2 Lec 17 (Exam 3): Immune Mediated Disorders
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Minor Aphthous Ulcers
patient presents with painful ulceration on the labial mucosa that is about 1cm and has erythematous borders. Patient was recently under a great deal of stress but sore resolved in about a week w/out scarring. What is the diagnosis?
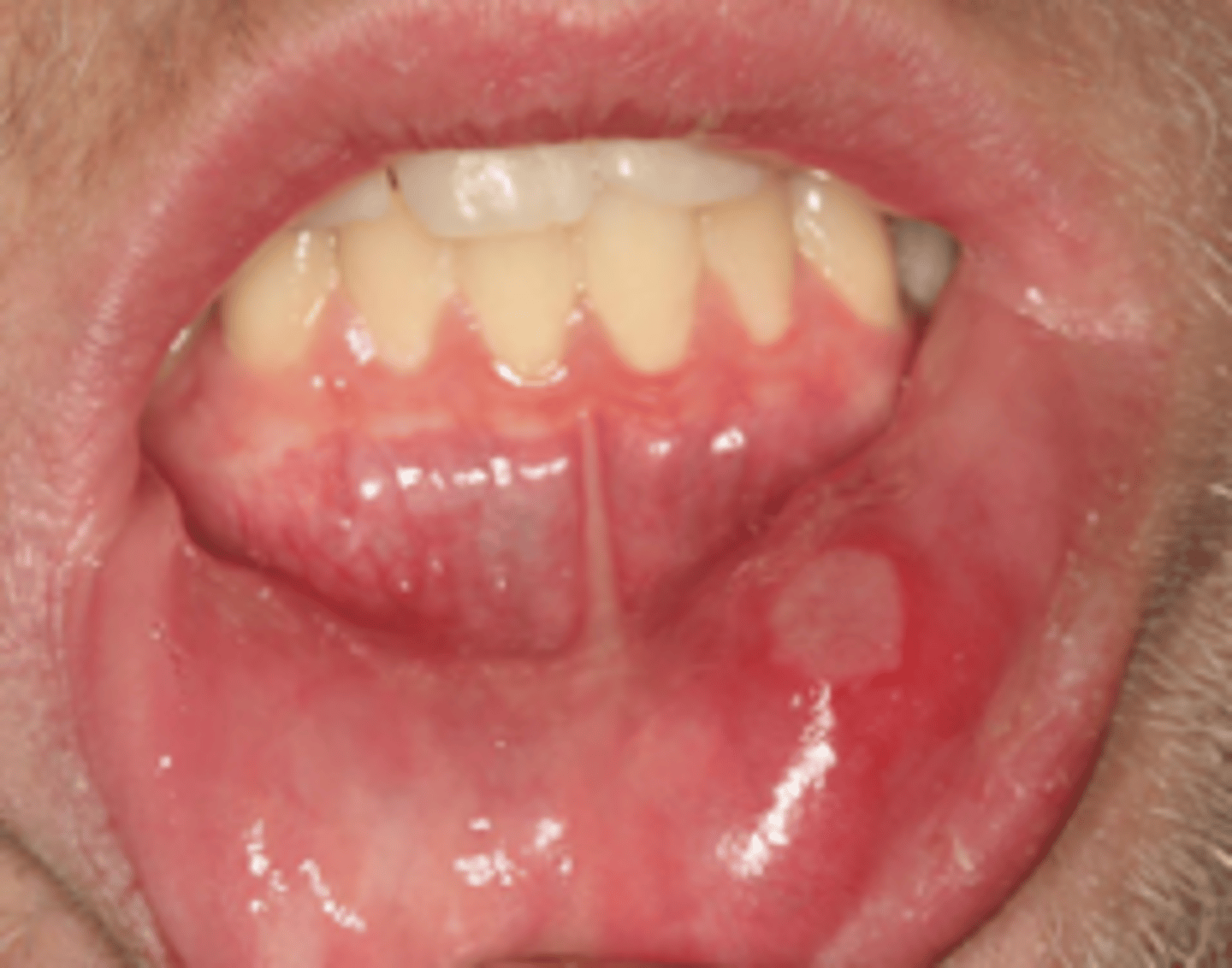
non-keratinized mucosa
what type of mucosa do Minor Aphthous Ulcers present on?
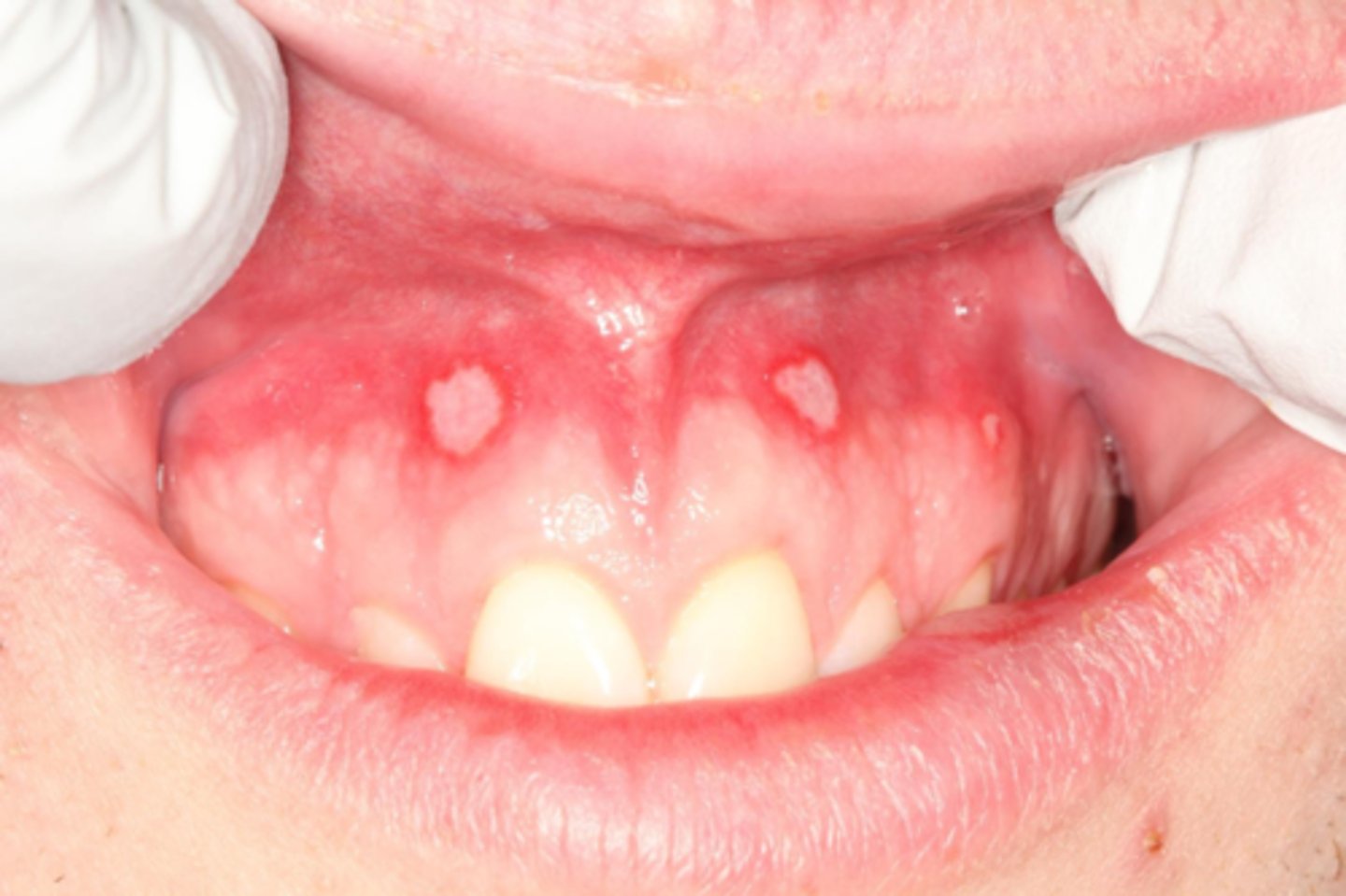
Major aphthous ulcers
patient presents with painful ulceration on the labial mucosa that is about 1cm and has erythematous borders. Patient was recently under a great deal of stress. After 4 weeks patient comes back to your office and says that the ulcer just recently healed, and you notice a scar that it left behind. What is the diagnosis?
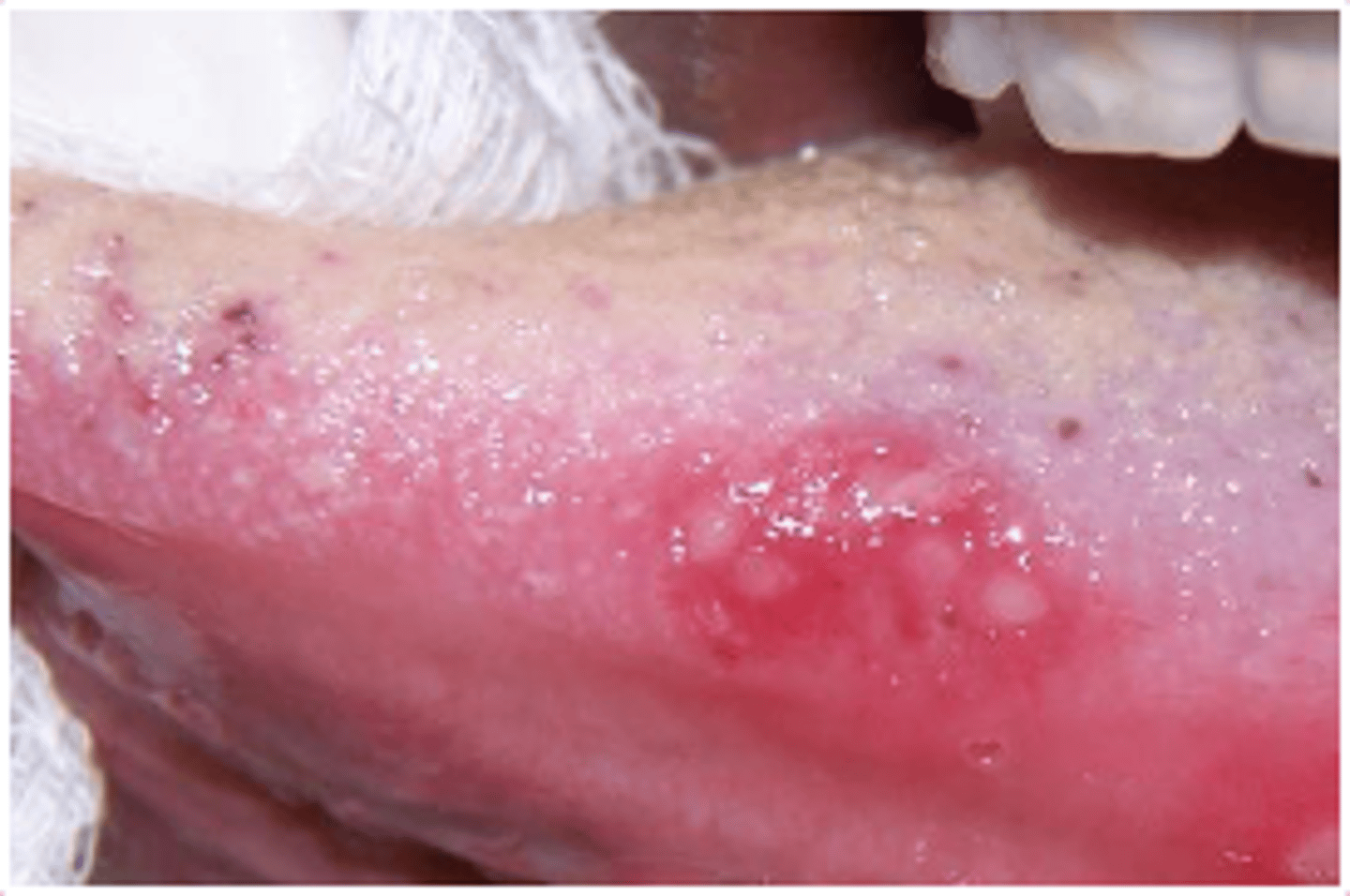
Herpetiform Aphthous Ulcers
ID the pathology:
T cells
Minor aphthous ulcers are mediated by what cells?
Allergies/hypersensitivity
Genetic predisposition
Hormonal influences
Nutritional deficiencies
Smoking cessation
Trauma
what are some things that could cause a Minor aphthous ulcer?
Behcet Syndrome
ID the pathology:
-Systemic vasculitis
-recurrent oral lesions PLUS 2 more (Arthritis, genital lesions, skin lesions, eye involvement)
-associated with HLA-B51
Behcet Syndrome
this condition is associated with HLA-B51:
Japanese/ Mediterranean
Behcet Syndrome most commonly affects what patient population?
Behcet Syndrome
patient presents with recurrent aphthous ulcer on the on the buccal mucosa. Patient also admits to similar lesions on the genitalia and well eye lesions. What is the diagnosis?
recurrent genital ulcerations
eye lesions
skin lesions
positive pathergy test
in order to be diagnosed with Behcet Syndrome, you must present with recurrent oral lesions and at least 2 other manifestations. What are the options?
Reactive arthritis (Reiter syndrome)
this condition is associated with HLA-B27:
male
Reactive arthritis (Reiter syndrome) has a _____ gender predilection
Reactive arthritis (Reiter syndrome)
ID the pathology:
-Arthritis, urethritis, uveitis, rash palms/soles
-male predilections
-HLA-B27
-associated with some infectious component (Chlamydia trachomatis Campylobacter,
Salmonella, Shigella and Yersinia)
Celiac disease
this condition is associated with HLA-DQ2:
Celiac disease
ID the pathology:
-Systemic immune-mediated disorder triggered by dietary gluten in genetically susceptible persons
-Damage to small intestine mucosa
-HLA-DQ2
-Gluten sensitivity
Celiac disease
serology tests tTG ab and EMA are used to diagnose what condition?
Oral ulcerations
Diarrhea Anemia
Abdominal pain
Chronic fatigue
Reduced bone density
signs and symptoms for Celiac disease include:
Crohn disease
ID the pathology:
-Chronic, relapsing, inflammatory bowel disorder
-Genetic, immunologic and environmental
-Alteration of the intestinal microbiome or disruption of the mucosal epithelium
-symptoms include:
Oral ulcerations (30%) (lips, gingiva,
mucobuccal fold). Upper lip swelling,
Diarrhea, abdominal pain, Granulomas on biopsy
Cyclic neutropenia
ID the pathology:
-Rare hematological condition characterized by cyclic/fluctuations in neutrophils
-autosomal dominant
-susceptible to opportunistic infections
-Oral ulcerations
Periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis and adenitis
What does PFAPA stand for?
Sarcoidosis
ID the pathology:
-Multisystem inflammatory disease characterized by development of noncaseating granulomas
-Bimodal: 25-35 yrs and 45-65 yrs
-Most often in African-Americans (90%)
F>M
Fever, fatigue, anorexia, respiratory symptoms, visual problems dry cough, dyspnea, chest discomfort
Skin lesions (25%)
Head and neck (10-15%)
Oral Lesions: Well circumscribed brown-red or violaceous
papules, plaques or nodules
Submandibular lymphadenopathy, and/or xerostomia
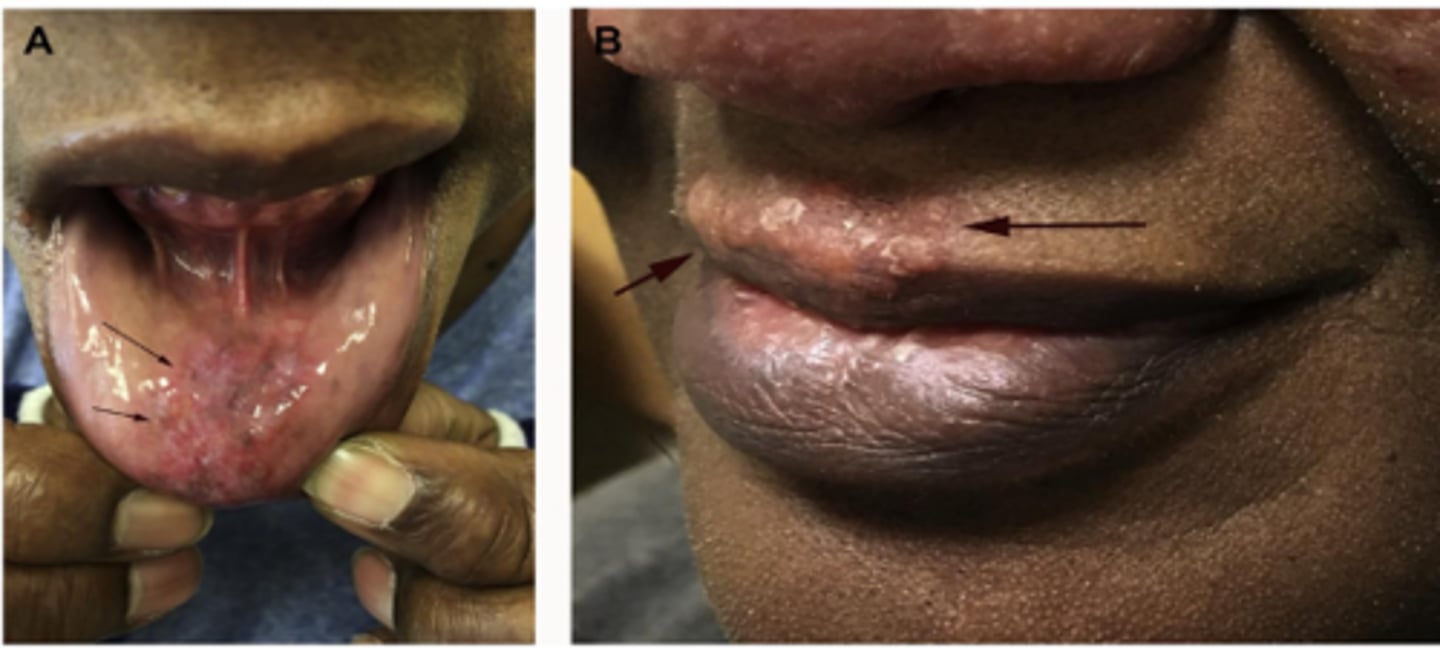
Sarcoidosis
this oral pathology is associated with histoligical granulomatous formation:
African-Americans
Sarcoidosis most commonly affects what patient population?
Heerfordt syndrome
this syndrome is associated with sarcoidosis and is characterized by parotid swelling, uveitis, and facial nerve palsy:
Lofgren syndrome
this syndrome is associated with sarcoidosis and includes erythema nodosum, bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, arthralgia:
Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome
ID the pathology:
◦Facial paralysis
◦Fissured tongue
◦Cheilitis granulomatosa
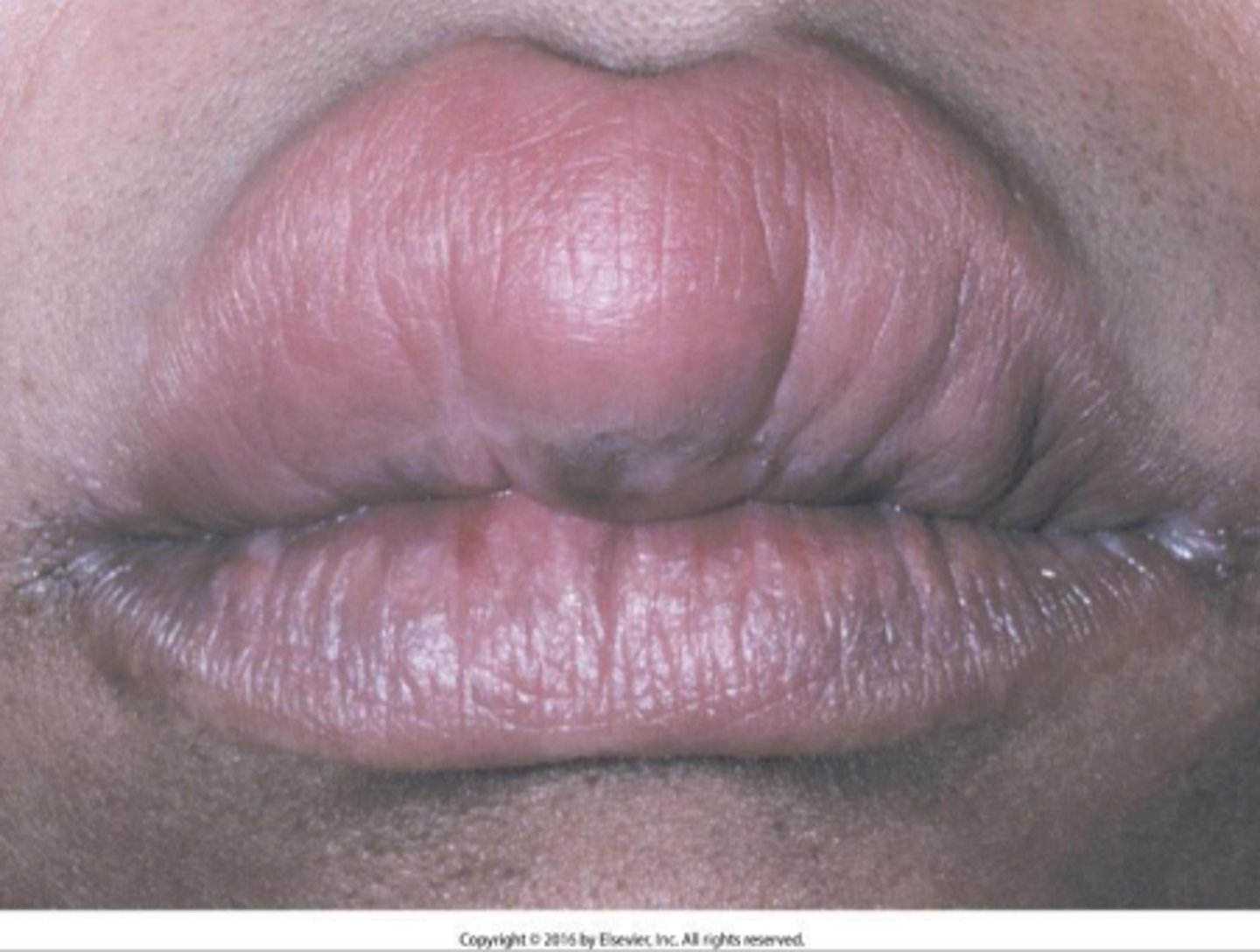
Orofacial Granulomatosis
ID the pathology:
-Clinical presentation Lips-most common
location (cheilitis granulomatosa)
-Nontender, persistent swelling Intraoral- edema, ulcers, papules
-Idiopathic disorder (diagnosis based on exclusion)
-Abnormal immune reaction
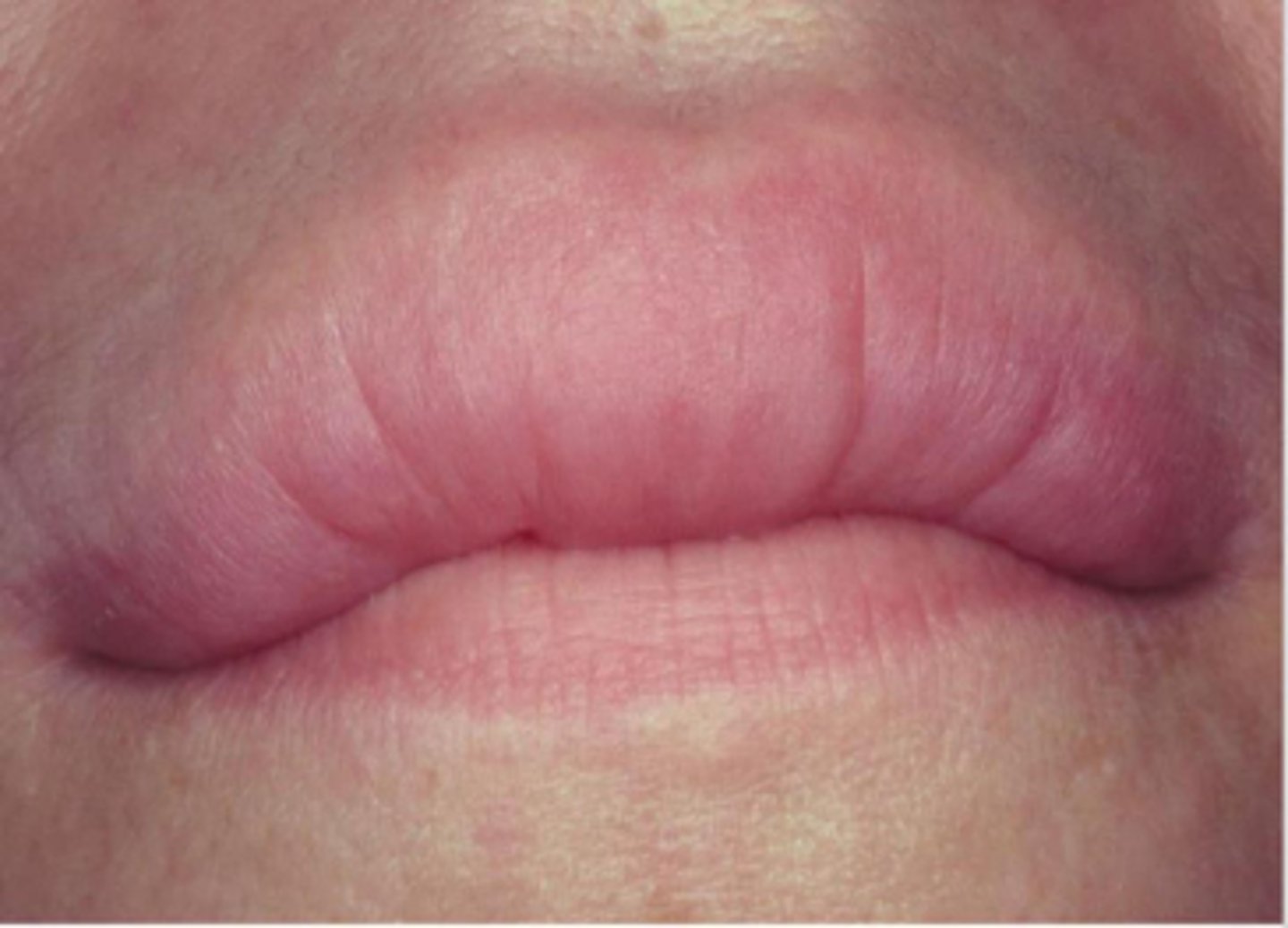
Facial paralysis
Fissured tongue
Cheilitis granulomatosa
What is the Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome triad?
Cheilitis granulomatosa of Miescher
ID the pathology:
persistent lip swelling is the only manifestation noted in patients with cheilitis granulomatosa
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) Wegeners
ID the pathology:
-Destructive and progressive, multiorgan autoimmune disease
- superficial form includes Strawberry gingivitis and Nasal symptoms
◦Vasculitis
◦Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs)
Oral manifestions:
◦Hyperplastic gingiva
◦Ulcerations
◦Labial mucosal nodules
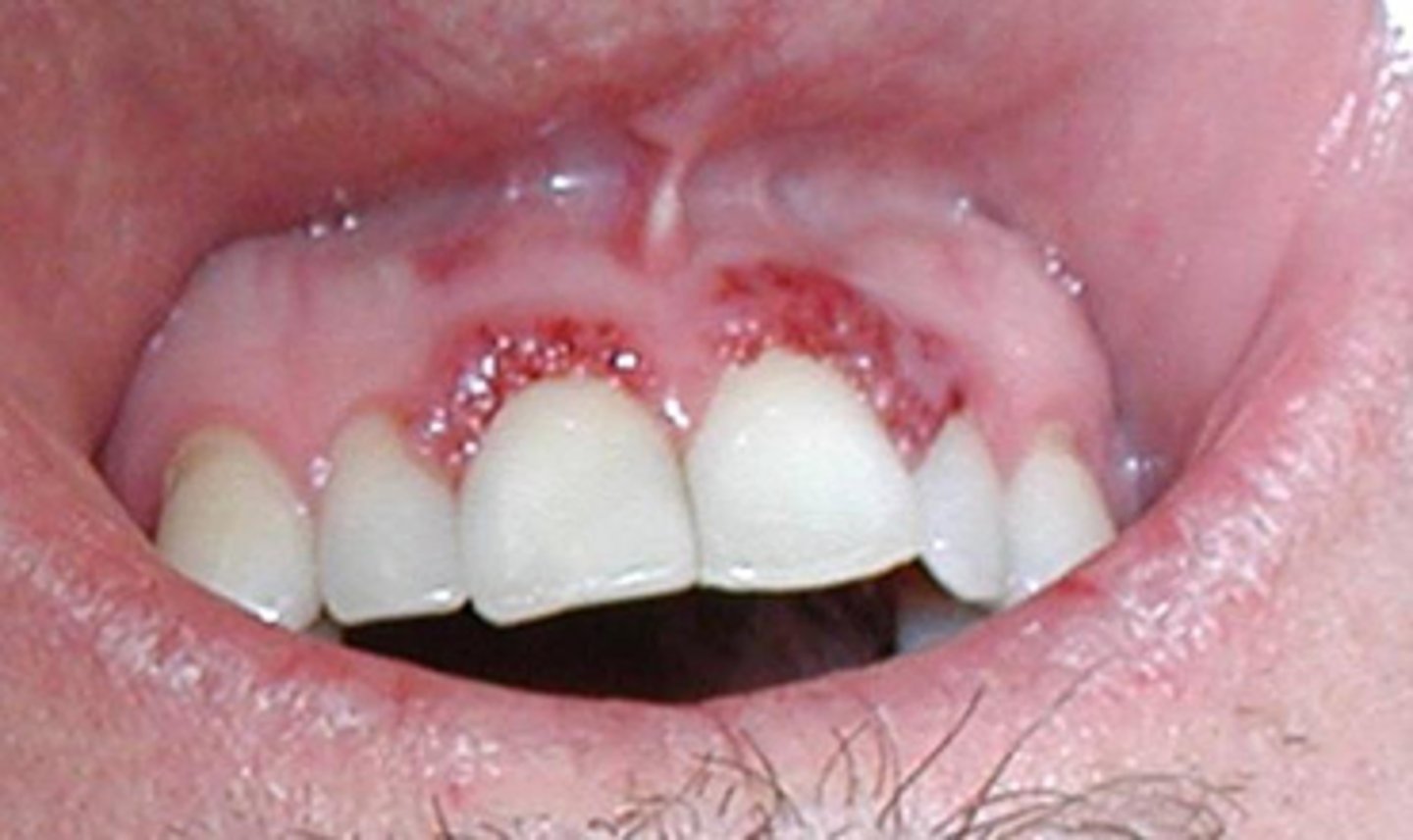
Allergic Contact Stomatitis
ID the pathology:
-Pt using new cinnamon toothpaste
Symptoms:
Burning sensation, *sloughing of mucosa
Itching/tingling
Signs:
Sloughing tissue Erythema

Lichenoid Contact Reaction to Dental Restorative Material
ID the pathology:
-Hypersensitivity reaction (Type IV)
-Occurs in the location in contact with the material, Mostly amalgam
-Appears lichenoid clinically and histolopathologically
-Patch test positive
-unilateral presentation
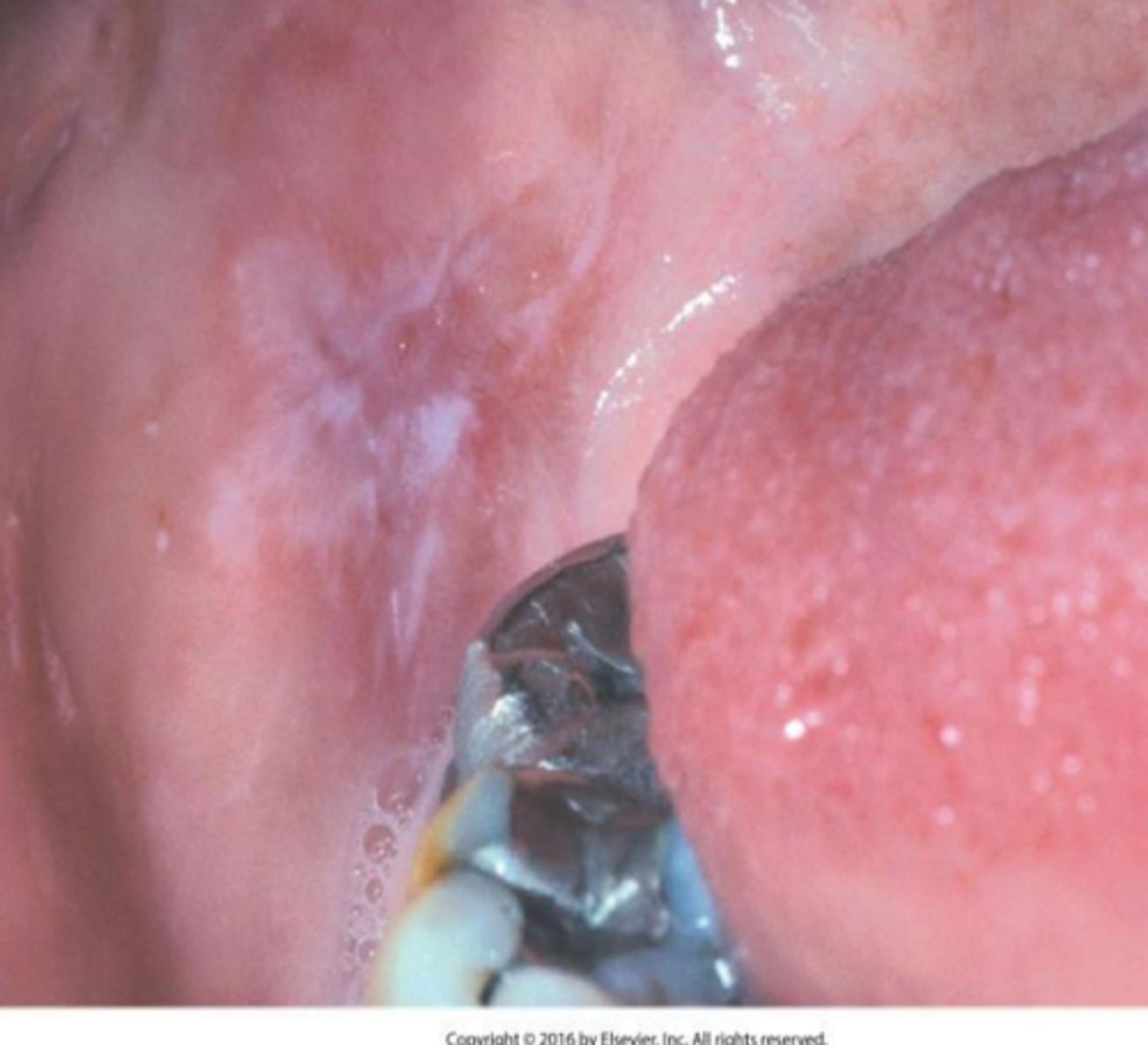
Angioedema
ID the pathology:
-Diffuse edematous swelling of soft tissues •
Affects subcutaneous/submucosal tissues
Causes
◦Type I Hypersensitivity (IgE)
◦Contact allergic reaction
◦Drugs (ACE Inhibitors)-occurs within hours of use
◦Activation of complement pathway
-◦Rapid onset; IgE mediated
◦Affects face, lips, tongue, pharynx, larynx Itching Erythema