diuretics and such
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Furosemide brand
Lasix
are osmotic diuretics used long term
NO
are CAIs usually used for kidney issues more or glaucoma more
GLAUCOMA— otherwise like “swimming up the river”
why are diuretics actually class D for preg most the time
decrease placental perfusion
why are thiazides better in osteoporosis
bc loop diuretics potassium wasting
hzt brand
Microzide
Spironolactone brand
Aldactone
Triamterne +HZT brands
Dyazide, Maxzide
Bumetanide brand
Bumex
Metolazone brand
Zaroxolyn
Torsemide brand
Demadex
Chlortalidone brand
Hygroton
Eplerenone brand
Inspra
Triamterene brand
Dyrenium
Natriuretics agents def
drugs that ↑renal Na+ excretion. Almost always cause ↑ water excretion
nat are always diuretics bc increase urine outflow
Loop diuretics
Furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide, ethacrynic acid
Thiazides
HCTZ, metolazone, chlorothiazide, chlorthalidone, indapamide
K+- sparing diuretics
spironolactone, eplerenone, amiloride, triamterene
CAI (list em)
acetazolamide
what does diuertic mean
increases urine volume
another word for additive effects
synergistics
one drug increases effect of other disproportionately
reasons for edema?
excessive Na intake — take in more water
liver cirrhosis— scarring in liver causes HTN in liver veins
heart failure— not strong enough to pump forcefully through periphery (left side) or not letting enough blood in (right side failure)
main ions affected by diuertics
na, k, cl, water
diuretics other ions transported
H, hco3, ca, mg, organic ions
goal of diuretics
increase excretion of salt and water
what is diuretic resistance
causes: renal failure, cirrhosis, heart fail, drug induced (NSAIDs— decreasing blood flow), high intake of Na
from PATHOLOGIES
think less blood flow means the drug can’t get around the body to do its job
what prevents diuretic resistance
cont IV of loop diuretic
Hypertrophy def
organ gets bigger bc its cells swell up
cause of diuretic braking
overuse of diuretic
you get rid of sodium SO FAST it upreg Na transporters/hanging on to Na unnecessarily/diminishing diuretic effects
diuretic resistance causes
excess Na
nsaids
emboli (kidney/renal block)
diuretic resistance net effect
reduced diuretic absorption bc of decreased renal perfusion
is cai recommended as diuretic
nahhhh fam
Vasopressin— list drugs
desmopressin, vasopressin
Vasopressin antagonists
conivaptan
Osmotic diuretics:
mannitol, glycerol
what is most effective diuretic?
loop diuretic
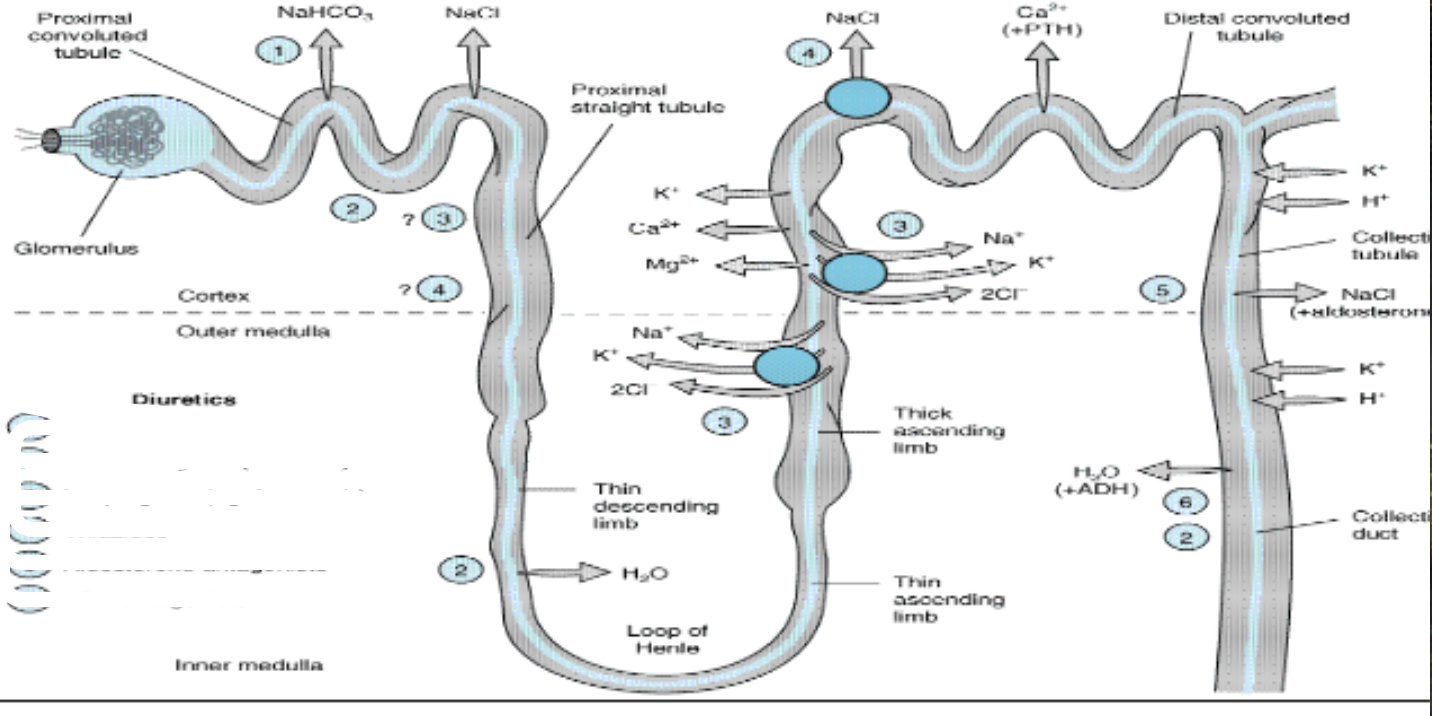
where is acetazolamide working
1
where do osmostic agents work
2
which is seocnd most effective diuretic
thiazide
where do loop diuretics work
3
where do thiazides work
4
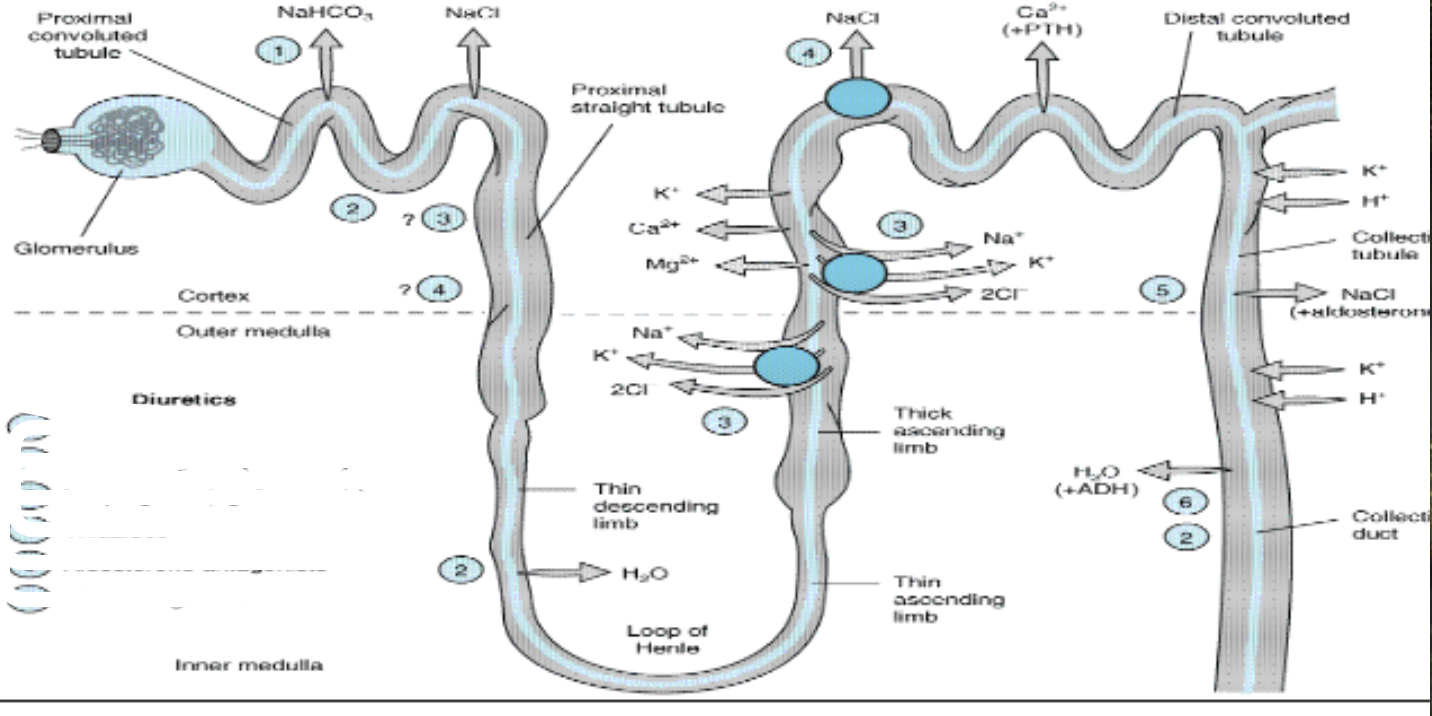
where do aldosterone antagonists work
5
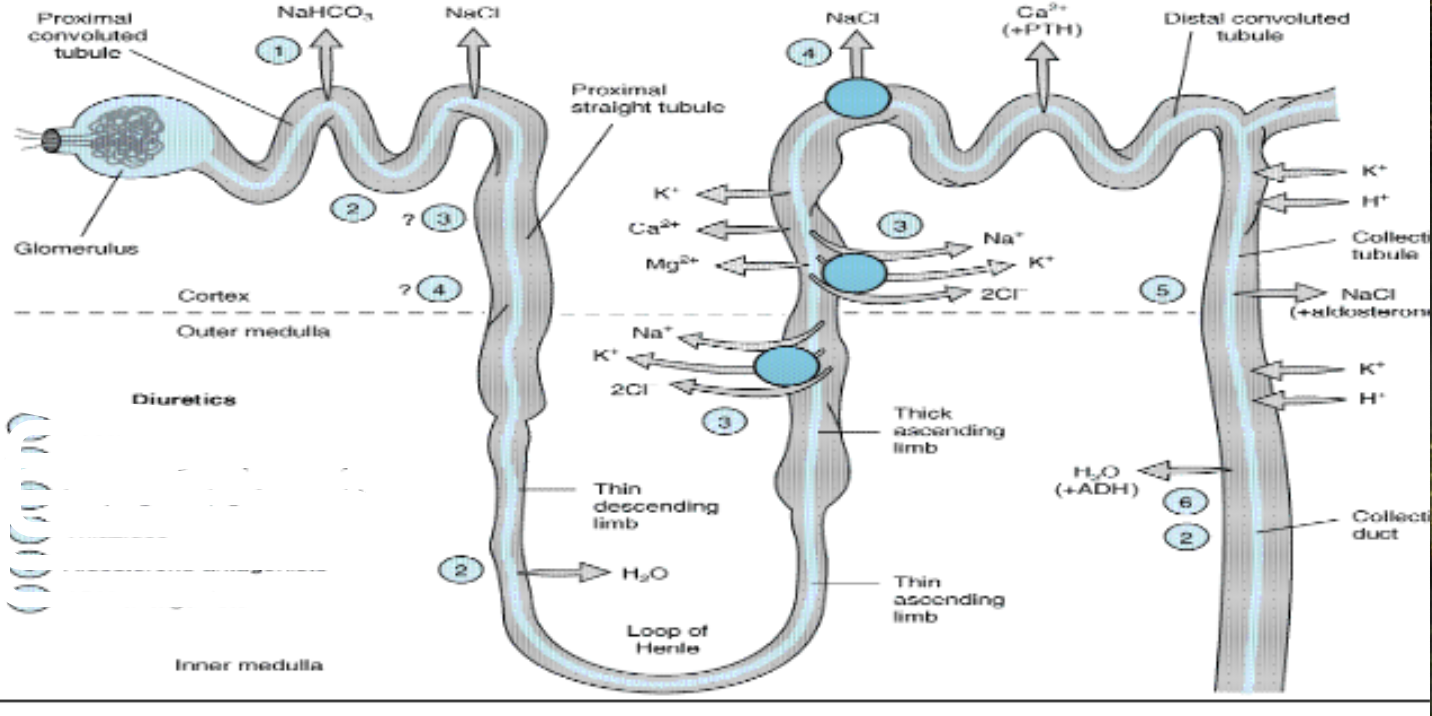
where do ADH antagonists work
6
what is potassium sparing diuretics
aldosterone antagonists
when water permeability is high, do diuretics work better or worse and WHY
WORSE
diuretics do better when the salt is trapped into the tubule to be excreted, meaning water is forced to stay in the tubule with it. if water could just diffuse into the tubule, then there would be less Na excretion
why take ACEIs and ARBs with diuretics?
synergistic effect
diuretics start the RAAS system which can then re-increase the blood pressure which defeats the purpose! so aceis and arbs block the raas from kicking in as well
loop diuretic channel involved
na/k/2cl symport
site of loop diuretic
thick ascending loop of henle
what other synthesis does loop diuretic cause and what is result
pge2 synth to increase renal blood flow
loop diuretic what should you not take with it
don’t take nsaids
(bc causes pge2 synthesis)
loop diuretic effects
loss of na, k, cl, ca, mg
reabsop uric acid— lots of urination
decrease vascular resistance
decrease pressure in pulmonary
loop diuretics black box warning
profound diuresis leading to electrolyte abnormalities
Furosemide, Bumetanide preg class
c
Torsemide, Ethacrynic acid preg class
b— but according to experts its D
what preg drugs ok?
bc, D and X are no buenoooo
loop diuretic ADR
hypokalemia
hypocalcemia
hyperglycemia
photosensitivity
ototox
alkalosis (with K deficient comes H+ def)
increase LDL, decrease HDL (the good cholesterol)
why does hypokalemia cause hyperglycemia
what does hypokalemia cause
cardiac arrhythmia
hyperkalemia affects
muscle twitching, cramps
digoxin toxic up or down with diuretics
up bc hypokalemia lets moer dioxgoin bind to na/atpase
usally blocks channel to let more Na in cell, causing more Ca in to increase heart contractions
bad if heart not lit in heart failure
what heart condition do loop diuertics increase risk of
qt prolongation
what happens with lithium and loop diuretics
increaes lithium reabsorption in place of sodium— can create toxicity
what do corticosteriods do with loop diuertics
increase hypokalemia (think mineralocorticoid/aldosterone like effects— K wasting)
anticoag effect with loop diuertics
increase bleed risk bc
why do loop diuretics increase ototox with aminoglycosides
compounded effect
food, sucralfate, Cholestyramine, Colestipol— increase or decrease levels of loop diuertics?
decrease bc bind drug in the GI
rel pot of furosemide
1
bumetanide rel pot
40
which loop diuretic mostly hepatic (liver) excreted
torsemide
torsemide rel pot, and one other special fact! Ooo!
3
also longest acting
ethacrynic acid rel pot
0.7 (least potent or effective)
thiazide diuretic moa
distal convulated tubule— inhibit SYMPORT of na/cl
BY decreasing Na in at this point, more prox tubule absorption of water and Na
so you ABSORB a bit more water BEFORE the collecting duct — cauase mild dehydration so you absorb water earlierrrr in the kidney
what does thiazide diuertics do
decrease Na, Cl reabsorption— water follows
decreases blood volume, arteriolar resistance
what does thiazide do to Ca levels and WHY
hypercalecemia— DECREASE excretion
bc cells are “sodium hungry” bc its all getting execreted— activate Na/Ca antiporter to get sodium in, pumping Ca back into blood
is acting LIKE parathyroid hormone
thiazide ADRS
hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypercalcemia, hyperglycemia,
allergy reactions to sulfonamide, hyperuricemia, photosensitivity,
up LDL, up TG, ↓HDL, rash
thiazide ind
dema due to HF, hepatic cirrhosis, chronic renal disease
Also osteoporosis, nephrogenic diabetic insipidus
def diabetic insipidus
excessive thirst bc of ADH trouble
thiazide preg class
b
most potent thiazide
metolazone (APPARENTLY?)
renally (kidney) excreted thiazides
chlorothiazide, HCTZ, Trichlormethiazide
majority of Hydroflumethizide, Metolazone, Chlorthalidone
hepatic (liver) excreted thiazide
Indapamide
what could thiazides OR loop be used for
HTN
heart failure
renal failure (have to use both)
hyperkalemia
what is unique ind for thiazides
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Osteoporosis (↓ Ca2+ excretion)
unique ind for loop
Acute pulmonary edema
Nephrotic syndrome (proteins allowed through glom capillary)
Hypercalcemia (↑ Ca2+excretion)
what is another name for aldosterone antagonists
K+ sparing diuretics
what do the Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics do
stop Na from entering principal cells of collecting duct from urine
K flows out of principal cells in opp direction so when that’s stopped K is s p a r e d
Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics names
triamterene
amiloride (Midamor)
Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics when to adjust dose
anuria (no urine output), pregnancy
Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics AMILORIDE when to adjust dose
chronic renal failure
Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics TRIAMTERENE when to adjust dose
hepatic and renal disease
Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics ADR
hyperkal
metabolic acidosis— moves in same direction into cell as H+
potential hyperkalemic specific ddi with Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics
acei, arb, K supplements or NSAIDs
Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics which more potent
triamterene (0.1); amiloride is literally 1 so tenfold less potent
Na channel inhibitor subtype of K sparing diuretics when renally elminated (kidney)
amiloride
Mineral corticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) subtype of K+ sparing diuretics names
spironolactone
eplerenone
what do the Mineral corticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) subtype of K+ sparing diuretics do
prevent aldosterone from hitting its receptors, which prevents upreg of ENaC channels (so less Na reabsorbed/more lost in urine), results in water loss (diuresis)
what does aldosterone do
increase ENaC channels
increase Na/K atpase activity
increase K/H secretion
think water and Na SAVING
Mineral corticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) subtype of K+ sparing diuretics which more selective
eplerenone compared to spironolactone
spironolactone brand
aldactone
eplerenone brand
inspra