Cell Structures and Cell Cycle - Lab Quiz
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Interphase includes
G1, S, G2
G1
Growth or gap 1. Newly formed cell grows and performs its function. Each chromosome is 1 chromatid.
S Phase
DNA replicated and centrioles copy.
G2
Growth or gap 2. Cell grows and prepares for mitosis. Each chromosome has 2 chromatids.
Mitosis includes
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis
Prophase
Chromosomes of 2 chromatids condense and are visible with light microscope. Nucleus and nucleolus break down. Centrosomes with centrioles move toward opposite poles. Mitotic spindle of microtubules grow from centrioles to cell midline. Mitotic spindle attaches to chromosomes.
Metaphase
Chromosomes aligned at middle of cell, with one chromatid facing each pole. No nucleus is visible.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate from each other. Each chromatid is now its own chromosome with its own centromere. Sister chromatids move to opposite poles along mitotic spindle microtubules.
Telophase
Chromosomes are at opposite poles in the cell. Nucleus reforms from vesicles, surrounding each set of chromosomes. Mitotic spindle breaks down completely.
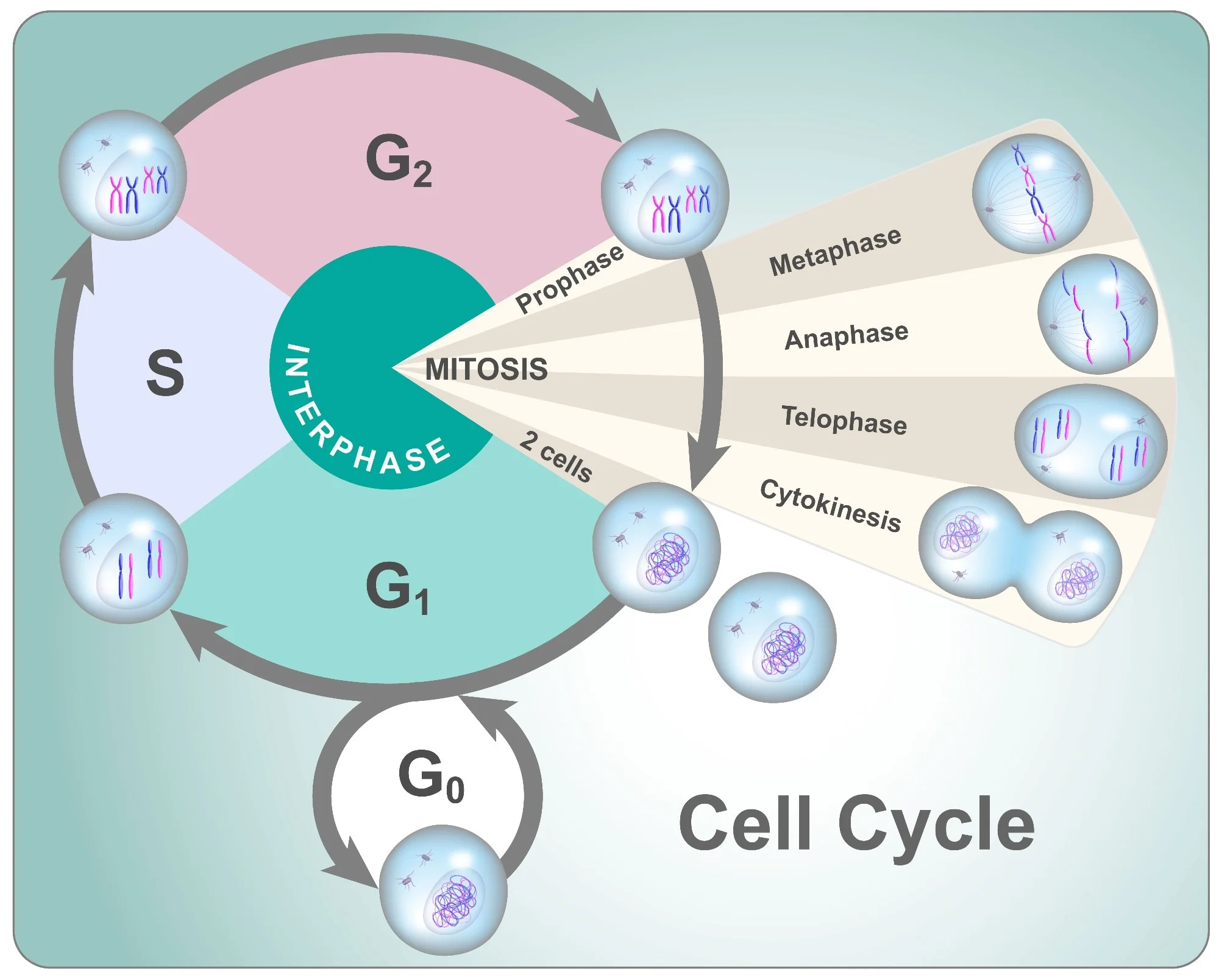
Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm distributed between 2 daughter cells as plasma membrane pinches in.
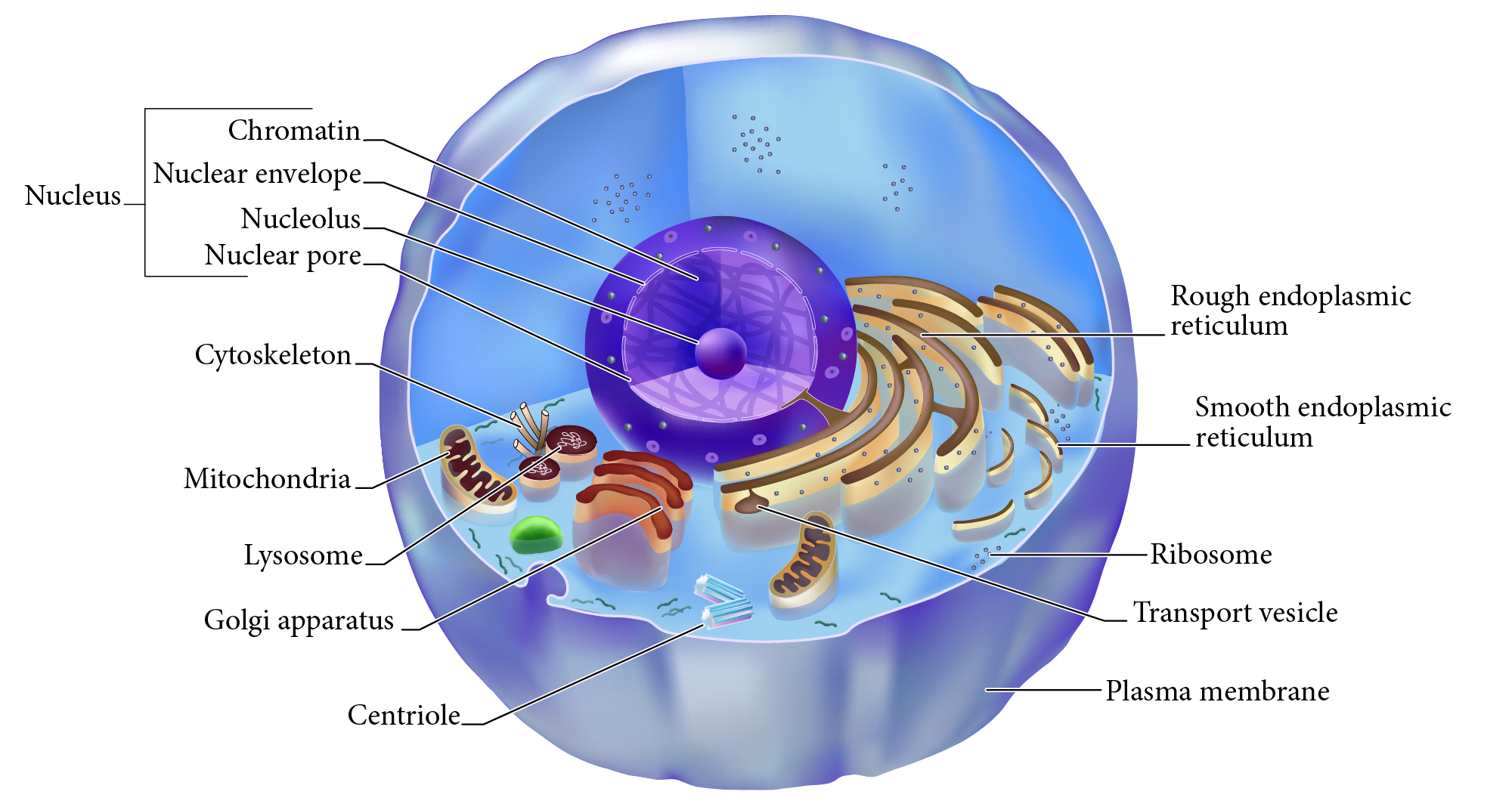
Nucleus
Double membrane structure with most of the cell's DNA genetic library.
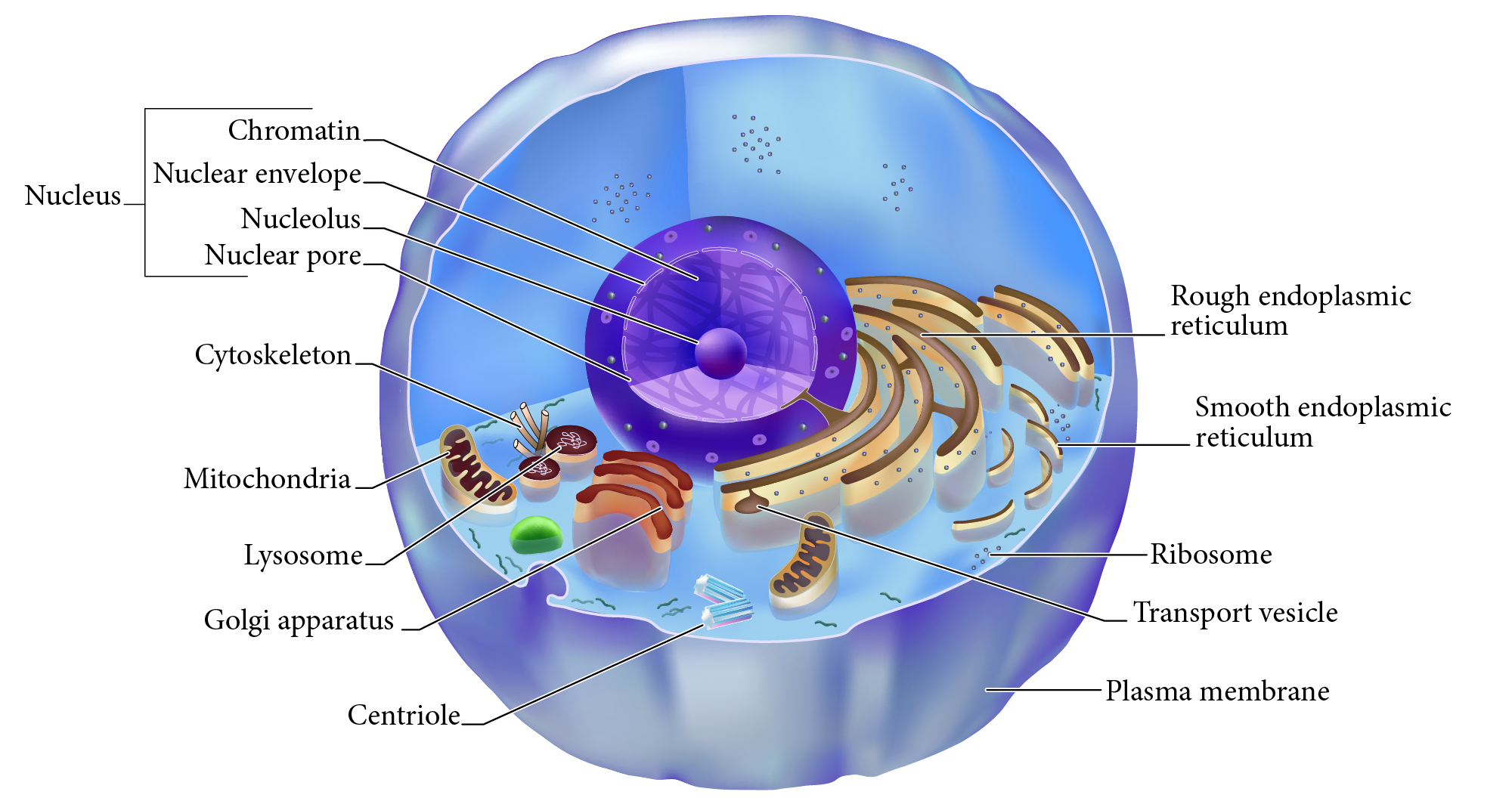
Nuclear envelope
Double layered membrane surrounding the nucleus.
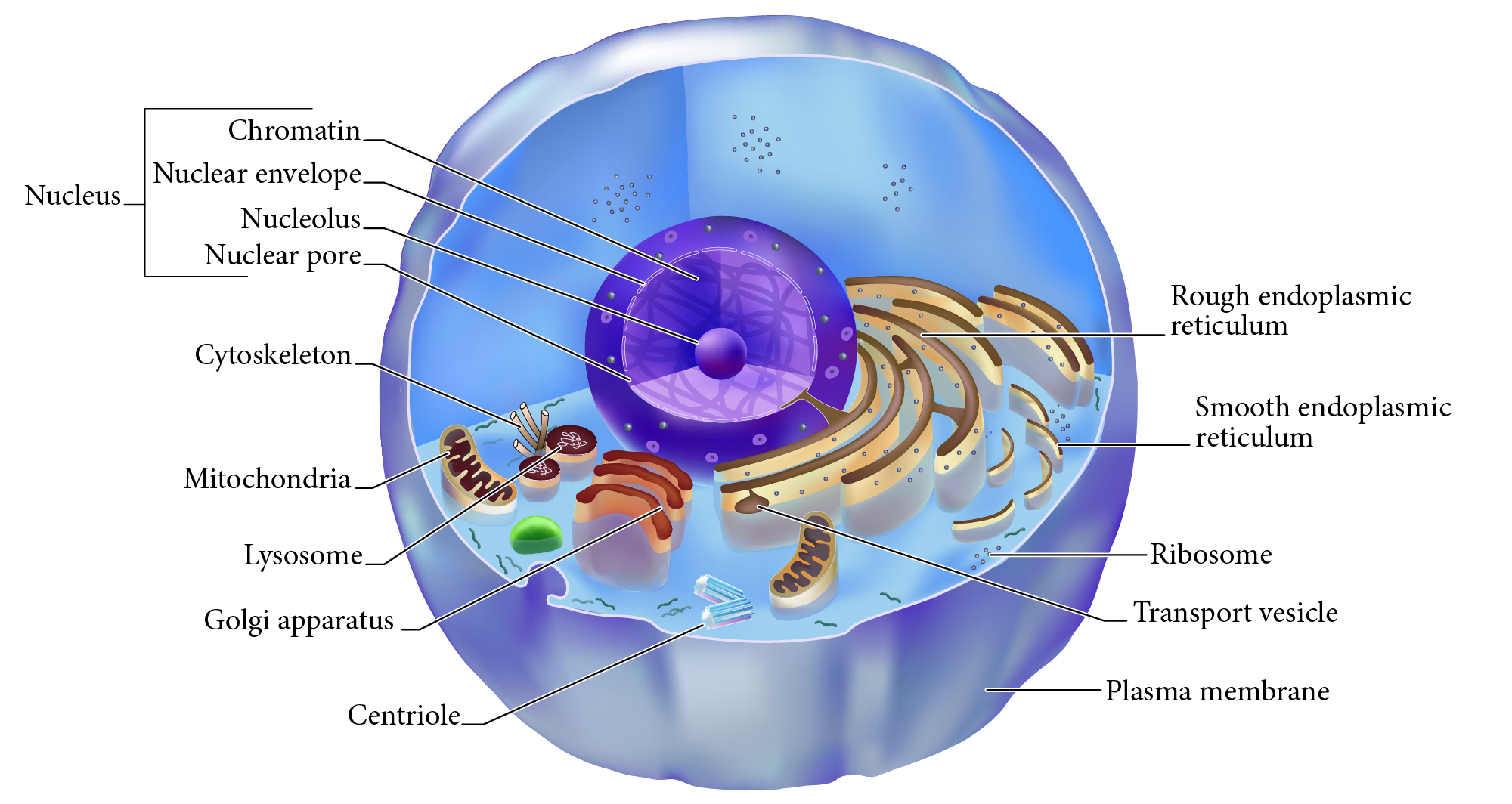
Nucleolus
Darkly staining area of nucleus, site of rRNA synthesis.
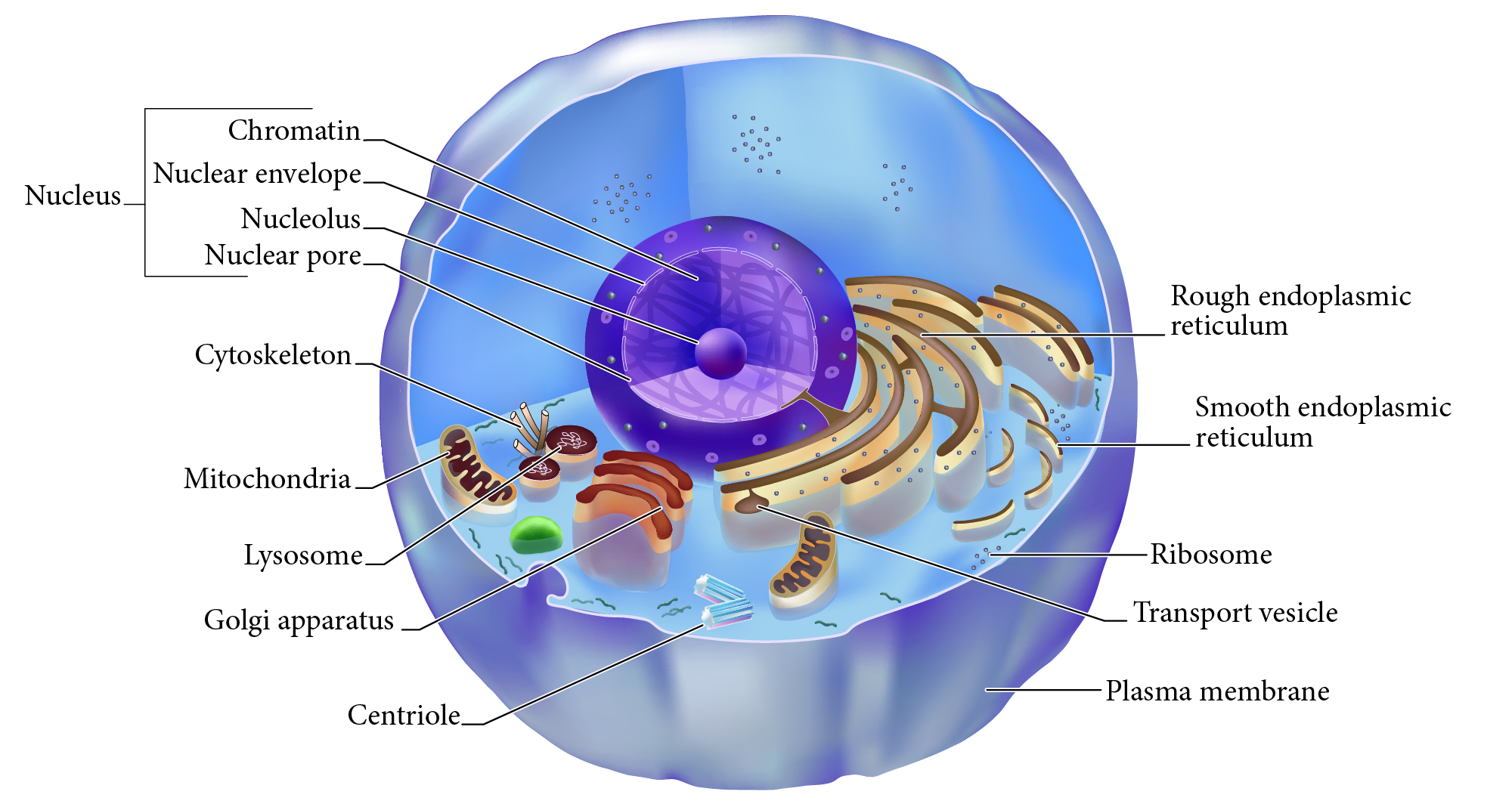
Chromatin
DNA complexed with organizing proteins as extended strands.
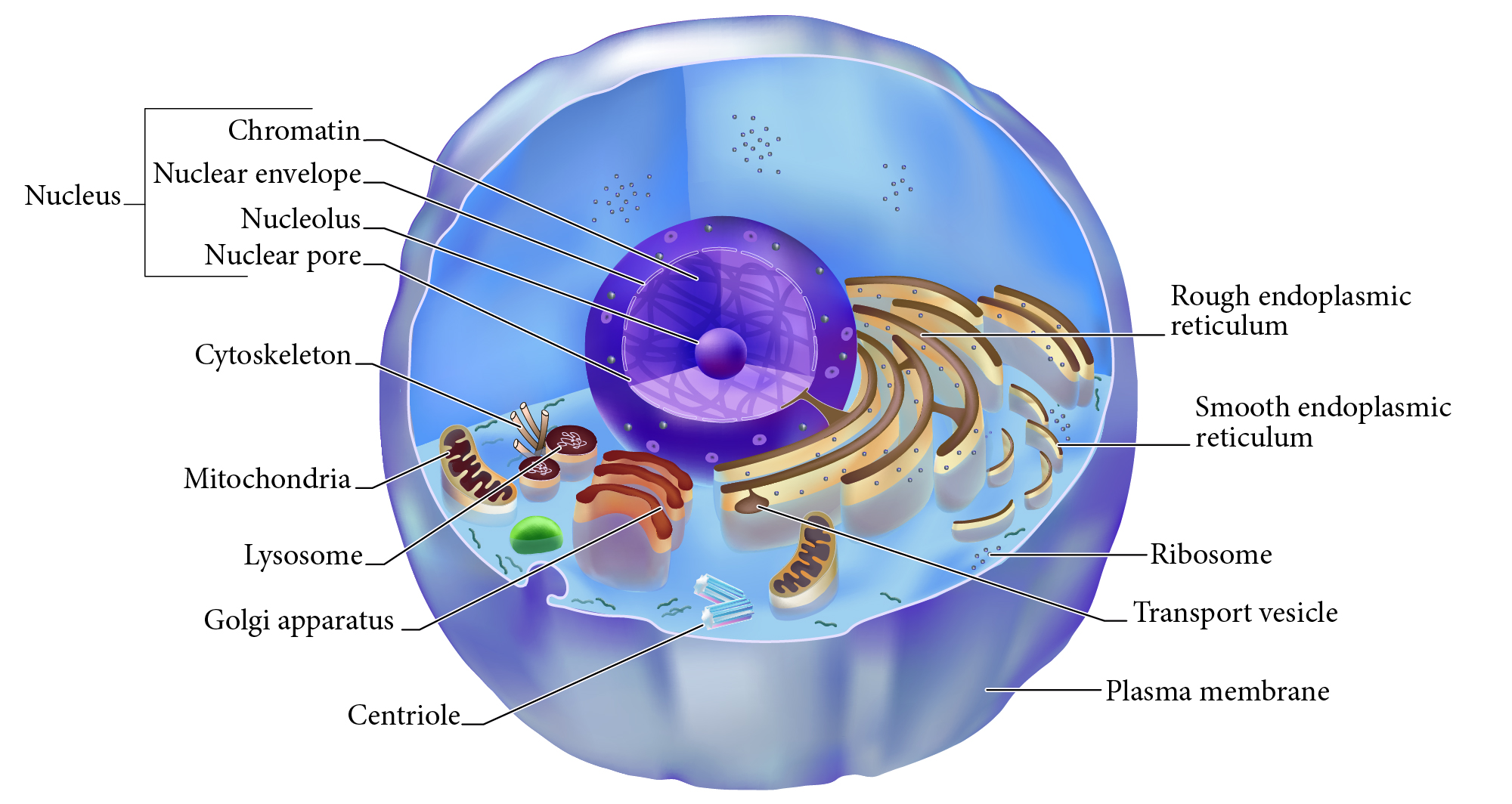
Nuclear Pore
Protein-lined connection through nuclear envelope to transfer between nucleus and cytoplasm.
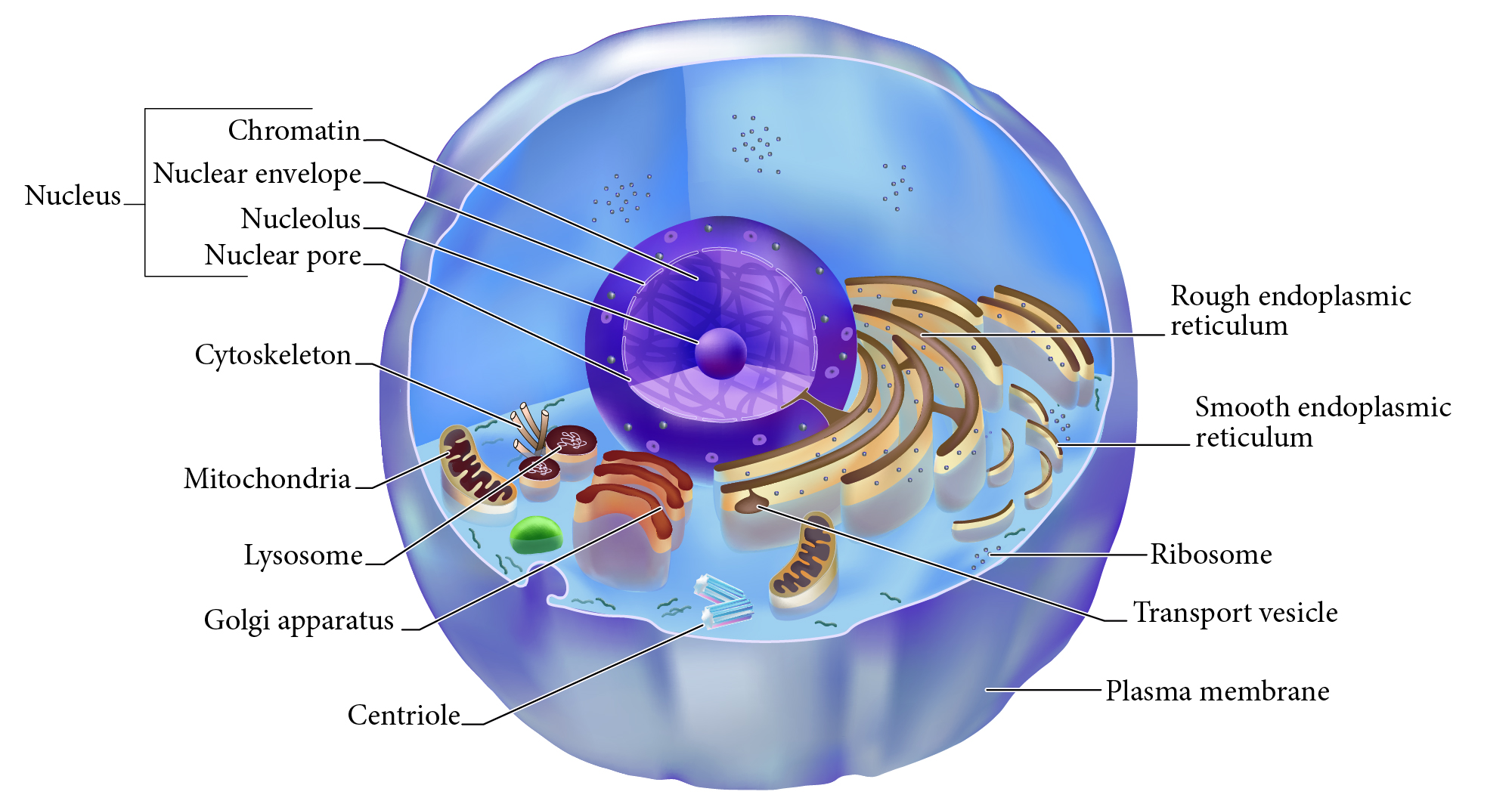
Cytoskeleton
Protein scaffolding supporting cell shape and transport mechanisms. 3 types are microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules.
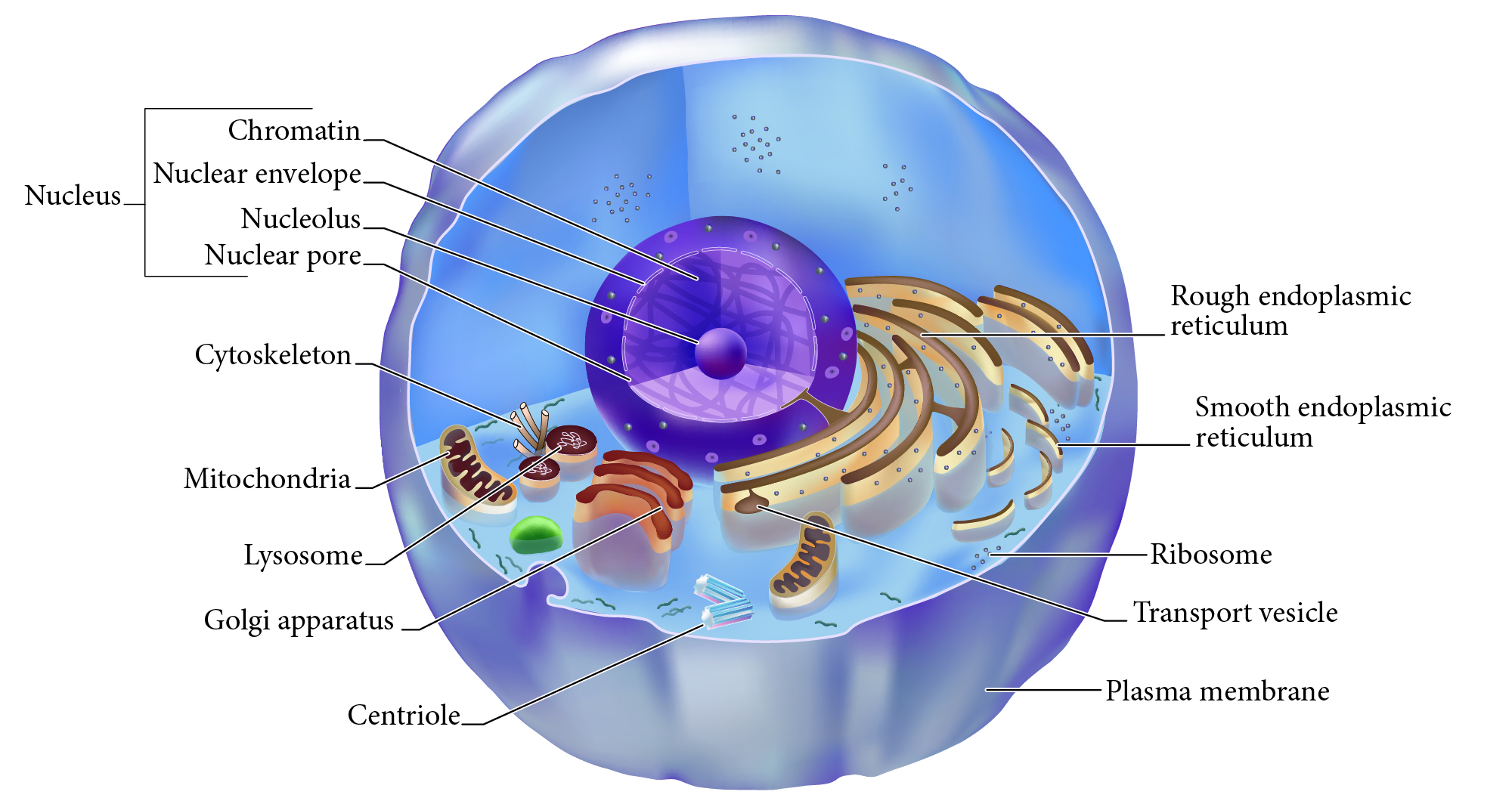
Plasma Membrane
Cell surface selectively permeable barrier, regulating transport into and out of cell.
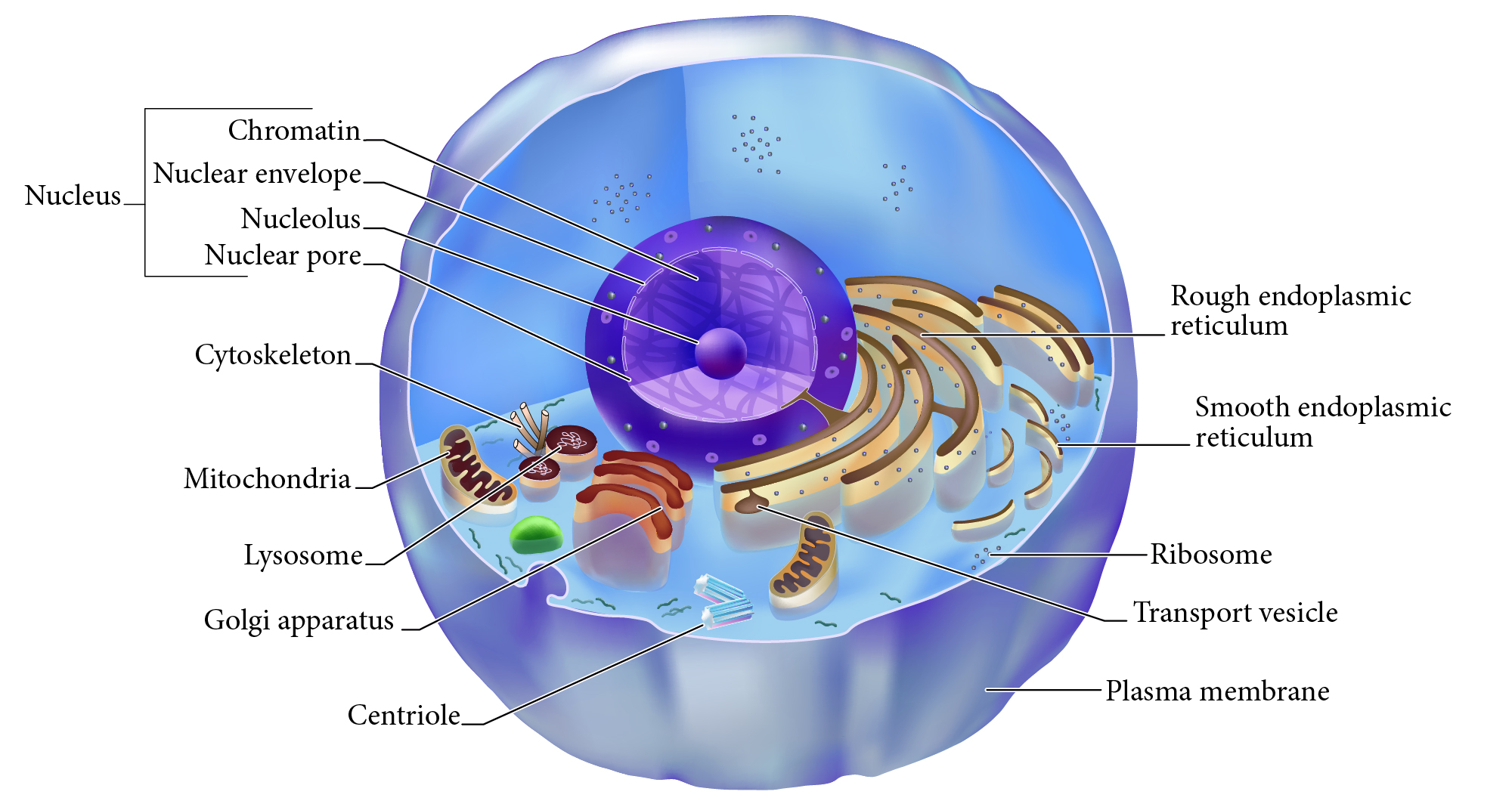
Ribosome
Structure of rRNA and proteins as site of protein synthesis. Can be free in cytoplasm or attached to RER.
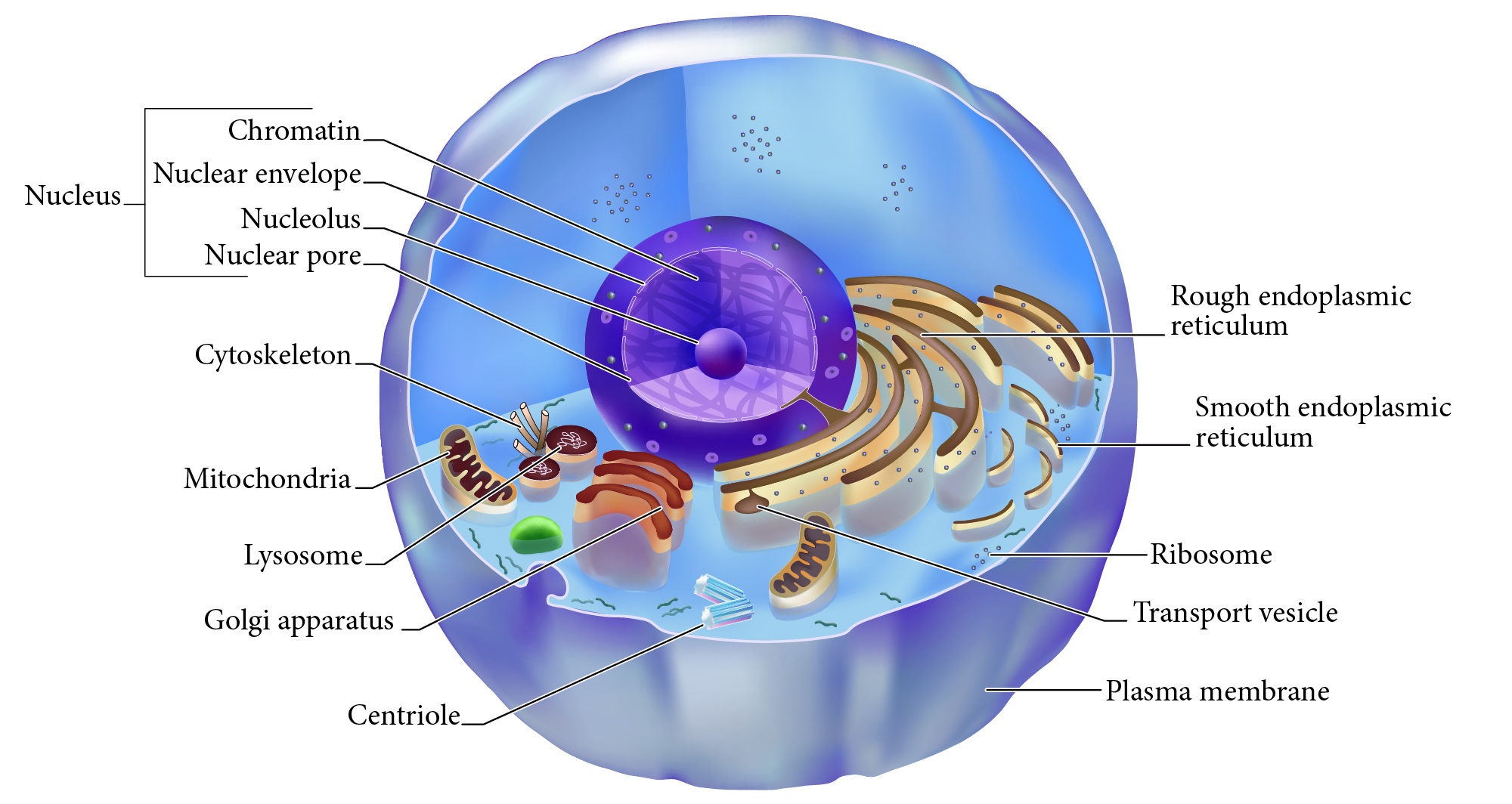
RER, Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Interlinked membrane canals with ribosomes attached externally. Proteins synthesized on ribosomes enter the ____ for further processing. Synthesizes phospholipids.
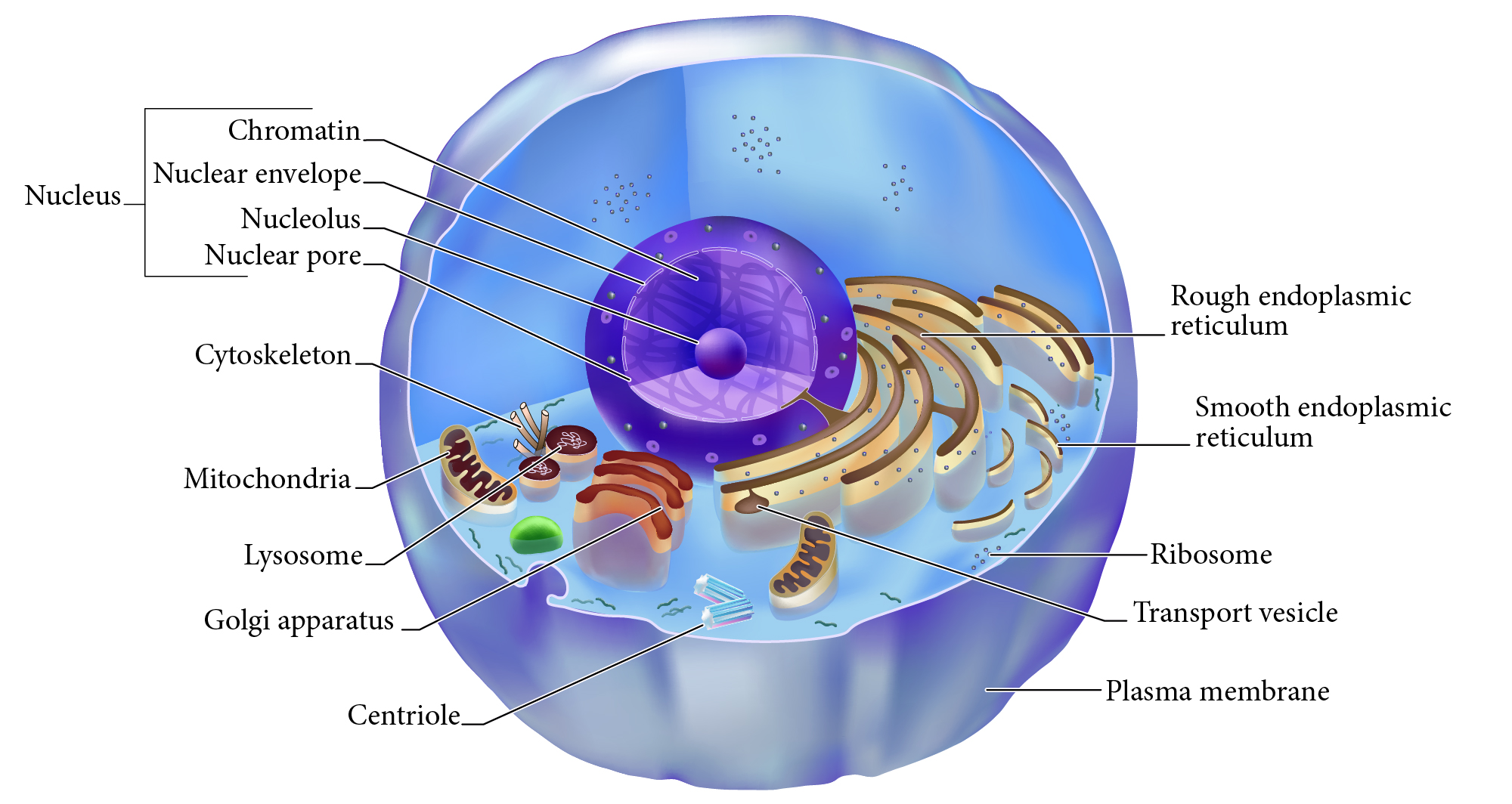
Mitochondrion
Double membrane organelle; aerobic cell respiration makes most cell ATP energy source.
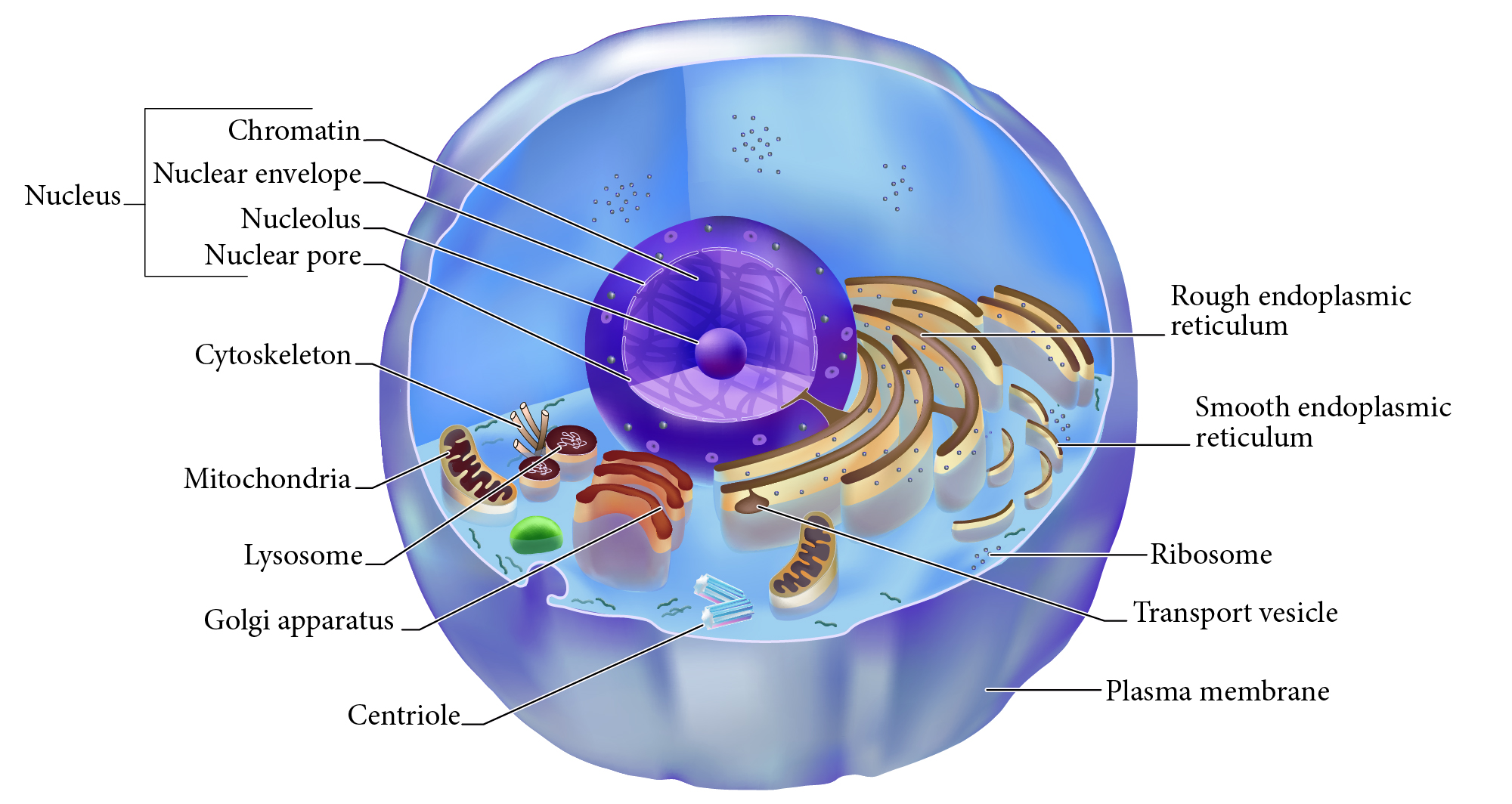
Lysosome
Membrane vesicle of digestive enzymes. Digestion of worn out organelles and cellular components.
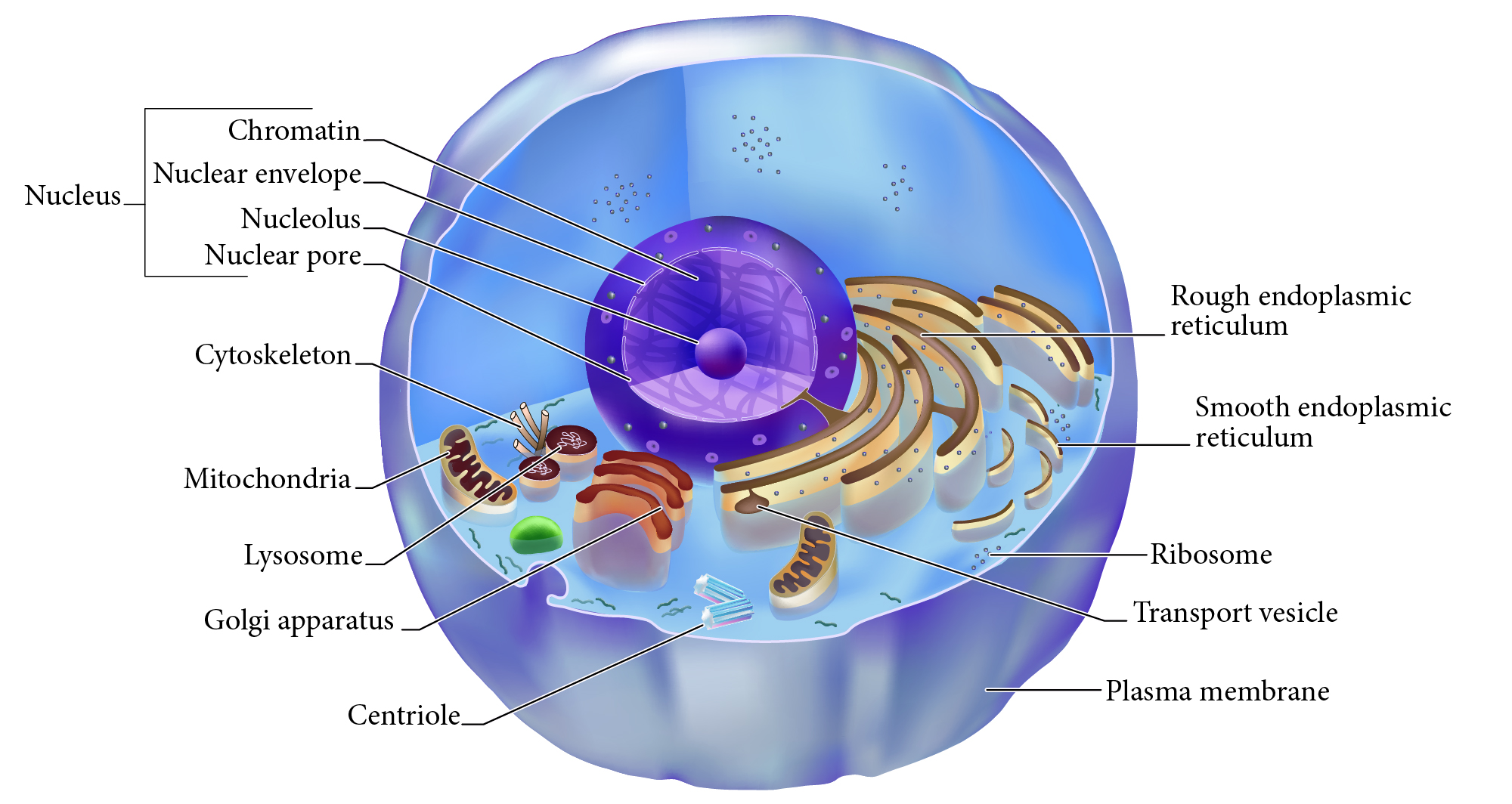
SER, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Membrane tubes without attached ribosomes. Functions vary by cell, such as lipid metabolism, detoxification, and storing calcium.
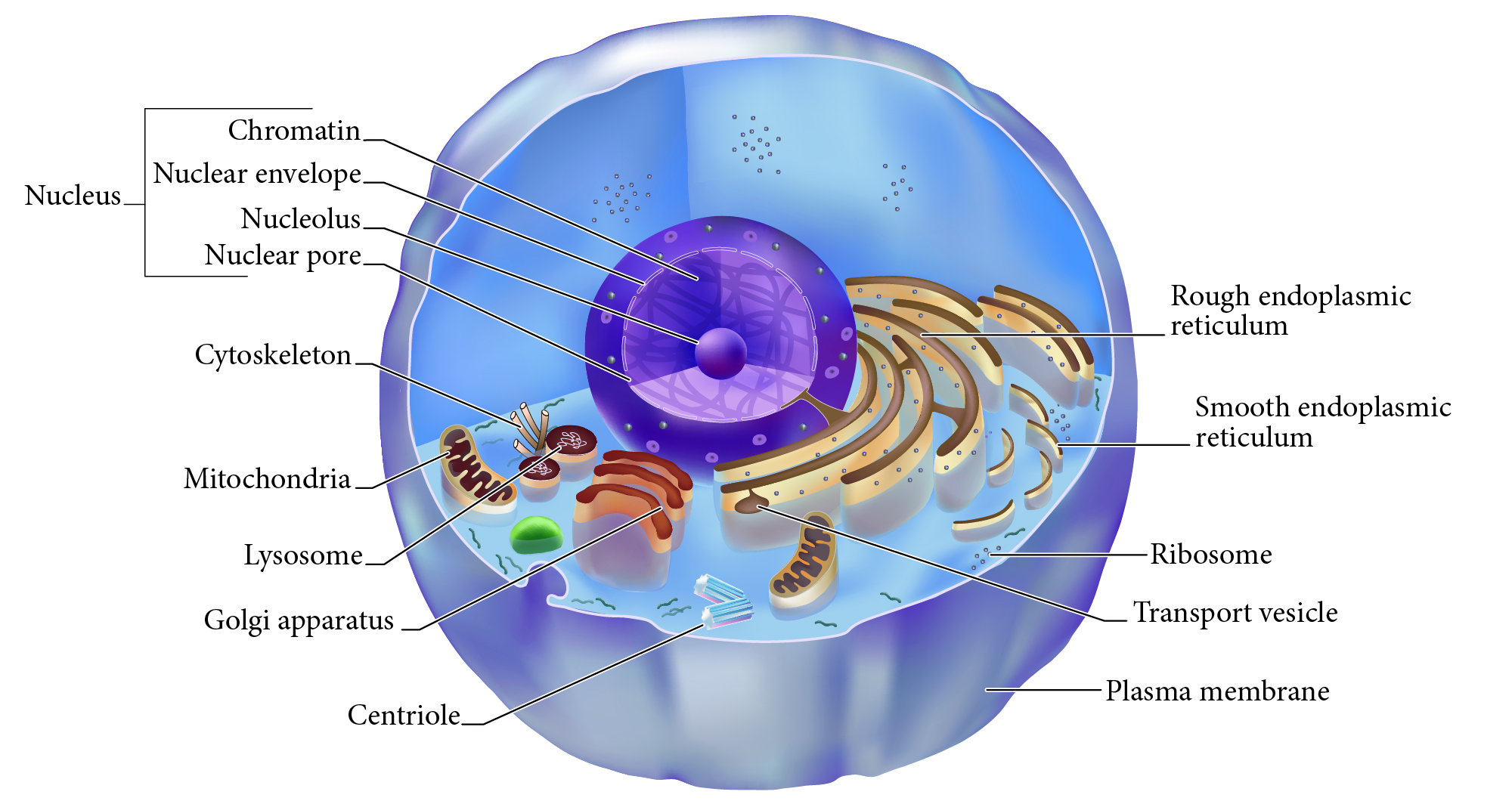
Centriole
Structures in cytoplasm area called centrosome which organize cytoskeleton protein fibers during cell division.
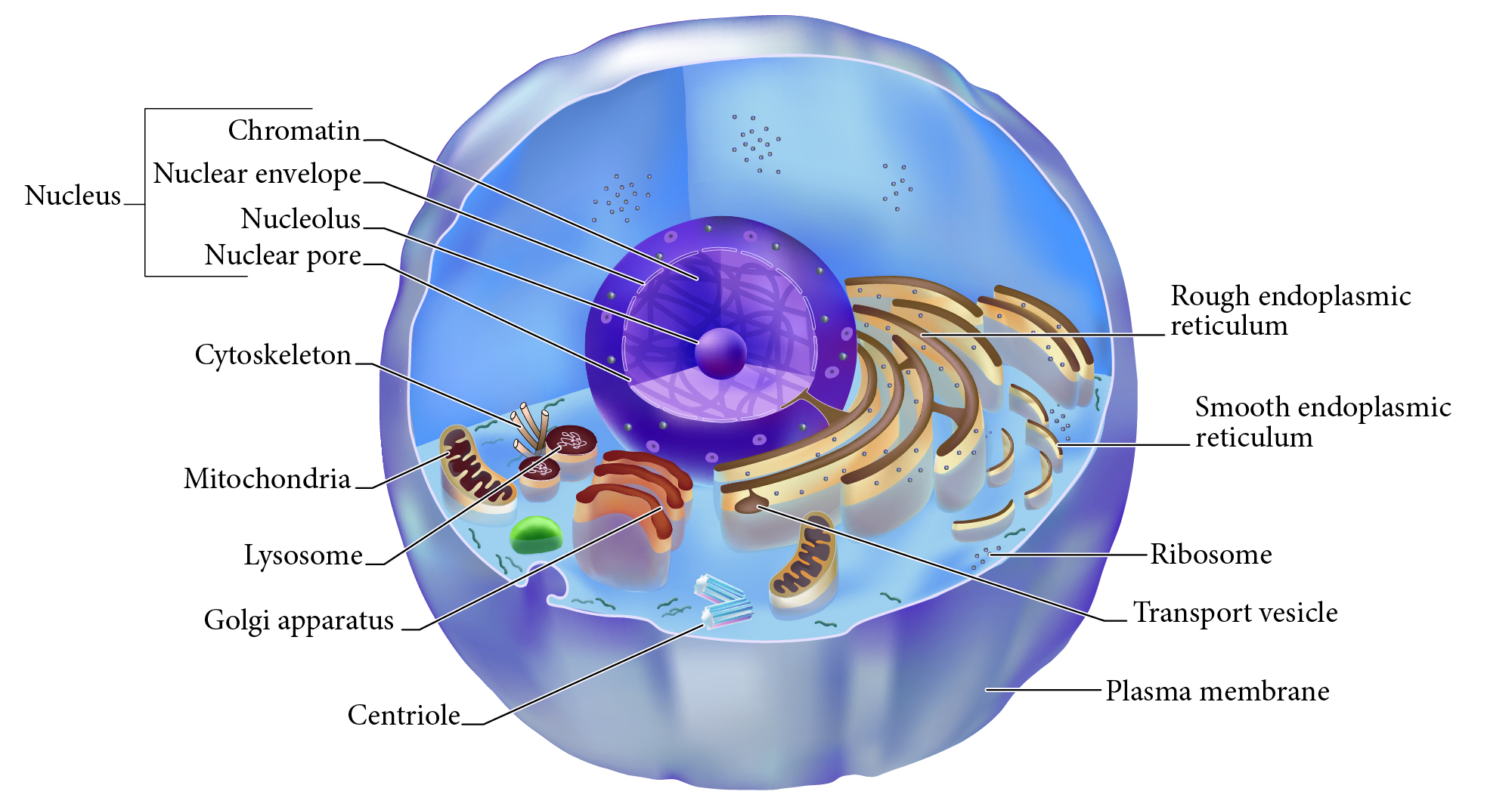
Golgi apparatus
Membrane bound organelle of flat sacs that transport and process proteins imported from RER.
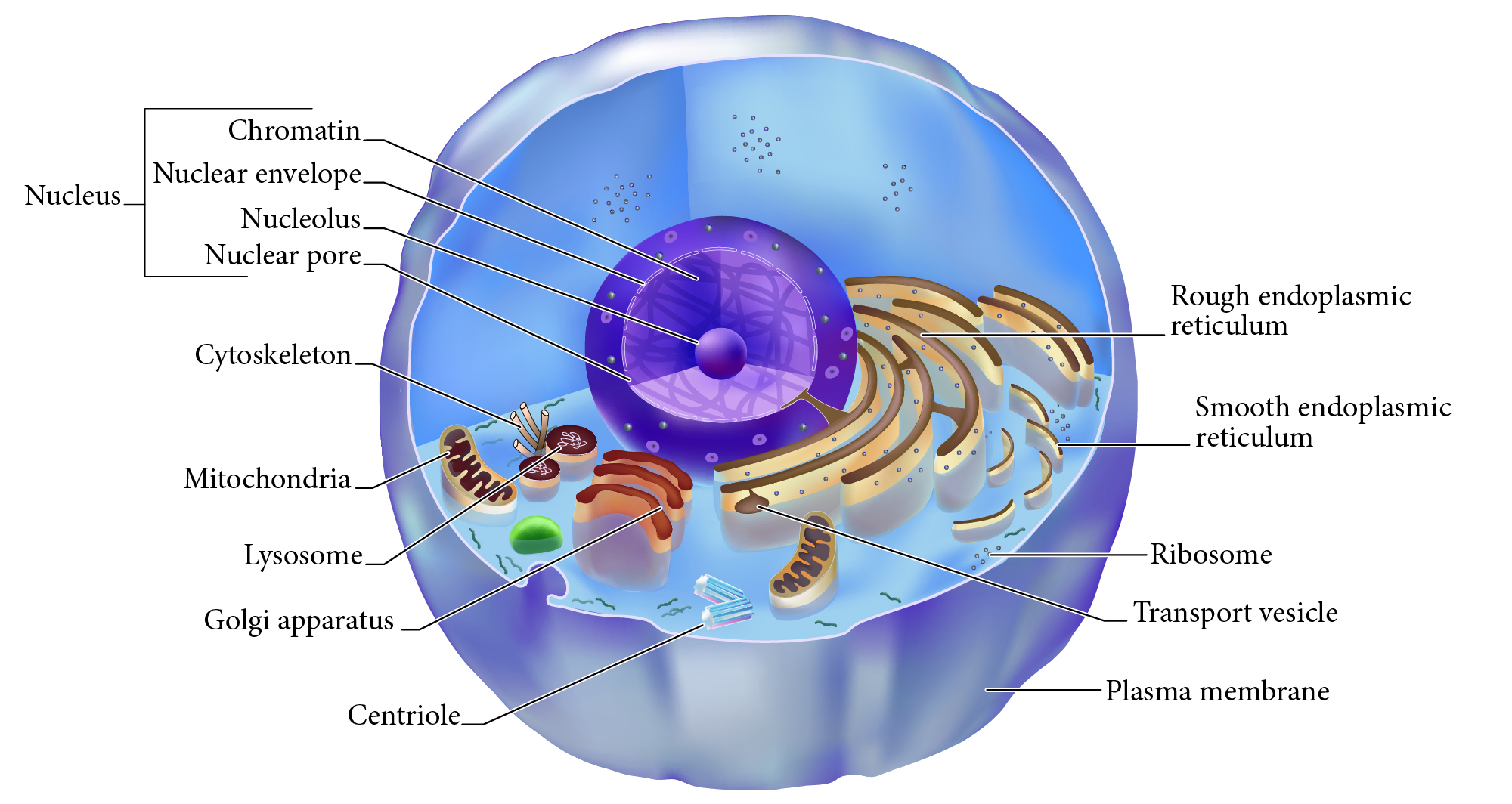
Transport vesicle
Membrane bound organelle that shuttles between other membranes to move membrane components, protein products, etc.
(Plasma Membrane) Cholesterol
stabilize fatty phospholipids in the bilayer
more __________ between the phospholipids makes the membrane more stable, less fluid.
(Plasma Membrane) Proteins
can be peripheral, attaching to the one edge of the bilayer, or integral, extending into the fatty acids.
Some integral transmembrane _______ cross the entire bilayer as channels or other transporters. Some membrane ______ function as enzymes or receptors for cell signals.
(Plasma Membrane) extracellular fluid
the outer face of the proteins and phospholipids can have associated glucose molecules as small chains of carbohydrates.
(Plasma Membrane) Glycolipids
have glucose attached to phospholipids
(Plasma Membrane) Glycoproteins
have glucose attached to proteins
(Plasma Membrane) Carbohydrates
on the cell surface are identifiers for the type of cell, tissue, organ, and even organism