Textiles - Final Exam
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Mercerization
Fabric finish that uses sodium hydroxide for cotton yarns or fabrics to increase the lustre and dyeability.
Gray Goods
Refers to fabric as it comes off the loom, knitting machine, or whatever machine made it, before it is bleached, dyed, or otherwise finished.
Durable Finish
Fabric finish that may last for the life of the product, but its effectiveness diminishes with use or age. (Ex: wrinkle resistance).
Crocking
Color transfers to another fabric from rubbing together.
Renewable Finish
Fabric finish that can be applied by the consumer or reapplied by the dry cleaner.
Permanent Finish
Fabric finish that lasts the life of the item.
Bleeding
Loss of color in water or other solutions; may color other fabrics present.
Overprinting
Fabrics that have first been dyed and then printed.
Converted Goods
Fabrics that have received wet, or finishing treatments, such as bleaching, dyeing, or embossing.
Temporary Finish
Fabric finish that lasts until the item is washed or dry-cleaned the first time.
Migration
Color movement to adjacent areas or fabrics; (red and white striped shirt).
Colorfastness
Refers to resistance to change in any color characteristic or to transferring color to another object.
Pigments
Insoluble color particles that are held on the surface of a fabric by a binding agent (glue). Does not have affinity for fiber.
Dyes
An organic compound that is water or other carrier soluble. Has affinity for fibers.
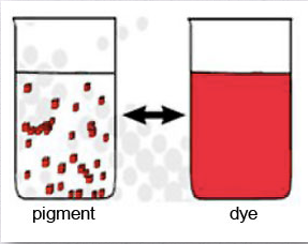
Pigments do not have an affinity for fibers so they are kept on with a binding agent while Dyes do have an affinity for fibers.
What is the difference between pigments and dyes?
Prefiber Dyeing
Fiber Dyeing / Stock Dyeing
Yarn Dyeing
Piece Dyeing
Product Dyeing
What are the five processes of dyeing?
Prefiber Dyeing
Color is added with the dope before it is extruded into a fiber.
Fiber dyeing/Stock dyeing
Color is added to loose staple fibers before yarn spinning.
Yarn dyeing
Color is added after the fibers have been spun into yarns.
Piece dyeing
Color is added to a bolt or roll of fabric.
Product dyeing
Color is added after the fabric is cut and sewn into the finished product.
Resist Printing
Blocks color absorption on different parts of the yarns or fabrics.
Batik
Tie-dye
Ikat
Screen Printing
Stencil Printing
What are the different methods of resist printing?
Textile Fiber Products Identification Act of 1960.
The percentage of fiber content listed in order of predominance by weight (generic fabric names).
Name of the manufacturer or the company’s RN #
Country of origin
What is TFPIA?
Permanent Care Labeling Regulation of 1972
Required accurate, permanently attached and legible label or tag that contains regular care information and instructions
Label must state:
Washing method
Water temperature
Drying method
Drying temperature
Ironing temperature
Procedures to be avoided
If multiple care methods are appropriate for the product, the manufacturer is not required to list them all on the label
Reversible garments are required only to have removable, not permanent, care labels.
If the care-label instructions are followed and some problem develops during care, the manufacturer is liable (Consumer should contact the Federal Trade Commision, FTC).
What is the Care Labeling Act?
The crockmeter is used for colorfastness tests that works by rubbing a square of white, bleached fabric against the fabric being tested, indicating how much dye will transfer due to crocking.
How does the Crockmeter work and what does it tell us about tested fabrics?
Spun Yarns
Yarns made from short staple fibers; all natural fibers except silk are staple fibers.
Filament Yarns
Yarns made from long filament fibers.
A natural, cellulosic fiber.
Cotton (Type of fiber)
A manufactured, regenerated fiber.
Rayon (Type of fiber)
A natural, protein fiber.
Wool (Type of fiber)
A natural, protein fiber.
Mohair (Type of fiber)
A natural, protein fiber.
Silk (Type of fiber)
A natural, cellulosic fiber.
Flax (Type of fiber)
A manufactured, synthetic fiber.
Acrylic (Type of fiber)
A manufactured, synthetic fiber.
Spandex (Type of fiber)
A manufactured, synthetic fiber.
Polyester (Type of fiber)
Warp (Wovens)
The yarns that run lengthwise (vertically) in woven fabrics.
Weft (Wovens)
The yarns that run crosswise (horizontally) in woven fabrics.
Wale (Wovens)
In a twill weave, each warp or weft yarn floats across two or more weft or warp yarns, forming a distinct diagonal line.
Warp (Knits)
Yarn is fed to the needles from the end, forming loops in the direction of the wales; vertical.
Weft (Knits)
Yarn is fed to the needles from the side, forming loops across a course; horizontal.
Wale (Knits)
A vertical column of stitches in knits.
Course
A horizontal row of stitches in knits.
Embroidered
Fabrics decorated by hand or by machine with a surface-applied thread.
Embossed
Fabrics that produce flat or raised designs by passing through hollow, engraved metal calendar rolls.

Burnout
Fabrics produced by printing a chemical solvent on a blend fabric made of different fiber groups, dissolving one fiber to leave sheer areas.
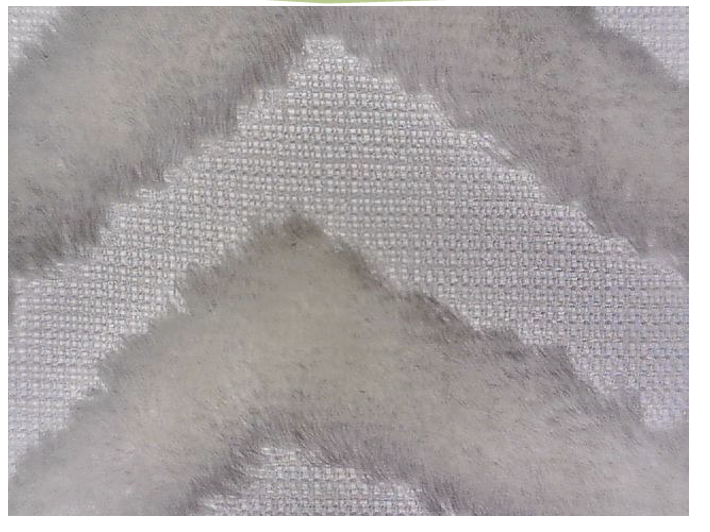

Plisse
Fabrics converted by printing sodium hydroxide onto cotton lawn or printcloth gray goods, creating a striped appearance.

Sueded
A process for fine silky fabrics where the fabric is moved under rollers with abrasive paper to create a soft texture.

Flocked
A process where a fine natural or synthetic surface fiber is applied onto a base fabric.

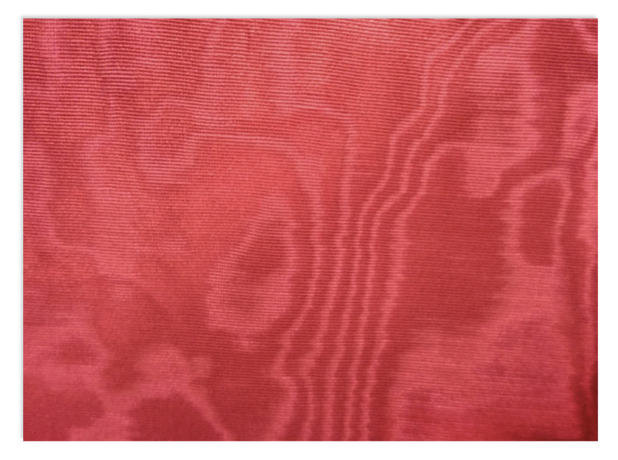
Moiré
Fabrics that have a wood grain or watermarked appearance.

Yarn Dyed
Yarn that can be dyed in skeins, on cones, or wound on warp beams, used for structural designs like plaids and stripes.

Direct/Application Print
Color applied directly to the fabric in the desired pattern and location.

Batik
A hand process where hot wax is applied to fabric to create a design.

Overprinting
Fabrics that have been dyed first and then printed.
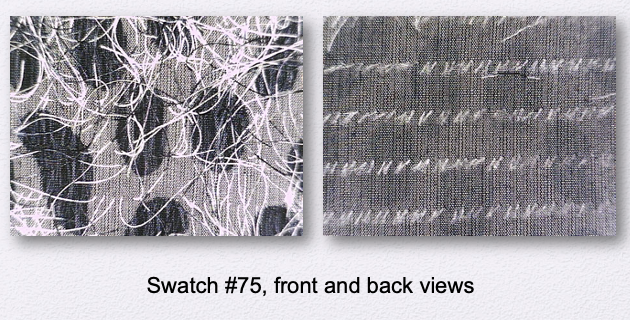
Duplex Print
Roller printing with a pattern on both sides of the fabric.

Glazed
Fabric passed through a finishing solution, partially dried, and calendered to polish the surface.

Prepared for Printing
PFP
Turns/Twists per Inch
TPI