DNA replication
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
DNA replication
synthesis of new strands of DNA with the exact same base sequences as original strands
required for:
growth
replacement of damaged tissues
reproduction to provide cells that develop into gametes
semi-conservative replication
begins w/ separation of a parent DNA molecule into 2 single strands by breaking H bonds between bases
each single strand used as a template for assembly of a replica
semi-conservative bc includes one new strand and one conserved from parent molecule
keeping one og strand and complimentary base pairing ensures genetic continuity with high degree of accuracy between generations
role of helicase
unwinds double helix and separates the 2 strands by breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs
role of DNA polymerase
links nucleotides together to form new strands using parent strand as template
each nucleotide in the new strand has the base that is complementary to the base of the nucleotide on the template strand
new strands assembled on each template strand are identical in base sequence to the other strand
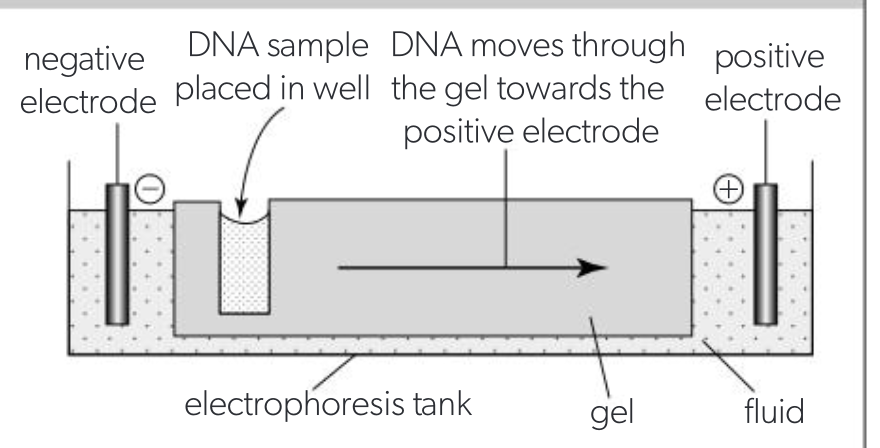
gel electrophoresis
separates mixtures of charged macromolecules using an electric current
electrodes placed at both ends of gel, DNA moves towards anode, wells into which DNA is loaded are at the cathode
gel restricts movement, small molecules move faster than larger ones
gel electrophoresis therefore separates DNA on the basis of size of molecule
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
used for copying DNA artificially
needed:
DNA sample
taq DNA polymerase: heat stable DNA polymerase
primers: short DNA strands that bind to DNA in the sample after it has been split into single strands by heat. primers bind at the point where DNA polymerase should bind and start copying. 2 primers needed one for each single strand
DNA nucleotides: for assembling new strands
temperature cycles:
95 celsius to separate the 2 strands
cooled to 53 to allow primers to bind
increased to 73, encouraging taq polymerase to begin replicating from the primer onwards, producing 2 copies of double stra
applications of PCR and gel electrophoresis
forensic investigations: evidence
paternity tests: all bands in childs profile will also be in the profile of the mother or true father
DNA profiling process
DNA sample collected from saliva/mouth
PCR used to make copies of DNA
short tandem repeats used
gel electrophoresis used to separate DNA fragments according to length, generating pattern of bands
all bands in child’s profile must be in one of parent’s profiles
directionality of DNA polymerase
replication must occur in the 5’ to 3’ direction, adding nucleotides to the 3’ end of a single strand
replication on leading strand
made continuously, following the replication fork as it opens
RNA primer is assembled at the start of the leading strand to create binding point for DNA polymerase
DNA polymerase can then assemble any length of new strand
replication on the lagging strand
made discontinuously in short fragments, away from the replication fork
DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to growing chain but soon reaches previous RNA primer beyond which new strand of DNA already assembled
replication has to be reinitiated close to the replication fork with another RNA primer
series of short lengths of DNA assembled on the lagging strand - okazaki fragments
function of enzymes in replication
helicase: unwinds double helix
DNA primase: adds a primer (short length of RNA)
DNA polymerase III binds to lagging strand at 3’ end of RNA primer and adds DNA nucleotides away from replication fork
DNA polymerase I removes RNA primer and replaces it with nucleotide but leaves a nick
DNA ligase seal nick by forming sugar phosphate bond and joins okazaki fragments together
DNA primase adds primer to 3’ end of leading strand
DNA polymerase III binds and assembles DNA towards replication fork continuously
correcting base mismatches
when DNA polymerase III recognises a base mismatch, it excises the incorrect nucleotides, moves back along template strand and re-inserts correct base pair - this is DNA proofreading