Lab 5: Primary and Secondary Growth in Stems
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Thorn?
Modified stem
Spine?
Modified leaf (mod. stipules)
Prickles?
Epidermal outgrowths
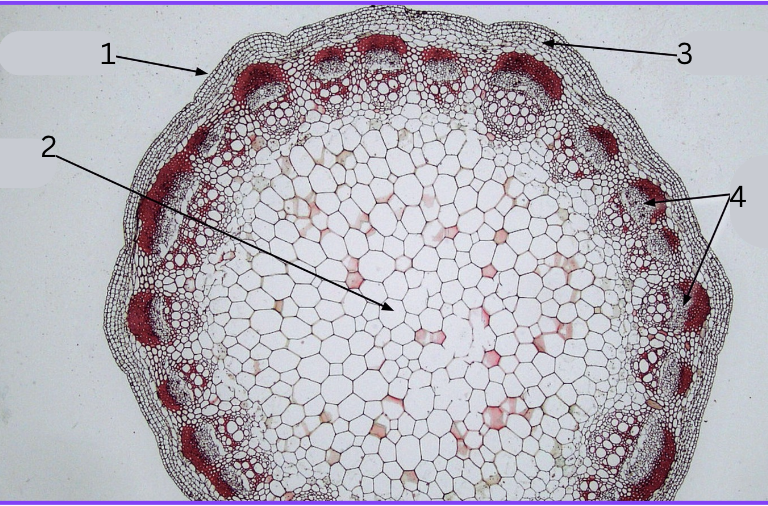
Dicot or monocot stem?
Dicot
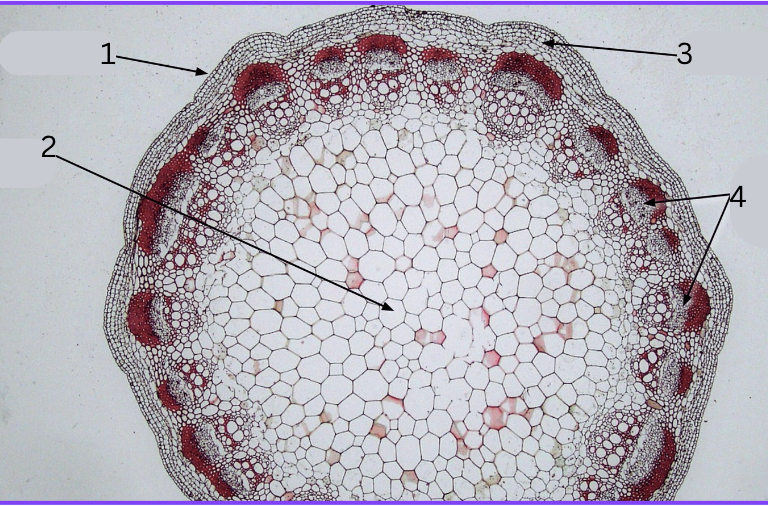

What is 1, 2, 3, and 4?
Epidermis
pith
cortex
vascular bundle
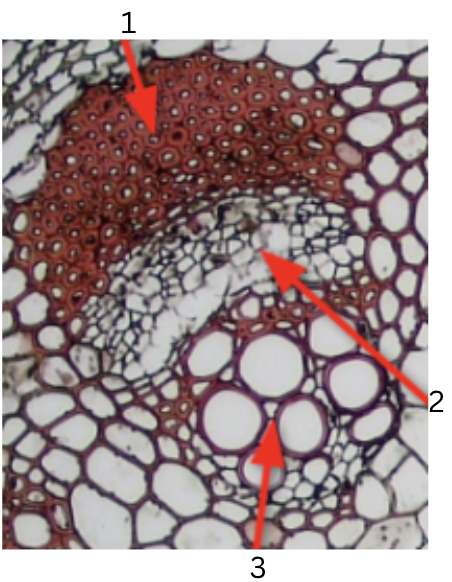
What is 1, 2, and 3?
phloem
vascular cambium
xylem
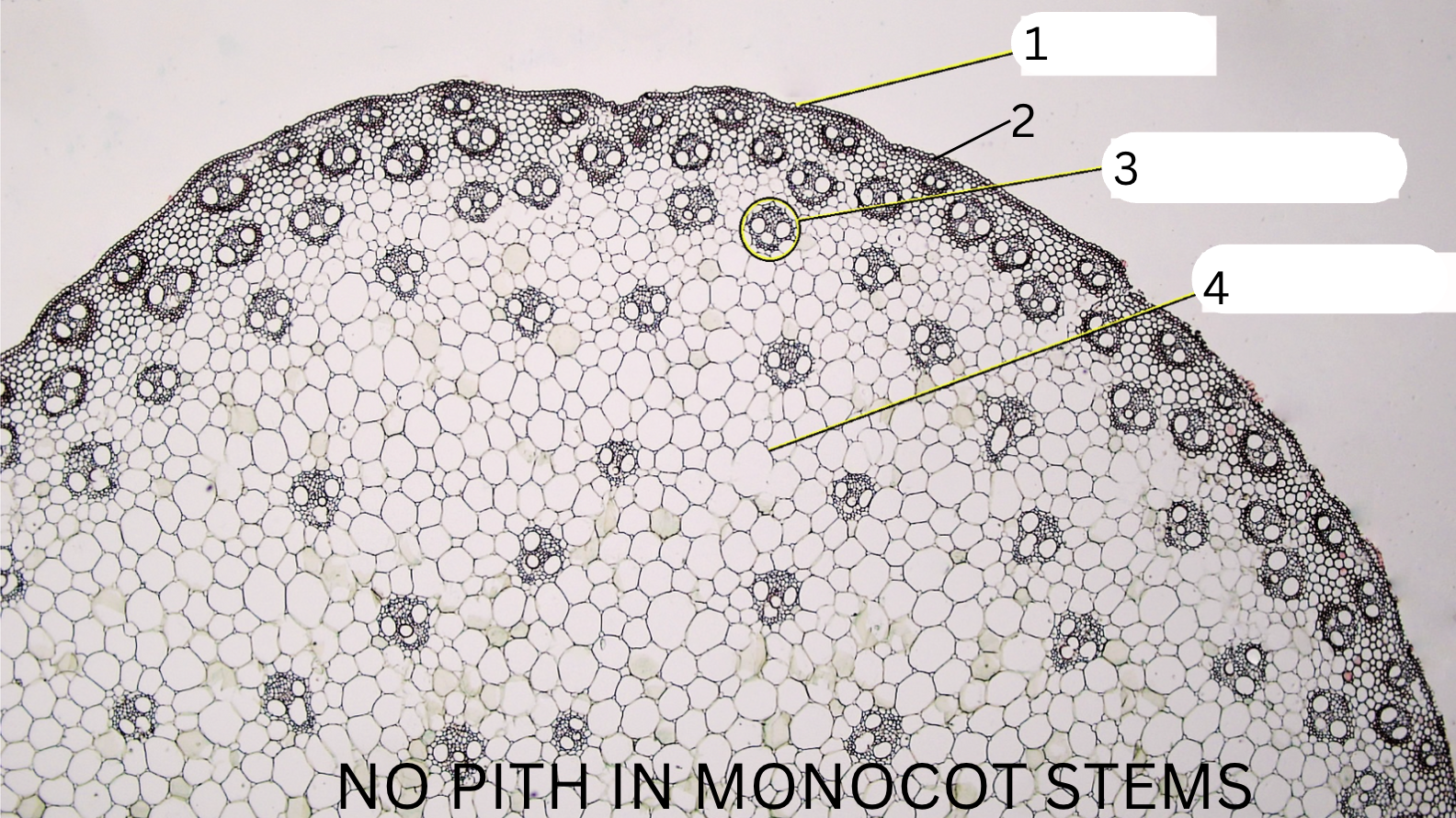
Monocot or dicot?
Monocot
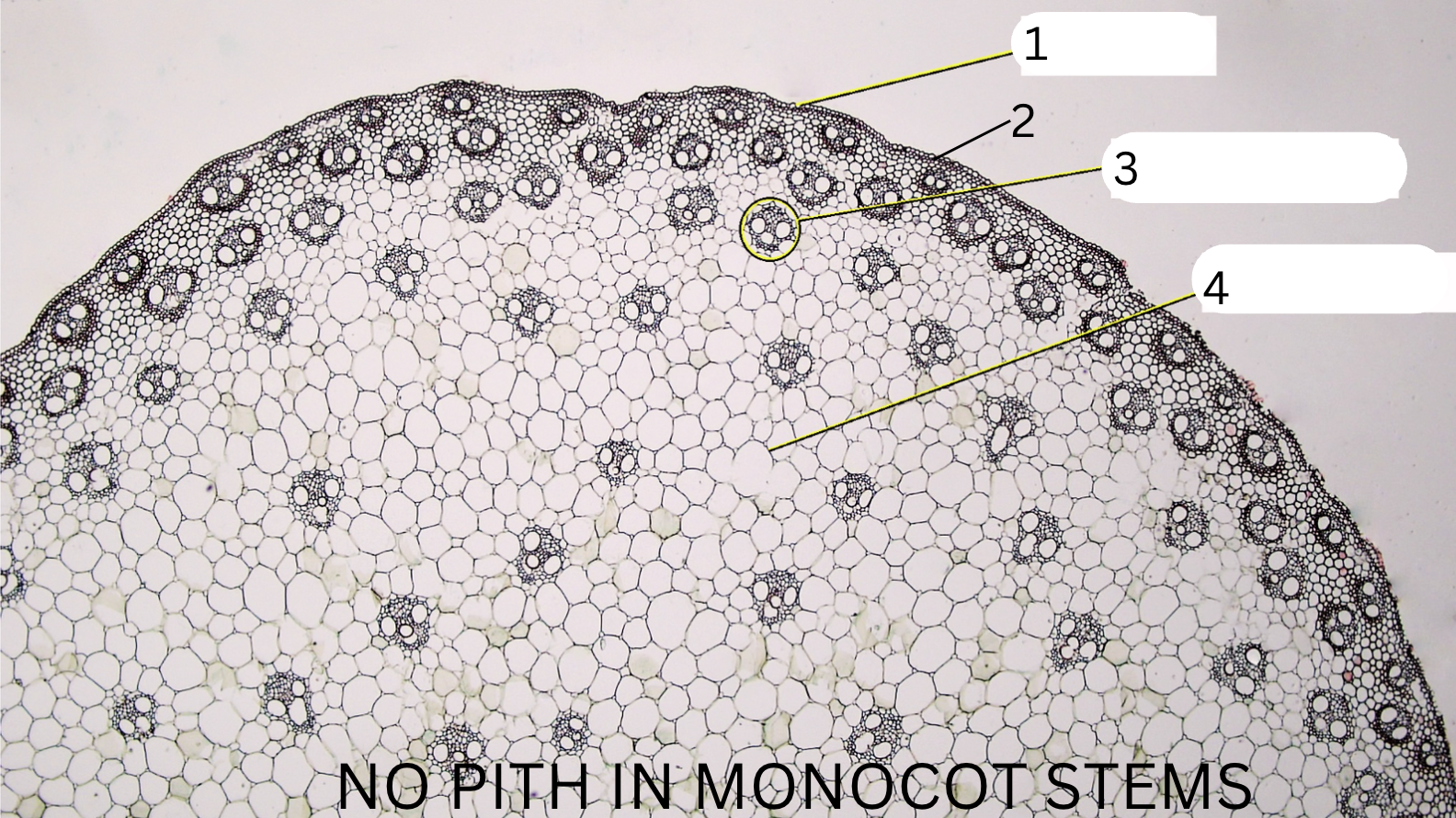
What is 1, 2, 3, and 4?
Epidermis
hypodermis
vascular bundle
ground tissue (no distinction b/t pith and cortex)
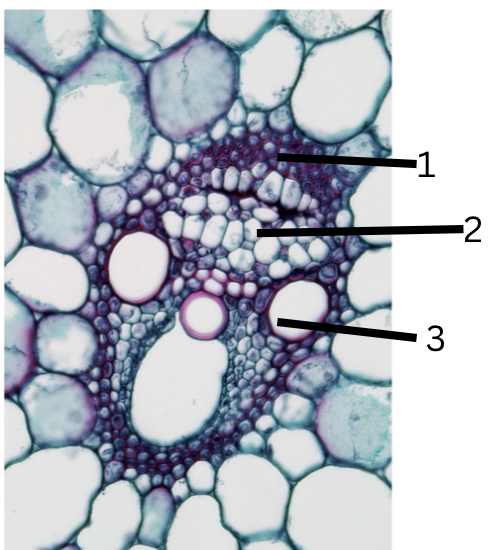
What is 1, 2, and 3?
bundle sheath region
phloem
xylem
what is transverse view?
Top view, cross section, literally looking from the top.
What is radial view?
view that goes through center. longitudinal section
What is tangential view?
view that doesn’t go through center-chop it off from the side like scraping off some ham. Longitudinal section.
What are the secondary growth in dicots stems that are studied in the lab?
Quercus and Tilia dicot wood-both genuses
What view is this? How do you know?
Transverse or cross section- the vessels are big white circles and the rays comes from up to down like a twizzler.
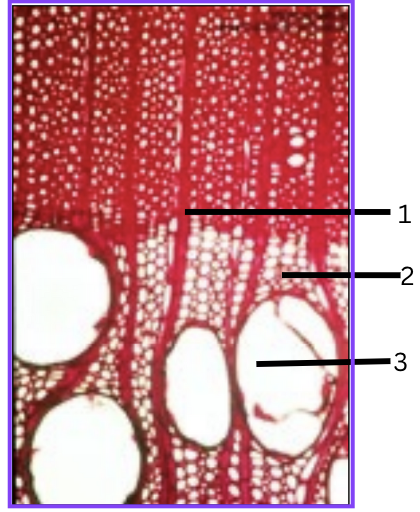
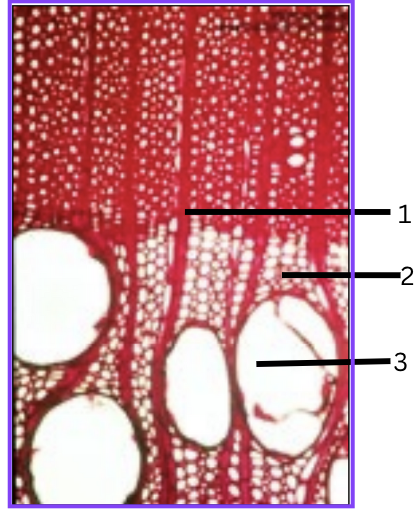
What is 1, 2, and 3?
ray parenchyma
tracheids
vessels
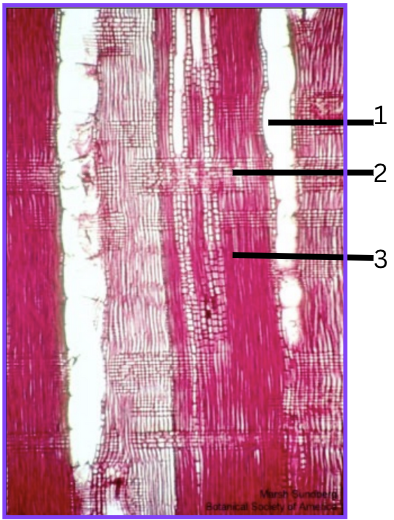
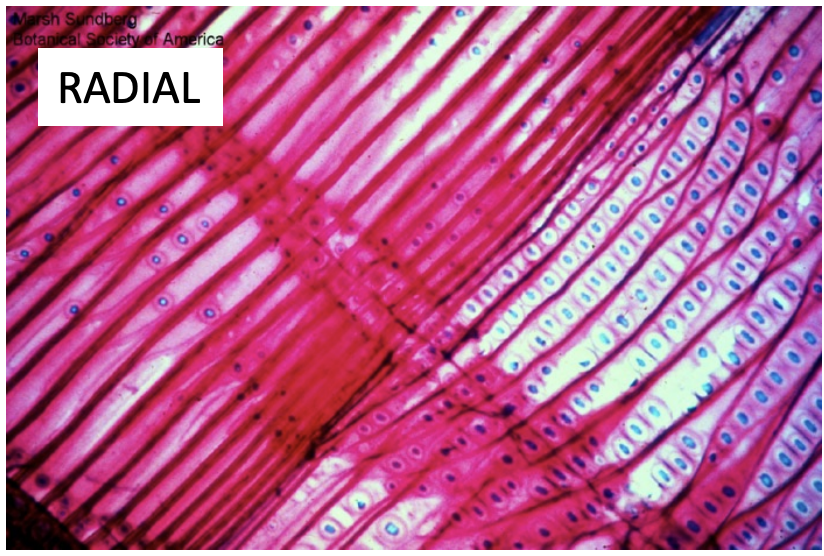
What view is this? How do you know?
Radial view because the rays are brick walls and the vessels are long white things.
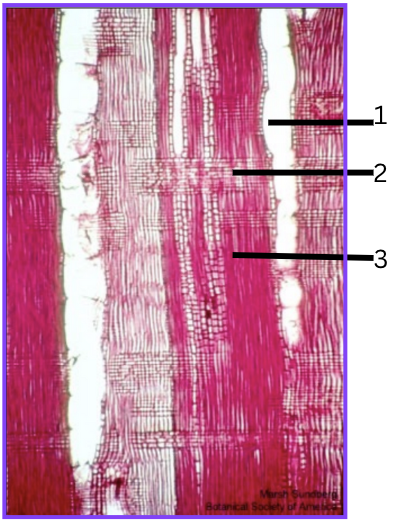
What is 1, 2, and 3?
vessel
ray parenchyma
tracheids
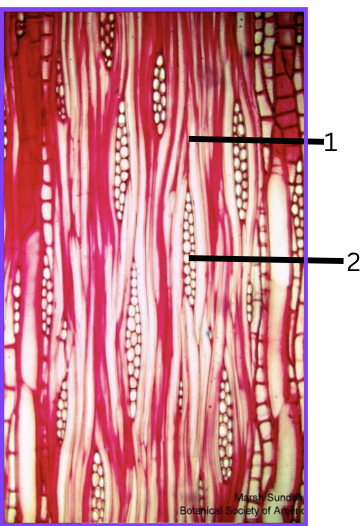
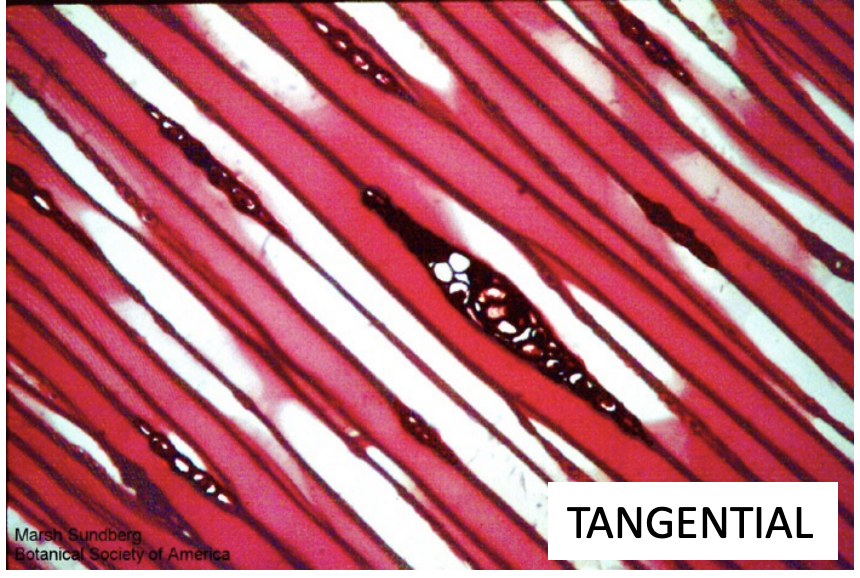
What view is this? How do you know?
Tangential because the ray are in little vaginas that are circles.
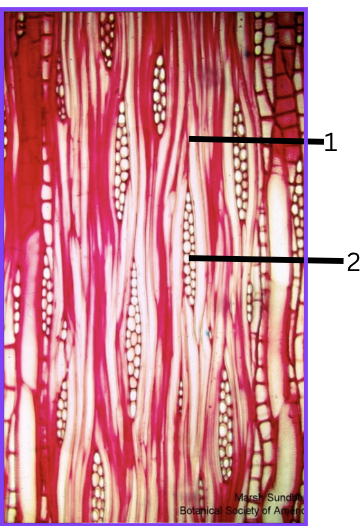
What is 1 and 2?
vessels
ray parenchyma
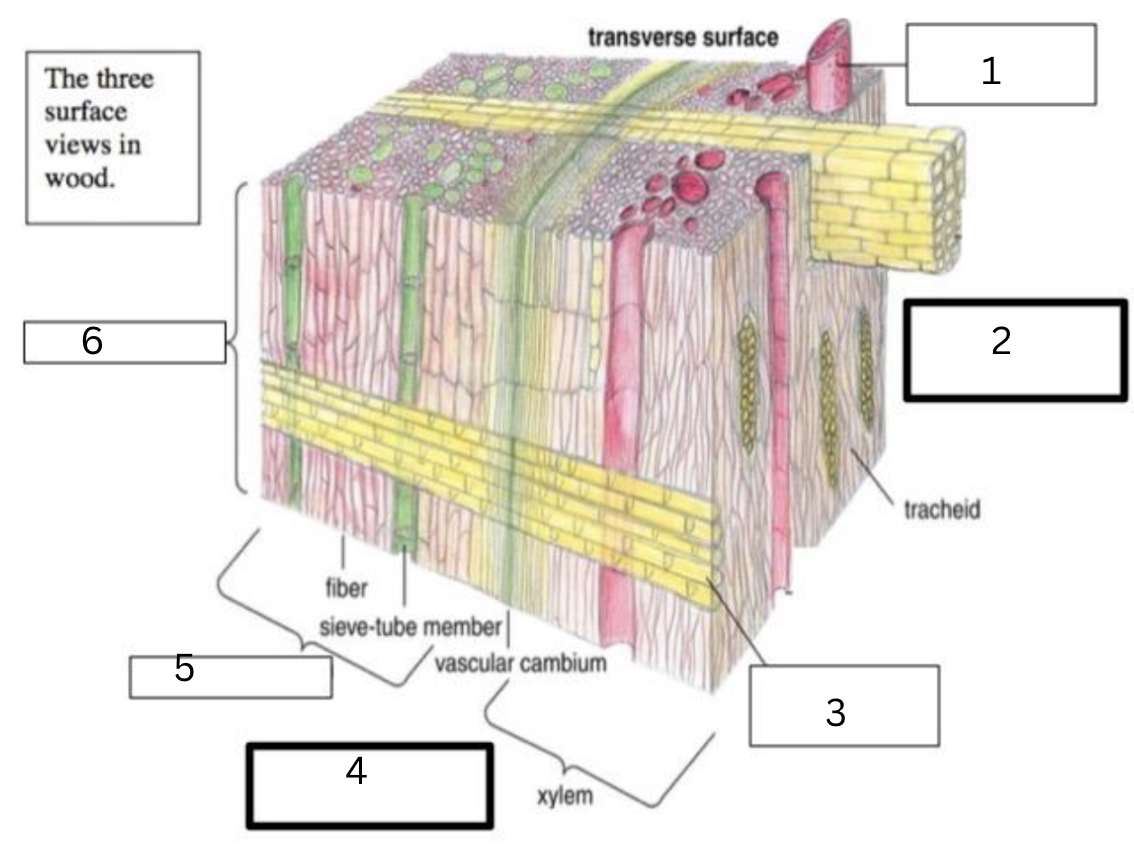
What is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6?
vessel
tangential surface
ray
radial surface
phloem
bark
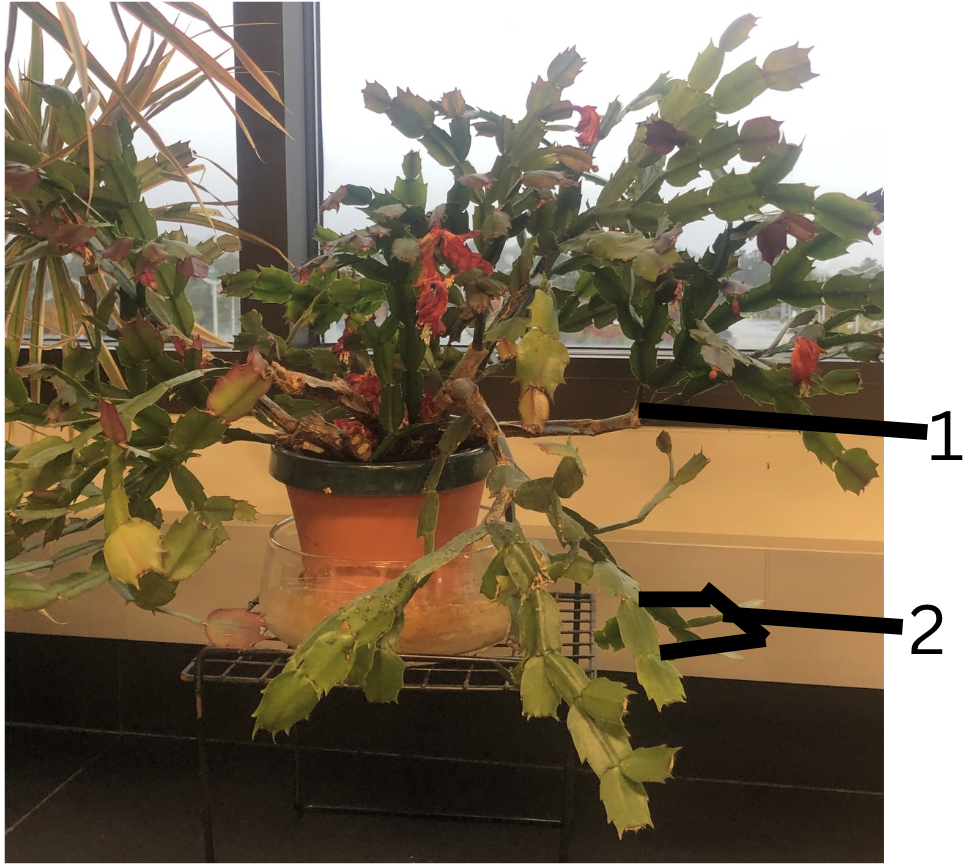

Name plant
Name modified stem
What is 1 and 2
Holiday cactus
Cladophyll (flattened stems)
1. node and 2. internode
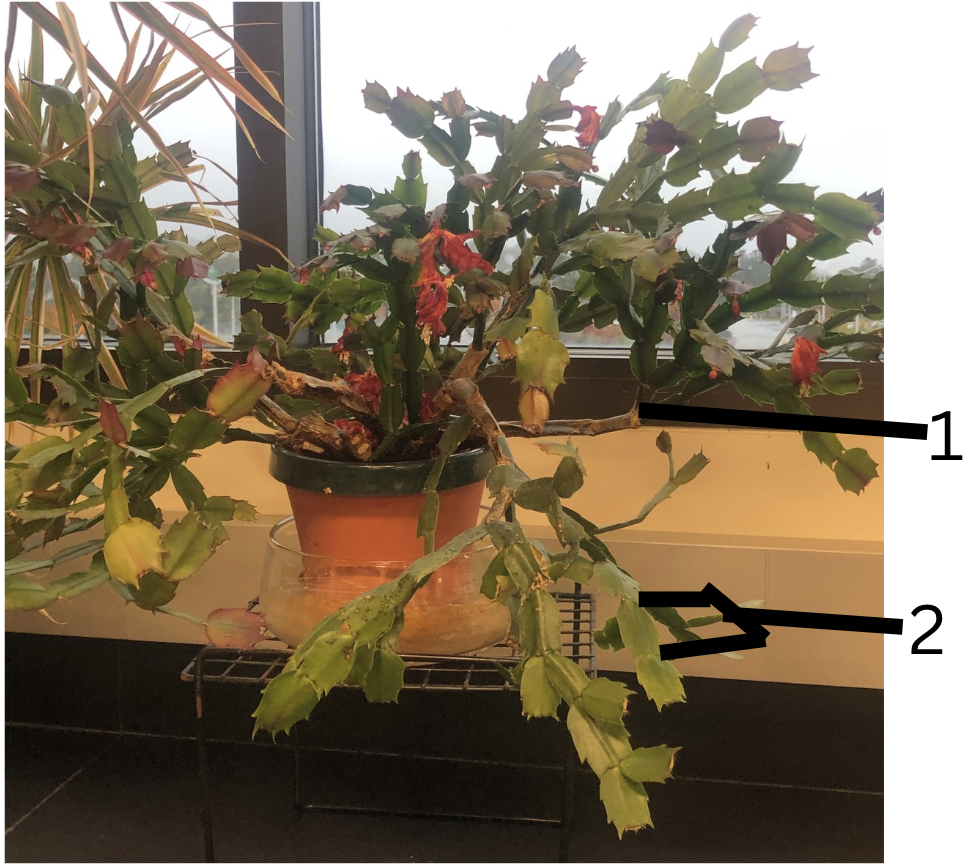

Is this primarily for storage or support, why?
Function: Storage and photosynthesis(support).
Why: Photosynthetic structures, enabling the plant to capture sunlight, but they can also store water and nutrients in drought-prone environments (such as in cacti).
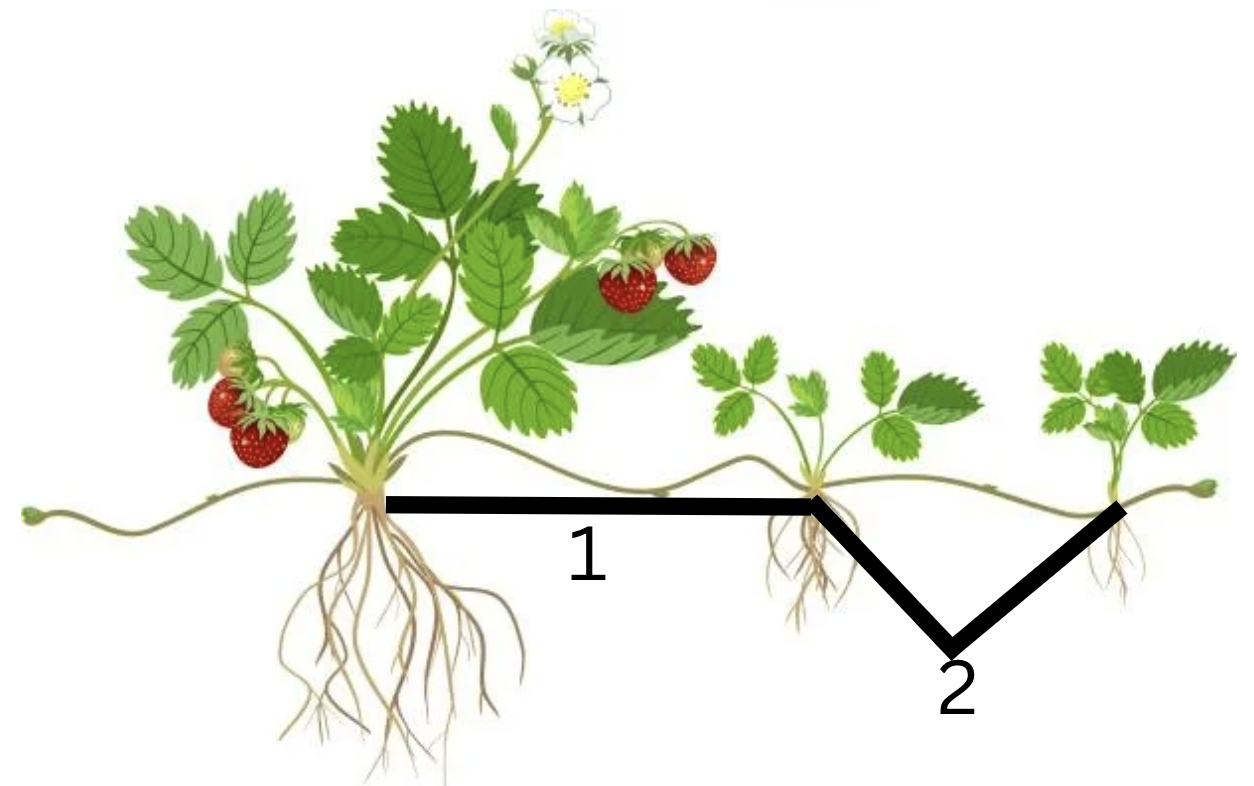
Name plant
Name modified stem
What is 1 and 2
strawberry
stolons
1.internode and 2.node
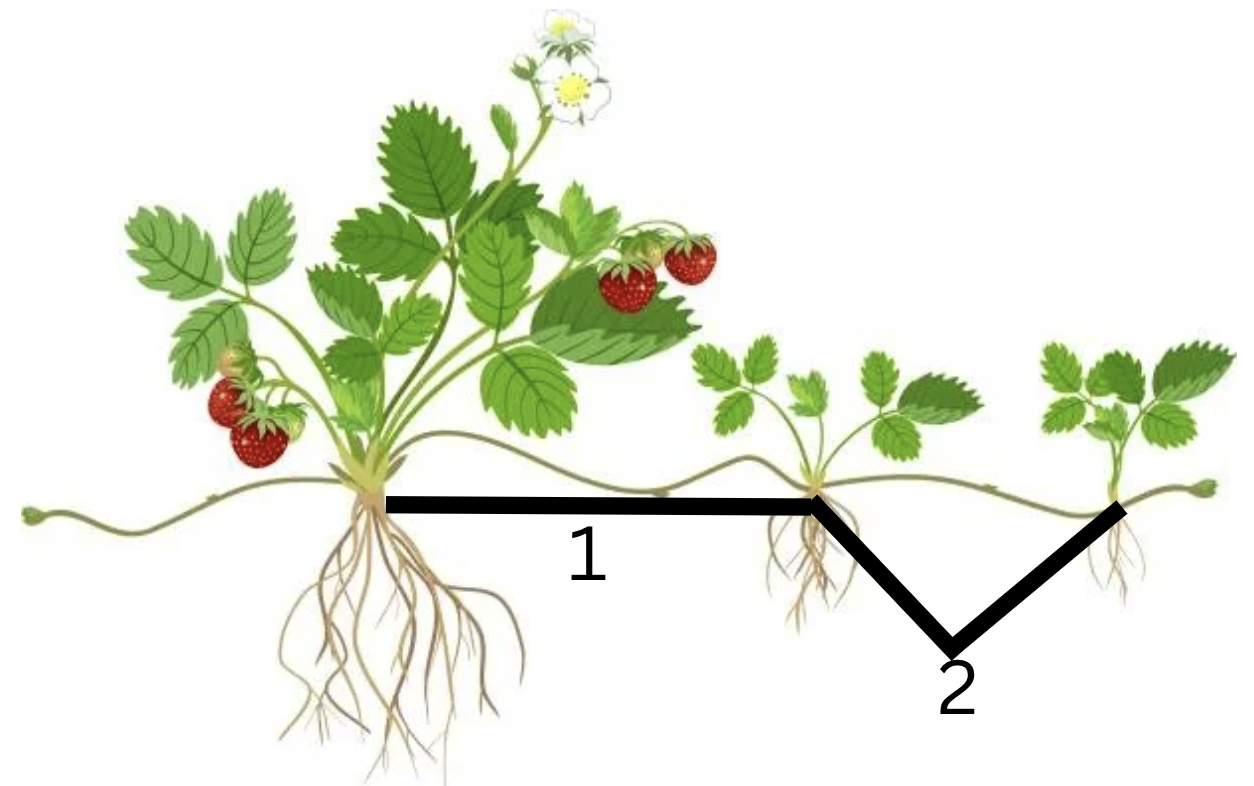
Is this primarily for storage or support, why?
Function: Storage (via runners) and reproduction/support.
Why: The strawberry plant uses stolons, which are horizontal stems that grow along the soil surface. Store nutrients and also produce new plants. Help the plant propagate.
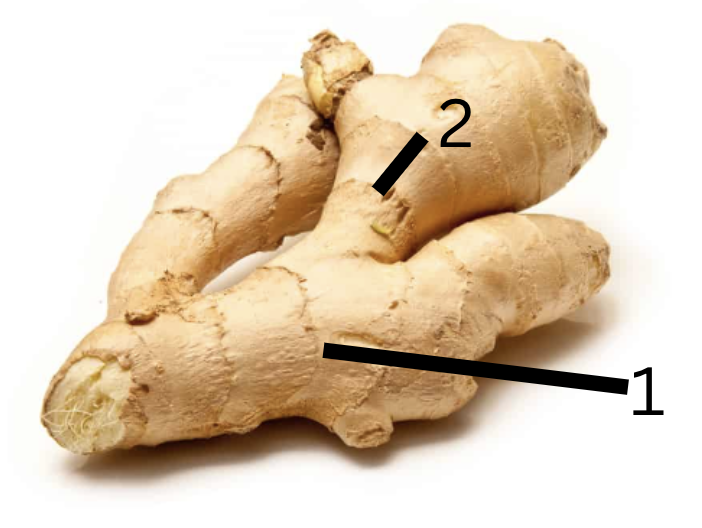

Name plant
Name modified stem
What is 1 and 2
tropical ginger
rhizome
1. node and 2.internode
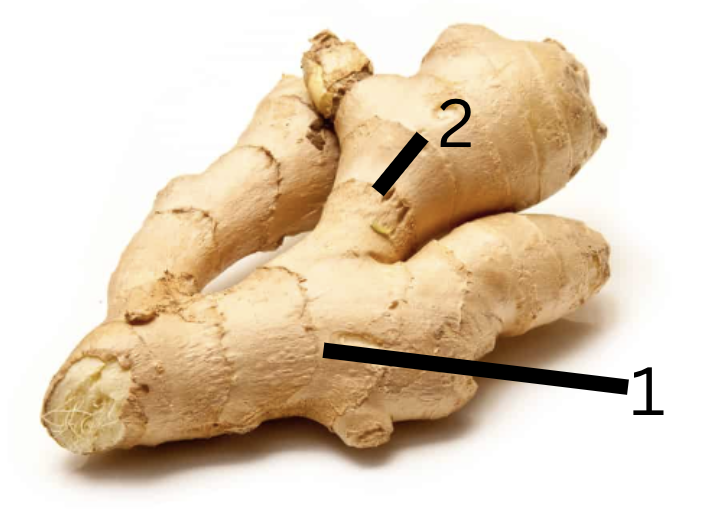

Is this primarily for storage or support, why?
Function: Storage (via rhizomes).
Why:Store energy in their underground rhizomes. Accumulate starches and other nutrients, which help the plant survive periods of dormancy and regenerate in the next growing season.
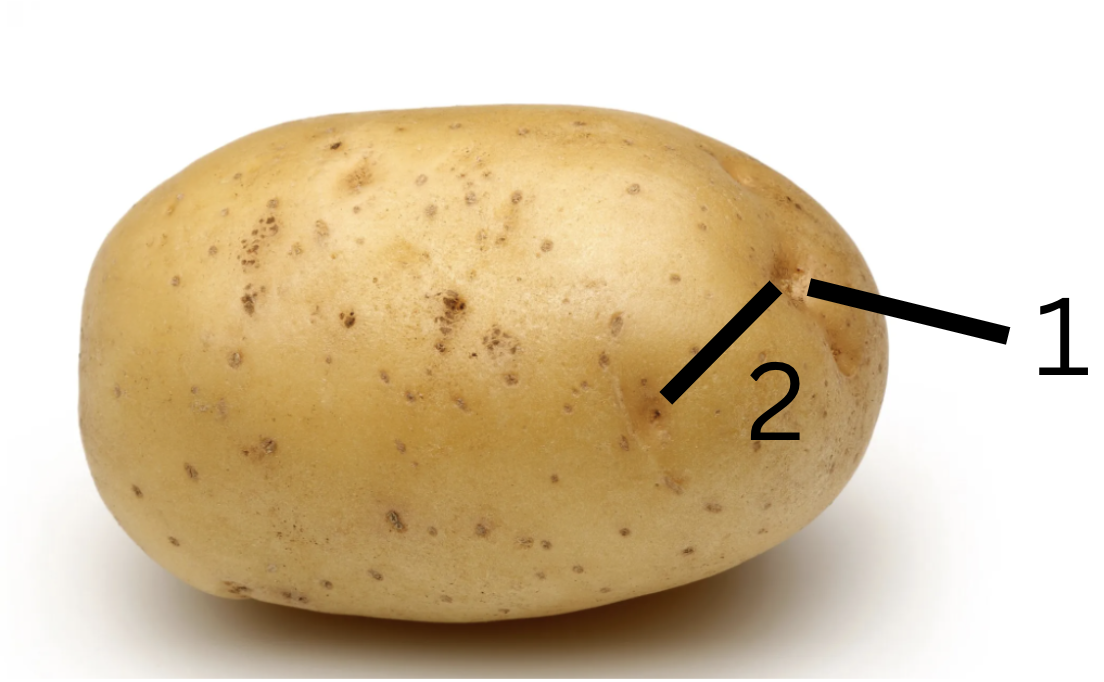
Name plant
Name modified stem
What is 1 and 2
white potato
tuber
1.node and 2.internode
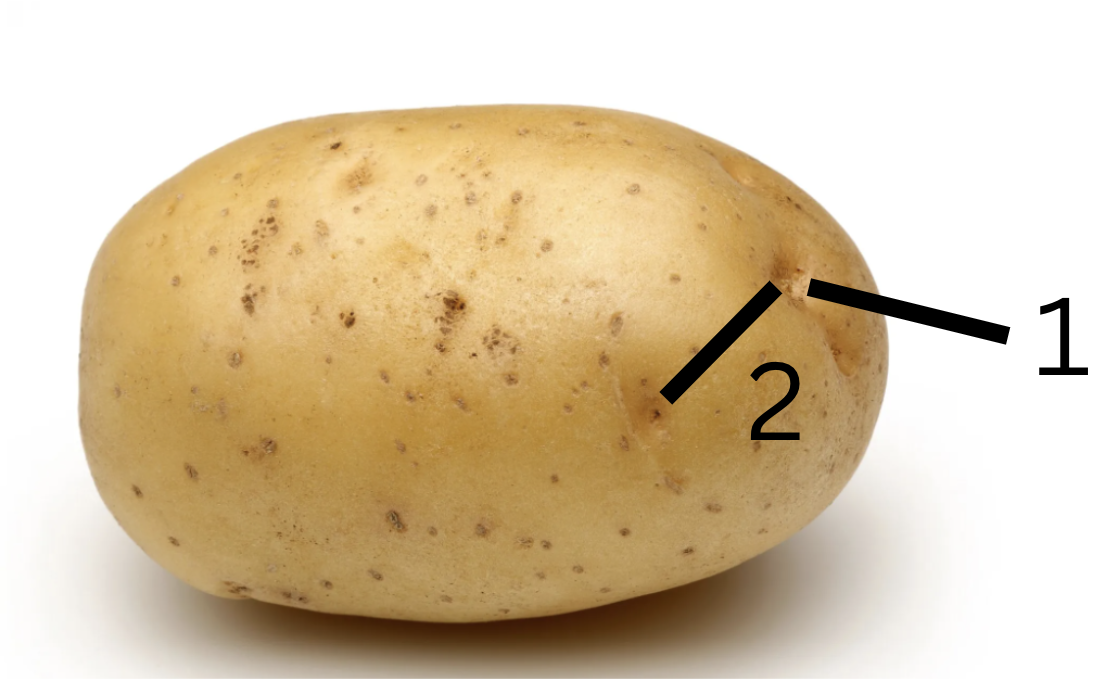
Is this primarily for storage or support, why?
Function: Storage. Mod stems-tubers
Why: Store starch as an energy reserve. Enable the plant to survive through unfavorable conditions like winter, and they can sprout new shoots to grow new plants in the next season.
Name plant
Name modified stem
What is 1 and 2
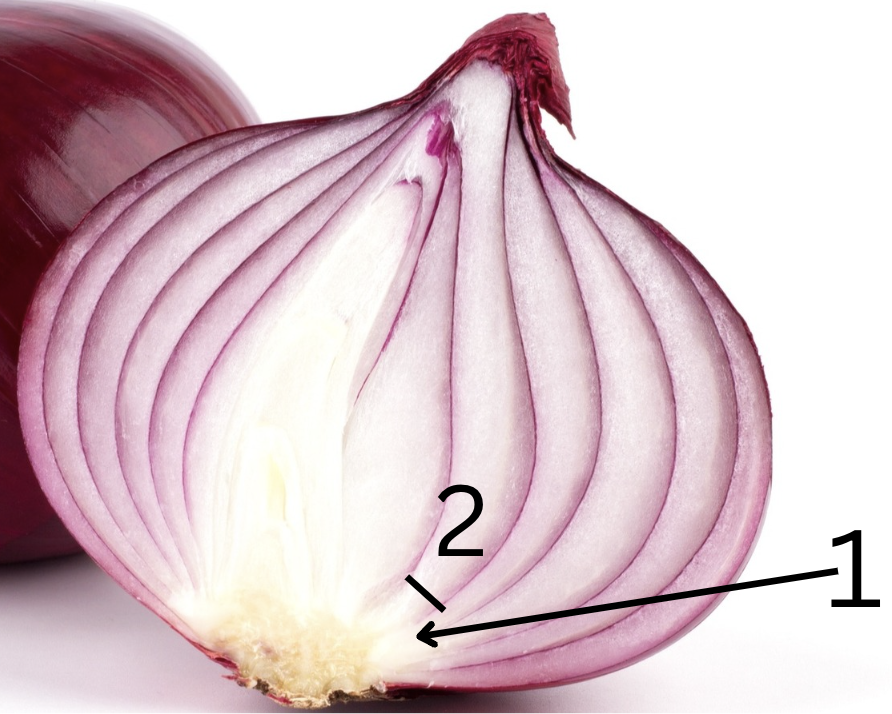
onion
bulb
1. node and 2.internode
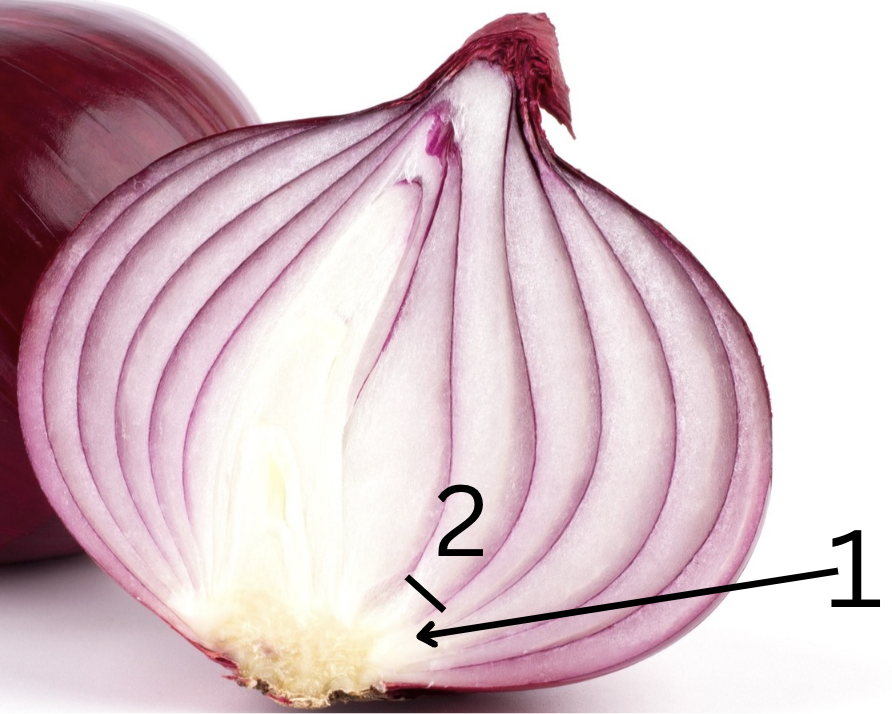
Is this primarily for storage or support, why?
Function: Storage.
Why: Onions are modified bulbs, which are underground storage organs. They store nutrients, primarily sugars and starches, which the plant can use to grow new shoots and flowers in the next growing season.
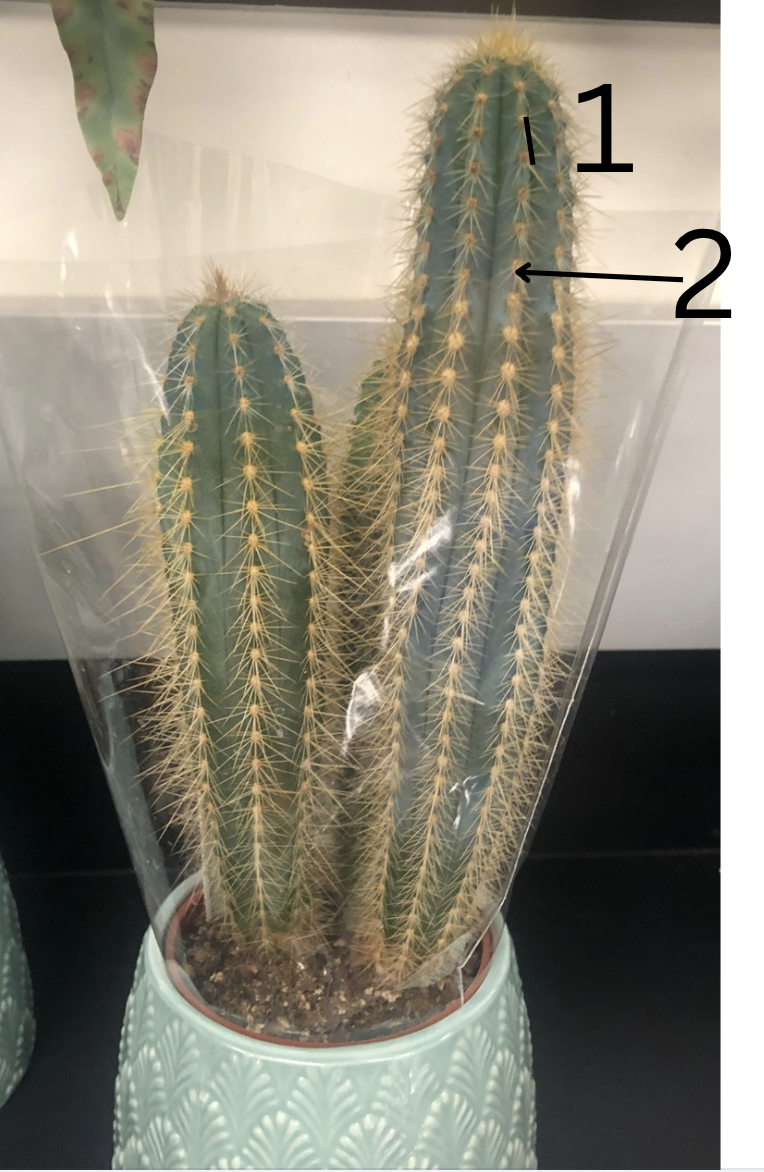

Name plant
Name modified stem
What is 1 and 2
cactus-xerophytic
stem succulence
1.internode and 2.node
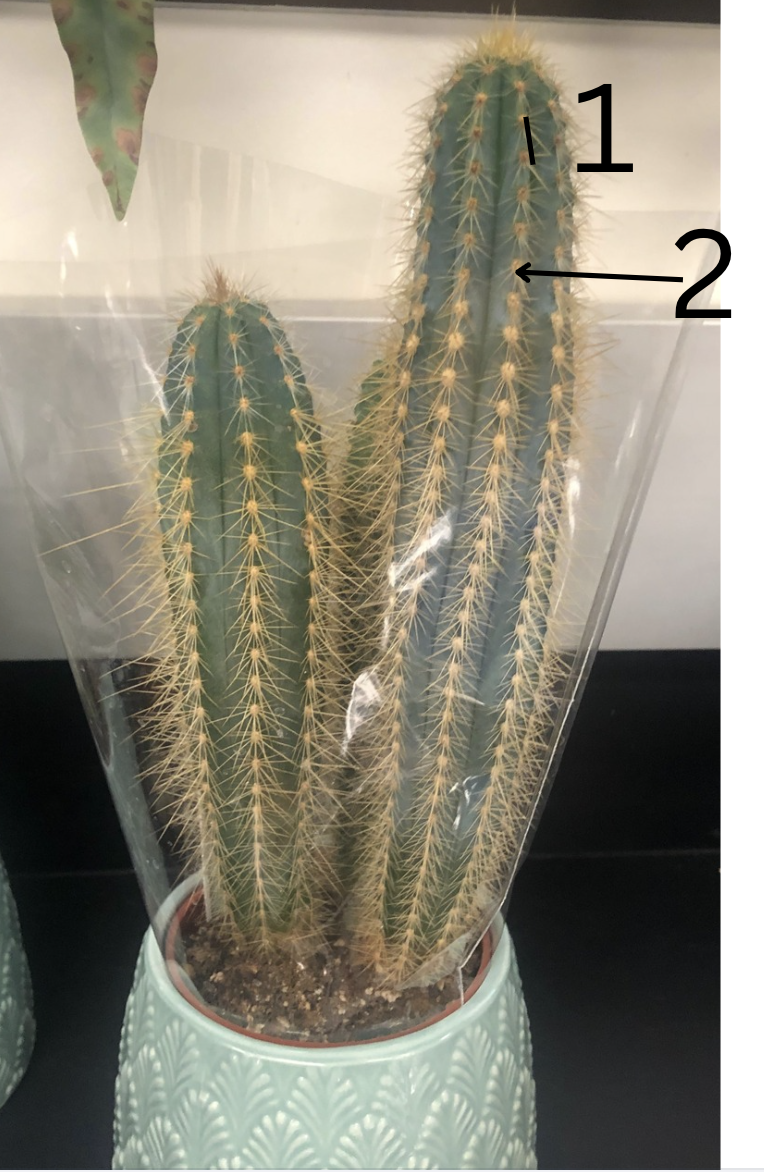

Is this primarily for storage or support, why?
Function: Storage (mainly water) and photosynthesis.
Why: Cacti have specialized stems (often thick and fleshy) that store water. These stems are adapted to arid environments where water storage is essential for survival.
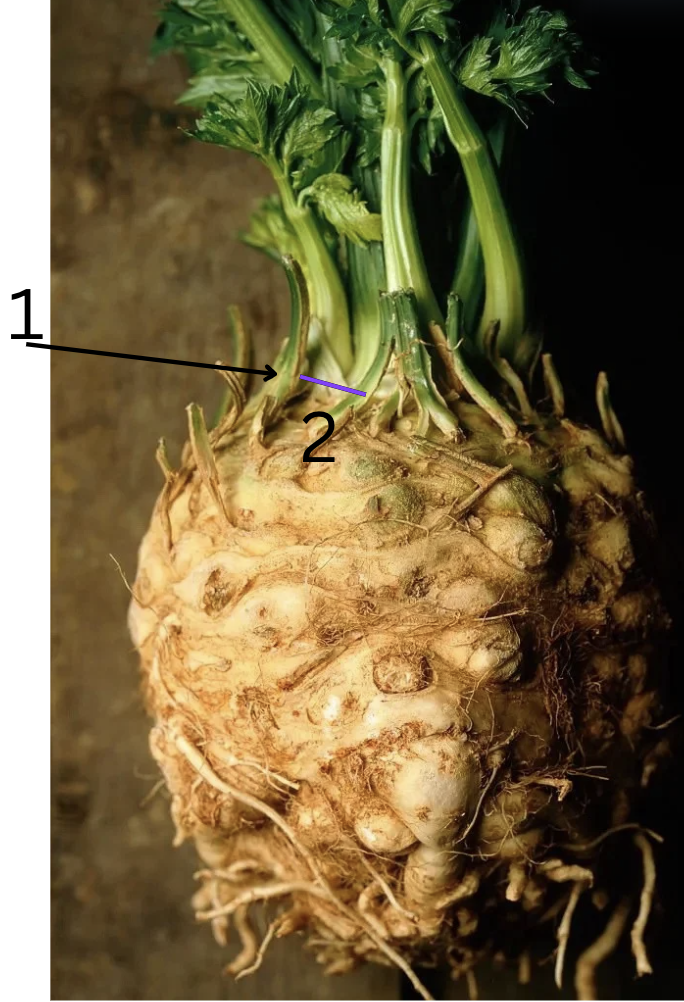

Name plant
Name modified stem
What is 1 and 2
celeriac (celery)
Mod. hypocotyl
1.node and 2.internode
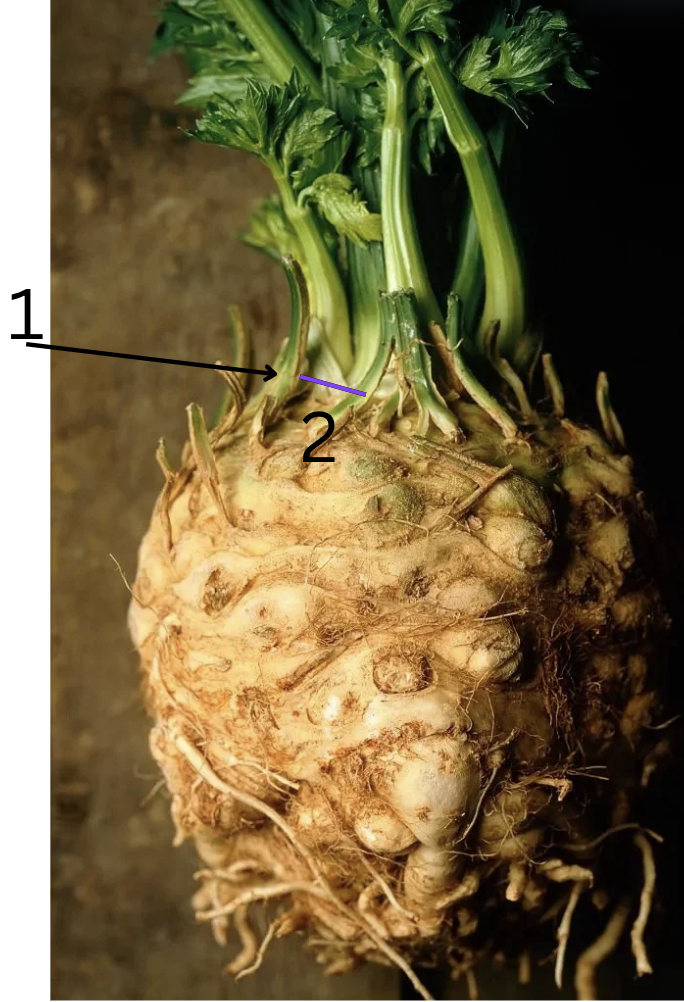

Is this primarily for storage or support, why?
Function: Support and water storage.
Why: The thick, fleshy stalks of celery are modified petioles (leaf stalks) that provide structural support for the leaves. They also store water, allowing the plant to survive in conditions where water might be sparse.
Do conifers have vessels and fibers?
NOOOO! Only have tracheids, no vessels and fibers, therefore softwood
Distinguish monocot stems from an herbaceous dicot stem
Monocot stem- Scattered vascular bundles, vasc. bundle looks like a face, no defined pith and cortex
herbaceous dicot stem-vascular bundles are arranged in a ring, defined pith, potential for secondary growth
Distinguish herbaceous stems from an woody dicot stem
Herbaceous dicot stems- more soft, no bark, but has secondary thickening
Woody dicot stems- have bark, growth rings, hard and rigid stems, significant secondary growth.
What is a cladophyll?
Stems that resemble leaves in function and appearance, arise from the axils of a shoot, and have determinate growth May be cylindrical or flattened
What is a stolon?
Runners- Aboveground horizontal shoots, which sprout and produce a new plants.
Long internodes
What is a hypocotyl?
Connects the root (radicle) to the shoot (above-ground parts). Transitional structure between the embryonic root and the growing seedling. Roles in support, elongation, storage, and the early transport of nutrients.
what is a rhizome?
Belowground stems that burrow into the ground just below the soil surface.
Function in propagation
Short internodes and usually have small, scale-like leaves that are not photosynthetic.
Buds from the axils of the leaves make new branches that will grow to become aboveground shoots.
What is a tuber?
Thick, belowground stems found at the tips of rhizomes or stolons
“eyes” are actually lateral buds, and the tuber body is comprised of many parenchyma cells that contain amyloplasts with starch.
What is a corm?
Short, thick underground storage stem with thin scaly leaves
Thick, expanded stem stores starch, and the leaves that surround it are non-photosynthetic and papery.
What is a bulb?
Relatively small stem surrounded by thick, fleshy leaves.
Stores its nutrients in its fleshy leaves
What is a stem succulence?
Thick, fleshy stem adapted for storing water. Found in dry or arid environments where water is scarce.
Ground tissue comprised of parenchyma and located in center of some roots and stems
Pith
Primary tissue that gives rise to epidermis
protoderm
trees from this ground include pines and firs
gymnosperm
flattened photosynthetic stem
cladophyll
trees from this group have wood comprised of vessels and tracheids
angiosperms
modified stem creating a sharp projection
thorn
tissue rarely found in stems unless they grow underground
hypodermis
refers to the smaller diameter xylem produced later in the growing season
summerwood
horizontal above ground stem
stolon
arrangement of the vascular bundles in a typical monocot stem
scattered
light colored wood in a tree trunk that still conducts
sapwood
region of stem where leaves attach
node
gas exchange areas on the surface of bark
lenticels
collective region of cork cells, phelloderm, and the cork cambium
periderm
parenchyma tissues b/t the epidermis and vascular tissues.
cortex
Corn, monocot or dicot
monocot
scientific name for corn
Zea mays
What is a stele?
Central part containing tissue from pro cambium(pith, pericycle, and vasc tissue)
Primary function of stems?
Support the above ground organs of a plant.
Transports water and minerals from the roots up to the leaves, flowers, and fruits
Conducts photosynthetic products from the leaves to the stem and roots
Some stems are modified for…
food or water storage, photosynthesis, vegetative reproduction, and other functions
How do monocot and dicot stems differ?
In organization of primary tissues.
What do stems typically have?
epidermal layer, ground tissue(cortex and pith) underneath the epidermis, and VASC bundles.
Vascular bundles are arranged in different patterns among…
stems, petioles, and leaves. Roots, stems, and leaves have distinctive tissue zones and tissue arrangements.
What are the vessel elements in a vasc bundle?
Red cells with more enormous, thicker cell walls.
Where is the vasc cambium? What does it produce?
b/t xylem and phloem. Produce secondary xylem and secondary phloem after the first year of growth, adding diameter of stem.
What does phloem look like?
Contain sieve tube cells with large diameters but thin cell walls. Distinguished by the companion cells at the corners of the sieve tubes.
Do monocot stems develop secondary growth?
NOOOOO. NO secondary growth like dicots. only dicots have. Also, NO VASC CAMBIUM!
is there a distinctive ground tissue in monocot stems? dicots?
monocots-NO, no distinction b/t pith and cortex
dicots- yes. pith and cortex(roots don’t have pith)
What is a hypodermis? Fxn?
Underneath the epidermis (epidermis and sclerenchyma cells)
Gives mechanical support to grass like bamboo and other long lived monocots
growth rings?
One year growth of xylem. Secondary xylem accumulates in the middle portion of the stem, and over the years, produces growth rings.
Do dicots and conifers have secondary growth?
Stems and roots of many dicots and conifers produce considerable secondary growth after the primary growth is completed.
What do plants produce during secondary growth?
secondary xylem, secondary phloem, and cork cells
What is wood?
secondary xylem
What is the outermost layer of a woody stem or root consist of?
Bark
What is the bark composed of?
Secondary phloem, periderm(cork cells)
What is periderm?
Secondary tissue produced by the cork cambium. Cork cells, phelloderm, and the cork cambium
What do cork cells contain?
Suberin, a lipid that protects and insulates the inner tissues of the stem.
What are lenticels?
Replaces the stomata as it’s responsible for the gas exchange in newer, primary tissues. Composed of loosely-arranged cork cells.
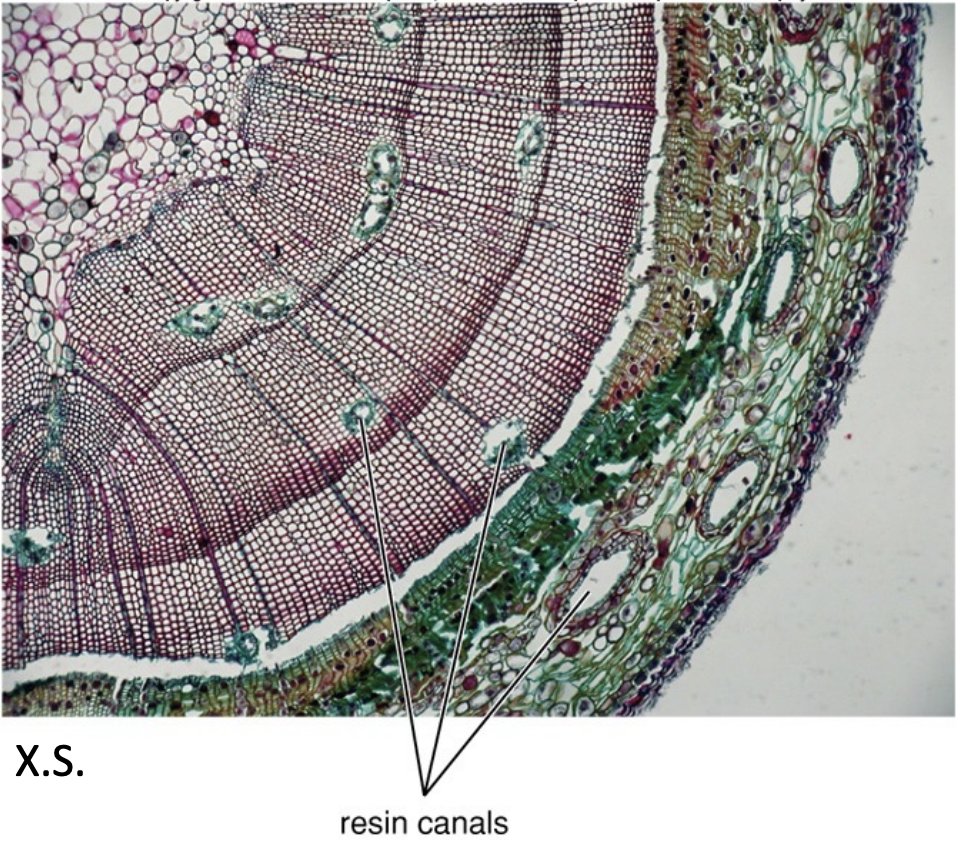
What is this?
pine wood:Just tracheids and resin canals and ray
What is this?
pine wood-tracheids and ray
What is this?
pine wood-ray, tracheids, and resin
how do you differentiate a growth ring from the ray parenchyma?
growth rings=horizontal
ray=vertical, moving with the xylem
How does the vessel differ from the tracheids?
Vessels- wide diameter, larger, thicker, empty white space
Tracheids=skinny, narrow, pink, bordered pits
What does the xylem comprise of? What are they?
vessels, tracheids, and ray
Vessels- widest diameter
Fibers=smaller diameter and thicker cell walls
Tracheids=smaller diameter and thinner cell walls