Biology Test 1
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
State the scientific method in order:
1) Make an observation
2) Ask a question
3) Form a hypothesis answering the question
4) Make a prediction based on the hypothesis
5) Experiment to test prediction
6) Analyze the results
7) If hypothesis was wrong go back to step 3
8) Report results
What is a hypothesis?
A tentative answer to a scientific question. Never proven but supported or refuted. (Prediction)
What is a theory?
More broad or general than a hypothesis. It is supproted by a large amount of evidence.
What is the control group?
The group used for comparison to the experimental group.
What is the experimental group?
Also known as the treatment group. This group differs by one variable.
What is a doubleblind experiment?
This is when neither the people giving nor recieving the treatment know that it is the treatment. It is ideal.
What is inductive reasoning?
From a number of observations, a connection is drawn.
Observation → Pattern → Hypothesis → Theory
What is deductive reasoning?
From a general premise, specific results are predicted.
Theory → Hypothesis → Observation → Confirmation
What is the dependent variable?
The effect, y-axis
What is the independent variable?
Cause/variable being manipulated, x-axis
Five characteristics that make something alive?
Organization, metabolism, evolution, reproduction, response
What is the biological hiearchy order?
Biosphere
Ecosystem
Community
Population
Organism
Organs
Tissues
Cells
Organelles
Molecules
What is the taxonomy order?
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
What are the three domains?
Archaea, Eukarya, Bacteria
What are the four kingdoms within the Eukarya domain?
Plantae, animalia, protista, fungi
What would the term Homo Sapiens be considered?
Bionomial nomenclature.
What are valence electrons?
Electrons in the outermost shell.
What are isotopes?
Atoms that differ in the amount of neutrons.
What is the octet rule?
Elements with a full out shell are most stable.
What is matter?
Anything that takes up space.
What is an element?
A substance that cannot be broken down anymore while still retaining it’s properties.
What are the essential elements?
¼ of elements are essential for life. 96% of living matter is made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen.
What is a compound?
A substance with two or more elements in a fixed ratio.
What is half-life?
The time it takes for ½ of a substance to decay.
What is a covalent bond?
The sharing of a pair of valence electrons.
Why is H2O polar?
Oxygen hogs the electrons thus making part of the molecule negative and part of it positive.
What is a hydrogen bond?
A bond between two covalently bonded polar molecules. This bond is pretty weak.
For example) H20 - H2O
What is an ionic bond?
The bonding of charged atoms (ions).
What is a cation?
A positively charged atom.
What is an anion?
A negatively charged atom.
What is Van der Waals?
A bond that occurs when there is a weak asymetrical arrangment of electrons. Basically, when atoms get very close there is a change that the electrons will move to one side allowing for a very short period of attraction.
What is cohesion?
The property of hydrogen bonds holding water together. Water adhering to water. This also causes surface tension.
For example) Water going from roots to leaves up a stem.
What is a specific heat?
Why does water have a high specific heat?
Specific heat is the heat required to raise a specific amount of a specific substance a specific amount.
Water has a high specific heat due to the ability of hydrogen bonds to absorb heat when broken and release heat when formed. This minimizes temperature changes.
Why does water have a high heat of vaporization?
Many hydrogen bonds must be broken to evaporate water.
Why is ice less dense than water? What are the benefits of this?
Ice is less dense than water because the water molecuels are spaced further out due to hydrogen bonds. The main benefit to life is that lakes don’t completely freeze allowing animals that live in water to survive.
What type of solvent is water and why is it called that?
Water is called the universal solvent. Polar water molecules are attracted to ions letting water pull things apart.
Ions dissolve things through hydration shells.
What is an aqueous solution?
When water is the main solvent in a solution.
What is adhesion?
Water attracting to different molecules. Also helps water go up a stem.
How does water moderate temperature?
It moderates temperature through absorbing heat in the warm air and releasing it to cooler air.
(This is why coastlines are cooler)
What is a calorie (cal)?
The heat required to raise one gram of water by 1 oC.
Remember that water resists change in temperature and state!
What is one specific way that water helps maintain life?
It maintains homeostasis through temperature regulation.
What is hydrophobic?
Having no affinity for water.
Ex) Oils, waxes, fats.
These are nonpolar.
What is hydrophillic?
Having an affinity for water.
Ex) Acids, bases, etc.
Polar.
What is an amphiphile?
Having an affinity for both.
Ex) Detergent, phospholids.
These have hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
What is a mol?
6.02 × 10²³ molecules are in any substance.
What is a molecular mass?
The sum of the atomic mass of all molecules. Add the atomic masses together.
What is molarity?
The number of moles of solute in a liter of solution.
What are acids?
Substances that donate H+ (protons) to a solution.
Any acid is XH → X + H+
What are bases?
Substances that absorb H+ (protons) from solutions.
What is the pH scale?
Goes from 0→14. It is the concentration of protons in a solution.
0<x<7 is an acid. (More protons as goes down)
7<x<14 is a base. (Less protons as goes up)
What are buffers?
Substances that stabilize or maintain pH. They help maintain homeostasis.
Ex) Carbonic acid in the body.
What is organic chemistry?
The study of compounds that contain carbon.
What type of shape do single carbon bonds have?
Tetrahedral
What shape do carbon double bonds have?
Planar
What can single bonds do that doubles cant?
They can flip and rotate.
What are four ways that structure can be different?
Length, double bond position, branching, and rings.
What are structural isomers?
Two compounds with the same formula but different structures.
What are cis-trans isomers? What is the cis isomer? What is the trans isomer?
Isomers with a double bond that resists twisting. This cis isomer has X on the same side. The trans has X on different sides.
What is an enantiomer?
Mirrored isomers. The L isomer is left and the D isomer is right.
Why are enantiomers special?
Some enantiomers are only effective on one side. (L or D)
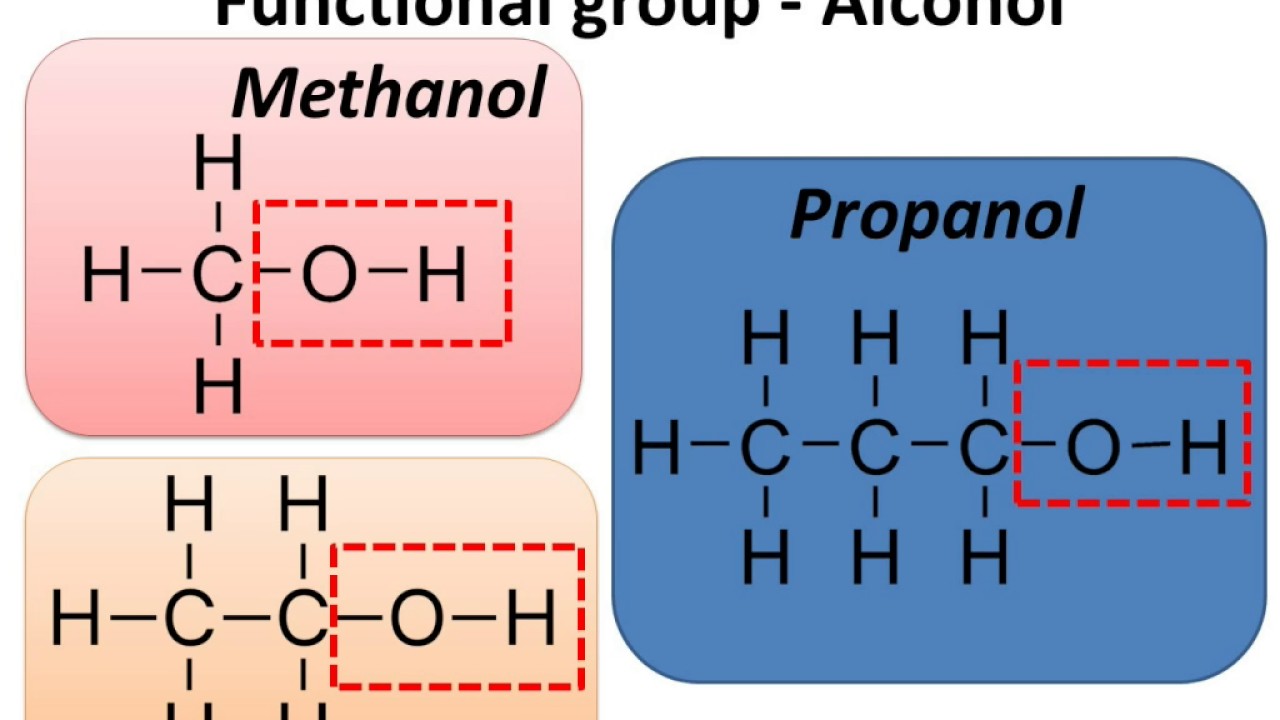
What is the hydroxyl group?
-OH (alcohol)
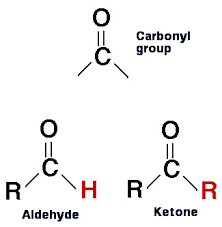
What is the carbonyl group?
C(double)O (ketone aldehyde)
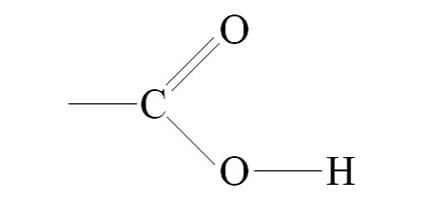
What is the Carboxyl group?
-COOH (carboxylic acid or organic acid) (acid)
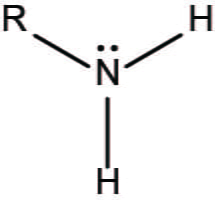
What is the amino group?
-NH2 (amine) (base)
What is the sulfahydryl group?
-SH (Thiol)
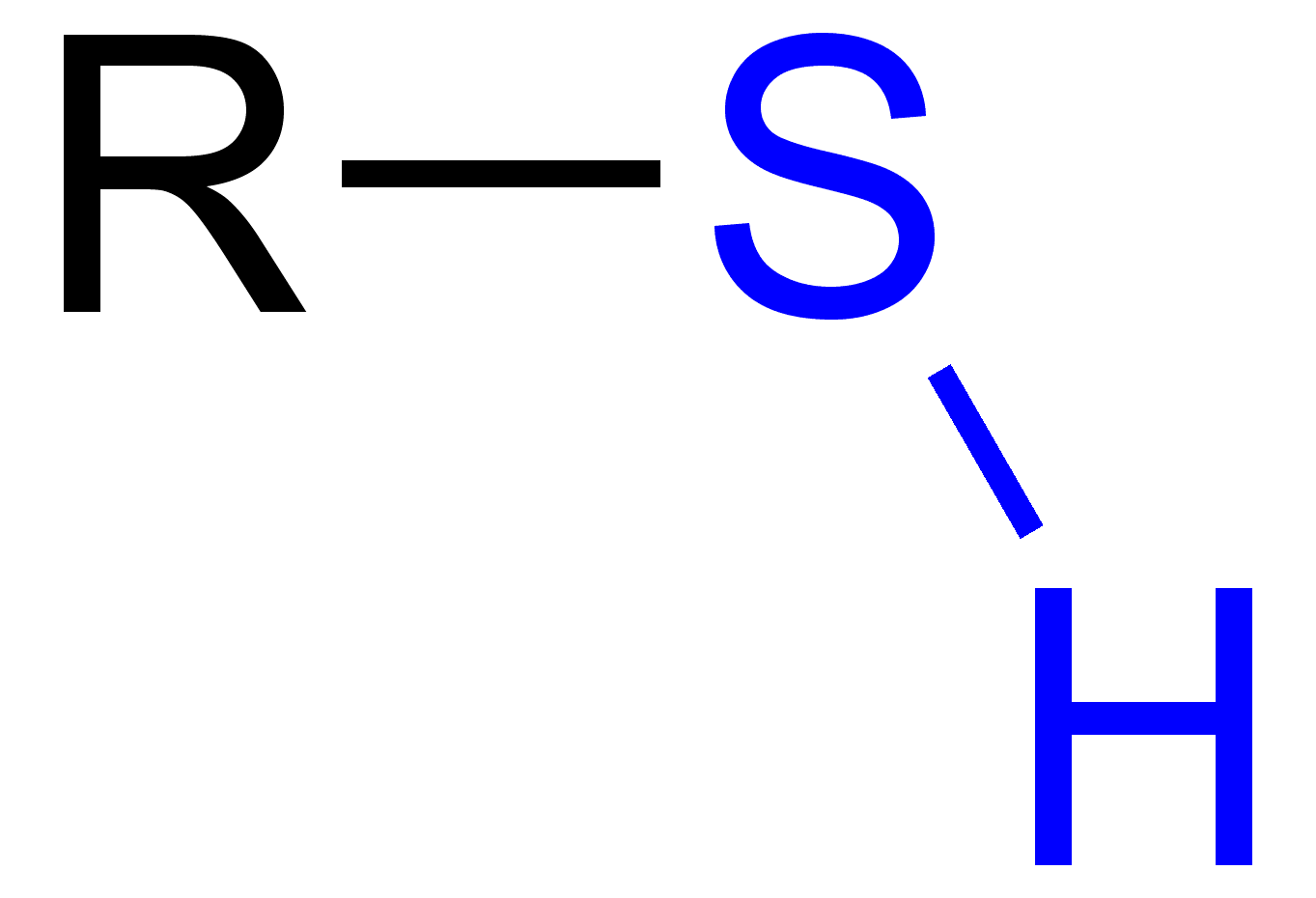
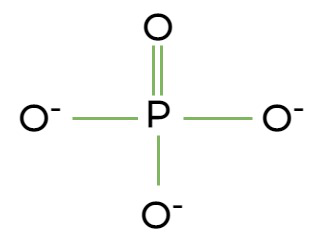
What is the phosphate group?
-OPO32- (organic phosphate)
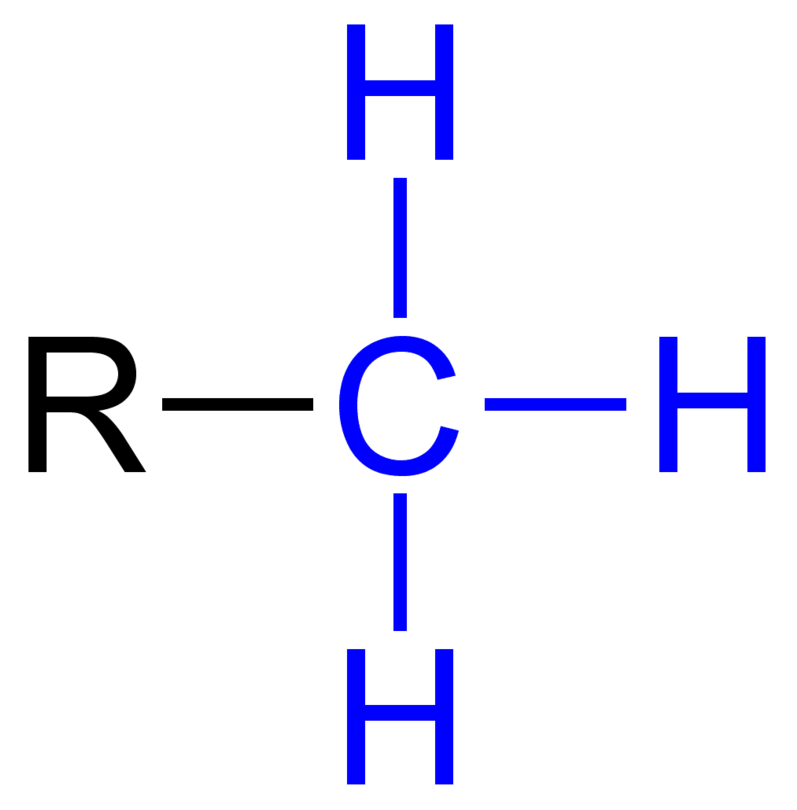
What is the methyl group?
-CH3 (Methylated compound)
What are monomers?
Singular molecules (smaller)
What are polymers?
Many molecules (bigger)
What is a dehydration reaction?
The process of removing a water molecule to synthesize a polymer.
What is the hydrolysis process?
Breaking down a polymer by adding a water molecule.
What are carbohydrates?
Molecules with C, H, and O.
What does it mean if a molecule ends in -ose?
It is a sugar. (carbohydrate)
What are monosacharides?
Carbohydrate monomers. Ex) Glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose
What are disacharides, oligosacharides, and polyscharides?
Carbohydrate polymers. Oligoscharides are medium sized.
Ex) Maltose, sucrose, starch, cellulose, and chitin.
What are trioses, pentoses, and hexoses?
Three, five, and six carbon sugars.
What other form can glucose take?
It can be in a circle with different properties.
What is the difference between alpha and beta?
Alpha and beta have linkages on different sides.
What is different about cellulose?
It is a sugar but can’t be digested. It is a beta.
Why is chitin similar to cellulose?
Both are undigestible sugars.
What are exoskeletons made of?
Chitin
What are lipids used for?
Long term energy.
Name some monomer and polymer lipids:
Monomer: Glycerol, fatty acides
Polymer: Triglycerides, fats, waxs, oils, phospholids, and steorids.
What process turns glyceride into triglyceride?
Dehydration
What is a fat that our bodies really like and it’s semi-good for us? Has a lot of hydrogen.
Saturated fat
Which fat is lacking hydrogen?
Unsaturated fat.
Which fat is more saturated and goes through hydrogenization?
Trans-fat.
What is the difference betwene ketose and aldoses?
Ketose: Carbonyl group in the carbon skeleton
Aldoses: Carbonyl group at end of carbon skeleton.