1. General Evaluation of the Gastrointestinal System
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What are important aspects of the history? These aspects are important in evaluating what?
S
F
M
C
signalment
feeding and housing
metabolic status
cardiovascular status
pain
Colic is not a ________ but a ________ ________, and can be ________ or ____-________.
diagnosis; clinical sign; intestinal; non-intestinal
What are some common symptoms associated with colic?
L
S
K
E
P
L
N
E
looking or biting at sides
stretching out
kicking at belly
excessive rolling
pawing
lip curl
not eating
excessive lying down
What are the main components of a physical exam?
G
F
general (hydration, endotoxemia, septicemia)
focused (gastro intestinal, gut sounds, feces, extra intestinal)
What are the components of a colic work up?
D
S
P
R
N
detailed history
signs of colic
physical exam
rectal exam
nasogastric intubation
What heart rate is considered mildly elevated?
40-60
What heart rate is considered moderately elevated?
60-80
What heart rate is considered severely elevated?
over 80
What respiratory rate is considered mildly elevated?
20-30
What respiratory rate is considered moderately elevated?
30-40
What respiratory rate is considered severely elevated?
over 40
What are components of the laboratory exams?
C
B
U
F
CBC and inflammatory markers
biochemistry
urinalysis
fecal analysis
What are components of the biochemistry aspect of the laboratory exam?
L
G
E
B
G
lactate
glucose
electrolytes (acidosis)
BUN/creatinine (dehydration)
GGT (right dorsal displacement)
What are normal lactate levels?
< 2 mmol/L
What lactate levels indicate poor prognosis?
> 6 mmol/L and or peritoneal lactate 2X serum
What is normal glucose level?
80-100 mg/dL
What glucose level indicates a poor prognosis?
> 300 mg/dL
What indicates endotoxemia?
severe neutropenia or diverging PCV/TP
What is the heart rate when dehydration is 6%?
40-60
What is the CRT when dehydration is 6%?
2
What is the PCV when dehydration is 6%?
40
What is the TP when dehydration is 6%?
7
What is the creatinine when dehydration is 6%?
1.5-2
What is the skin when dehydration is 6%?
2
What is the eyes when dehydration is 6%?
±
What is the MM moisture when dehydration is 6%?
moist
What is the MM color when dehydration is 6%?
pink
What is the heart rate when dehydration is 8%?
61-80
What is the CRT when dehydration is 8%?
3
What is the PCV when dehydration is 8%?
45
What is the TP when dehydration is 8%?
7.5
What is the creatinine when dehydration is 8%?
2-3
What is the skin when dehydration is 8%?
2-3
What is the eyes when dehydration is 8%?
±
What is the MM moisture when dehydration is 8%?
tacky
What is the MM color when dehydration is 8%?
pink
What is the heart rate when dehydration is 10%?
81-100
What is the CRT when dehydration is 10%?
4
What is the PCV when dehydration is 10%?
50
What is the TP when dehydration is 10%?
8
What is the creatinine when dehydration is 10%?
3-4
What is the skin when dehydration is 10%?
3-4
What is the eyes when dehydration is 10%?
+
What is the MM moisture when dehydration is 10%?
dry
What is the MM color when dehydration is 10%?
red
What is the heart rate when dehydration is 12%?
> 100
What is the CRT when dehydration is 12%?
> 4
What is the PCV when dehydration is 12%?
> 50
What is the TP when dehydration is 12%?
> 8
What is the creatinine when dehydration is 12%?
> 4
What is the skin when dehydration is 12%?
> 4
What is the eyes when dehydration is 12%?
++
What is the MM moisture when dehydration is 12%?
dry
What is the MM color when dehydration is 12%?
cyanotic
Why is passing a naso-gastric tube so important in a horse with colic?
they cannot vomit and the stomach can rupture if the pressure is not relieved
Depending on the horse’s behavior, what needs to be done before passing a nastro-gastric tube?
P
S
physical restraint (twitch)
sedation with an alpha 2 agonist
Where does the NG tube pass through first? How do you know when to stop? What happens next?
ventral meatus; measure the difference between the end of the tube to the end of the horse’s throat; once you reach the horse’s throat, angle the head relative to the neck and apply slight pressure to get the horse to swallow the tube
Where do you have to make sure you are before you continue advancing the NG tube into the stomach? What can be done to help?
in the esophagus; blow in the tube while advancing because it can help to dilate the esophagus
How do you check if you’re in the esophagus?
look and feel the tube
Once you are in the stomach with the NG tube, what needs to be done?
6-8 pumps of water once in the stomach to create a siphon
What does reflux mean? What is a significant amount?
any fluid that we get back in addition to what we put in; if we get 1-2 L more than we put in
What are other reasons to pass a NG tube?
O
R
obstruction
reflux
What does it mean if you get reflux from the NG tube?
O
I
obstruction
ileus
What are we evaluating when it comes to information about the reflux obtained from the NG tube?
V
C
O
C
F
volume
color
odor
consistency
feed material
Why does reflux occur if there is ileus?
SI motility is reduced and fluid accumulates into the stomach
How can a NG tube be caused as a treatment?
R
R
N
routine medication
relieve choke
nasogastric decompression
What is the most common complication when it comes to NG tubes?
nose bleeds
What are other complications associated with NG tubes that can be avoided with careful use>
A
P
aspiration
perforation
Prior to performing a rectal exam, what needs to be prepared?
Y
C
P
yourself
client
patient
What other aspects are important prior to performing a rectal exam?
R
S
A
restraint
sedation
additional measures
What are common and normal things you should feel on rectal exam?
A
C
S
O
F
P
aorta (midline)
caudal border of left kidney (left)
spleen (left abdominal wall)
one of the bands of the cecum (right)
fecal balls in small colon (right)
pelvic flexure sometimes (right)
What are abnormal findings on a rectal exam?
C
I
T
M
F
T
P
G
I
D
crepitus
irregular or rough surface
thickened wall
masses
firm tubular small bowel
tight bands
painful areas
gas filled LI
impacted LI
distended SI
What is the main possible complication associated with rectal exams?
rectal tear
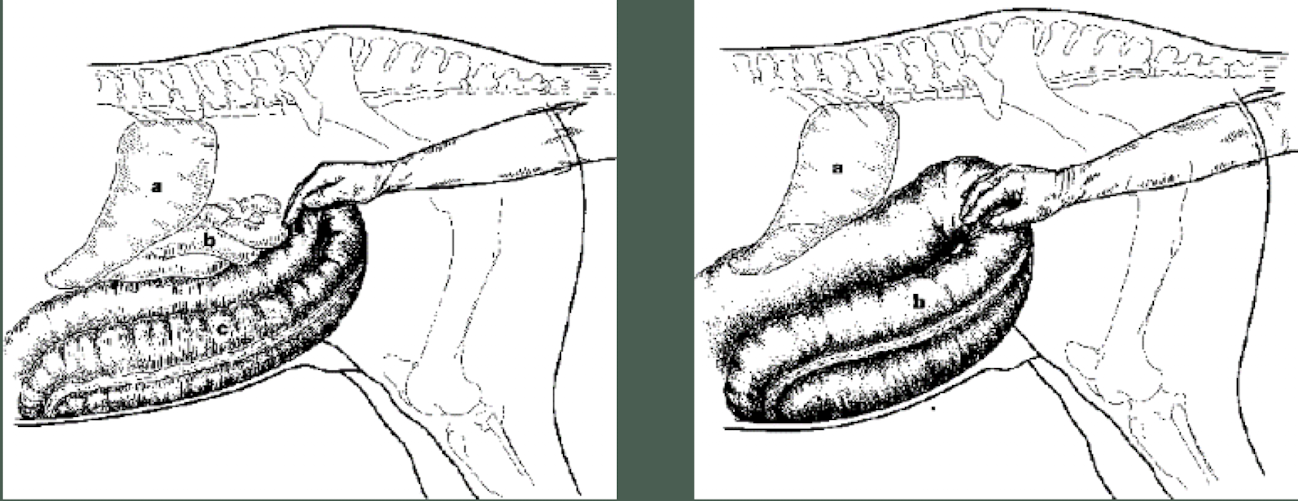
What is being palpated in this picture?
pelvic flexure
What is a common issue that horses without enough water or horses that have been recently moved from pasture to stalls have?
pelvic flexure impaction
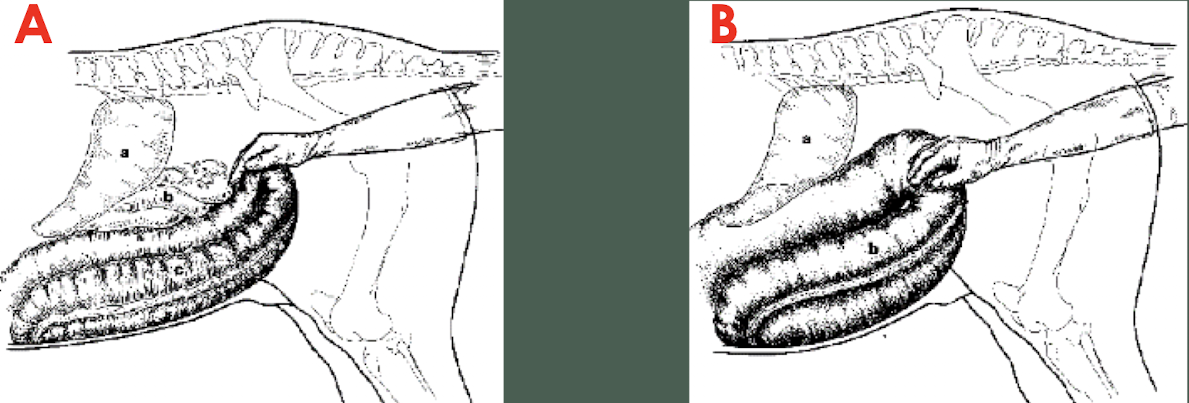
The horse had a hoof abscess and is stabled on straw. What is the most likely problem in picture B?
impaction
What are reasons to perform an abdominocentesis?
D
S
T
P
diagnosis
surgery
treatment
prognosis
What type of patient preparation is done with abdominocentesis?
sterile prep and can use a little bit of lidocaine on the skin
What are the possible techniques when it comes to abdominocentesis?
needle or teat cannula
If using the needle technique, where should you insert it?
ventral midline at the lowest point of the abdomen
If using the teat cannula technique, where should you insert it? Why?
right of ventral midline; you do not want to puncture the spleen
Can you use an ultrasound when performing an abdominocentesis? Why or why not?
yes; allows you to maximize your chances of getting fluid because you can visualize it
What should normal abdominal fluid look like?
pale/translucent yellow
What information can be obtained from abdominal fluid?
G
L
P
gross aspect
lab analysis
prognosis
What gross aspects of abdominal fluid can be evaluated?
C
S
T
color
smell
turbidity
What other information can be evaluated from abdominal fluid?
V
C
L
D
T
L
volume
color
leukocyte count
differential count
total protein
lactate
What is the normal volume of abdominal fluid?
slow drip that is not profuse or streaming
What is the normal color of abdominal fluid?
yellow and clear
What is the normal leukocyte count of abdominal fluid?
< 5000 cells/uL
What is the normal differential count of abdominal fluid?
< 50% neutrophils
What is the normal total protein of abdominal fluid?
< 2.5 g/dL (usually < 1.5 g/dL)
What is the normal lactate of abdominal fluid?
< 2 mmol/L
When is the prognosis bad based off of abdominal fluid?
if the abdominal fluid appears serosanguinous and changes from pale yellow
What are possible complications associated with abdominocentesis?
C
A
S
B
O
cellulitis
abscess
splenic puncture
bleeding
omental herniation
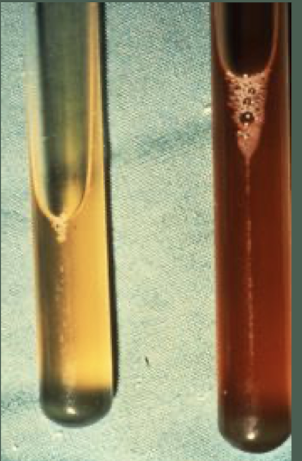
You are an equine surgeon and a colleague referred you a horse with colic. He felt small intestinal distention on rectal exam and got the peritoneal fluid depicted in the image on the left. You see the horse a couple of hours later and get the sample in the image on the right. Does this horse need surgery?
yes
What type of probe is best to use with ultrasound?
2-5 MHz curvilinear transducer
What is a good approach for ultrasound?
C
P
D
consistent systematic approach
position of transducer and marker
depth of the field of view
What type of technique is used in a horse with colic? How long does it usually take?
fast localized abdominal sonography (FLASH); 15 minutes
What are the 7 locations viewed with FLASH ultrasound?
V
G
S
L
D
R
T
ventral
gastric
spleno-renal
left middle third
duodenal
right middle third
thoracic
What information can be obtained with ultrasound?
L
P
W
D
C
A
location
peristalsis
wall aspect
diameter
content
abnormal structures