Final Study Guide
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
Which macromolecule is made up of amino acids?
A. Lipids; B. Carbohydrates; C. Protein; D. Nucleic Acids
C. Protein
Which macromolecule is made up of sugars, starches, and fiber?
A. Lipids; B. Carbohydrates; C. Protein; D. Nucleic Acids
B. Carbohydrates
Which macromolecule is made up of fats and oils?
A. Lipids; B. Carbohydrates; C. Protein; D. Nucleic Acids
A. Lipids
Which macromolecule is made up of nucleotides?
A. Lipids; B. Carbohydrates; C. Protein; D. Nucleic Acids
D. Nucleic acid
Which macromolecule makes up a cell membrane?
A. Lipids; B. Carbohydrates; C. Protein; D. Nucleic Acids
A. Lipids
Which macromolecule makes up butter?
A. Lipids; B. Carbohydrates; C. Protein; D. Nucleic Acids
A. Lipids
Which macromolecule makes up DNA?
A. Lipids; B. Carbohydrates; C. Protein; D. Nucleic Acids
D. Nucleic acid
What are the 5 steps of the scientific method
Observe
Hypothesize
Experiment
Analyze
Share
Describe the observation step of the scientific method
Use the 5 senses to note a detail, fact, or occurrence
Describe the hypothesis step of the scientific method
Develop a testable prediction based on prior observation and knowledge
Describe the experimentation step of the scientific method
Conduct experiment, with controls, repeat
Describe the analysis step of the scientific method
Evaluate findings, quantify data
Describe the sharing step of the scientific method
Share findings with like-minded individuals
How do enzymes speed up reactions?
Lowering activation energy

Identify how many protons, electrons, and neutrons nitrogen has
Protons- 7; Electrons- 7; Neutrons- 14

Identify how many protons, electrons, and neutrons phosphorus has
Protons- 15; Electrons- 15; Neutrons- 30
Is baking soda (pH 9) basic, acidic, or neutral?
Basic
Is vinegar (pH 2.5) basic, acidic, or neutral?
Acidic
Is water (pH 7) basic, acidic, or neutral?
Neutral
Which of the following determines how an atom interacts with other atoms?
A. Protons; B. Electrons; C. Neutrons
B. Electrons
Which of the following determine an atoms identity?
A. Protons; B. Electrons; C. Neutrons
A. Protons
Which of the following adds to an atoms weight but does not determine an atoms identity?
A. Protons; B. Electrons; C. Neutrons
C. Neutrons
What is peer review?
A process by which a group of experts evaluate a report and determine if it is high enough quality to publish in a scientific journal
What are the 5 properties that make water so amazing?
Adhesion, cohesion, high heat capacity, universal solvent, less dense in solid form
Which property of water makes most substances easily dissolvable in water?
Universal solvent
Which property of water means organisms can survive in liquid water below ice?
Less dense in solid form
Which property of water creates surface tension?
Cohesion
Which property of water makes water release a large amount of energy as it cools?
High heat capacity
Which property of water makes water able to move easily?
Adhesion
What type of bond does water make with other water molecules?
A. Ionic; B. Covalent; C. Hydrogen; D. Mutualistic
C. Hydrogen
What type of bond does hydrogen make with oxygen to form water molecules?
A. Ionic; B. Covalent; C. Hydrogen; D. Mutualistic
B. Covalent
Which of the following is NOT considered a lipid?
A. Steroids; B. Phospholipids; C. Cellulose; D. Lard
C. Cellulose
Which of the following is NOT considered a carbohydrate?
A. Sucrose; B. Chitin; C. Galactose; D. Phospholipids
D. Phospholipids
Which of the following is NOT a reason or cells to divide?
A. Growth; B. Reproduction; C. Replacing dead/damaged cells; D. Strength
D. Strength
Which of the following groups does NOT have a cell wall?
A. Bacteria; B. Plants; C. Fungi; D. Animals
D. Animals
Which type of cell division creates four genetically unique gametic daughter cells?
Meiosis
Which type of cell division creates two genetically identical somatic daughter cells?
Mitosis
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic shared by all living organisms?
A. Homeostasis; B. Growth; C. Breathing; D. Evolution; E. Producing waste
C. Breathing
True or False?
Cancer can be easily avoided once a cure is found
False
True or False?
Centrioles control spindle fibers during mitosis
True
True or False?
DNA is replicated during the G1 phase of interphase
False
True or False?
Cancer occurs when cells divide uncontrollably during meiosis
False
In DNA, the D stands for what?
A. Dextrose; B. Deoxyribose; C. Diamer sucrose
B. Deoxyribose
Under what circumstances does cancer occur?
A. Mutations build up knocking out checkpoints and tumor suppressing genes
B. When you are of advanced age
C. Cell division occurs out of control
D. All of the above
E. A&C only
E. A&C only
What kind of fat is liquid at room temp, and includes kinked hydrocarbon chains with one or more single or double bonds?
A. Saturated; B. Unsaturated; C. Trans; D. Hydrogenated
B. Unsaturated
What kind of fat is solid at room temp, and includes unkinked hydrocarbon chains with single bonds only?
A. Saturated; B. Unsaturated; C. Trans; D. Hydrogenated
B. Saturated
What part of the cell does a prokaryotic cell lack?
A. Ribosomes; B. Cell wall; C. Cell membrane; D. Golgi apparatus
D. Golgi apparatus
Why?
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles
Which if the following is NOT present in all cells?
A. Nucleus; B. DNA; C. Ribosomes; D. Cell membranes
A. Nucleus
Why?
Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus
What part of the cell processes fats, sugars, and toxins?
A. Rough ER; B. Smooth ER; C.Mitochondria; D. Golgi apparatus
B. Smooth ER
Which of the following is true of enzymes?
A. They are a class of proteins
B. They speed up chemical reactions
C. They are made of ribosomes
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
True or False?
According to the currently accepted definition of life, viruses are considered living
False
True or False?
Bias is hoping for a particular outcome
True
True or False?
Running an experiment once or twice is sufficient for accurate data
False
True or False?
A control group is the group being manipulated to test for an outcome
False
True or False?
In a double blind experiment, neither the experimenter nor the participant know who is in the test group or placebo group
True
Which of the following is an example of homeostasis?
A. A fungus attacking a population of insects that has grown out of control
B. Consuming an excessive amount of pizza
C. A bird excreting a salty tear to lower the body’s salt content
D. An exterminator killing pests in a home
C. A bird excreting a salty tear to lower the body’s salt content
Which subatomic particle is negatively charged, and can be passed or shared between atoms?
A. Protons; B. Electrons; C. Neutrons
B. Electrons
Which subatomic particle is positively charged?
A. Protons; B. Electrons; C. Neutrons
A. Protons
Which subatomic particle has a neutral charge?
A. Protons; B. Electrons; C. Neutrons
Neutrons
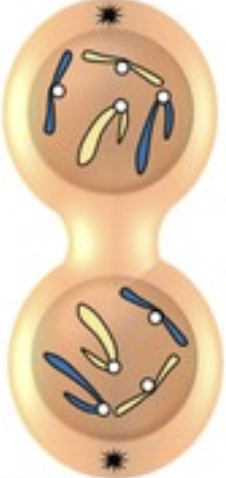
Name this phase of mitosis
Telophase
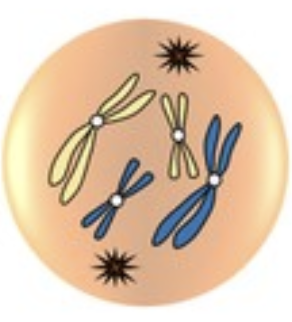
Name this phase of mitosis
Prophase
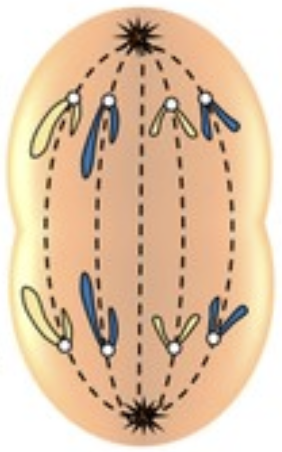
Name this phase of mitosis
Anaphase
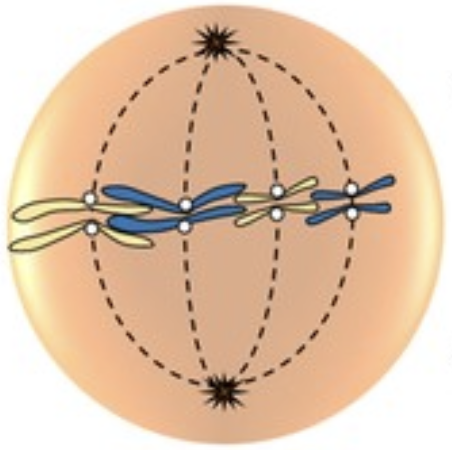
Name this phase of mitosis
Metaphase
List in order of magnitude:
Egg cell, mitochondria, giraffe, carbon atom, adenine molecule, basketball
Carbon, adenine, mitochondria, egg cell, basketball, giraffe
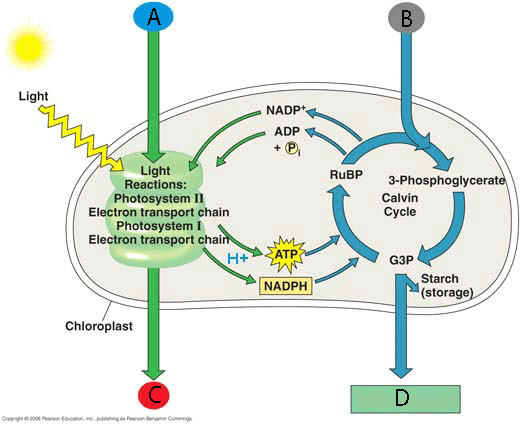
Label the photosynthesis diagram with the following; Oxygen (O2), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Glucose (C6H12O6), Water (H2O)
A- Water (H2O)
B- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
C- Oxygen (O2)
D- Glucose (C6H12O6)
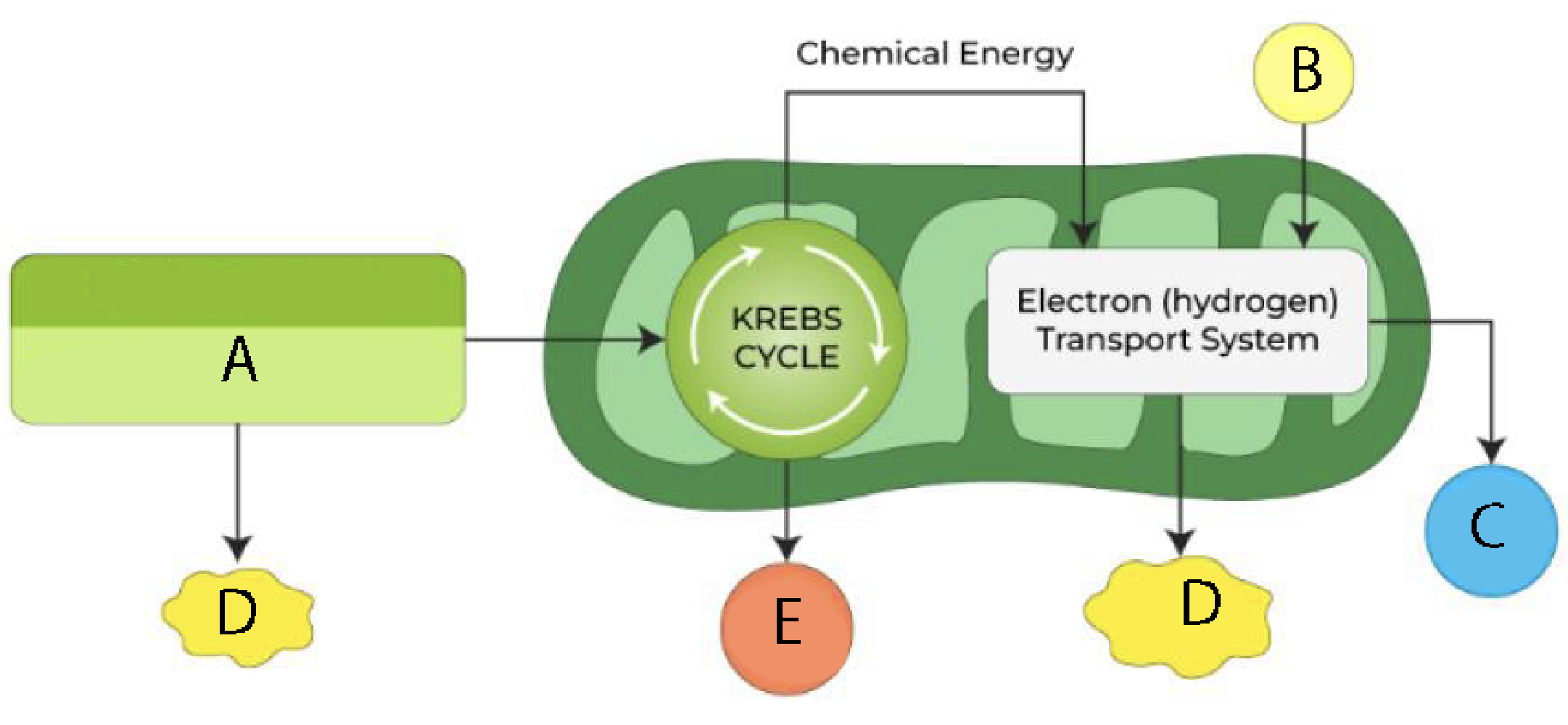
Label the cellular respiration diagram with the following: Oxygen (O2), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Glucose (C6H12O6), Water (H2O), ATP
A- Glucose
B- Oxygen (O2)
C- Water (H2O)
D- ATP
E- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
What is the function of a ribosome?
Protein synthesis
What is the function of a cell wall?
Structure in plant cells
What is the function of a cell membrane?
Protect genetic information
What is the function of an organelle?
Functional unit of the cell
What is the function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
Processing nutrients, detoxifying poisons/alcohol
What is the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Management of intracellular and extracellular transportation
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
“Mailroom” distribution center
What is the function of the vesicles?
Packaging extracellular material
What is the function of the central vacuole?
Water supply for plant cells
What is the function of the chloroplasts?
Energy processing for plant cells
Who is the less credited co-father of evolution?
A. Charles Darwin; B. Alfred Wallace; C. Jean Batiste Lamarck; D. Charles Lyell; E. Gregor Mendel
B. Alfred Wallace
Who came up with the uniformitarianism “use it or lose it” theory of evolution?
A. Charles Darwin; B. Alfred Wallace; C. Jean Batiste Lamarck; D. Charles Lyell; E. Gregor Mendel
C. Jean Batiste Lamarck
Who is considered the father of inheritance?
A. Charles Darwin; B. Alfred Wallace; C. Jean Batiste Lamarck; D. Charles Lyell; E. Gregor Mendel
E. Gregor Mendel
Who is the often credited co-founder of evolution?
A. Charles Darwin; B. Alfred Wallace; C. Jean Batiste Lamarck; D. Charles Lyell; E. Gregor Mendel
A. Charles Darwin
Who is the geologist who asserted the theory that the Earth is millions of years old?
A. Charles Darwin; B. Alfred Wallace; C. Jean Batiste Lamarck; D. Charles Lyell; E. Gregor Mendel
D. Charles Lyell
Put the following elements of protein synthesis in order: transcription, translation, RNA, DNA
DNA → Transcription → RNA → Translation
What are the 3 main differences between DNA and RNA
DNA is double-stranded; RNA is single-stranded
DNA is deoxyribose; RNA is ribose
DNA has thymine; RNA has uracil
Create a complementary strand: ACAGTCGAT
TGTCAGCTA
Create an mRNA strand: ACAGTCGAT
UGUCAGCUA
What is the functional role of RNA polymerase?
A. Extracting exons
B. Transcription
C. Translation
D. Deoxyribose nucleic acid duplication
B. Transcription
What is the functional role of DNA polymerase?
A. Extracting exons
B. Transcription
C. Translation
D. Deoxyribose nucleic acid duplication
D. Deoxyribose nucleic acid duplication
What is the functional role of a spliceosome?
A. Extracting exons
B. Transcription
C. Translation
D. Deoxyribose nucleic acid duplication
A. Extracting exons
What is the functional role of a ribosome?
A. Extracting exons
B. Transcription
C. Translation
D. Deoxyribose nucleic acid duplication
C. Translation
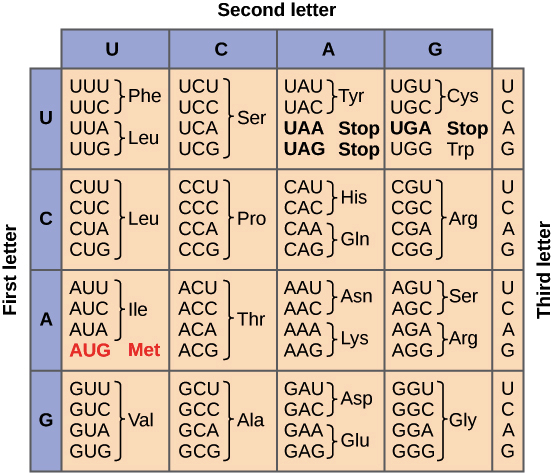
Convert the mRNA strand into an amino acid chain :
AUGGUUGAGCGUACAUAUUGA
MET-VAL-GLU-ARG-THR-TYR-STOP
What kind of selection created the corn we have today?
A. Natural selection
B. Sexual selection
C. Artificial selection
D. Acquired selection
C. Artificial selection
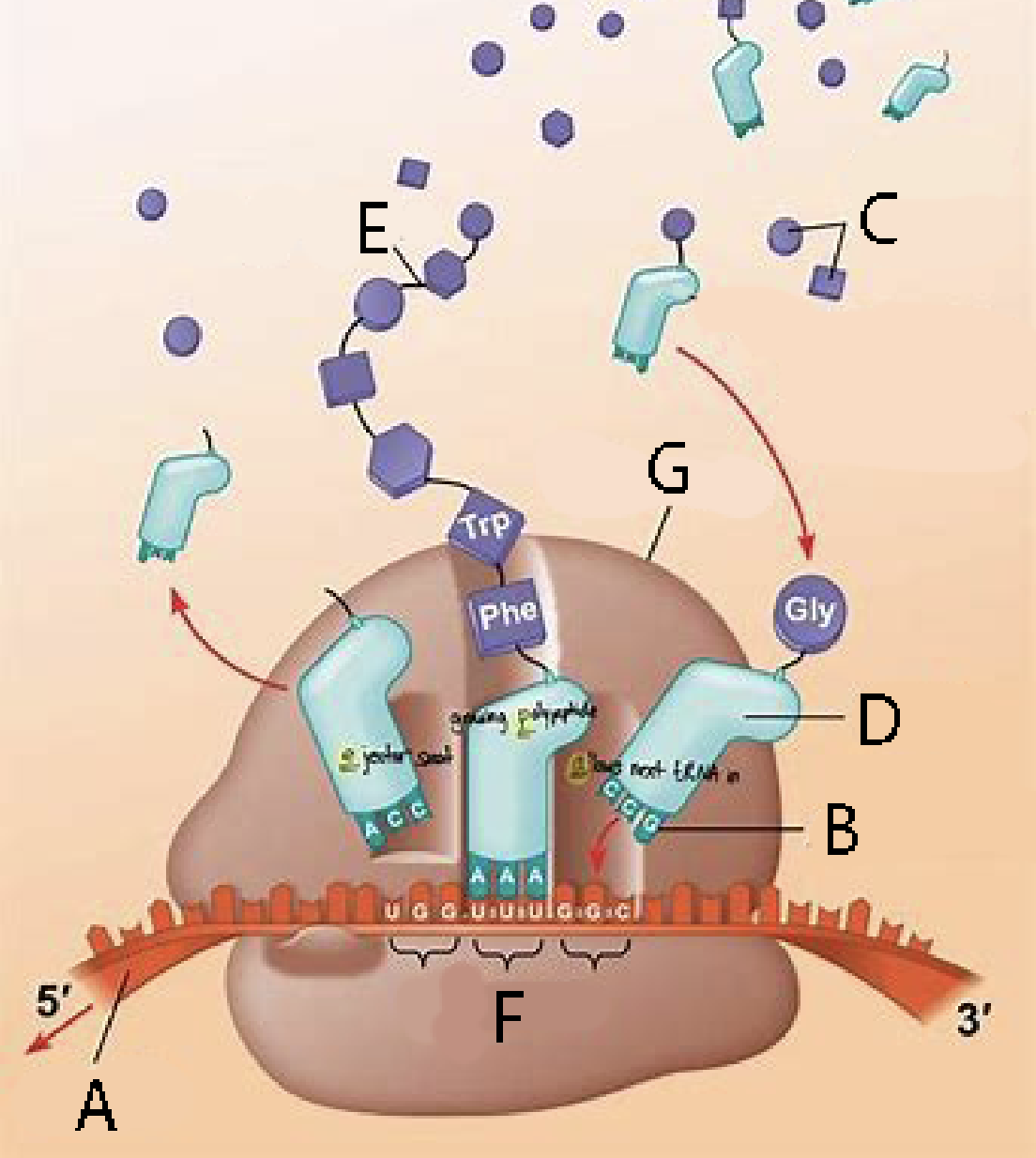
Label the diagram of translation with one of the following:
mRNA
tRNA
Codon
Anticodon
Amino acids
Polypeptide (amino acid chain)
Ribosome
A. mRNA
B. Anticodon
C. Amino acids
D. tRNA
E. Polypeptide (amino acid chain)
F. Codon
G. Ribosome
Order the following by size; gene, chromosome, nucleotide, codon
nucleotide, codon, gene, chromosome
Droughts and floods are considered which kind of stressor that encourages natural selection?
A. Predation; B. Sexual Selection; C. Physiological Stress; D. Competition
C. Physiological Stress
Who published “On the Origin of Species” in 1859, first describing natural selection?
Charles Darwin
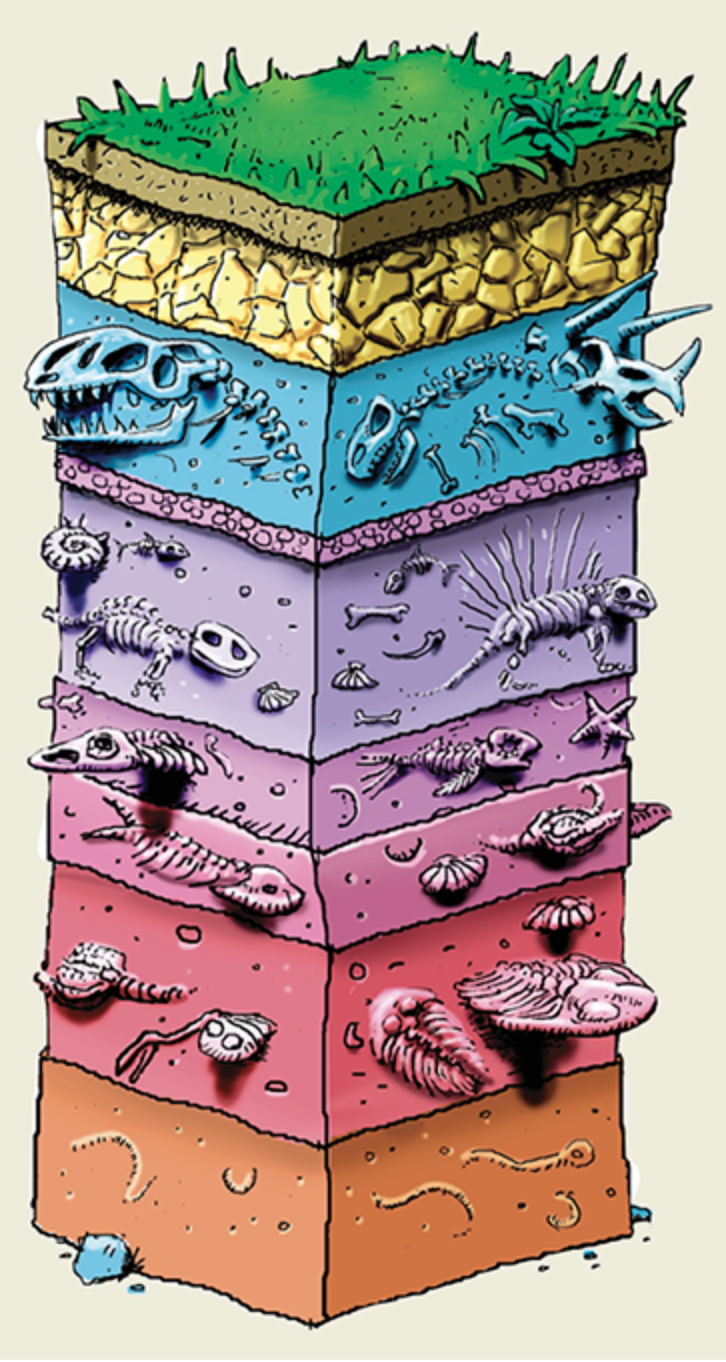
What type of evolutionary evidence is this?
The fossil record
Which type of evolutionary evidence does the following definition describe: “Large events that wipe out many creatures, allowing a new set of living beings to flourish”
A. Catastrophism
B. Uniformitarianism
A. Catastrophism
Which type of evolutionary evidence does the following definition describe: “Slow, gradual changes continuously amounting to large changes over large periods of time”
A. Catastrophism
B. Uniformitarianism
B. Uniformitarianism