Ch 9 The Tides
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
The tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the _______ and the _______ on Earth's oceans.
sun
moon
Diurnal
One high tide and one low tide occur each day.
Semidiurnal
Two high tides and two low tides occur each day.
Semidiurnal mixed
High tides and low tides reach different levels.
The greatest height to which a tide rises is known as _________ tide, whereas the lowest point is known as _______ tide (on any given day). (Remember to use only one word per blank.)
high
low
A mixed-tide system has two different high-water levels and two different low-water levels per day. The highs are called _______ high water, and the lows are called _________ high water.
higher,
lower
Currents in coastal waters associated with tides are called _______ currents.
tidal
___________ are caused by the gravitational attraction between Earth's oceans with the Sun and the Moon.
tides
Equilibrium tidal theory
Tides are mathematically ideal wave forms and behave uniformly.
Dynamic tidal analysis
Tides are natural and are modified by landmasses, basin geometry, and Earth's rotation.
A diurnal tide has ________ high and low tide(s) each day, whereas a semidiurnal tide has _________ high and low tide(s) each day.
one
two
True or false: The center of mass of the Earth-Moon system is exactly halfway between the two.
False- Because Earth is so much larger than the Moon, the center of mass is about 1700 km beneath Earth's surface.
What is the difference between low and high tides?
Low tide is the lowest height on the coast to which the tide reaches on a given day, and high tide is the highest point.
Rank the water levels of a mixed-tide system according to height. Put the highest water level on top.
higher high water
lower high water
higher low water
lower low water
As Earth rotates through the two water bulges created by gravity and inertia, any point on its surface will experience ______ tidal high(s) and ______ tidal low(s) per rotation.
two; two
The movement of water associated with flood and ebb tides is known as tidal ______.
currents
The centripetal force is constant and equal to the ______ force of the Sun or the Moon acting at Earth's center.
gravitational
What is the name of the method by which oceanographers study tides as they occur naturally?
Dynamic tidal analysis
Why is the Sun tide less influential to Earth than the Moon tide?
The Sun is very far away from Earth.
Where is the center of mass in the Earth-Moon system?
Approximately 1700 km beneath Earth's surface
What type of tide occurs when the Moon is in the positions marked by the straight arrows in this image?
Please give one word as your answer.
neap
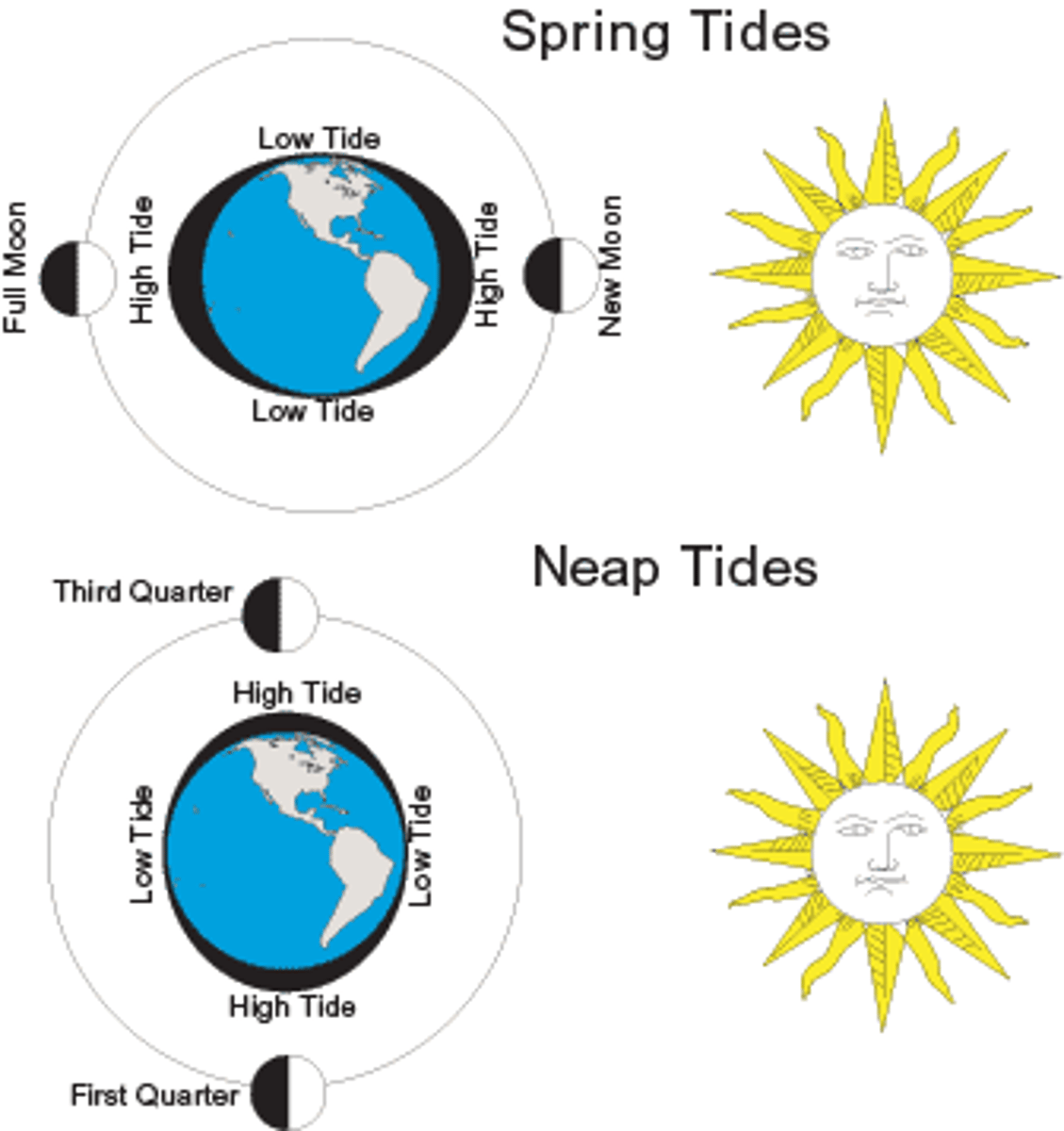
A declinational, or diurnal, tide includes ______ low tide(s) and ______ high tide(s) each day.
one; one
The two high and two low tides experienced by a point on Earth's surface, as it rotates through the water bulges created by inertia and gravity, result in a ______ pattern.
semidiurnal tide
The Sun's role in producing tides is greater during the Northern Hemisphere __________ because Earth is closer to the Sun at this time of year.
winter
The ______ tide wave is discontinuous, can be considered a shallow-water wave, and is impacted by the Coriolis effect.
natural
Which of the following statements correctly describe the Sun tide? (Choose all that apply.)
It is weaker than the Moon tide.
The tidal day of the Sun is shorter than the tidal day of the Moon.
Tidal motion occurs ______.
at all depths
spring tide
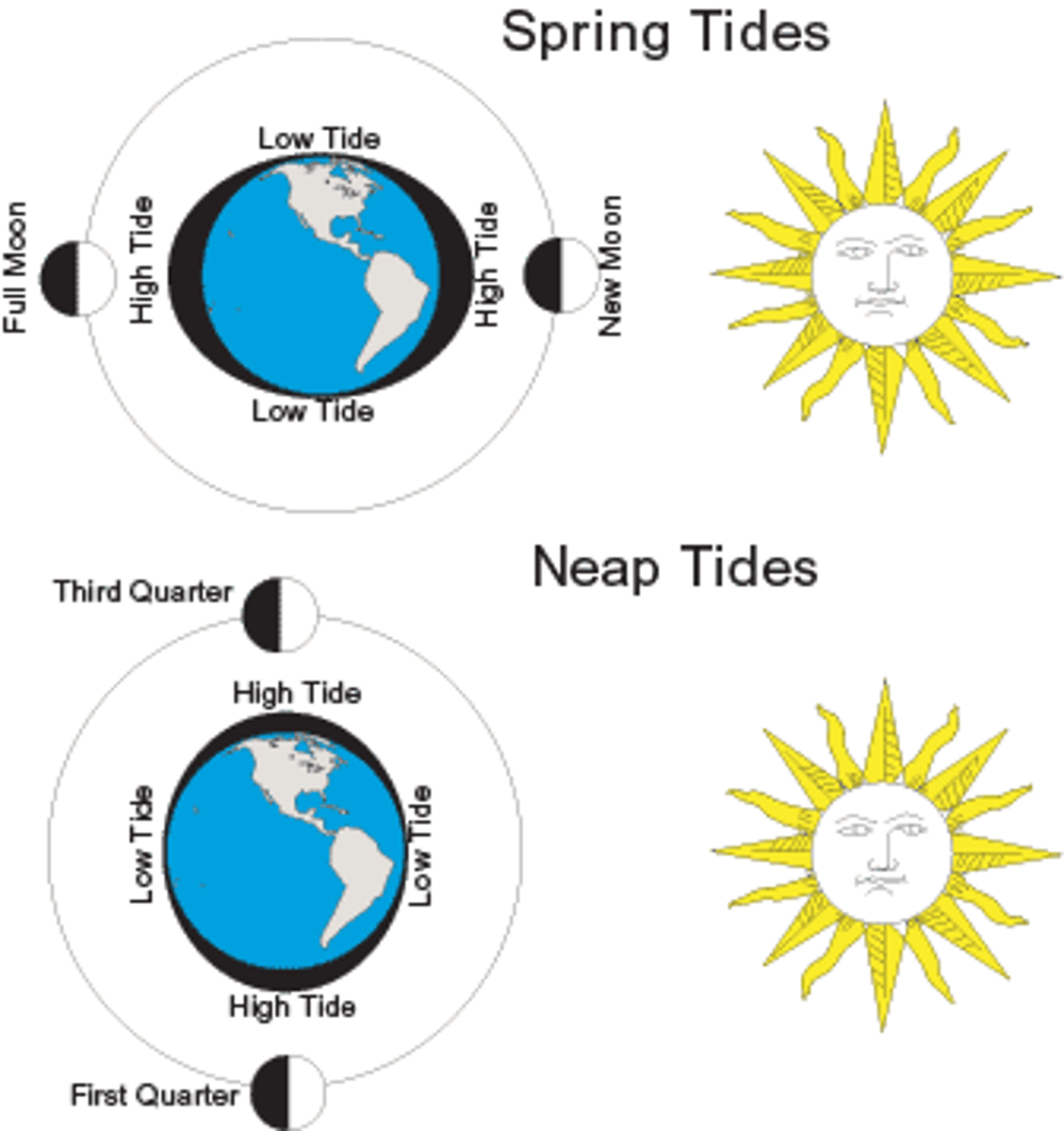
A declinational tide is also known as a ______ tide.
diurnal- Diurnal patterns occur once per day.
What do cotidal lines represent?
The location of the tide crest at set time intervals- The set time intervals are generally one hour apart.
Why does the Sun play a greater role as a tide producer in winter (Northern Hemisphere) than summer?
Earth is closer to the Sun during the Northern Hemisphere winter.
Due to ______, standing wave tide current movement is deflected to the right in the Northern Hemisphere, resulting in a clockwise motion of the water. As a result, the position of the high-tide crest moves counterclockwise.
the Coriolis effect
Which of the following factors describe the natural tide wave as compared to the water-covered model tide wave? (Select all that apply.)
The natural tide wave is discontinuous.
The natural tide wave can oscillate in ocean basins like a standing wave.
The Coriolis effect plays a role in natural tide wave behavior.
Ocean tides are ______, as they are the result of combining progressive and standing wave tides with diurnal and semidiurnal characteristics.
complex
True or false: Tidal motion only affects the uppermost portion of the ocean.
False- TIdal motion at depth can produce internal waves.
The __________ lines shown on this image mark the locations of the tide crest at set time intervals.
cotidal
______ is famous for its large tidal range of 11.7 m (35 ft), which is created by the matching of the tidal period to this narrow bay's natural oscillation period.
The Bay of Fundy- This large difference between high and low tides occurs at the head of the bay; at the bay's entrance, the range is only 2 m.
The standing wave tide in an ocean basin is changed by the Coriolis effect and results in the tide crest rotating ______ around an ocean basin and the tidal current rotating ______.
counterclockwise; clockwise
A tidal bore is a ______.
fast-moving, rising tide
Why is understanding ocean tides complex? (Select all that apply.)
They can be created by the combination of both standing and progressive waves.
They result from different types of tides interacting.
Accurate daily tide predictions are created using ______.
actual local measurements and astronomical data
The Bay of Fundy is famous for ______.
having a very large tidal range
What types of information are provided by a tide table? (Select all that apply.)
The water levels of high and low water
Date and time of high-water levels
Date and time of low-water levels
A tidal _________ is created when a fast-moving rising tide moves toward land in the form of a spilling wave front.
bore
Who are the primary users of tidal current tables published for coastal locations?
Boaters and sailors
Large amounts of energy can be obtained from tides in places that have ______ tidal ranges or narrow channels with ______ tidal currents.
large; swift
Why are astronomical data alone not enough to predict daily tides?
There are so many specific factors to consider that actual measurements are needed.
Tidal power is ______ when compared to other energy sources because of the complicated installation process and the periodic low-power production times.
expensive
____________ __________ give the dates, times, and high- and low-water levels at primary tide stations.
tide tables
To create ______, currents in important locations are measured and then studied to determine how they are related to tidal changes.
tidal current tables
If you were interested in creating energy from tides, which of the following two situations would you look for?
A location with a large tidal range
A place with swift tidal currents in a narrow channel
Choose the reasons why tidal power generally is more expensive to generate than other energy sources. (Select all that apply.)
-The tides do not continuously have the same amount of energy available.
-The locations that work to create tidal power are often remote.
-The installation of the power systems can be complicated.