Iran Notes (unfinished)
5.0(2)Studied by 9 people
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:16 AM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards

What is the official name of Iran?
Islamic Republic of Iran
2
New cards
List three things that make Iran unique
1. Geography
2. Islamism
3. Foreign domination of proud and ancient civilization
3
New cards
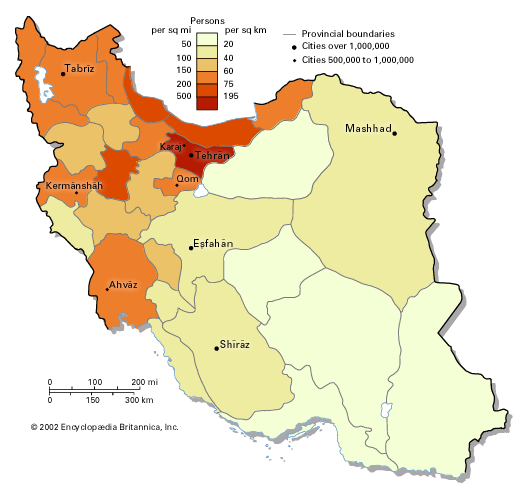
Explain how its geography makes Iran unique
* Much of territory is inhospitable
* Population concentrated in arable areas in the northwest
* Frequent invasions
* Central location and easy access due to lack of natural barriers
* Massive oil deposits
* Focused on resource extraction
* Rentier-state
* Geopolitically important for other states
* Population concentrated in arable areas in the northwest
* Frequent invasions
* Central location and easy access due to lack of natural barriers
* Massive oil deposits
* Focused on resource extraction
* Rentier-state
* Geopolitically important for other states
4
New cards
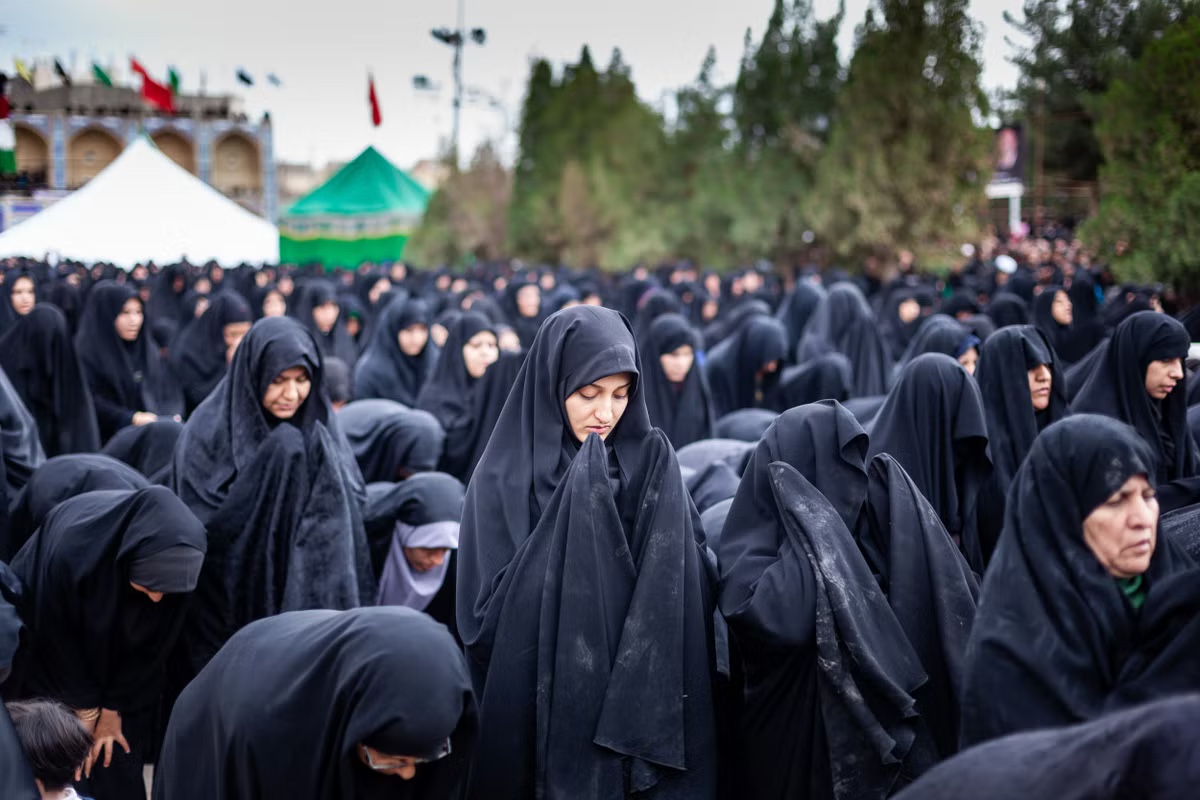

Explain how Islamism makes Iran unique
* Traditionally Shia
* Khomenei created a %%theocratic system%% rooted in Islamism
* Fundamentalist Islam
* Literal reading of Koran
* Scripture-based rules known as “%%Sharia%%”
* Socialist-style integrated %%church-state%%
* %%Clerics%% participate directly in politics
* Oversee elected politicians
* Root many laws in Koranic morality
* Khomenei created a %%theocratic system%% rooted in Islamism
* Fundamentalist Islam
* Literal reading of Koran
* Scripture-based rules known as “%%Sharia%%”
* Socialist-style integrated %%church-state%%
* %%Clerics%% participate directly in politics
* Oversee elected politicians
* Root many laws in Koranic morality
5
New cards

Explain how the foreign domination of a proud and ancient civilization made Iran unique
* %%Nationalistic%% and proud of accomplishments
* %%Persian empire%% once world’s largest land empire
* Desire to restore former glory and bitterly resent foreign interference
* 1800s: Under growing pressure from European powers
* 1900-1940: %%Controlled by Britsh and Russians%%
* Force Iran to grant them rights to oil
* 1950s-1979: Strong %%American influence%%
* Support Shah
* Suppress Islamism and liberal political opposition
* Strong nationalist, anti-foreign sentiments remain today
* As a result, Iranians resent foreign interference
* %%Persian empire%% once world’s largest land empire
* Desire to restore former glory and bitterly resent foreign interference
* 1800s: Under growing pressure from European powers
* 1900-1940: %%Controlled by Britsh and Russians%%
* Force Iran to grant them rights to oil
* 1950s-1979: Strong %%American influence%%
* Support Shah
* Suppress Islamism and liberal political opposition
* Strong nationalist, anti-foreign sentiments remain today
* As a result, Iranians resent foreign interference
6
New cards
Who controlled Iran from 1900-1940s, and who controlled Iran from 1950s-1979?
* 1900-1940s: Britain and Russia
* 1950s-1979: America
* 1950s-1979: America
7
New cards
Who introduced a theocratic system in Iran?
Khomeini
8
New cards
What grows influence increases on Iran from the 1800s to the 1940s?
The Western powers, US, UK, Russia, eager for access to oil
9
New cards
Who rules Iran before 1979?
* Monarchs known as Shahs
* Increasingly secular
* Increasingly secular
10
New cards
What happened in 1906?
* Iranian elites force the Shahs to introduce the following changes:
* Limited democratic reforms, including the creation of a parliament
* Economic reforms
* Social modernizations
* Limited democratic reforms, including the creation of a parliament
* Economic reforms
* Social modernizations
11
New cards
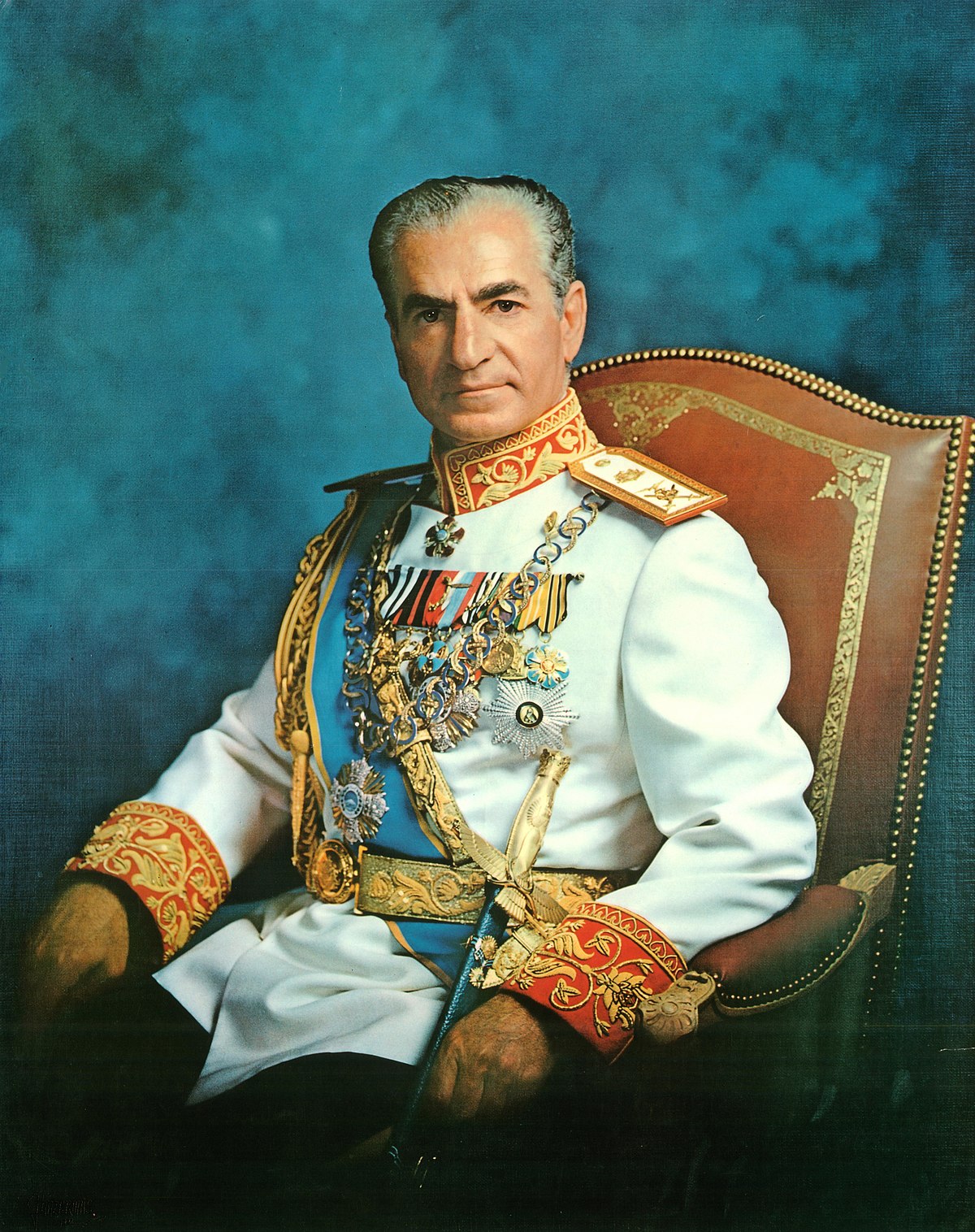

What happened in 1953?
* Rise in nationalism and wish for independence from West
* PM Mossadegh threatens to nationalize the oil industry and expel foreign companies
* In response, US and UK overthrow Mossadegh and restore power of Western-friendly Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi
* PM Mossadegh threatens to nationalize the oil industry and expel foreign companies
* In response, US and UK overthrow Mossadegh and restore power of Western-friendly Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi
12
New cards
Who was the last Shah and when did his rule end
* Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi
* 1975
* 1975
13
New cards
What happened in 1975?
* __Islamic Revolution__
* Inspired by cleric Khomenei’s rhetoric, young radicals protest Western influence
* Protests turn into revolution
* Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi flees
* Khomeini - formerly exiled - returns and creates theocracy by re-writing constitution
* Secular ideas purged
* Inspired by cleric Khomenei’s rhetoric, young radicals protest Western influence
* Protests turn into revolution
* Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi flees
* Khomeini - formerly exiled - returns and creates theocracy by re-writing constitution
* Secular ideas purged
14
New cards
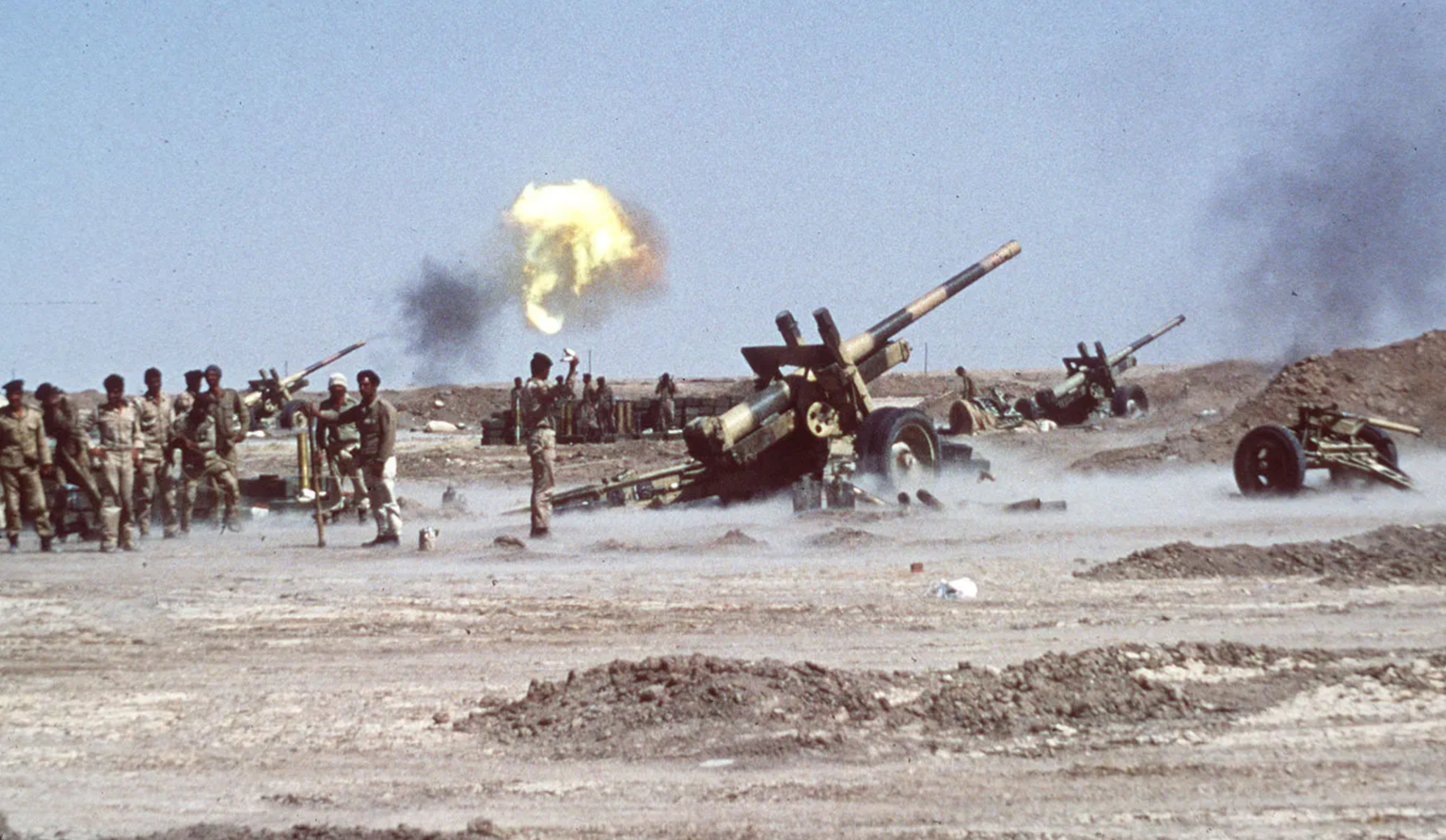

What happened from 1980 to 1988?
__Iran-Iraq War__
* Iraq fails to conquer Iran’s rich oil deposits
* 1 million Iranian casualties
* United Iranians behind new theocratic leadership
* Iraq fails to conquer Iran’s rich oil deposits
* 1 million Iranian casualties
* United Iranians behind new theocratic leadership
15
New cards
What happened between 1997 and 2003?
\
__Tehran Spring__
* Khomeini dies in 1989
* Steady loosening of social and political restrictions leads to victory of reformists in 1997 elections
* Under president Khatami, the strict behavioural laws are loosened further, more newspaper emerge and more public criticism is allowed
__Tehran Spring__
* Khomeini dies in 1989
* Steady loosening of social and political restrictions leads to victory of reformists in 1997 elections
* Under president Khatami, the strict behavioural laws are loosened further, more newspaper emerge and more public criticism is allowed
16
New cards

What happened in 2003?
* Ahmadinejad is elected as mayor of Tehran
* Hardline reactionaries - worried by reforms of Khatami - take over
* Outspoken newspapers forced to shut down, stricter social restrictions restored, reformers arrested or harassed
* Hardline reactionaries - worried by reforms of Khatami - take over
* Outspoken newspapers forced to shut down, stricter social restrictions restored, reformers arrested or harassed
17
New cards

What happened in 2009?
__Ahmadinejad regains presidency__
* Significant fraud reported
* Dissatisfied youth protests seriously challenge regime’s legitimacy
* Brutal crackdown
* Significant fraud reported
* Dissatisfied youth protests seriously challenge regime’s legitimacy
* Brutal crackdown
18
New cards
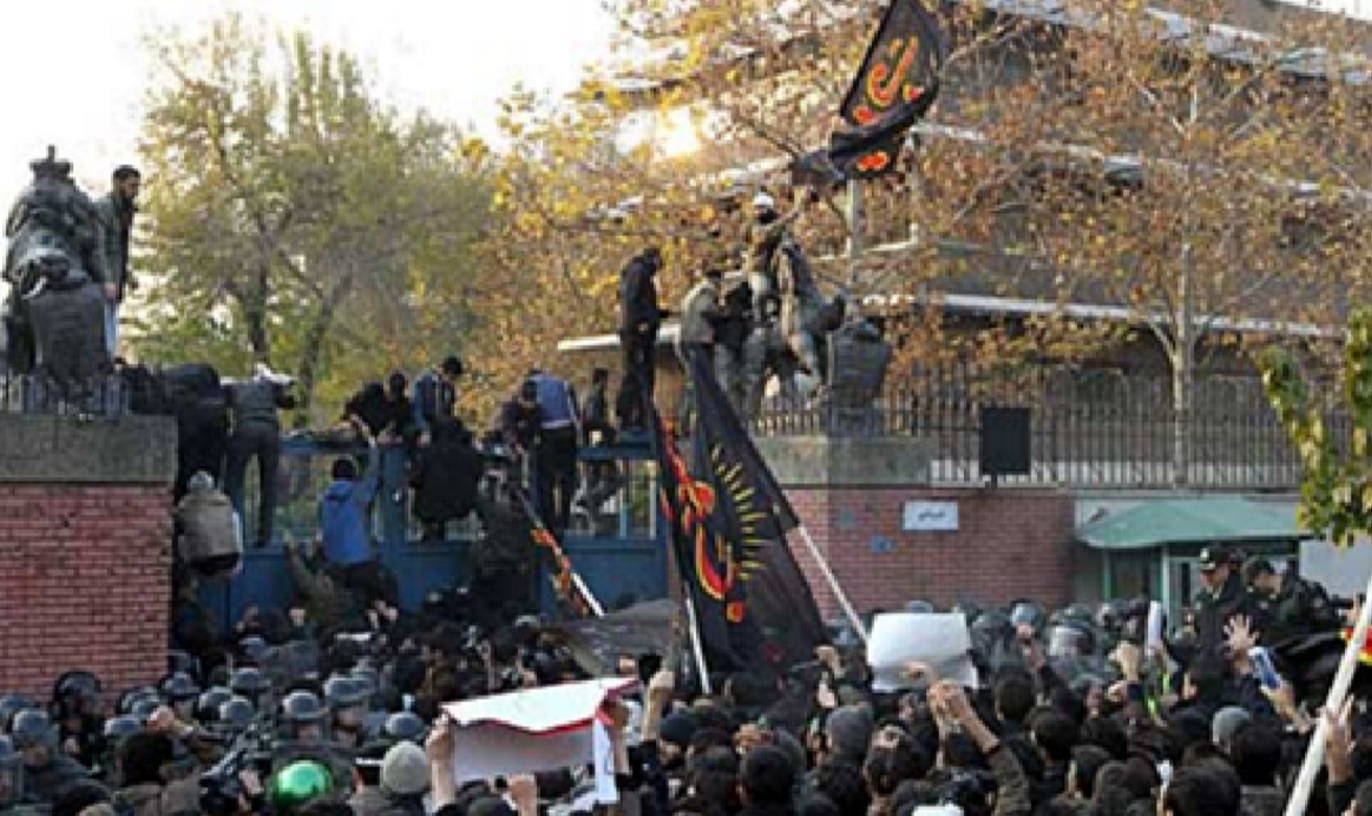
Describe the impact of the Arab Spring in Iran
* Iran was rocked by events in Tunisia and Egypt
* However, authorities were prepared and cut off internet services to prevent coordinated protests
* Protesters who did make it to the streets were arrested, beaten or killed
* Government-sponsored protests were encouraged to focus on Britain’s sanctions over nuclear programme
* UK’s embassy stormed while police watched
* However, authorities were prepared and cut off internet services to prevent coordinated protests
* Protesters who did make it to the streets were arrested, beaten or killed
* Government-sponsored protests were encouraged to focus on Britain’s sanctions over nuclear programme
* UK’s embassy stormed while police watched
19
New cards
Describe the current domestic situation in Iran
* Reformists continue to be restricted, harassed, jailed and purged from government institutions
* Divide between westernized urban youth and more conservative rural population
* Surprise election of relatively moderate conservative president Rouhani in 2013 may indicate a subtle shift away from the extremism of Ahmedinejad
* Wants to build ties with West
* Tentative nuclear deal reached with his support
* New hard-line president Raisi favoured by Khamenei
* Citizens’ voice who want social reform and engagement with the outside world not heard
* Divide between westernized urban youth and more conservative rural population
* Surprise election of relatively moderate conservative president Rouhani in 2013 may indicate a subtle shift away from the extremism of Ahmedinejad
* Wants to build ties with West
* Tentative nuclear deal reached with his support
* New hard-line president Raisi favoured by Khamenei
* Citizens’ voice who want social reform and engagement with the outside world not heard
20
New cards
Describe Iran’s international relations
* Relationship with West extremely tense because of nuclear weapons development
* Threats by US and Israel to attack and eliminate nuclear programme
* Threats by US and Israel to attack and eliminate nuclear programme
21
New cards
Describe the level of concentration of power in Iran’s government
Highly centralized unitary state with a single, powerful central government
22
New cards
When and by whom was the current constitution introduced?
By Khomeini in 1979
23
New cards
Iran’s institutions fulfill one or both of the following roles
Democratic and/or religious
24
New cards
What two types of law are present in Iran?
* Sharia
* Religious law based on Mohammed and Koran
* Qanun
* Secular code law created by Majles
* Religious law based on Mohammed and Koran
* Qanun
* Secular code law created by Majles
25
New cards
Describe the Assembly of Religious Experts
* Half democratic and half religious
* 86 members elected by citizens for 8-year terms
* Guardian Council can reject candidates
* Meet for one week a year
* Choose supreme leader and can technically also dismiss him
* 86 members elected by citizens for 8-year terms
* Guardian Council can reject candidates
* Meet for one week a year
* Choose supreme leader and can technically also dismiss him
26
New cards
Describe the Supreme Leader
* Top religious and political institution
* Head of state and church and chief executive
* “Faqih”
* Ultimate interpreter and defender of Shariah
* Islamic tradition of “Jurist’s Guardianship”; responsibility as guardian of poor and marginalized
* Oversees all of society
* Expected to champion rights of ordinary people
* Appointed for life by Assembly of Religious Experts
* Head of state and church and chief executive
* “Faqih”
* Ultimate interpreter and defender of Shariah
* Islamic tradition of “Jurist’s Guardianship”; responsibility as guardian of poor and marginalized
* Oversees all of society
* Expected to champion rights of ordinary people
* Appointed for life by Assembly of Religious Experts
27
New cards
Describe what the Supreme Leader is empowered to do
* Decide what presidential candidates can run
* Dismiss president
* Command military and security forces and declare war
* Appoint top bureaucrats and judicial officials
* Appoint 6 out of 12 members of Guardian council
* Ensure government runs smoothly
* Dismiss president
* Command military and security forces and declare war
* Appoint top bureaucrats and judicial officials
* Appoint 6 out of 12 members of Guardian council
* Ensure government runs smoothly
28
New cards
Describe the Guardian Council
* Key religious institution that oversees government and society
* Oversees Majles and can veto legislation
* 12 members
* 6 appointed by Supreme Leader
* 6 appointed by Head of Judiciary and approved by Majles
* Deeply conservative
* Can disqualify presidential and parliamentary candidates
* Oversees Majles and can veto legislation
* 12 members
* 6 appointed by Supreme Leader
* 6 appointed by Head of Judiciary and approved by Majles
* Deeply conservative
* Can disqualify presidential and parliamentary candidates
29
New cards
What is the Guardian Council empowered to do
* Interpret constitution and Shariah
* Review actions by other institutions and laws passed by Majles
* Approve or reject all candidates for elected offices
* Review actions by other institutions and laws passed by Majles
* Approve or reject all candidates for elected offices
30
New cards
Describe the Majles
* Lower legislative house
* One of Iran’s democratic institutions
* 290 members elected through SMD for 4-year terms
* Powers
* Create legislation (Qanun)
* Approve state budget, appointments and treaties
* Approve or dismiss cabinet members
* Approve appointment of 6 of twelve members of Guardian council
* Limitations
* Cannot impeach president, Supreme Leader, Guardian Council or Expediency Council
* Subject to Guardian Council approval
* Laws must respect Sharia and are reviewed by Guardian Council and Supreme Leader
* Some argue that limits make it rubber-stamp role
* Dominated by conservatives
* One of Iran’s democratic institutions
* 290 members elected through SMD for 4-year terms
* Powers
* Create legislation (Qanun)
* Approve state budget, appointments and treaties
* Approve or dismiss cabinet members
* Approve appointment of 6 of twelve members of Guardian council
* Limitations
* Cannot impeach president, Supreme Leader, Guardian Council or Expediency Council
* Subject to Guardian Council approval
* Laws must respect Sharia and are reviewed by Guardian Council and Supreme Leader
* Some argue that limits make it rubber-stamp role
* Dominated by conservatives
31
New cards
Describe the Expediency Council
* Religious role
* Oversees democratic Majles
* 32 members appointed by Supreme Leader
* Most powerful men in Iran
* Upper house
* Can initiate own legislation and review Majles’ legislation
* Oversees democratic Majles
* 32 members appointed by Supreme Leader
* Most powerful men in Iran
* Upper house
* Can initiate own legislation and review Majles’ legislation
32
New cards
Describe the president
* Head of Government
* Top democratic institution
* Directly elected by citizens
* Still, Iran is no presidential system
* Powers more limited than in other countries
* Does not control military
* Can be dismissed by Supreme Leader
* Can be overruled by Guardian Council
* Limited to two consecutive four-year terms
* Top democratic institution
* Directly elected by citizens
* Still, Iran is no presidential system
* Powers more limited than in other countries
* Does not control military
* Can be dismissed by Supreme Leader
* Can be overruled by Guardian Council
* Limited to two consecutive four-year terms
33
New cards
What is Iran’s top democratic institution?
President
34
New cards
What is the president empowered to to?
* Develop budget and supervise economy
* Propose legislation
* Supervise bureaucracy
* Implement government policies
* Appoint cabinet
* Sing treaties and agreements
* Represent Iran internationally
* Propose legislation
* Supervise bureaucracy
* Implement government policies
* Appoint cabinet
* Sing treaties and agreements
* Represent Iran internationally
35
New cards
Describe the cabinet
* Appointed by president
* Manages day-to-day operations of government
* Supervises bureaucracy and budget
* Often develops law and policies
* Manages day-to-day operations of government
* Supervises bureaucracy and budget
* Often develops law and policies
36
New cards
Describe Iran’s bureaucracy
* Massive
* Many ministries or semi-public institutions and para-statals (government run businesses)
* Supervises much of economy and state-run businesses
* Mostly clerics with close ties to government leaders
* Many ministries or semi-public institutions and para-statals (government run businesses)
* Supervises much of economy and state-run businesses
* Mostly clerics with close ties to government leaders
37
New cards
Describe Iran’s court system
* Shariah and Qanun
* National Supreme Court is top court of appeal
* National Chief Justice supervises judiciary
* National Supreme Court is top court of appeal
* National Chief Justice supervises judiciary
38
New cards
Assess the level of judicial review in Iran
* Judiciary not independent of executive
* Supreme leader, Guardian Council and judges are constantly judging prospective laws and actions against Shariah
* Ultimately, constitutionality depends on sometimes politically-motivated decisions made by religious authorities
* Supreme leader, Guardian Council and judges are constantly judging prospective laws and actions against Shariah
* Ultimately, constitutionality depends on sometimes politically-motivated decisions made by religious authorities
39
New cards
Describe the Clerics of Qom
* Not formally in government
* Strong moral/intellectual influence over direction of authorities
* Qom: desert city full of religious schools and institutes
* Origin of Khomeini and Islamic revolution and centre Shia faith
* Strong moral/intellectual influence over direction of authorities
* Qom: desert city full of religious schools and institutes
* Origin of Khomeini and Islamic revolution and centre Shia faith
40
New cards
Describe Iran’s military
* 8th largest in the world
* Relatively well equipped
* Tradition of compulsory 2-year military service by most young men
* Not particularly political
* Relatively well equipped
* Tradition of compulsory 2-year military service by most young men
* Not particularly political
41
New cards
Describe the Revolutionary Guards
* Parallel force to military
* Created by Supreme Leader to act as loyal body guards
* 120,000 well-equipped and trained members
* Increasingly political force
* Created by Supreme Leader to act as loyal body guards
* 120,000 well-equipped and trained members
* Increasingly political force
42
New cards
When were the first elections held?
1906 following revolution
43
New cards
Describe Iran’s presidential elections
* Two-round runoff ballot
* Every four years
* Limited to two consecutive terms
* Must be approved by Guardian Council
* Competitive but not free
* Guardian council reject reformist candidates and women
* Every four years
* Limited to two consecutive terms
* Must be approved by Guardian Council
* Competitive but not free
* Guardian council reject reformist candidates and women
44
New cards
What was the development of elections in 1997
* “The thaw begins”
* Relatively unknown, moderate cleric Khatami wins presidency with over 70%
* Relatively unknown, moderate cleric Khatami wins presidency with over 70%
45
New cards
Describe Khatami’s policies when he was elected as president in 1997
* Advocates liberalization, achieved loosening of press censorship, fewer crackdowns on dissidents and restrictions on public behaviour
* Helped to rebuild Iran’s image on world stage
* Many liberals very disappointed with lack of progress; reforms systematically blocked by conservative Guardian Council
* Not a radical - never suggested abandoning theocratic structures
* Easily won re-election and stepped down at end of term limit in 2004
* Helped to rebuild Iran’s image on world stage
* Many liberals very disappointed with lack of progress; reforms systematically blocked by conservative Guardian Council
* Not a radical - never suggested abandoning theocratic structures
* Easily won re-election and stepped down at end of term limit in 2004
46
New cards
Describe the presidential election of 2005
* Guardian Council disqualified 1000 liberal candidates, leaving only 7
* Reformists unable to rally behind one candidate while conservatives settle on Ahmadinejad
* Ahmadinejad wins
* Some limited allegations of fraud
* Reformists unable to rally behind one candidate while conservatives settle on Ahmadinejad
* Ahmadinejad wins
* Some limited allegations of fraud
47
New cards
Describe Ahmadinejad’s political beliefs
* Deeply conservative in religious sense and socialist economically
* Hard-line conservatives approved of his efforts to roll back Khatami’s liberalization
* Hard-line conservatives approved of his efforts to roll back Khatami’s liberalization