BPSC 104 Lecture 8 (Secondary Growth)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Primary growth is produced by __.
Apical meristem (shoot and root)
Axillary meristem (axillary bud)
(Think how a → o)
Primary growth results in ____.
Increased shoot and root length
What are plants with ONLY primary growth called?
Herbaceous plants
What are plants with BOTH primary AND secondary growth called?
Woody plants
(Wood has width = secondary growth)
Secondary growth is produced by ___.
Lateral meristem
Types of lateral meristem
Vascular cambium
Cork cambium
(Producers of secondary growth)
What does the vascular cambium (type of lateral meristem) produce?
Secondary xylem = wood
Secondary phloem - part of bark
What does the cork cambium (type of lateral meristem) produce?
Periderm - most of bark
Sexual Reproduction (Advantages)
Most plants reproduce sexually
Advantages to the species
Genetic variation among offspring
May be more adapted to the habitat than parents
Increased chance of survival in different (changing environments)
Sexual Reproduction (Disadvantages)
Often requires two parents to reproduce
Requires a mechanism of pollen transfer
Expensive rproductive structures
Offspring may be less adapted to the habitat
Plant life cycles (sexual reproduction)
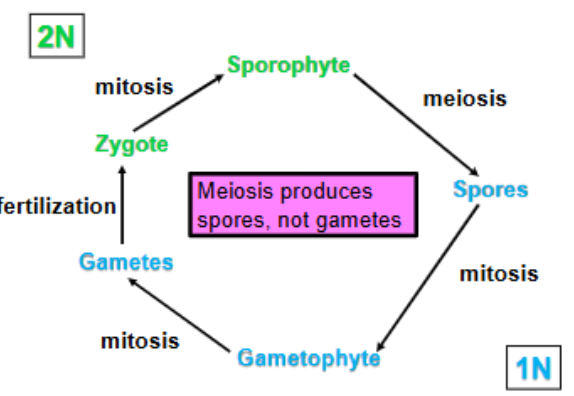
The plant life cycle consists of alternating haploid and diploid generations
Haploid = 1N = Gametophyte
Diploid = 2N = Sporophyte
Life cycles: Animals
Alternate between haploid and diploid
Short-lived unicellular haploid phase (gametes)
Diploid phase is longer-lived and multicellualr
Meiosis results in production of gametes
Gametes fuse immediately to restore the diploid state
Meiosis in plants produces ____?
Spores
Spores
Haploid cells
Divide by mitosis to produce a mulicellular haploid organism (gametophyte)
Haploid organism forms gametes by mitosis
Gametes
Fuse to form diploid zygote
Zygote divides by mitosis to form a multicellualr diploid organism (sporophyte)
Alternation of generations
multicellular haploid phase alternates with a multicellular diploid phase
1N alternates with 2N
Sporophyte
Diploid generation is multicellular
Produces sproes
Gametophyte
haploid generation is also multicellular
Produces gametes
Alternation of Generations
see
Plant life cycle (evolution)
During the course of evolutionary time
The Gametophyte (haploid) has been reduced in size and significance
Leads to smaller plant
The Sporophyte (diploid) has increased in size and significance
Leads to larger plant
Embrophyta (land plants) are distinctive in having protection for the embryo in the sporophyte generation
In evolution there was ____?
A shift from gametophyte-dominant life cycles to sporophyte - dominant life cycles
Gametophyte dominant life cycle → Sporophyte dominant
Bryophytes, gametophytes is:
Nutritionally independent
Larger, longer lived than the sporophtye
The sporophyte depends on the gametophyte for nutrition
In vascular plants, sporophyte is:
Nutritionally independent
Larger and longer lived than the gametophyte
The gametophyte depends on the sporophyte for nutrition
Angiosperm (flowering plant)
450,000 species
Extremely diverse
Monocots, eudicots and more
Have dominated land for more than 100 million years
Most are free living, and quite a few are parasitic for mycoherterotrophic
the plant we see is the sporophyte
Gametophyte is highly reduced
Distinctive characteristics of angiosperms
flowers
fruits
Double fertilization
Flowers are formed by ____?
Shoot apical/axillary meristems
Types of shoot apical/axillary meristems
Vegetative meristems are indeterminate
Floral meristems are determinate
Produce floral organs and gaemtes
When a plant produces, shoot meristems switch from produces leaves to reproductive organs
Flowers are usually arranged in clusters called ___?
Inflorescences
Inflorescences
differ in number and arrangement of branches, the arrangement of flowers on the branches, etc.
Examples of Inflorescences
Panicle
Spike
Raceme
Corymb
Simple umbel
Compound umbel
Head
Catkin
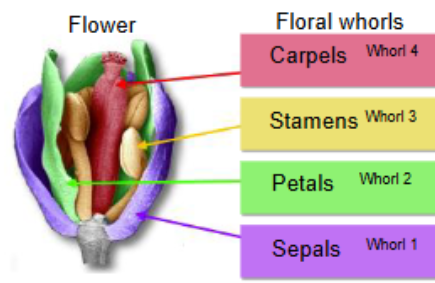
Whorls (4 types of organs on flowers)
Whorl 1 - Sepals
Whorl 2 - Petals
Whorl 3 - Stamens
Whorl 4 - Carpels
Parts of a flower
Pedicel
Attaches flower to main stem
Receptacle
Site of attachemnt of four floral whorls
Sepals (calyx)
Petals (corolla)
Both of these make up the Perianth
Stamens
Filaments, anthers
Carpels (pistil)
Stigma, style, ovary
Complete flower
Has all 4 whorls
Incomplete flower
does not have all 4 whorls
Flower Structure is variable
Perfect flowers - have stamens and carpels (bisexual)
Imperfect flowers - lack stems or carpels (unisexual)
Can be monoecious or dioecious
Monoescious (“single house”) (Imperfect flower)
Single sex male and female flowers occur on the same plants
Squashes are an example
Dioecious (“two houses”) (Imperfect flowers)
Male and female flowers are on different plants
Papaya is an example
The outer floral organs are ____?
Nonreproductive (sterile)
Outerfloral organs
Sepals (calyx)
Petals (corolla

Sepals (calyx) (outer floral organs)
outer whorl
Protect other floral organs in the bud
Maintain humidity
May be photosynthetic or pigmented like petals

Petals (corolla) (outer floral organs)
Pigmented (visible light, UV)
Thin and delicate
Attract pollinators
May have markings (nectar guides) to orient pollinators
Stamen (parts)
Filament
Anthers
Filament (part of stamen)
stalk to elevate anthers
Anthers (part of stamen)
produce pollen
Meiosis occurs in anthers (meiosis prod spores)
Produces 4 haploid spores (microspoes) that develop into pollen
Pollen has tough, resistant, “sculptured” wall
(When spores are male, we call them microspores)
When spores are female, we call them megaspores)
Pollen
male gametophyte and produces the sperm cells
Meiosis in anthers produces microspores
Each microspore divides to form:
Tube cell
Generative cell
Male gametophyte
Pollen will grow a tube through the carpel to reach the female gamete
Pistil (female part)
Composed of one or more carpels
Separate or fused
Carpel/pistil consists of:
Stigma
Style
Ovary
Stigma (carpel part)
upper surface of the pistil
Style (carpel part)
stalk to elevate stigma
Ovary (carpel part)
produces ovules
Megaspore (in ovule) develops into ___?
Female gametophyte (know the process)
Pollination
transfer of pollen to the stigma
Pollen is transferred many ways
Animals (birds, insects, bats…)
Wind
Pollen carried by wind is what causes allergies
Self pollination
Pollination does not always lead to fertilization because __?
Specific signals and interactions between the pollen and the pistil tissues are required for:
Pollen to germinate on the stigma
Pollen tube to grow through the style of the ovary
Sperm cell to be released into the ovule