Ant Test 1 Semester 1 All Quizlets combined
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Adenoma
Origin: Benign Glandular epithelium tissue
Adenocarcinoma
Origin: Malignant Glandular epithelium tissue
Papilloma
Origin: Benign Squamous epithelium tissue
Squamous cell carcinoma
Origin: Malignant Squamous epithelium tissue
Leiomyoma
Origin: Benign Conective tissue smooth muscle
Leiomyosarorma
Origin: Malignant Conective tissue smooth muscle
Leukemia
Origin: Malignant Hematopoietic tissue
Lymphoma
Origin: Malignant lymphoreticular tissue
Neuroma
Origin: Benign Neural tissue
Blastoma
Origin: Malignant Neural tissue
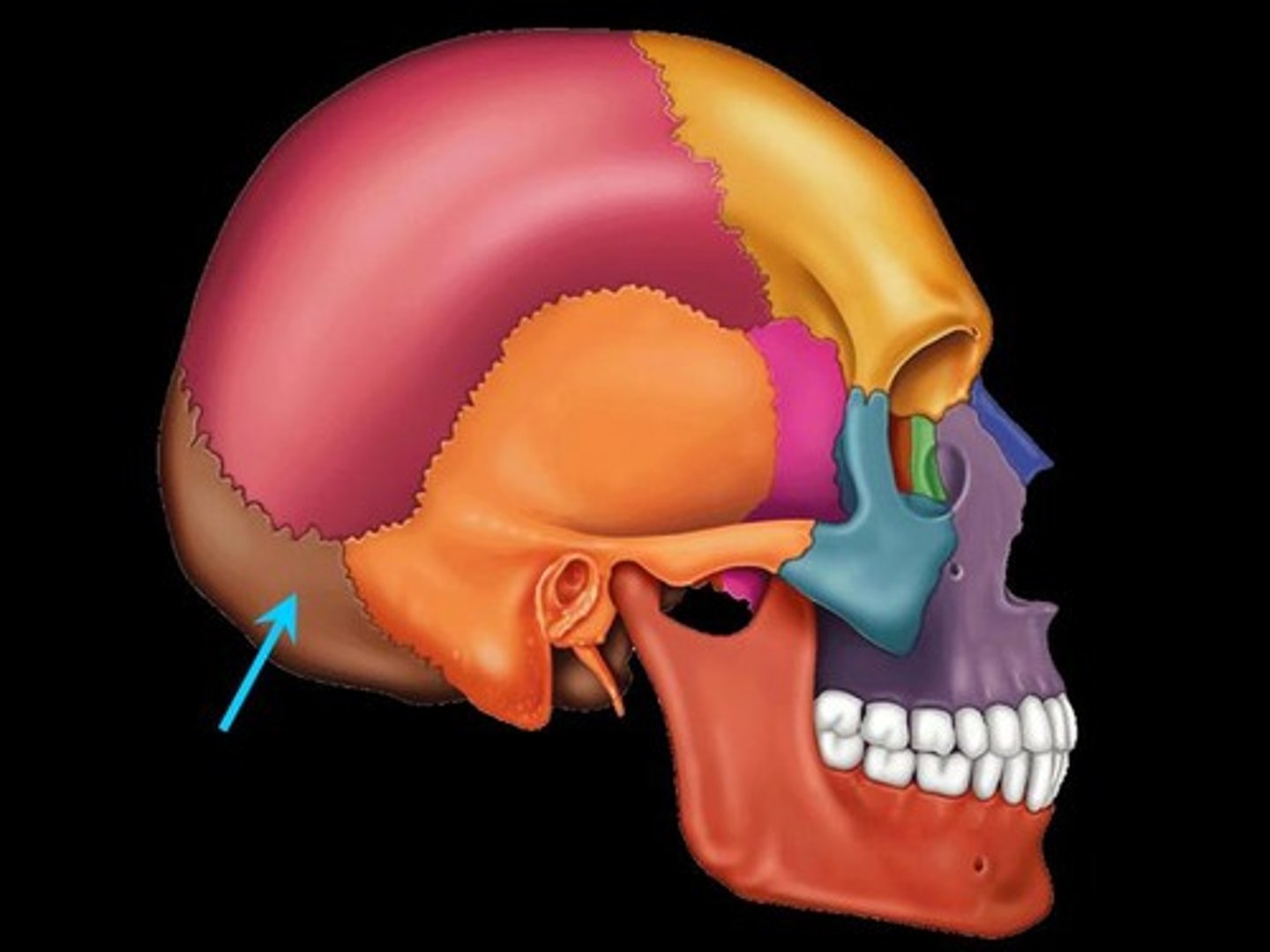
Occipital
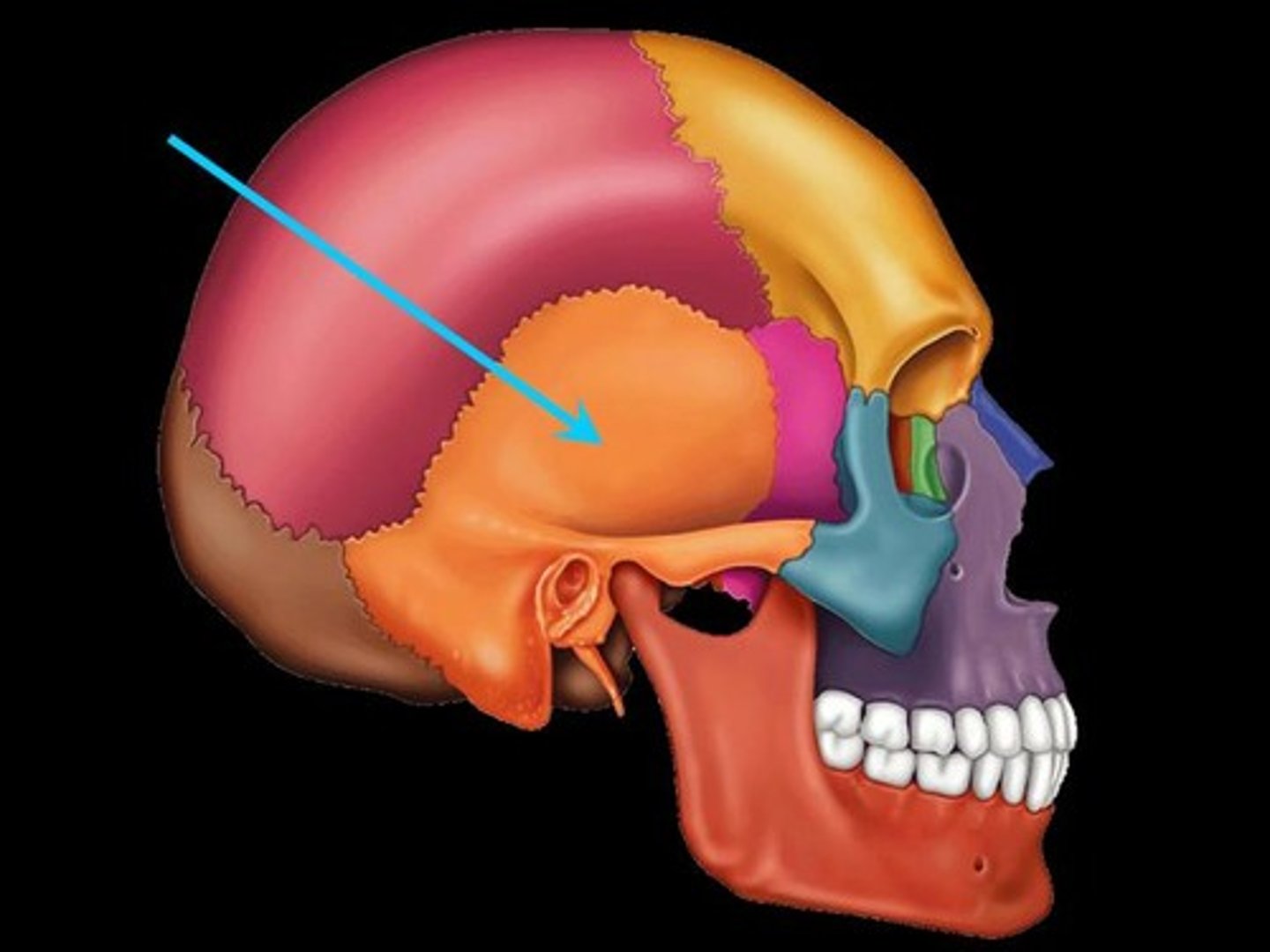
Temporal
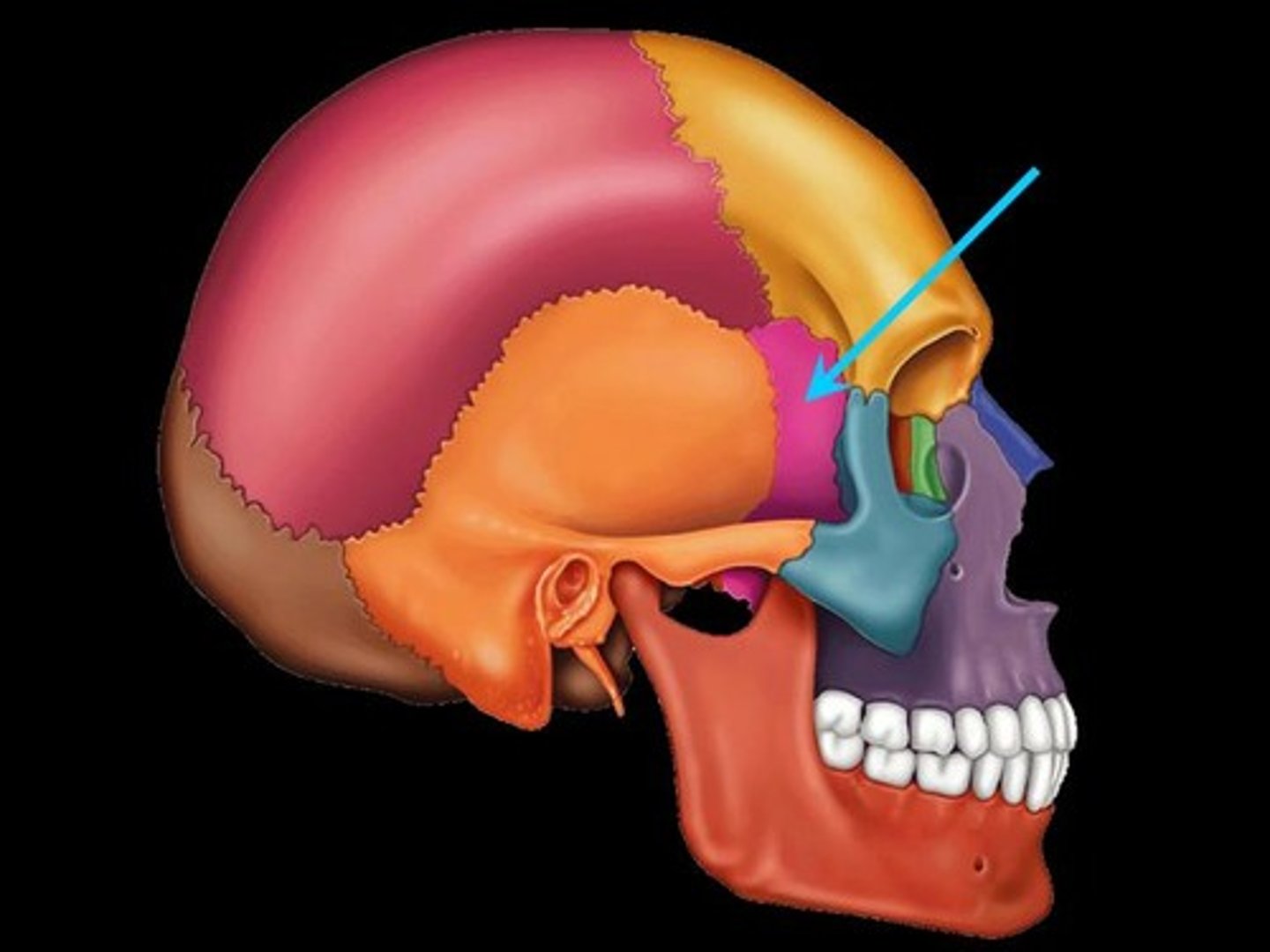
Sphenoid
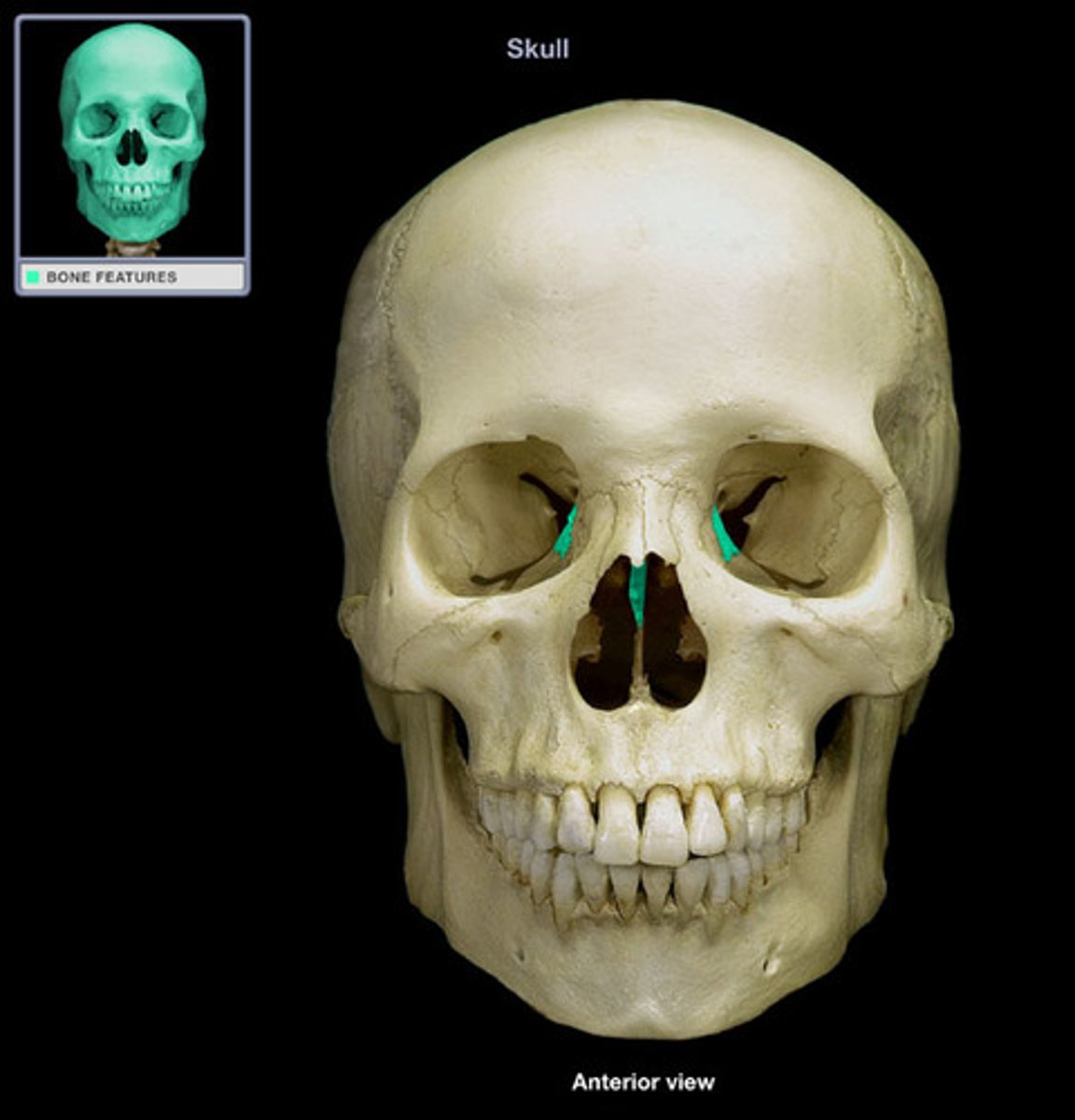
Ethmoid
Parietal
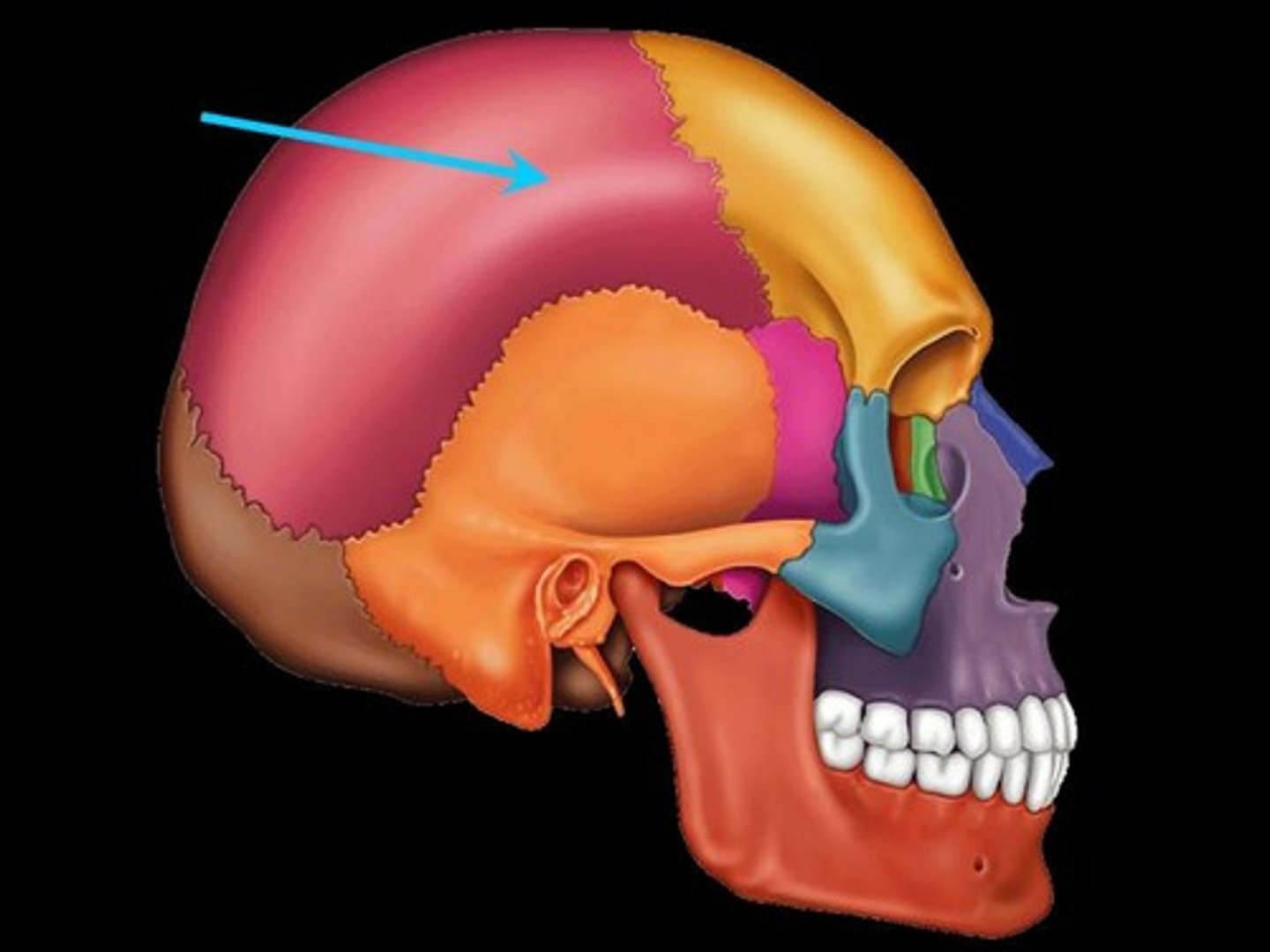
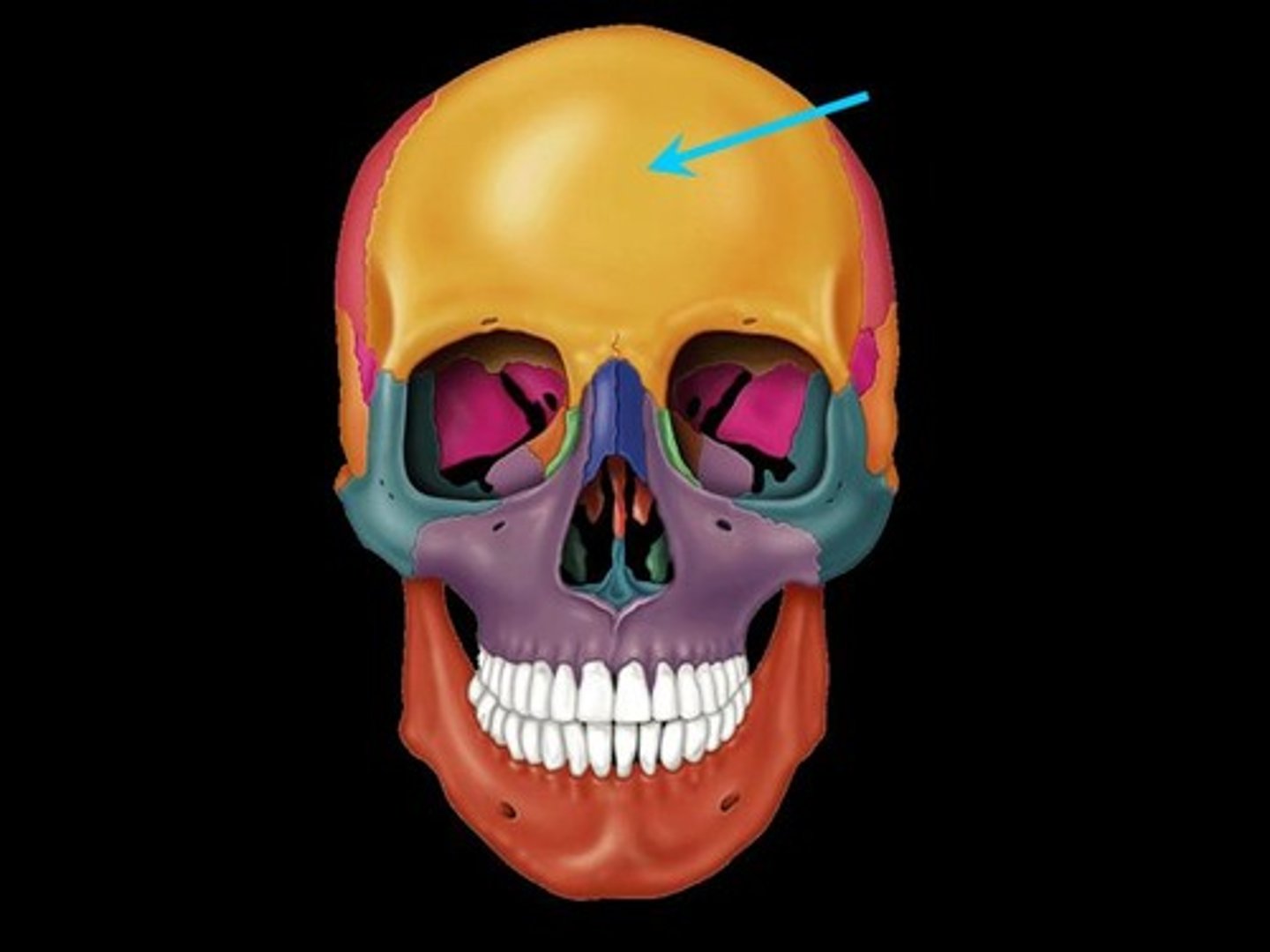
frontal
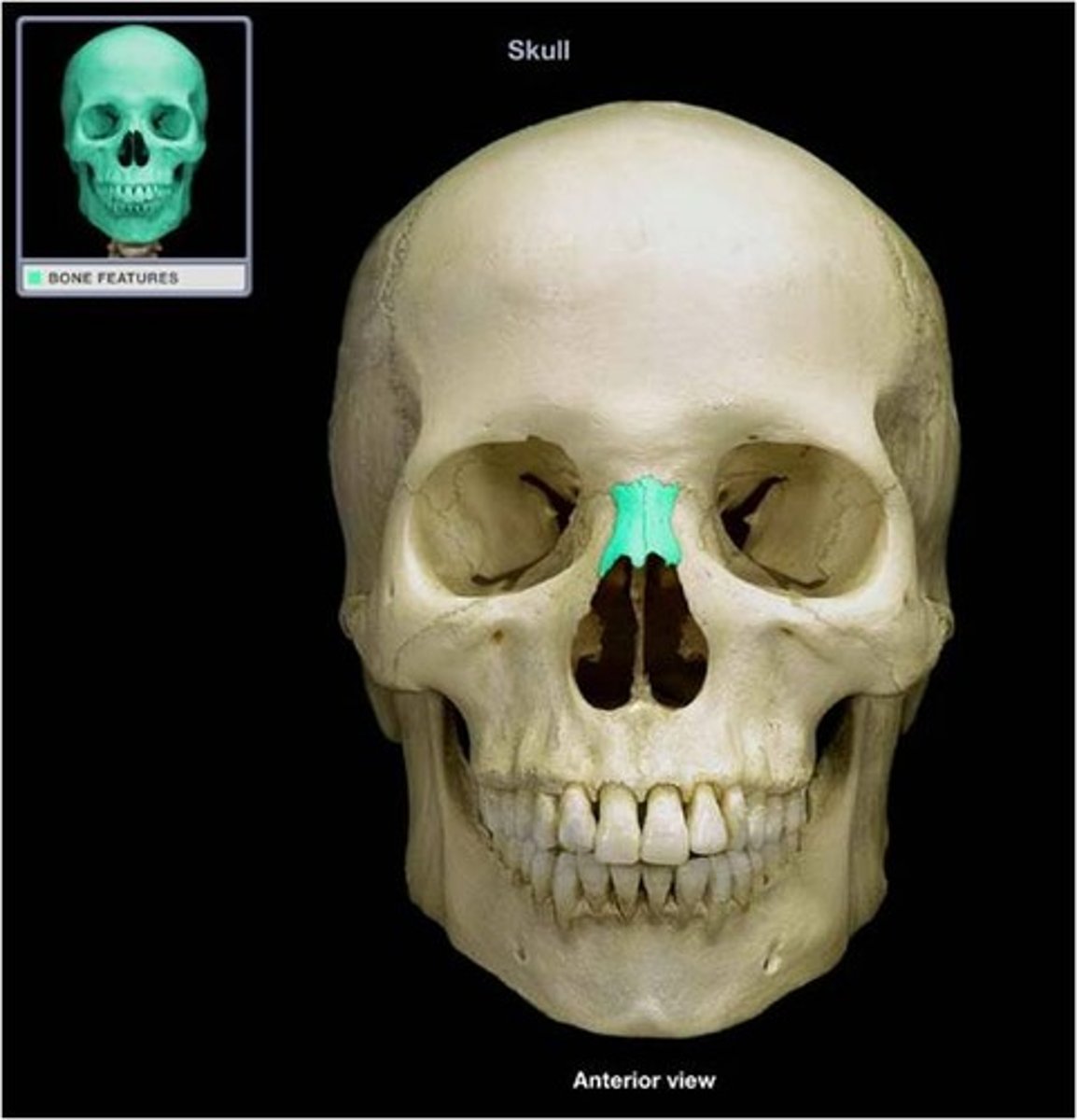
Nasal Bones Lateral
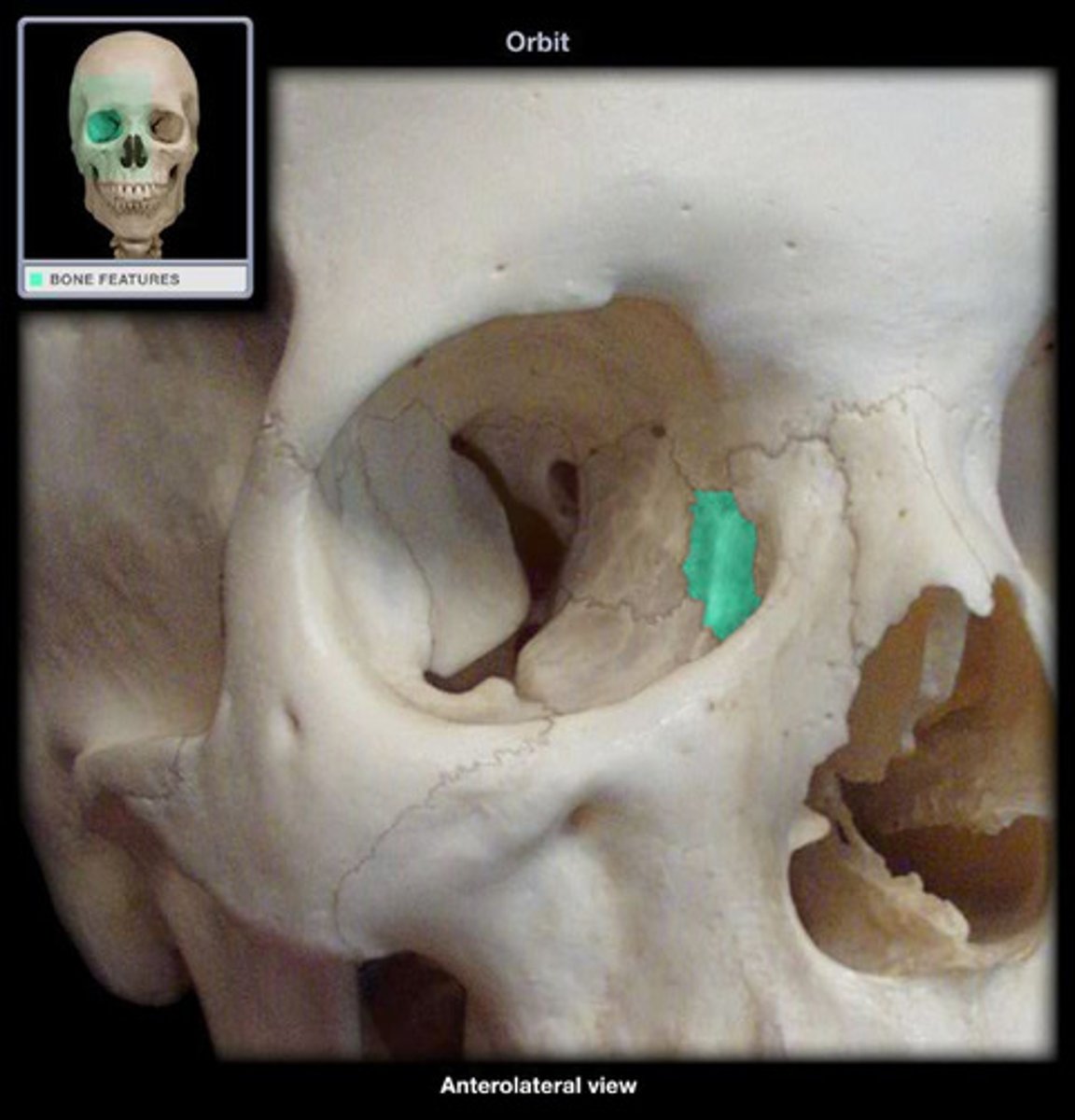
Lacrimal (2)
Maxilla (2)
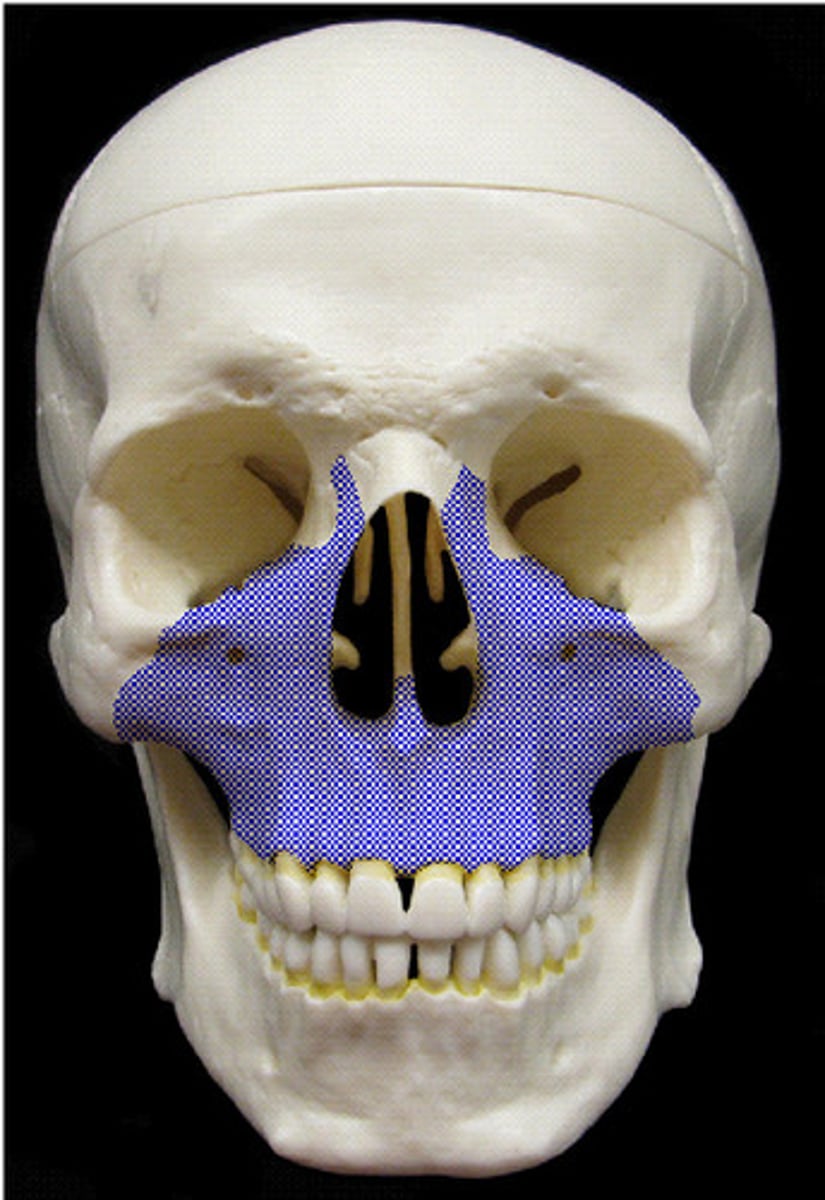
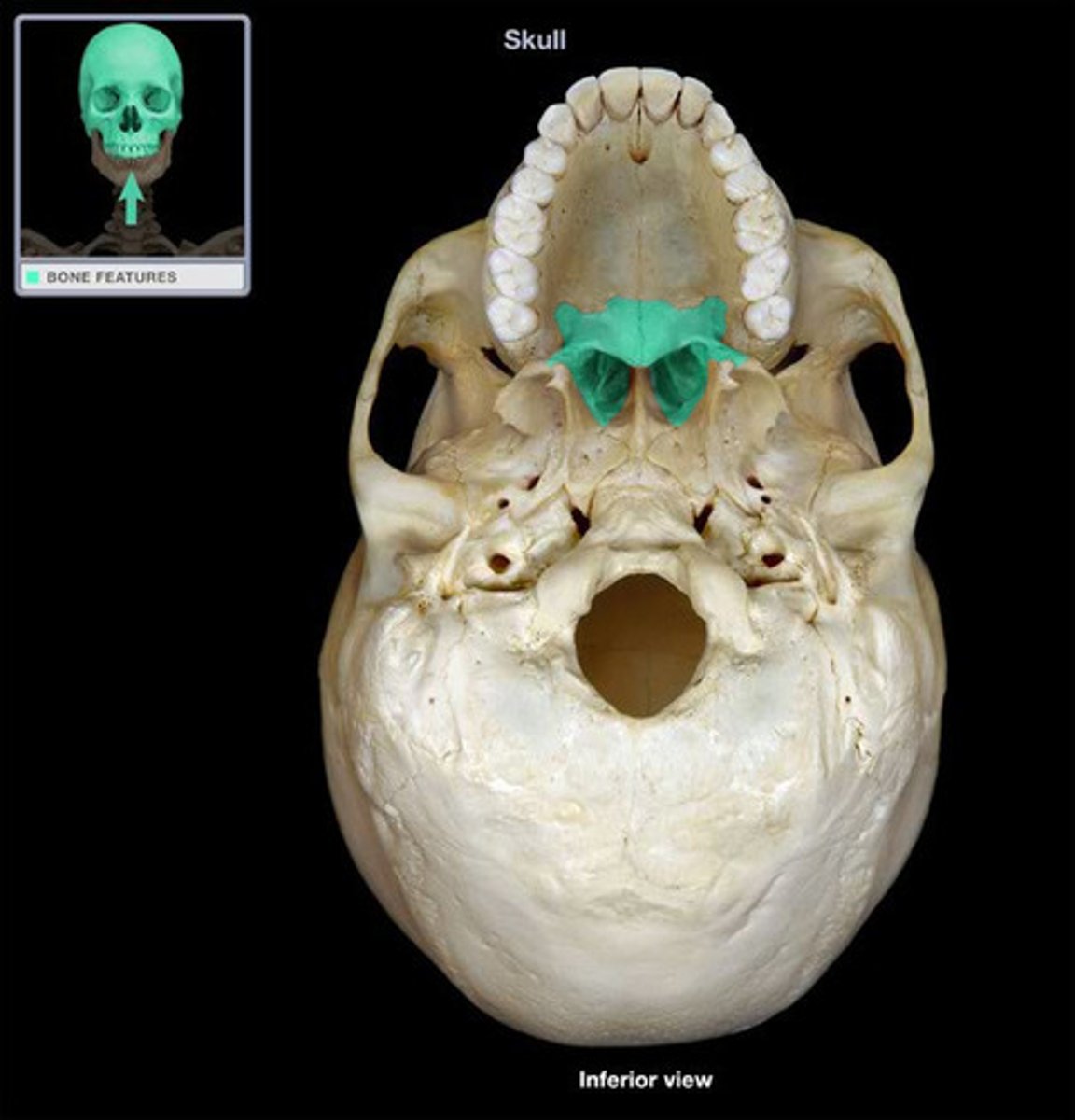
Palatine (2)
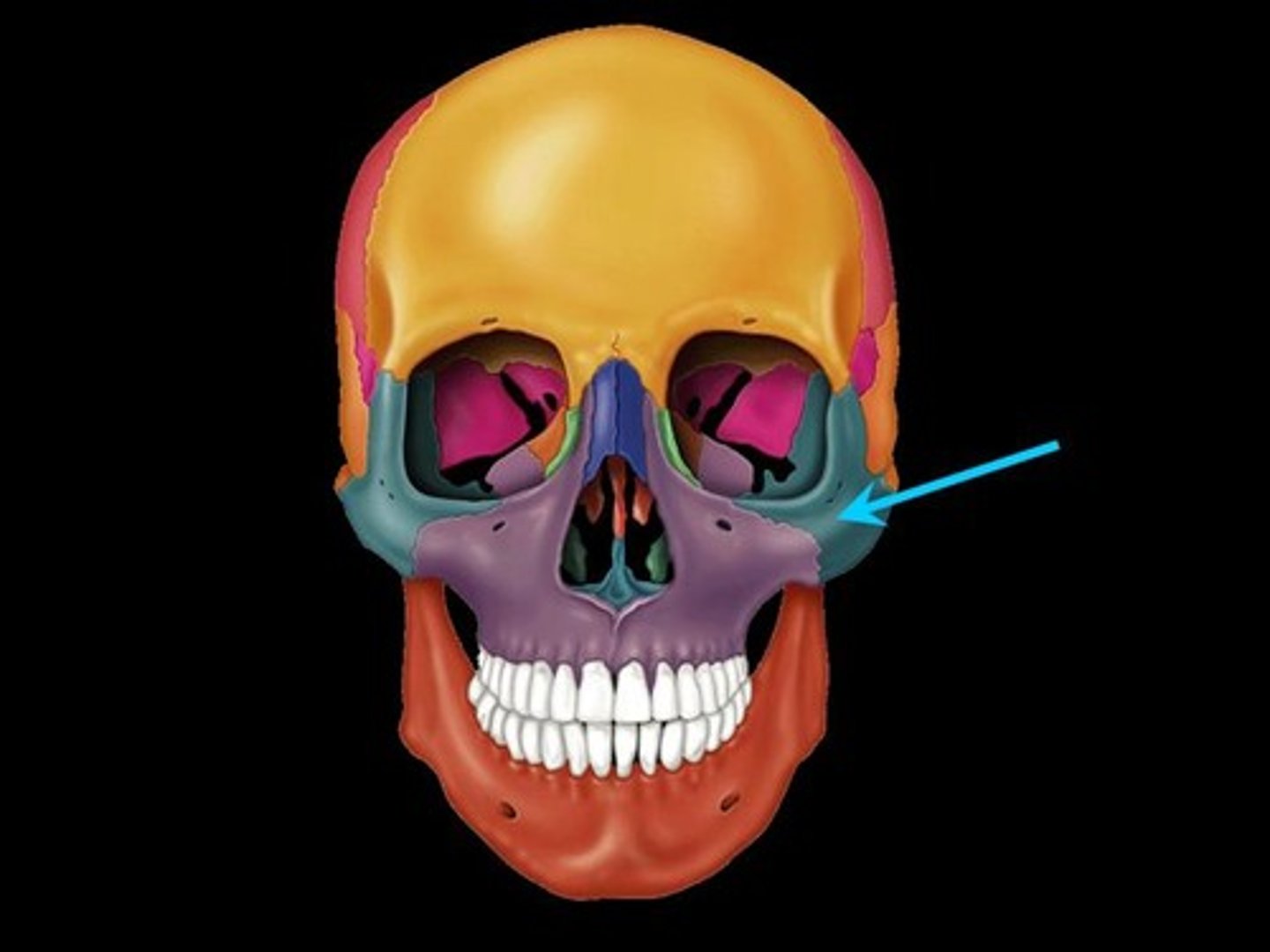
Zygoma (2)
Inferior Nasal Conchae(2)
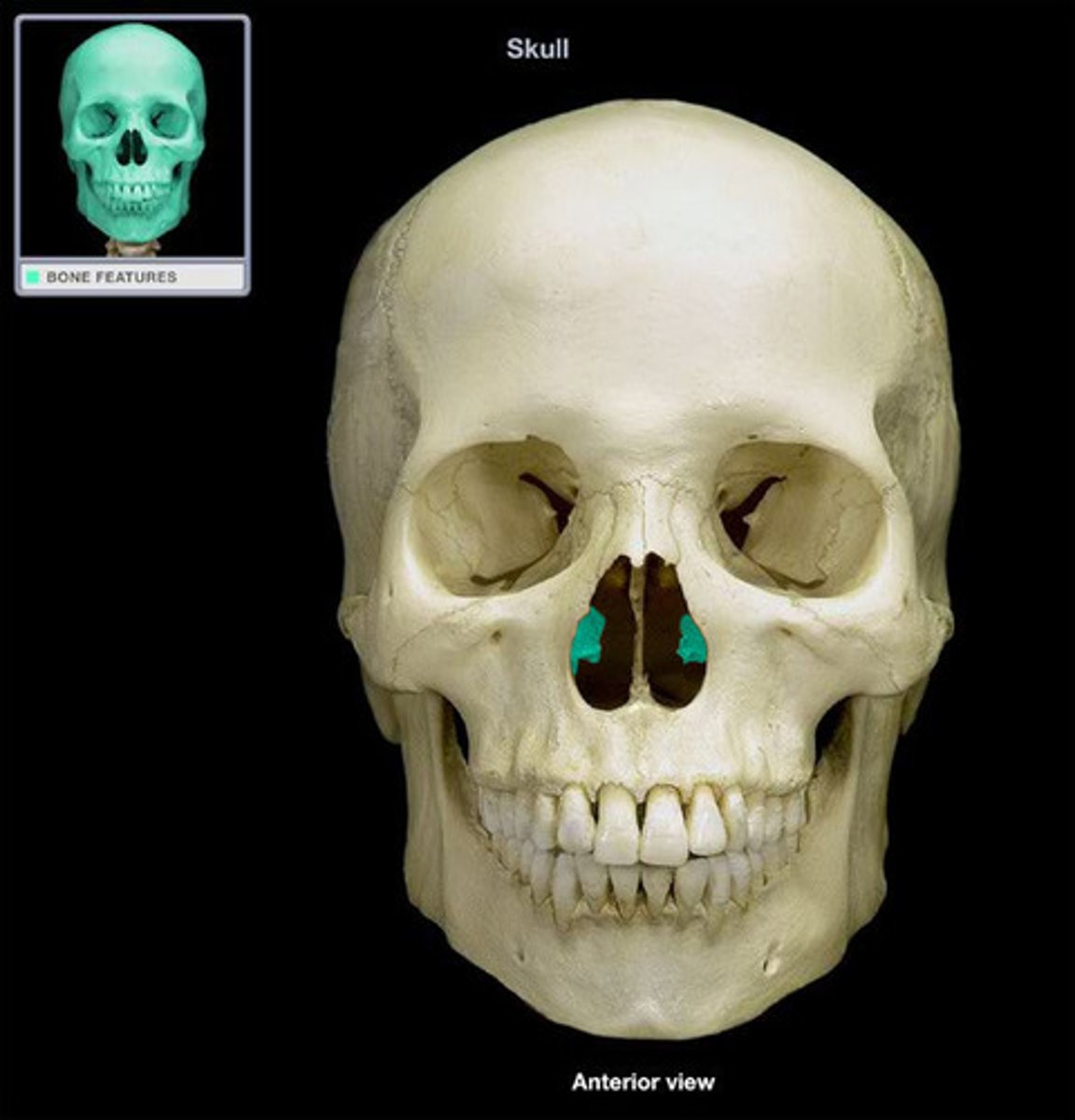
Vomer (1)
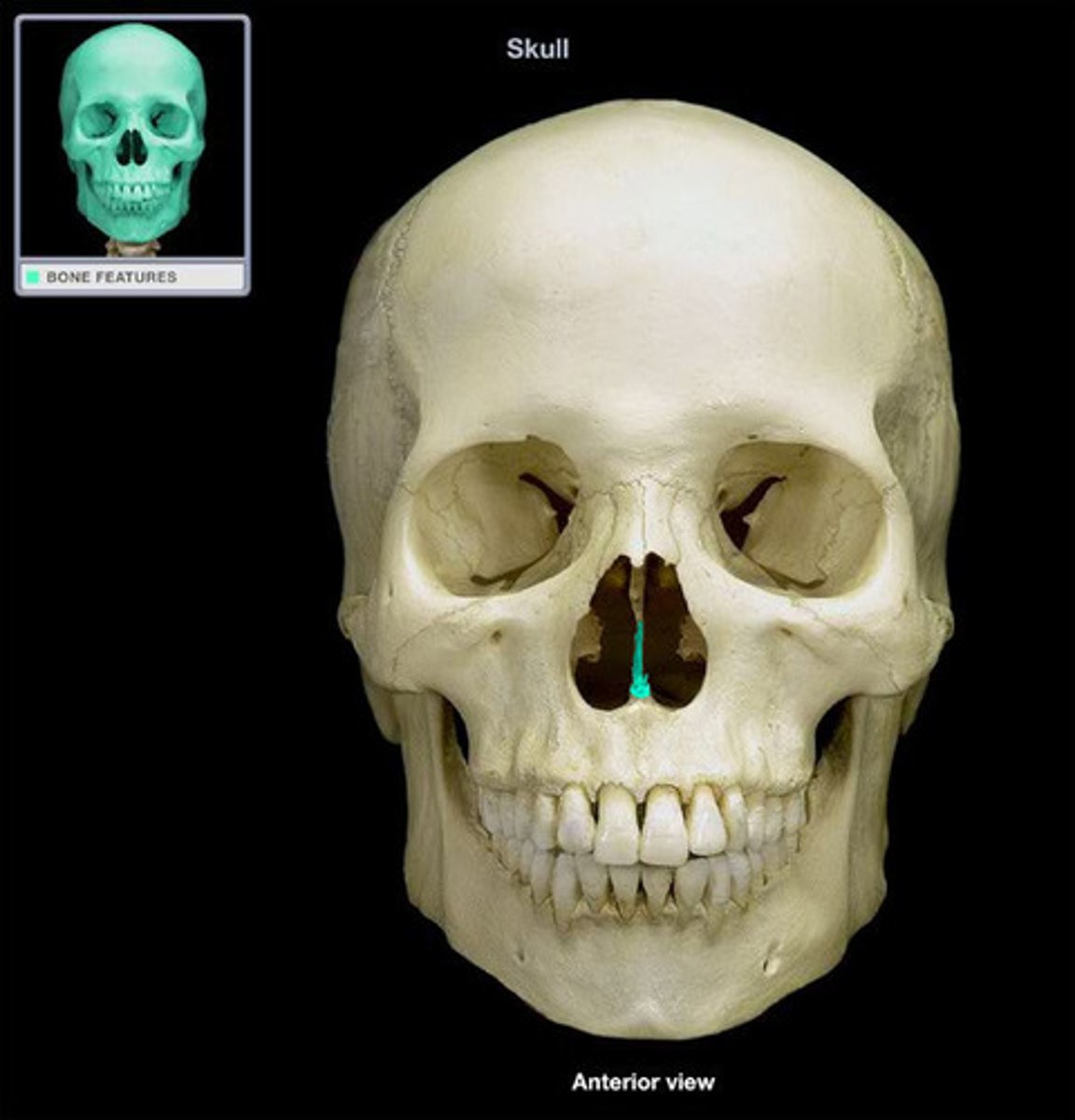
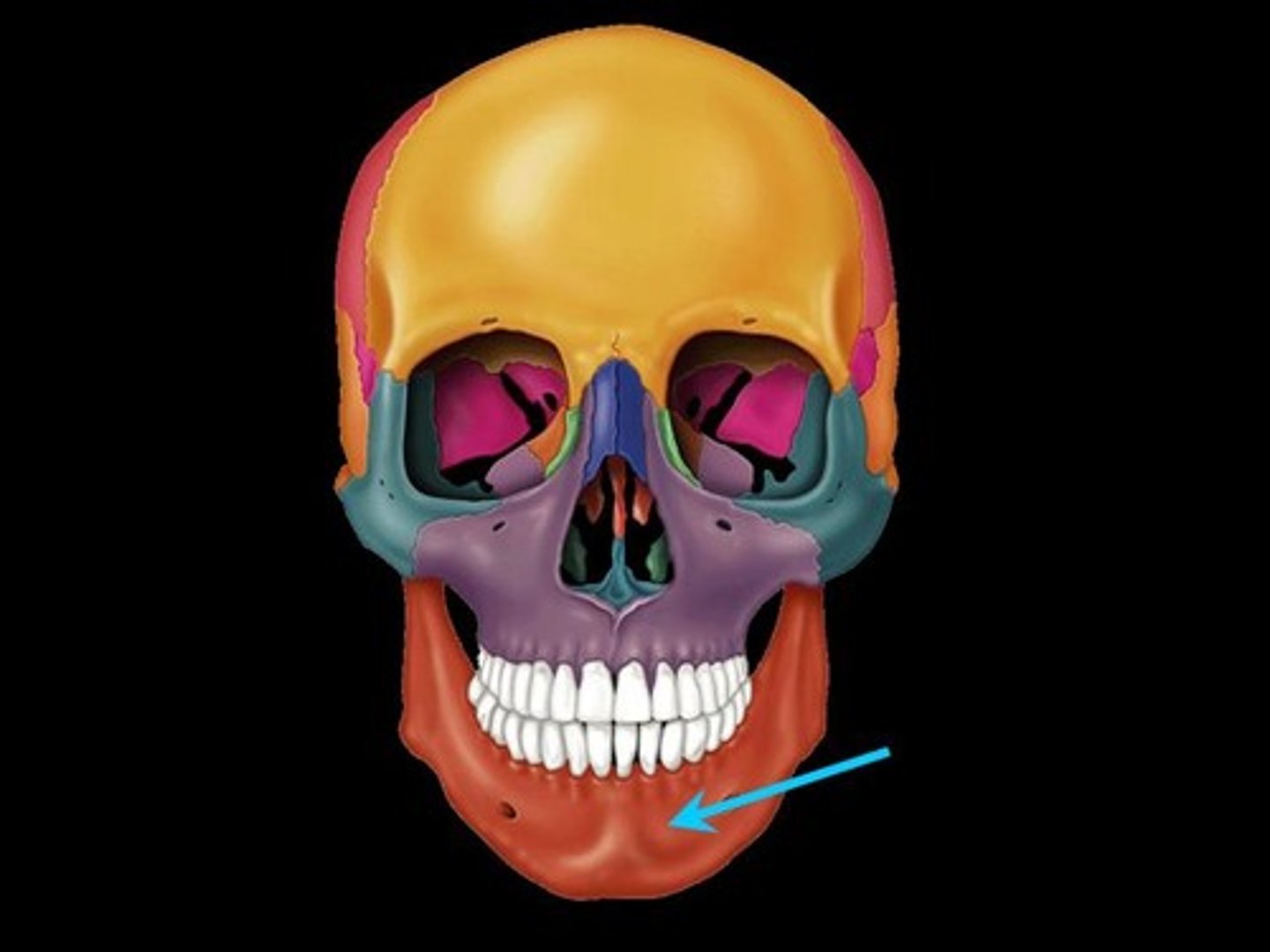
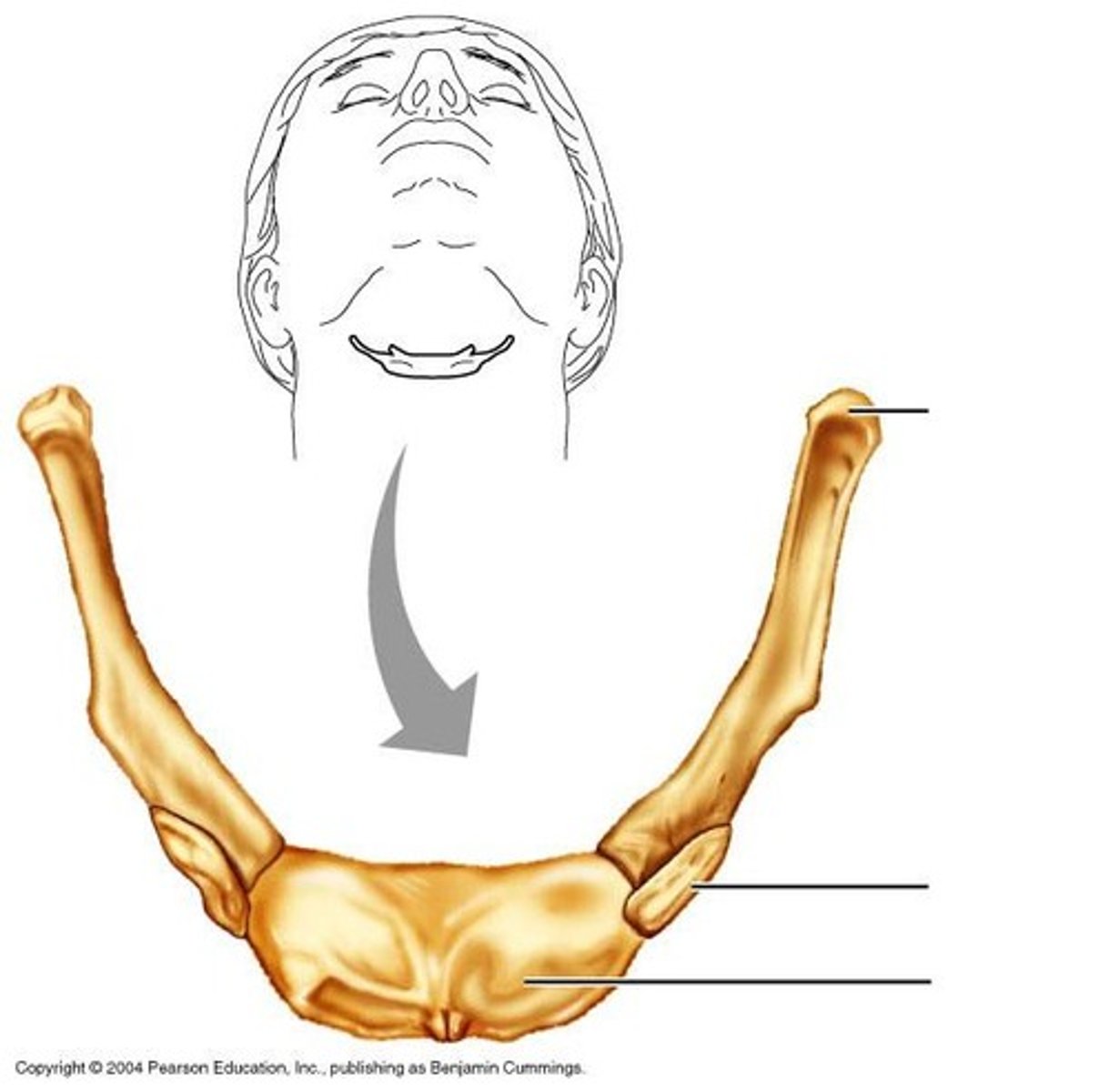
Mandible (1)
malleus (2)
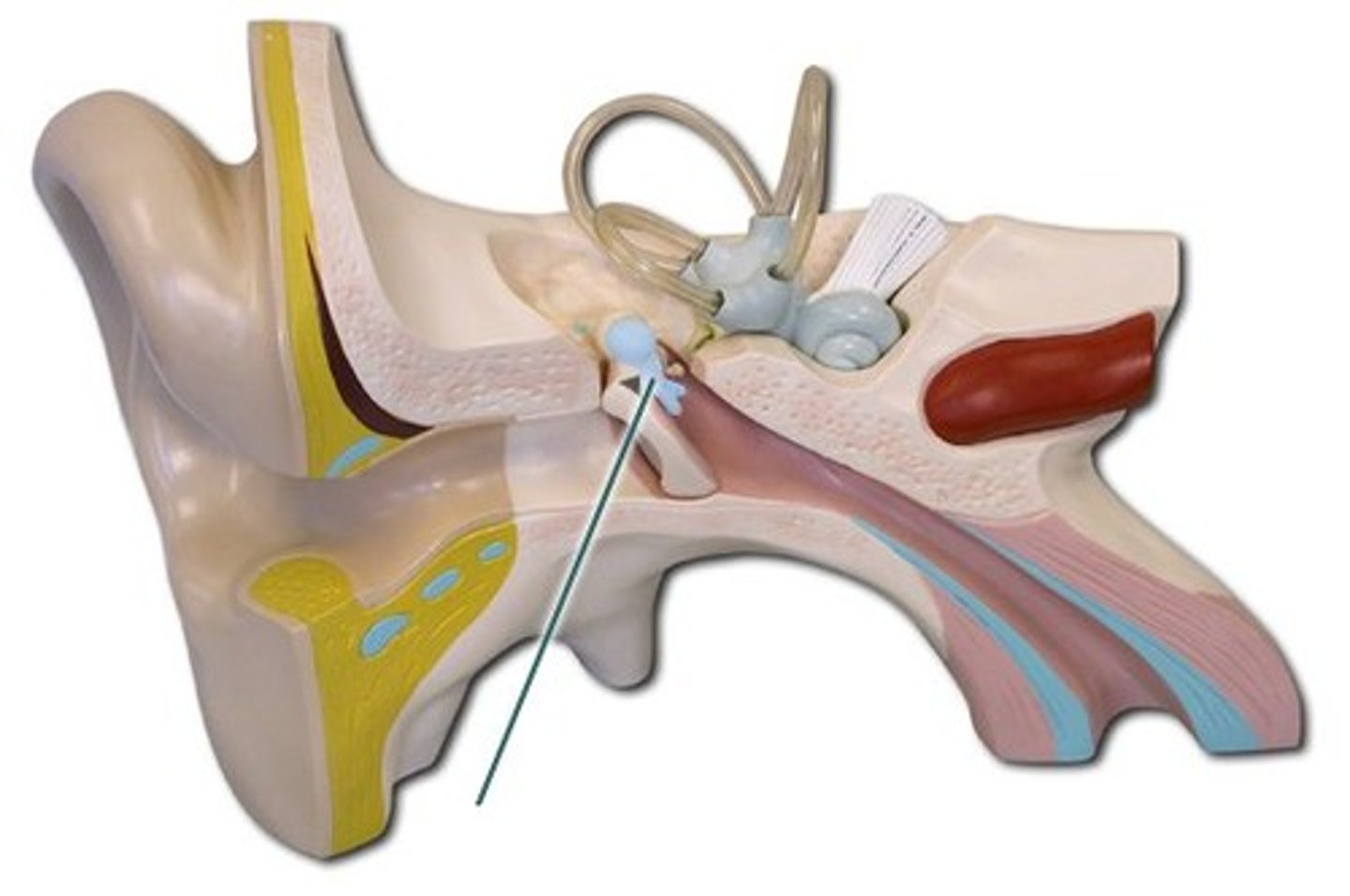
incus (2)
stapes
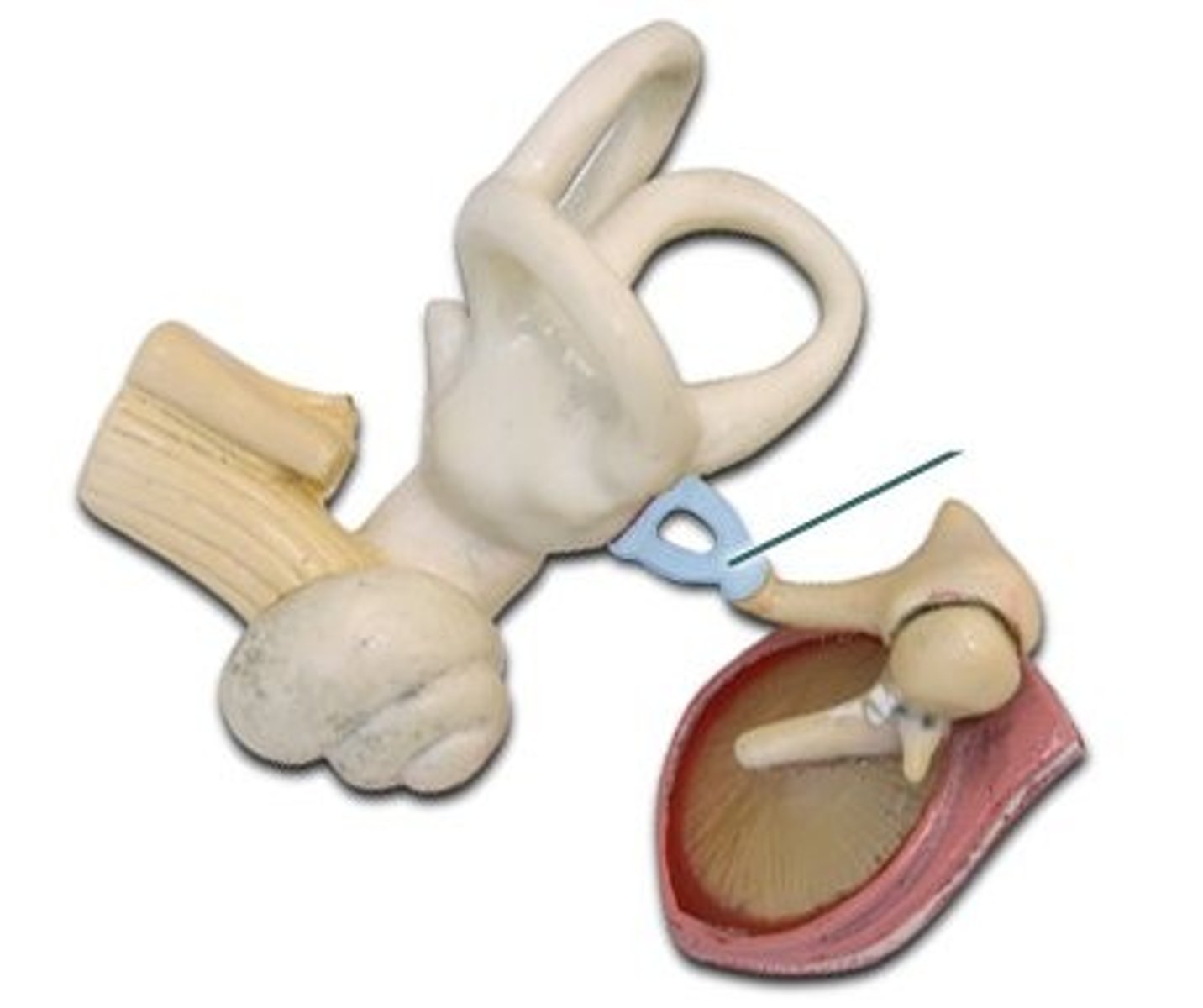
lingual/hyoid bone
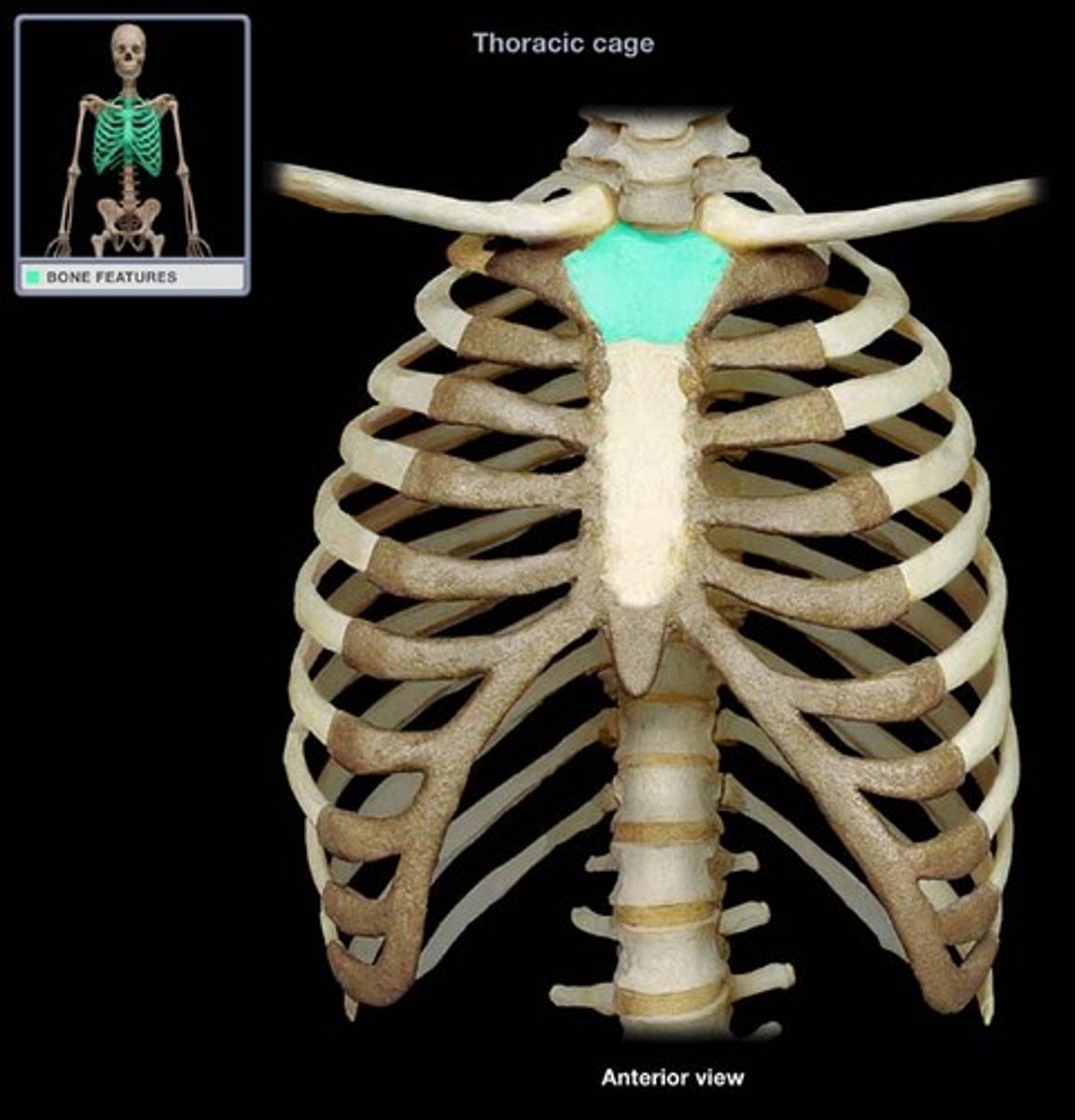
manubrium
body of sternum
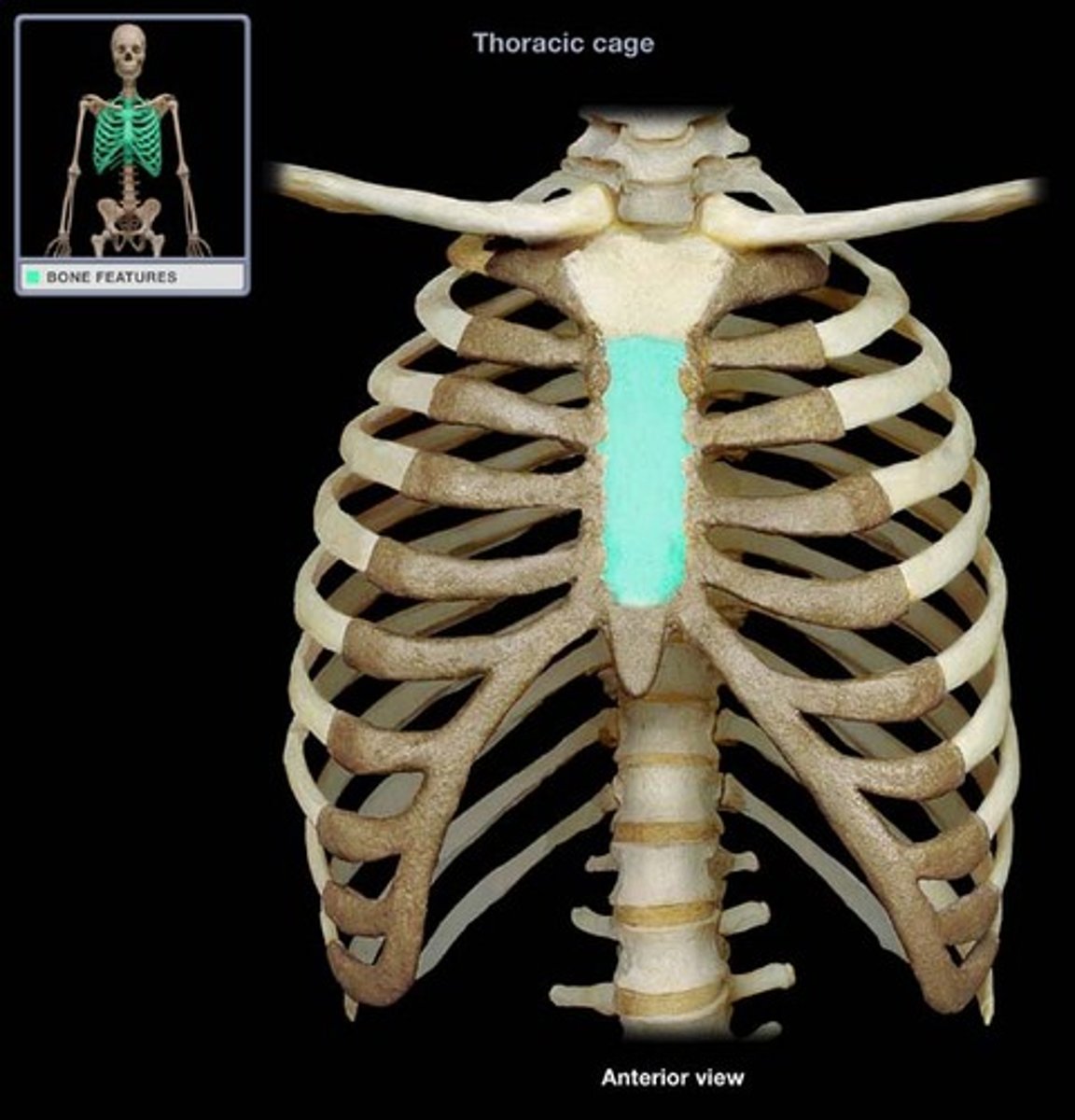
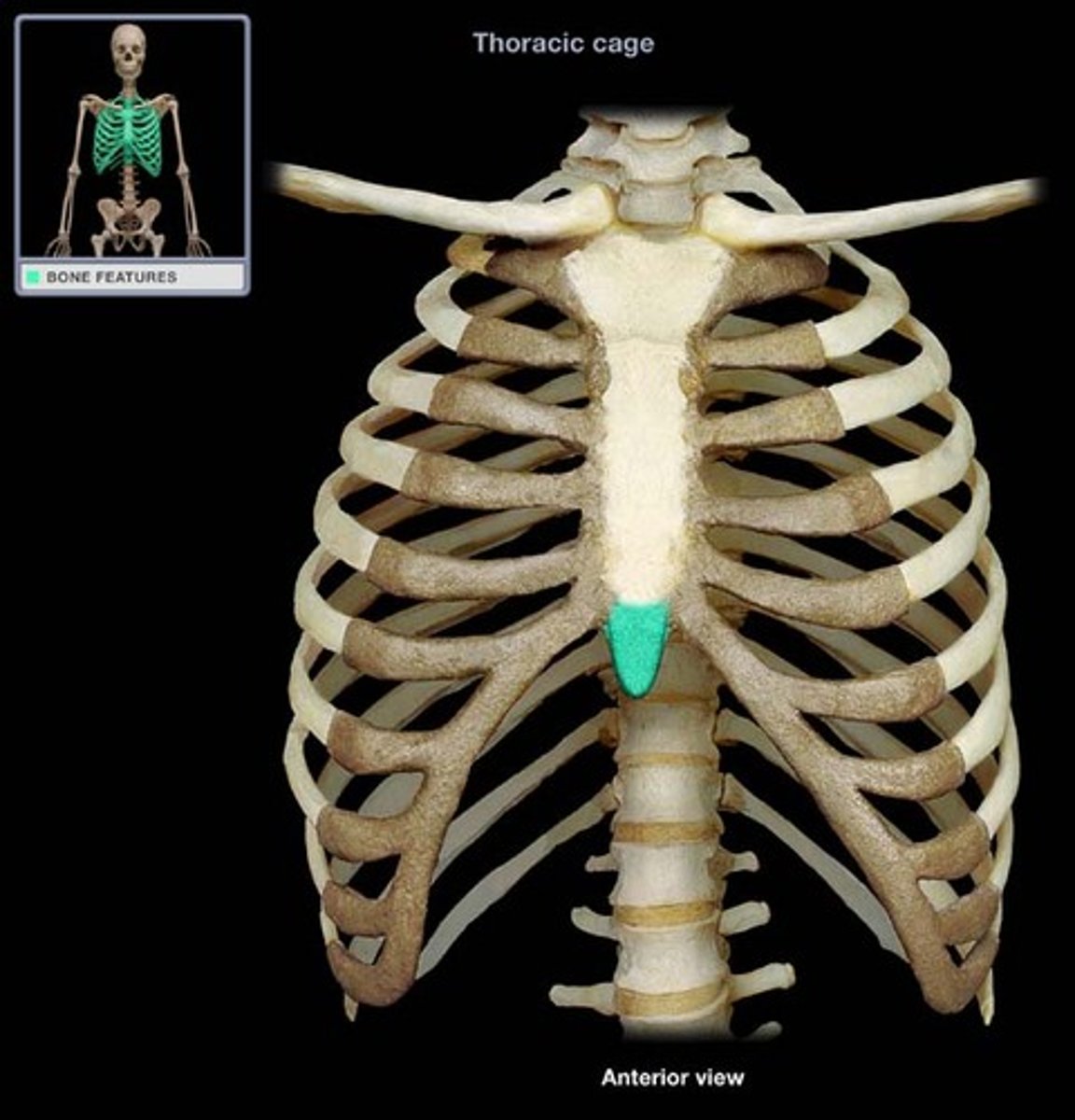
xiphoid process
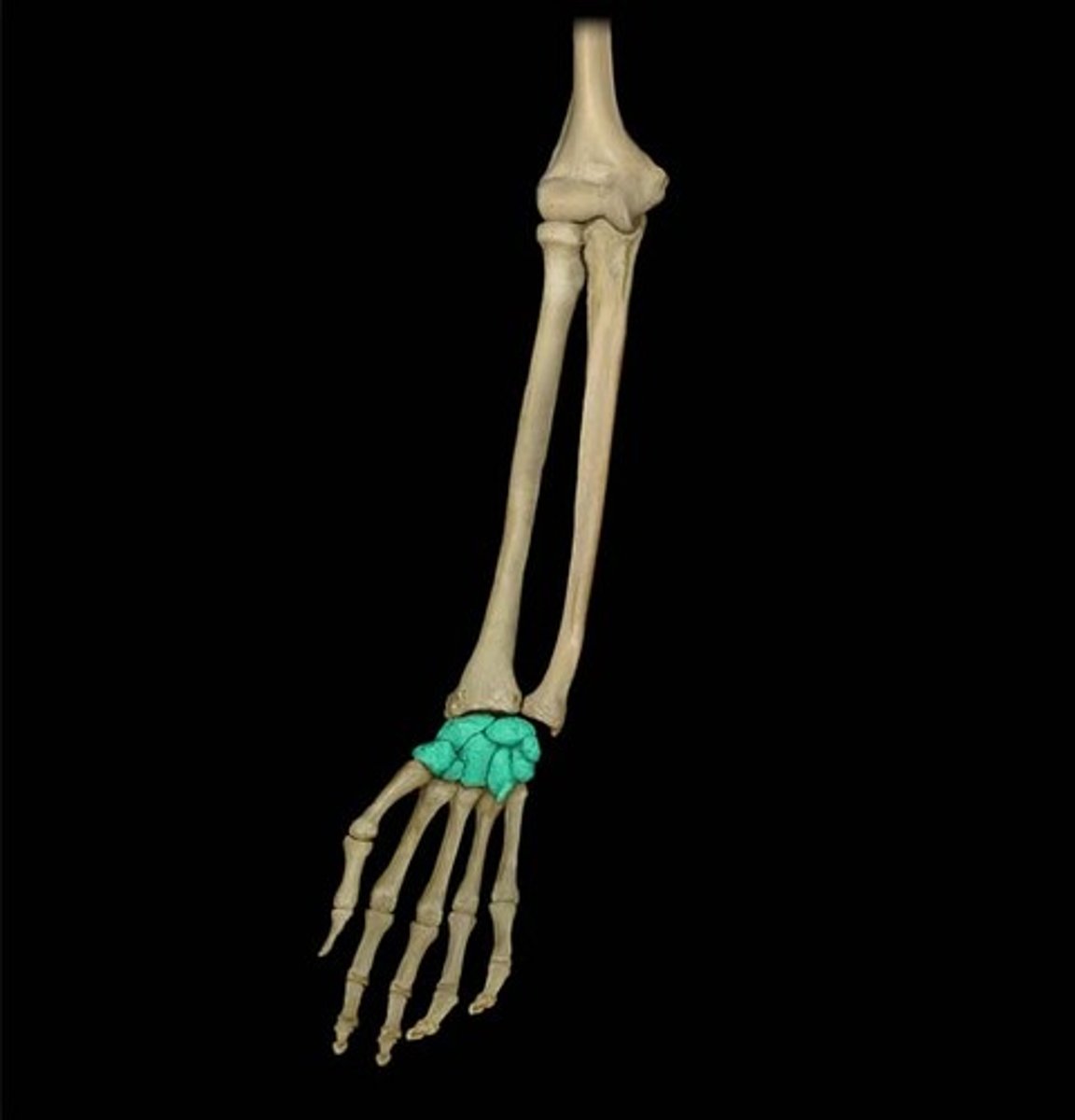
carpals
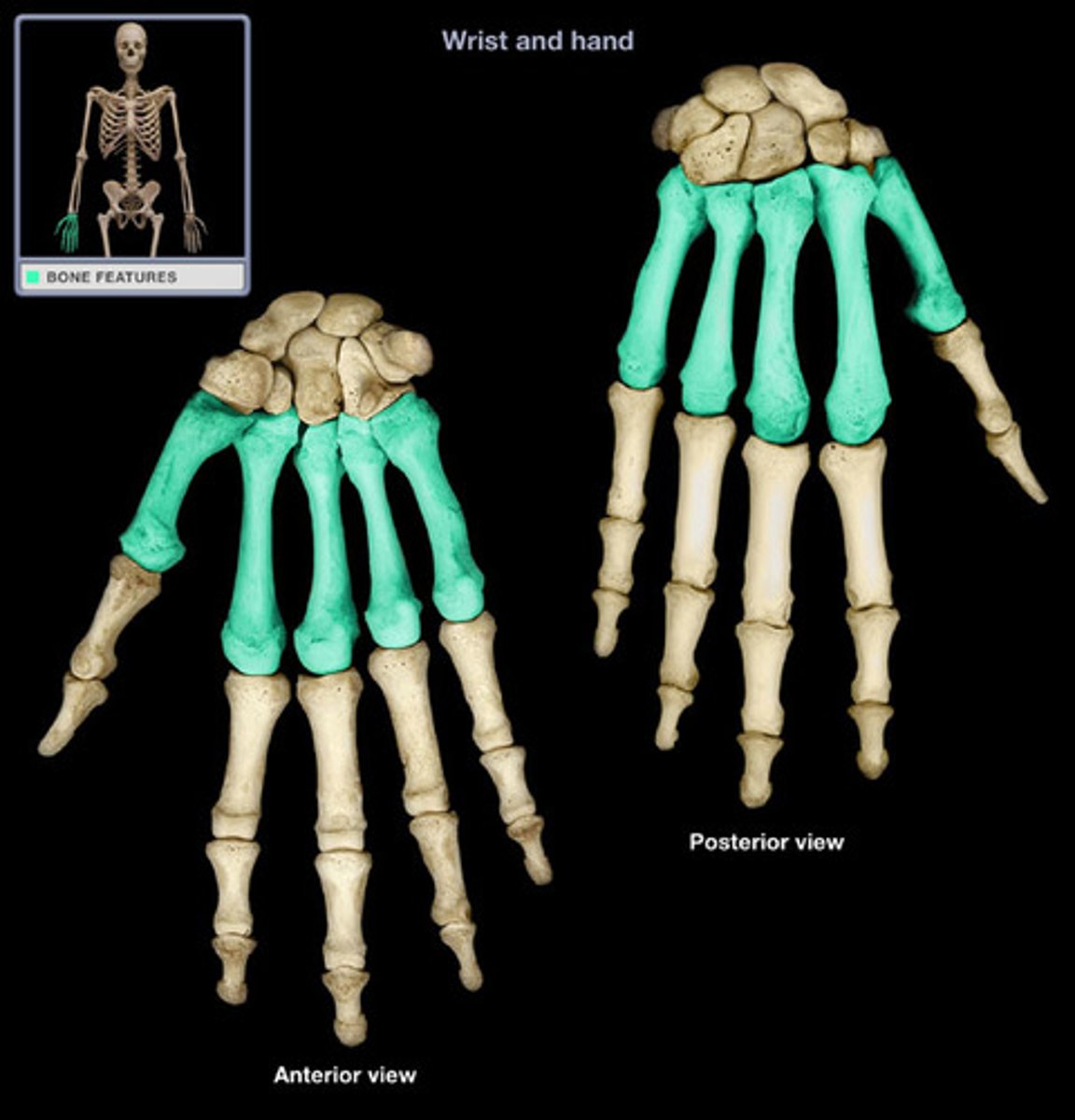
metacarpals
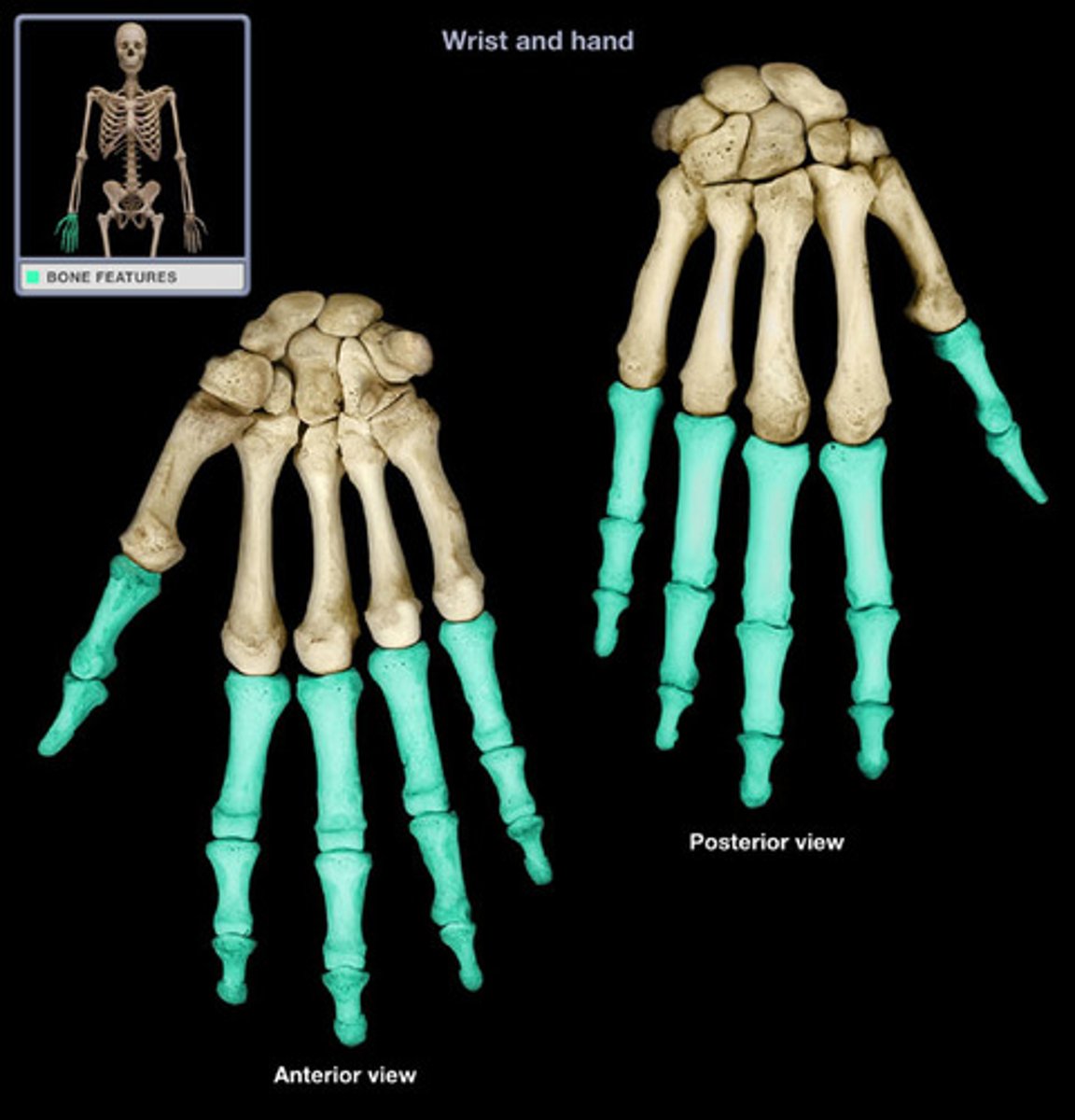
phalanges
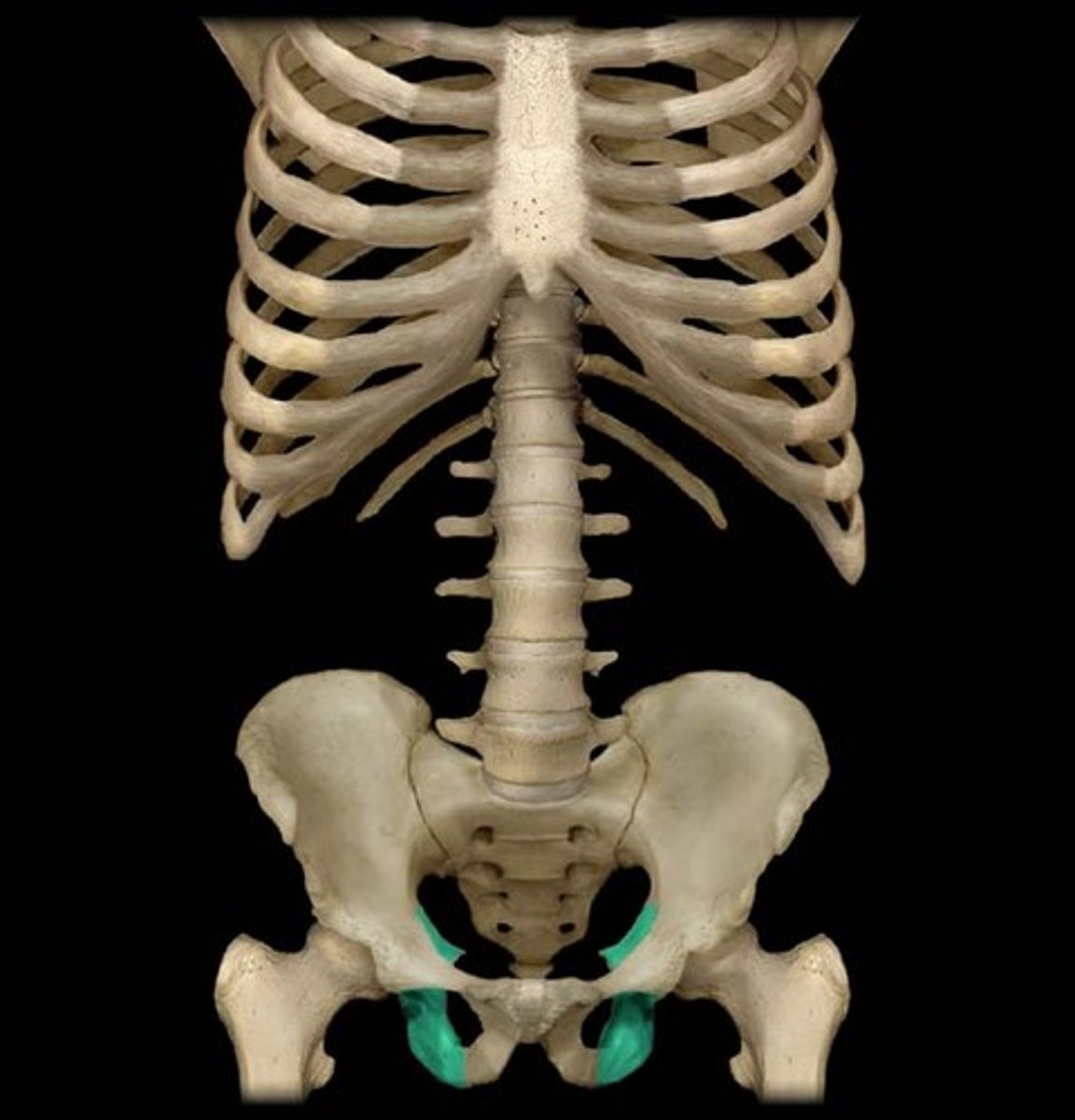
illium
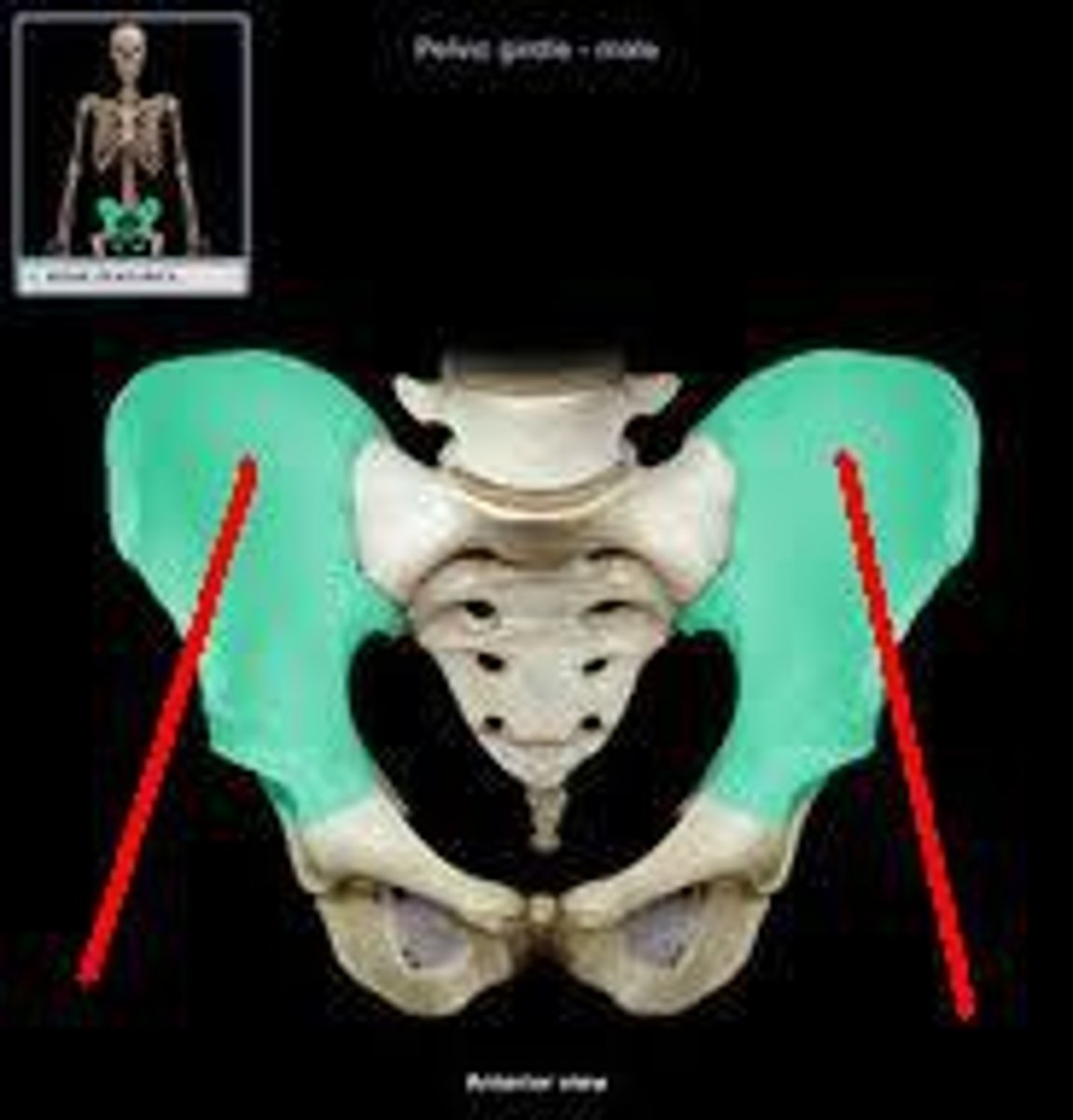
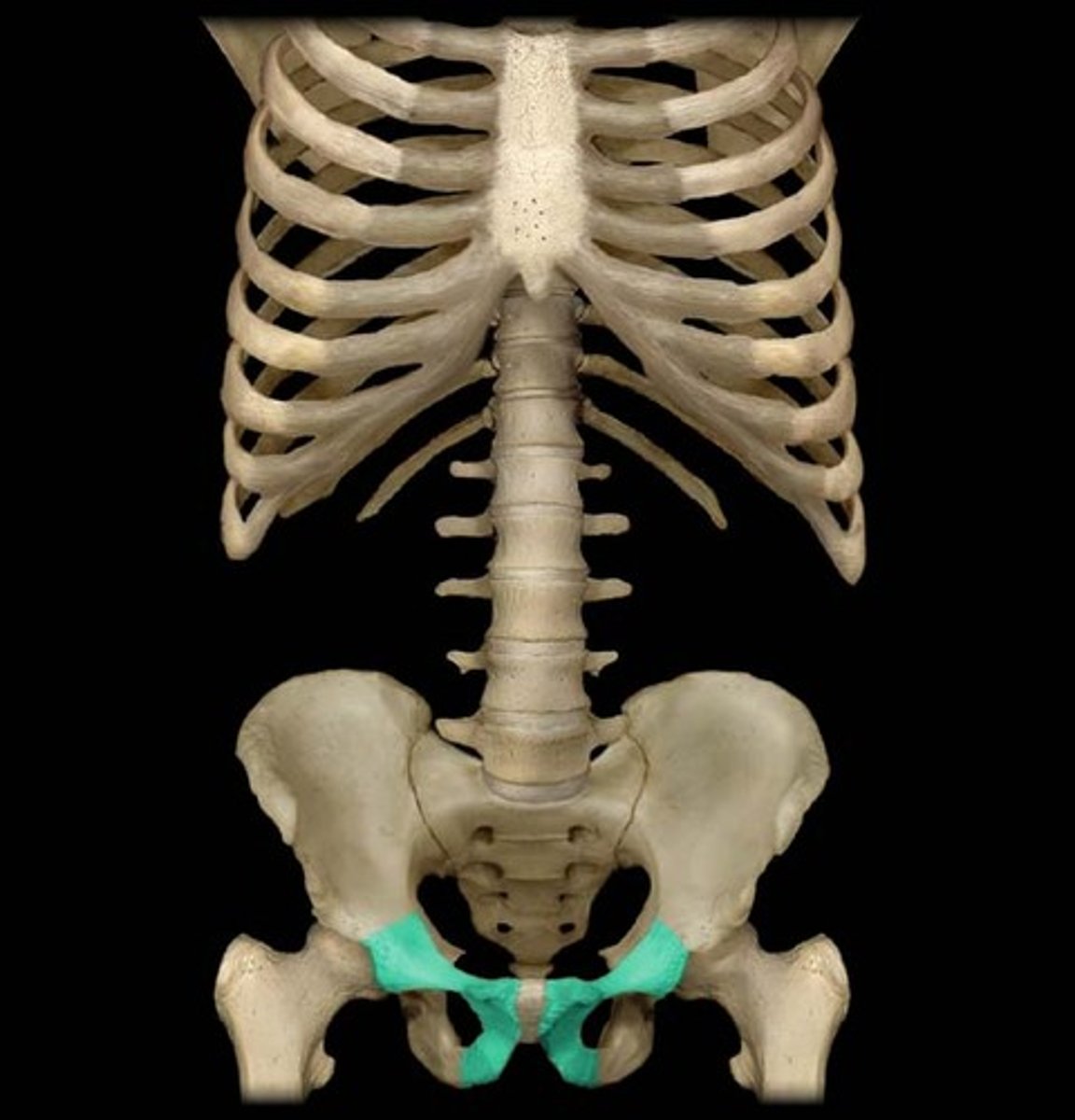
ischium
pubis
tarsals
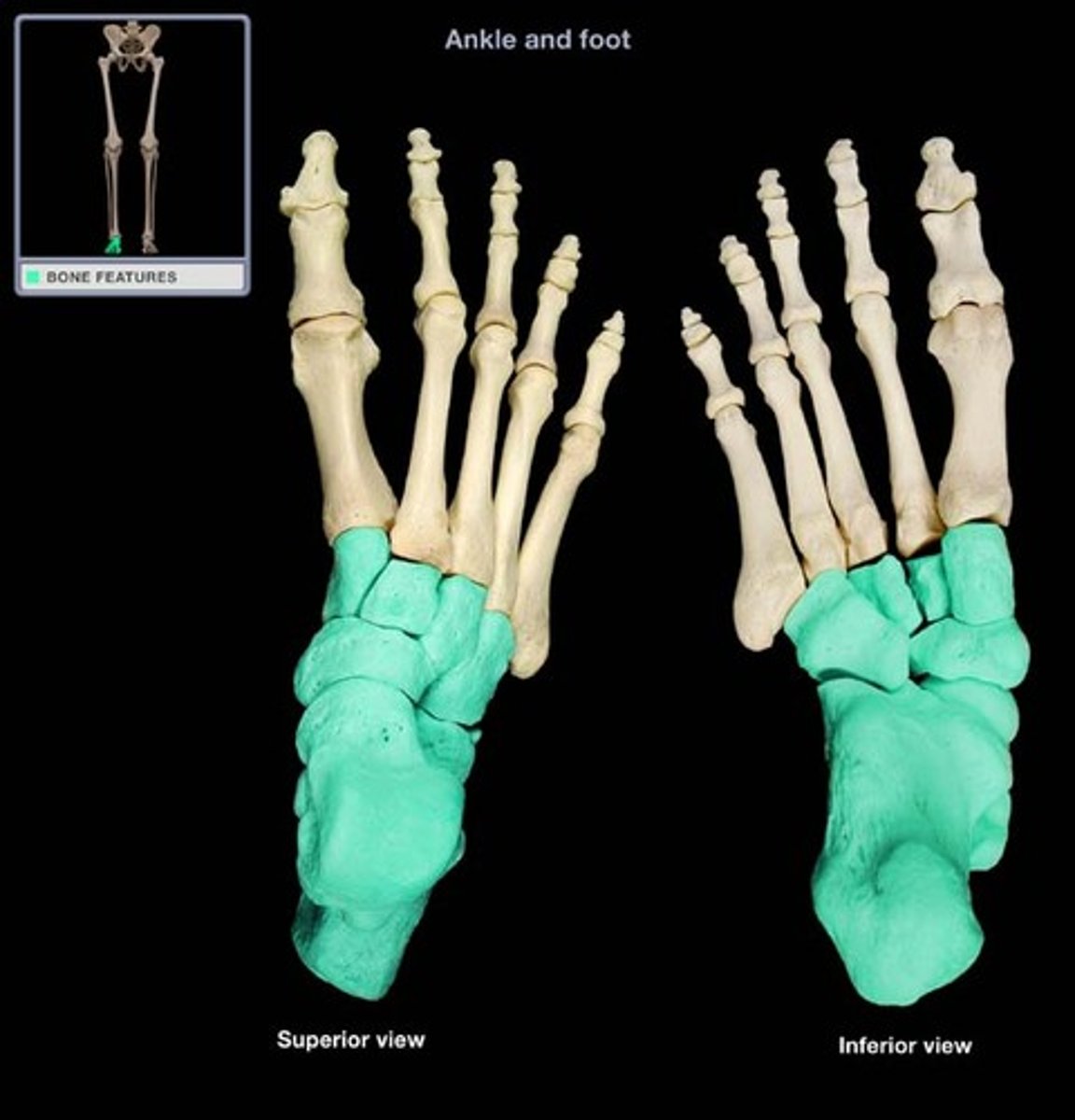
metatarsals
Cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
Cytoplasm
The jelly-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles.
Nucleolus
A structure within the nucleus that is involved in the production of ribosomes.
Organelle
Specialized structures within a cell that have specific functions.
Mitosis
A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell.
Germ Cells
Cells involved in sexual reproduction, such as oocytes and spermatozoa.
Somatic Cells
Any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells.
Plasma Membrane
The semipermeable membrane surrounding the cytoplasm of a cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
A network of membranes found throughout the cell and involved in protein synthesis.
Mitochondria
Organelles responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis.
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle that processes and packages proteins.
Peroxisomes
Organelles containing enzymes that help break down fatty acids and amino acids.
Lysosomes
Organelles responsible for digestion and waste removal within the cell.
Nucleus
The central organelle that contains the cell's DNA and controls its activities.
Nuclear Membrane
A double membrane that surrounds the nucleus and controls the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus.
Cell Cycle
The series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication.
Interphase
The phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows and DNA is replicated. Chromosomes replicate in this phase
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm following mitosis, resulting in two daughter cells.
G0 Phase
A resting phase where cells are not actively dividing.
what organelle is responsible for protien synthesis (site of protien synthesis)
ribosomes
whats the process of protein synthesis
ribosomes read the mRNA and translate the genetic code to amino acids strings, then chains and then protiens
what part of the cell is the main target for radiation exposure
nucleus, contains dna that defines cellular metabolism
prophase
what phase do chromotid condense into visible chromosomes
prophase
what phase do chromatids become attached at the centromere?
prophase
what phase do spindle fibers appear
prophase
what ohase do the nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear
metaphase
what phase do spinle fibers attach to each chromatid and chromosomes align across the center of the cell
anaphase
which phase do centromeres break apart, chromosomes move away from the center and the cleavage furrow appears
telophase
which phase does the nuclerar envelope and both nuclei appear, which phase do the cytoplasm and organelles divide equally, and it the end of cell division
what is one of the initial theories concerning the mechanism by which radiation kills cells
Lysosomes play a big role, agents are capable of altering the permeability of the lysosome membrane, causing release of the enzymes
what part cell cycle involves gene p53(guardian angel gene)
G1
what part of cell cycle is most radiosensitive
G2 phase and M phase
what part of cell cycle is most radioresistant
S phase
Which phase of the somatic cell cycle are ribonucleic acid and proteins synthesized?
G1 phase
what part of interphase is dna synthesized
S phase
which part of bone plays a role in metastic spread
periosteum
part of bone are commonly involved in osteosarcoma
metaphysis
common location of osteosarcoma
long bones of extremities (knee joint) jaws
part of bone commonly involved in chondrosarcoma
diaphysis or metaphysis
common location of chondrosarcoma
pelvis, ribs, vertebra, long bones (proximal part)
common location of Ewing sarcoma
long bone, may be multiple
part of bone commonly involved in Ewing sarcoma
diaphysis
Oral cavity (Common Histology)
Squamous cell carcinoma
Pharynx (Common Histology)
Squamous cell carcinoma
Lung (Common Histology) (commonly centrally located)
Squamous cell carcinoma
Breast (Common Histology)
invasive/Infiltrating ductal carcinoma
Colon and rectum (Common Histology)
Adenocarcinoma
Anus (Common Histology)
Squamous cell carcinoma
Cervix/vagina/vulva (Common Histology)
Squamous cell carcinoma
Endometrium/ uterine (Common Histology)
Adenocarcinoma
Prostate (Common Histology)
Adenocarcinoma
Brain (Common Histology)
Astrocytoma
carcinomas spread by way of the
blood and lymphatics
sarcomas spread by way of
the blood and often metastasis in lungs
bladder
6500cGy
femoral head
5200cGy
heart
4,000 cGy
eye lens
500-1000cGy
rectum
6000 cGy