NEUR305: Chemical Sensation
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is sensation?
DETECTION of the stimulus
The initial activation of the nervous system in response to a stimulus
What is perception?
INTERPRETATION of the stimulus
Our mental representation of the sensed stimulus
What is modality specific?
Sensory receptors are responsive to a single type of stimulus
What is sensory transduction?
Process of converting sensory signal to an electrical signal
Pathway of chemical sensory systems?
stimulus → electrical signals as graded potentials or action potentials → sensory ganglion cells → thalamus (exception smell) → primary sensory cortex → secondary cortices
What are receptive fields?
A sensory space where physiological stimuli can evoke a sensory neuronal response; better when it’s smaller!
Better spatial resolution corresponds to a…
smaller receptive field!
What are the three sensory systems involved chemical sensing?
Olfactory (smell), vomeronasal (pheromone sensing), gustatory (taste)
Odors are classified by…
Valence!
The classification of odors as pleasant/attractive AND unpleasant/repulsive
What sensory path skips the thalamus?
Olfactory
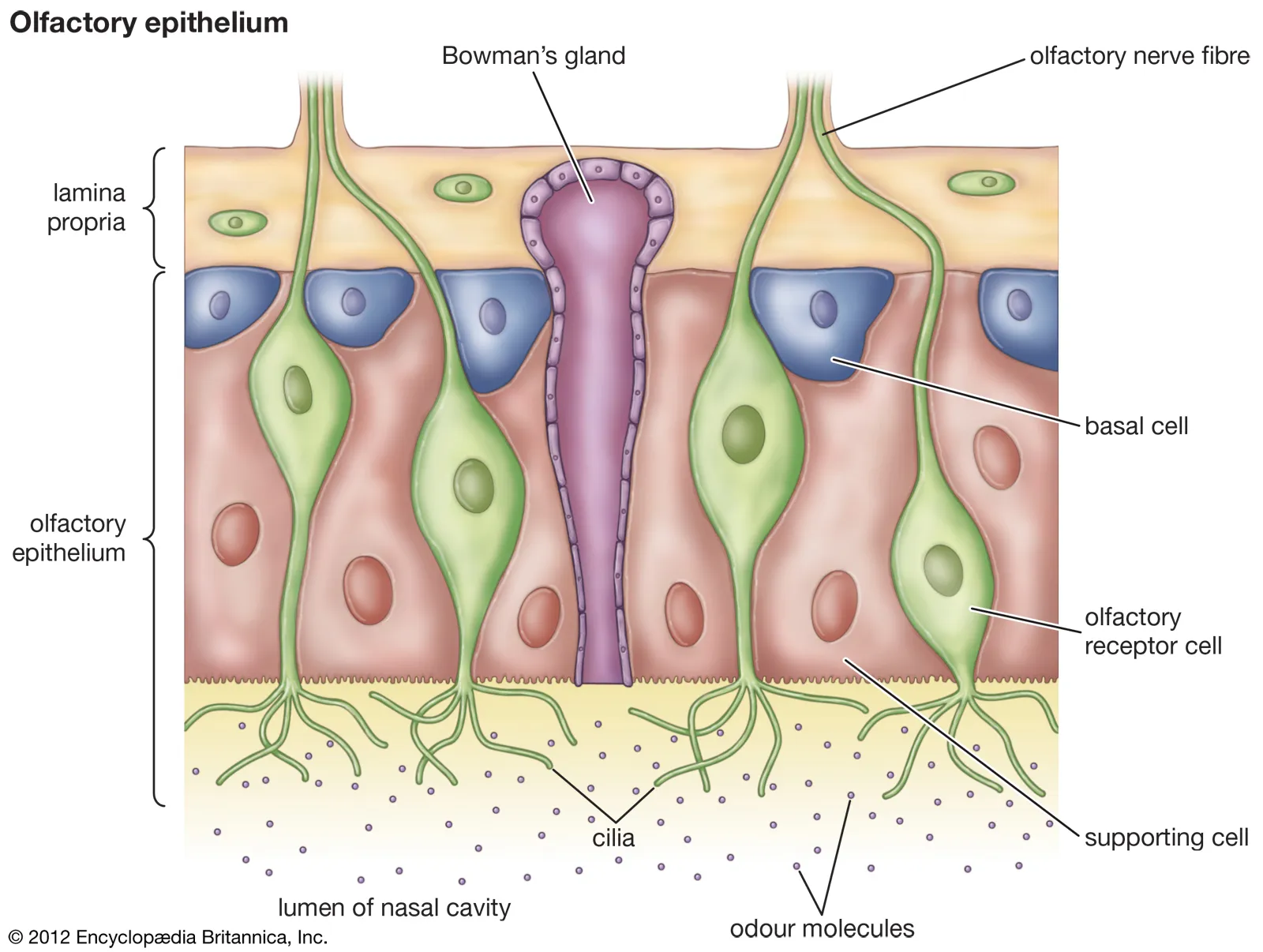
What are olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs)?
bipolar cells
small, unmyelinated axons
turned over/regenerated
has dendritic processes known as microvilli
Why might ORNs turned over/regenerated?
When damaged! They may encounter harmful chemicals that yield damage. Regeneration helps retain sensitivity.
What is the olfactory epithelium?
Thin tissue with odorant receptors embedded in it;
What is convergence?
Many different neuronal inputs coming together to affect one neuron
What is divergence?
One neuron branches out to affect many cells
With increasing receptor convergence you get…
DECREASED (can’t tell where signal is coming from) resolution and INCREASED (more area is covered) sensitivity
What does resolution refer to?
Being able to tell where a signal is specifically coming from (the originating neuron)!
What does sensitivity refer to?
Area covered by a neuron!
1 bipolar neuron activates 8,000 glomeruli is an example of…
DIVERGENCE
1 glomeruli receives information from up to 750 receptors is an example of…
CONVERGENCE
What does combinatorial coding mean for olfaction?
Olfactory system uses combinations of receptor types to reduce the number of receptors required to convey a broad range of odors!
Each olfactory receptor DOES NOT respond to a single odorant!
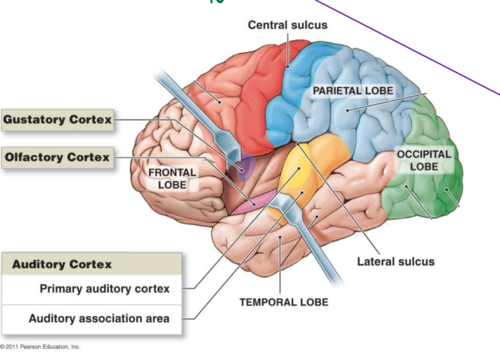
What is the pyriform cortex (PC)?
Primary olfactory cortex is involved both processing and coding of olfactory information (type and intensity); converged inputs from the glomeruli
What does temporal coding mean for olfaction?
Time activation encodes concentration, which encodes odor identity
Why do we associate memories with particular smells?
The olfactory bulb projects to the orbital frontal cortex to create a connection PRIOR to going to the thalamus!
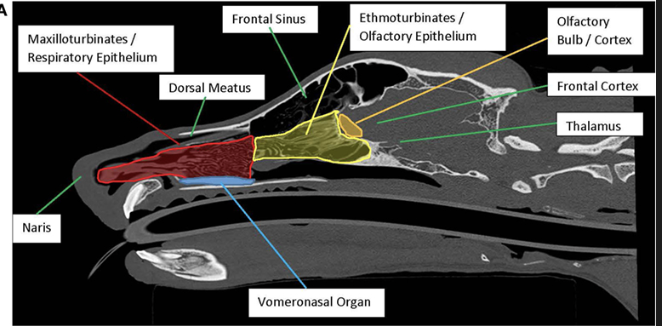
What is vomeronasal organ?
Tubular structure in nasal septum
Detects pheromones! Damage would interfere with pheromone effects but not with general sensing!
Anatomical evidence says no VNO in humans; but we may still use olfactory bulb!
What are pheromones?
Chemical substances produced and released into the environment affecting the behavior of others in its species.
What is the gustatory pathway
Taste buds → thalamus → gustatory cortex