AP EXAM GRIND
1/570
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
571 Terms
Hypothesis
tentative explanation - must be FALSIFIABLE - able to be supported or rejected
Operational Definition
clear, precise, quantifiable definition of your variables -allows replication and collection ofreliable data
Qualitative data
descriptive data (eye color)
Quantitative data
numerical data - IDEAL and necessary for statistics
Population
everyone the research could apply to
Sample
the people (or person) specifically chosen for your study
Correlation
Correlation doesn't = causation
Directionality problem
which direction does the correlation go?
(depression cause low self-esteem, low self-esteem causes depression, or a 3rd
variable?)
3
3rd variable problem
diff. variable is responsible for relationship (ice cream
and murder)
Positive Correlation
variables increase & decrease together
Negative Correlation
as one variable increases the other decreases
Correlation Coefficient
The stronger the # the stronger the
relationship REGARDLESS of the
pos/neg sign. Cannot be < or > than 1.
o Stronger relationships = tighter clusters
on graph
Experiments
purposefully manipulate variables to determine cause/effect
Variables
o Independent Variable: purposefully
altered by researcher to look for effect
▪ Experimental Group: received the
treatment (part of the IV); can have
multiple exp, groups
▪ Control Group: placebo, baseline
(part of the IV); can only have 1
o Dependent Variable: measured variable
(is DEPENDENT on the independent
Placebo Effect:
any observed effect on a behv. That is "caused" by the placebo (shows effectiveness of exp. Treatment). Usually fixed w/ blinded studies
Double-Blind:
Exp. where neither the participant or the experimenter are aware of which condition people are assigned to (drug studies)
Single-blind
only participant blind -
used if experimenter can't be blind
(gender, age, etc)
Confound
error/ flaw in study that is accidentally introduced (can be called a confounding variable)
Random Assignment
assigns participants to either control or experimental group at random -increase chance of equal representation among groups (spreads the lefties across both groups) - allows you to say Cause / Effect
naturalistic observation
observe ppl in their natural settings
case study
Studies ONE person (usually) in great detail
meta-analysis
combines multiple studies to increase sample size and examine effect sizes
Descriptive statistics
show shape of the data
Measures of Central Tendency
▪Mean: Average (use in
normal distribution)
▪Median: Middle # (use in
skewed distribution)
▪Mode: occurs most often
• Bimodal - has two
modes - usually
indicates good bad
scores
Skew
• Skews - created by outliers
o Neg skew = mean is to the left (neg side), mode is to the right
o Pos skew = mean is to the right
Measure of variation
• Range - distance by smallest and biggest #
• Standard deviation - avg. amount the scores are spread from the mean
(bigger # = more spread)
inferential statistics
establishes significance (meaningfulness)
STATISTICAL SIGNIFANCE
results not due to chance, exp.manipulation caused the difference in means
▪ p<.05 = stat. sig, smaller = better
EFFECT SIZE
data has practical significance - bigger = better
Ethical Guidelines
o Confidentiality: names kept secret
o Informed Consent: must agree to be
part of study
o Informed assent - minors AND their
parents must agree
o Debriefing: must be told the true
purpose of the study (done after for
deception)
o Deception must be warranted
o No harm- mental/physical
o IRB approval
Survey
usually turned into correlation- subject to self report bias - errors when collect survey data due to:
Social desirability
ppl lie to look good
Wording effects
wording can change the results of a survey
Random Sample (selection)
method for choosing participants for your study - everyone has a chance to take part, increases generalizability
Representative Sample
Sample mimics the general pop. (ethnic, gender, age)
Convenience Sample
select participants on availability - less representative and
less generalizability this way
Sampling bias
sample isn't representative, due to conv. sampling
Cultural norms
behvs of a particular group can influence research results
Experimenter bias / Participant bias:
experimenter/participant expectations
influences the outcome
Cognitive bias
bias in thinking/judgment
o Confirmation bias
find info that supports our preexisting beliefs
Overconfidence
overestimate our
knowledge / abilities
Hindsight bias
"I knew it all along"
Hawthorne effect
ppl change behavior when watched
Lens of HEREDITY VS ENVIRONMENT
Evolutionary psycs - study how natural
selection influences behavior
Heredity (nature)
How genes influence your behavior.
Genome
all of an organism's genetic material
Environment (nurture)
how outside situations influence your behavior (school)
o Twin / Adoption Studies:
o Genetics: identical twin will have a higher
percentage of also developing a disease
o Environment: identical twins raised in
different environments show differences
NERVOUS SYSTEM
• CENTRAL NS: Brain and spinal cord
• PERIPHERAL NS: Rest of the NS -
relays to Central NS
Peripheral NS
o Somatic NS: Voluntary movement, has
sensory and motor neurons
o Autonomic NS: Involuntary organs
(heart, lungs, etc) - contains the:
▪ Sympathetic NS: fight/flight
(generally activates - exception
digestion)
▪ Parasympathetic NS: rest / digest
(generally inhibits - exception
digestion)
NEURON
Basic cell of the NS
Dendrites
Receive incoming NTs (little hair things)
Axon
Action potential travels down
Myelin Sheath
speeds up AP down axon, protects axon
Synapse
gap without neurons
SENSORY neurons
receive sense: signals from environ.-send signal to brain
MOTOR neurons
signals to move - send signals from brain
Interneurons
cells in spinal cord /brain responsible for reflex arc
Reflex arc
important stimuli skips the brain and routes through the spinal cord for immediate reactions (hand on a hot flame)
GLIA
support cells - give nutrients and clean up around neurons
Neurons Fire w/ an Action Potential
ions move across membrane sends an
electrical charge down the axon
Resting potential
neuron maintains a -70mv charge when not doing
anything
Depolarization
charge of neuron briefly switches from neg to pos; triggers the AP
Threshold of depolarization
stimulus strength must reach this point to start the AP
All or nothing principle
stimulus must trigger the AP past its threshold, but does not
increase the intensity or speed of the response (flush the
toilet)
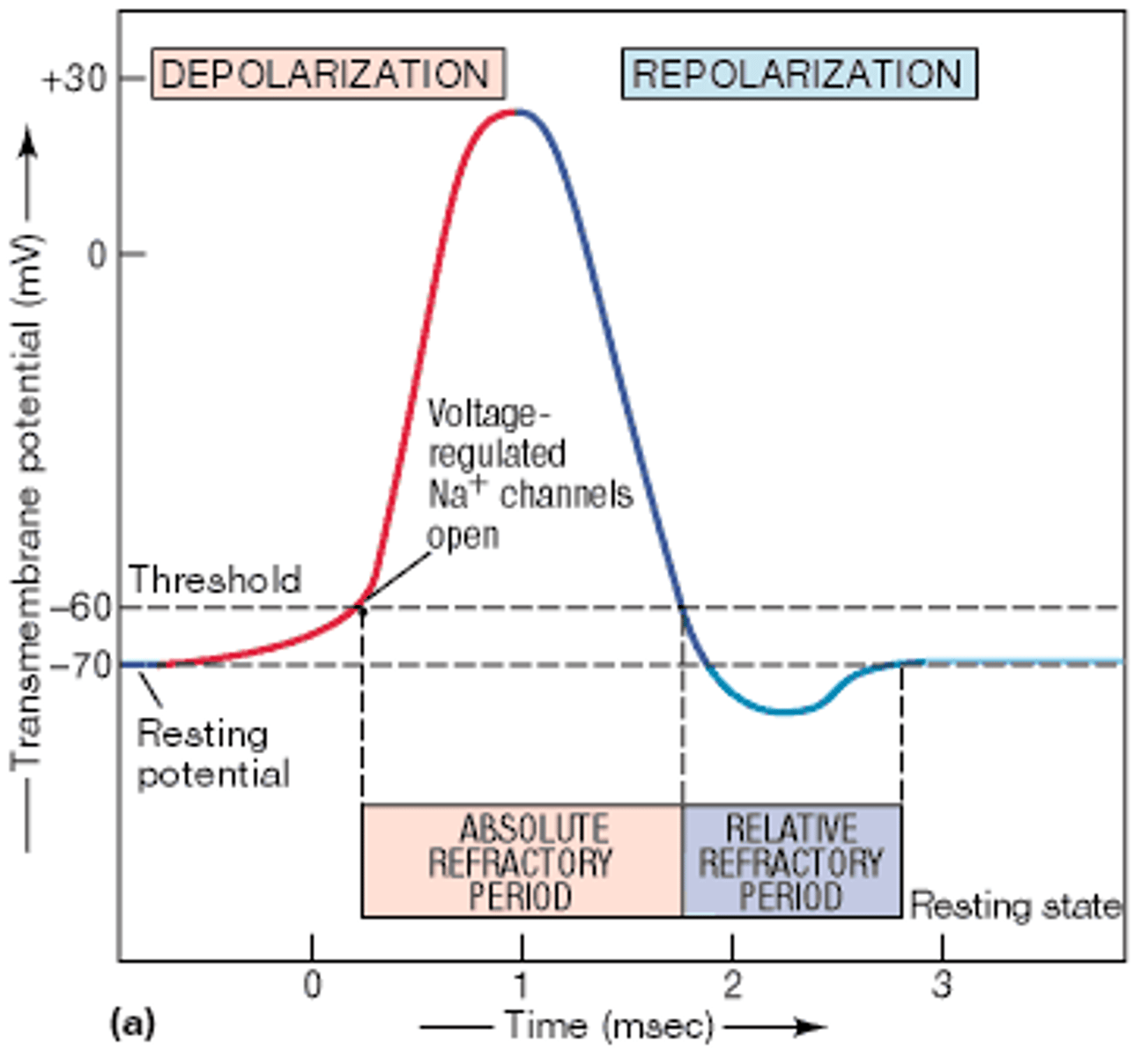
Refractory period
neuron must rest and reset before it can send another AP (toilet resets)
NEUROTRANSMITTERS (NT):
Chemicals released in synaptic gap, received by neurons.
Inhibitory
Stops AP
Excitatory
Causes next cell to fire
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
Glutamate
Major excitatory NT (glutes excite you!)
Dopamine
Reward (short term) &
fine movement - in hypothalamus,
assoc. w/ addiction
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Memory and movement -in hippocampus, assoc. w/ Alzheimer's
Norepinephrine
sympathetic NS
Endorphins
decrease pain
Substance P
pain regulation (abnormality increases pain and
inflammation)
HORMONES
if not in the nervous system, it's a hormone
Oxytocin
love, bonding, childbirth,
lactation
Adrenaline
fight/flight
Leptin
stops hunger
ghrelin
makes you hungry
Melatonin
sleep
• Agonist: drug that mimics a NT
drug that mimics a NT
Antagonist
drug that blocks a NT
Reuptake
Unused NTs are taken back up into the sending neuron.(antidepressants cause reuptake inhibition (block reuptake)
- treatment for depression
Depressants
Decrease NS activity (alcohol)
Stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions (caffeine and cocaine)
Hallucinogens
hallucinations and altered perceptions (Marijuana)
Opioids
relieve pain (endorphin agonists) (heroin)
Tolerance
Needing more of a drug to achieve the same effects
Addiction
must have it to avoid withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal
symptoms associated with sudden stoppage
Hind brain
- Cerebellum - movement, balance,
coordination, procedural memory
(walking a tightrope balancing a bell)
Brainstem
- Brainstem / Medulla - vital organs (HR,
BP, breathing)
- pons: bridge/relay
- Reticular activating system: alertness,
arousal, sleep, eye movement
Cerebral Cortex
higher order thought processes
- includes limbic system, lobes, corpus
callosum
Limbic System
▪ Amygdala: emotions, fear
▪ Hippocampus: episodic and semantic
memory (if you saw a hippo on
campus you'd remember it!)
▪ Hypothalamus: Reward/pleasure
center, eating behaviors - link to
endocrine system, homeostasis
▪ Thalamus: relay center for all but
smell
▪ Pituitary gland: talks w/ endocrine sys
and hypothalamus - release hormones
o Parietal Lobe: sensations and touch -
controls association areas - incudes:
• Somatosensory Cortex: map of our
touch receptors
• Temporal Lobe: hearing and face
recognition, language
vision
Frontal Lobe
decision making, planning, judgment, movement,
personality, language, executive function - includes the:
- Prefrontal cortex: front of frontal lobe - executive function
- Motor Cortex: back of frontal lobe - map of our motor receptors -controls skeletal movement