triple bonds making them useful in the pharmaceutical industry
Alkynes
Boiling and melting points is higher than alkenes due to their increase molecular interactions
Less
Alkynes are _____ dense than water
Molecular Weight
Physical State of Alkynes Varies With?
Hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, and hydration
Addition Reactions of Alkynes
Carboxylic Acid
ALKYNES: Oxidation, forms?
Propofol
Common Name of 2,6-DIISOPROPYLPHENOL
Propofol
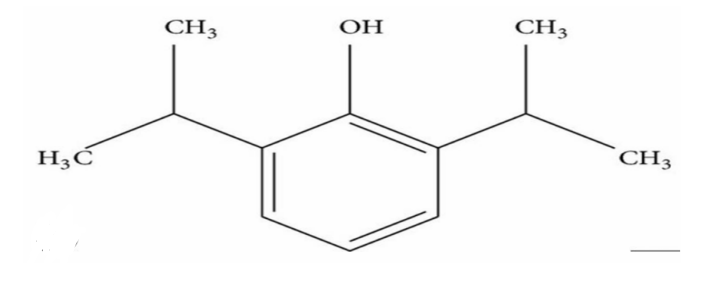
Propofol
ALKANE BASED DRUG:
Anesthetic
It is non-polar in nature with allows rapid pain penetration
Halothane, and Dodecane
Other alkane based drugs such as?
Halothane
An inhalation anesthetic—alkane is responsible for its low reactivity and increase stability
Dodecane
Used in spring creams—the alkaneenhances lipid solubility
Isotretinoin
Common Name of (2Z,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-DIMETHYL-9-(2,6,6-TRIMETHYLCYCLOHEX-1-ENYL)NONA-2,4,6,8-TETRAENOIC ACID
Isotretinoin
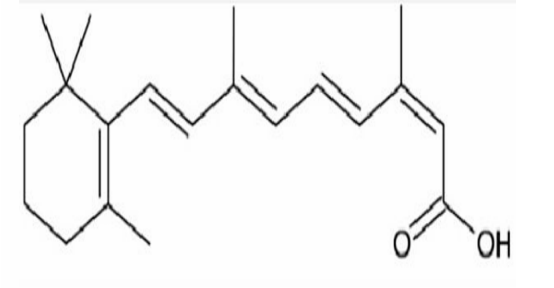
Isotretinoin
ALKENE BASED DRUG
Used in acne treatment—the presence of double bonds contributes to its reactivity in cell temperature/exposure
Simvastatin, and Tamoxifen
Other alkene based drugs example are?
Simvastatin
A cholesterol lowering drug—alkene: the double bond affects enzyme interaction
Tamoxifen
A breast cancer treatment—alkene structure influence estrogen receptors binding
Ethylene Estradiol
Common Name of (8R,9S,13S,14S,17R)-17-ETHYNYL-13-METHYL7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-OCTAHYDRO-6HCYCLOPENTA[A]PHENANTHRENE-3,17-DIOL
Ethylene Estradiol
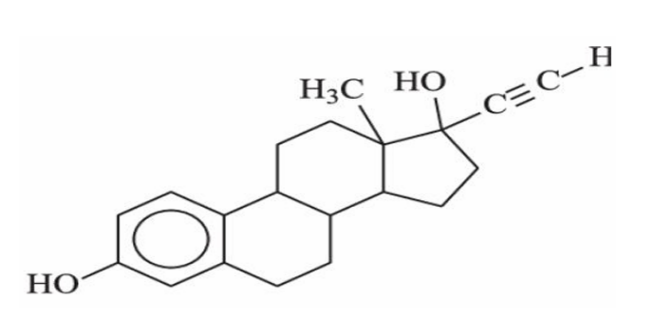
Ethylene Estradiol
ALKYNE BASED DRUG
A component of oral contraceptives, the triple bond increases metabolic stability and bioavailability.
Norethynodrel, and Lonafarnib
Other example of alkyne based drugs are?
Norethynodrel
A hormonal medication, the presence of triple bond—alkyne increase bioavailability
Lonafarnib
An anticancer drug, the triple bond—alkyne contributes to enzyme inhibition
Hydrocarbons
Many drugs contain ____________ structures, their physical and chemical properties determine their solubility, stability, and effectiveness in biological systems
Alicylic Hydrocarbons
FORMS RING STRUCTURE BUT DO NOT EXHIBIT AROMATICITY
Carbocylic Hydrocarbons
Alicylic Hydrocarbons is also known as?
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons
Used in Anesthetic, Solvents, and industrial applications due to their stability and chemical properties. (Found in pharmaceuticals, industrial solvents, and fuel additives)
Alicylic Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons that form rings but behave like aliphatic compounds.
Cyclopropane
ALICYCLIC HYDROCARBONS: anesthetic gas, used in medical procedures
Cyclohexane
ALICYCLIC HYDROCARBONS: used in the production of nylon and solvents
Cyclopentane
ALICYCLIC HYDROCARBONS: used in insulation and refrigerants
Nonpolar
Alicylic Hydrocarbons are _______, insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents.
Alicyclic Hydrocarbons
Boiling and melting points vary with ring size and substituents.
Less
Alicyclic Hydrocarbons are ____ dense than water
Substitution, and Addition
Alicyclic Hydrocarbons undergo _________, and ___________ reactions.
Hydrogenated
Alicyclic Hydrocarbons can be _________ to form alkanes.
Alicyclic Hydrocarbons
Reactivity influenced by ring strain (e.g., cyclopropane is more reactive than cyclohexane).
Ring Strain
Alicyclic Hydrocarbons’ reactivity influenced by _____________ (e.g., cyclopropane is more reactive than cyclohexane).
Smaller
The presence of ring strain (on Alicyclic Hydrocarbons) influences their chemical reactivity making _______ rings more reactive. Their stability, solubility and reactivity is useful in pharmaceutical and industry
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Contain benzene rings.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Examples are Anthracene, Benzo(a)pyrene, Corene.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Used in dyes, pigments, and pharmaceuticals.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Have delocalized electrons systems making them stable and highly useful in industrial applications
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Boiling point is higher than alkanes due to strong intermolecular forces
Slightly Soluble
Aromatic Hydrocarbons are nonpolar, they are _______________ in organic solvents.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
High stability due to resonance structures
Nitration, and Halogenation
Electrophilic Substitution of Aromatic Hydrocarbons