Chapter 2- Measurement and Experimental Techniques
| Quantity | SI Unit | Other Units | Instrument |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass | kilograms (kg) | grams, tonnes | Balance |
| Time | seconds (s) | hours, minutes | stopwatch |
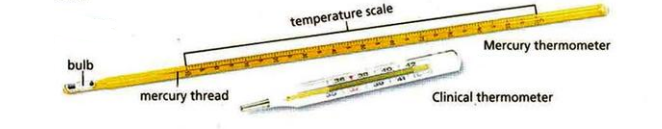
| Temperature | Kelvin (K) | Celcius, Ferhenheit | thermometers |
| Volume | cubic metre (m^3) | Litre, milliliters | measuring cylinder |
To ensure greater accuracy, pipettes, and burettes are used for measuring volume. To measure volumes of gases, gas syringe is used.
To avoid parallax error while taking readings, the volume of liquid is read from the top or bottom of the meniscus formed.
Methods for collecting Gases
Upward delivery: used to collect gases that are less dense than air and soluble in water, e.g. ammonia.
Downward delivery: used to collect gases that are denser than air and soluble in water, e.g. chlorine and sulfur dioxide.
Displacement of water: used to collect gases that are insoluble or slightly soluble in water, e.g. hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.

Methods for Drying of Gases
Concentrated sulfuric acid: used to dry most gases except ammonia.
Calcium Oxide: used to dry ammonia.
Fused calcium chloride: used to dry most gases.