MED IMAGING EXAM 2 ALL
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
US does not penetrate:
bone or air (air may interfere w/ study)
Second choice for abdominal abscess is:
US (but cannot pick up bowel lesions)
Acute abdominal series
PA CXR, flat plate, upright abdominal film
What is the imaging study of choice for a patient with appendicitis, pancreatitis, diverticulitis, small bowel obstruction, abscess or tumor, or trauma?
CT
Mesenteric lymph nodes are ususally:
benign
Prostate calcification are often secondary to:
BPH
Feeding tube placement
in distal duodenum or jejunum (used for enteric feeding)
Best way to evaluate esophagus:
endoscopy
pain w/ swallowing (often due to infection or esophagitis)
odynophagia
What do you need for severe dysphagia?
EGD (barium swallow maybe done first)
Worry for ______________ w/ chronic GERD
Barrett's esophagus (cells in esophagus look like cells that line the stomach)
What do you use to visualize strictures?
EGD or dilation
sphincter does not relax and esophagus becomes dilated and loses elasticity
achlasia
What looks similar to achlasia
Chaga's dz
collagen vascular disease that effects smooth muscle (esophagus dilates)
scleroderma
Candida esophagitis can be seen in:
HIV or immunocompromised pts
what is used for dx and tx of Mallory-Weiss tear
EGD
out-pouching of cervical esophagus (resulting from weakness in muscular wall)
Zenker's diverticulum (causing dysphagia)
Most common FB in children? Most common FB in adults?
Study of choice for FB?
coins; meat
EGD
What is used to visualize stomach or duodenum
UGI or EDG
CT is not a good scan for:
stomach or intestinal dz (when you are trying to look at inside linings - will not show ulcers)
____________ can detect 90% of duodenal ulcers
Contrast barium
Most common metastatic tumor of liver
colon CA
Dx of hepatitis
clinical/lab (imaging is used for seeing complications)
What is used for abscesses?
CT w/ IV and GI contrast
What can differentiate between jaundice from liver disease and obstruction of the common bile duct?
US
Which scan is preferred over barium enema but more uncomfortable
air contrast barium enema
_________ should be suspected if transverse colon is the most dilated region
Ileus
No appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, constipation, think:
appendicitis
**will often have appendicolith
Method for polyp removal
electrocautery during colonoscopy
___________ must be stopped for 48 hours after IV contrast administration
Metformin (can have lactic acidosis)
Non-invasive option for look at kidneys it pt cannot tolerate contrast
Renal US
first line evaluation after major trauma or for obstructive stone disease when IVP is contraindicated
CT
What should be ordered if there is visible hematuria w/ known trauma
CT scan
Abnormalities of the kidney
horseshoe shape
pelvic kidney
_______ is good for following benign appearing cysts
US
What is indicated if cyst has septa or internal echoes to r/o CA
CT
Renal stones can occasionally be ___________ within the parenchyma
radiolucent (which is why dye is helpful)
Stag-horn calculi
fill up entire renal pelvis
Intense one sided flank pain and hematuria - what tests are useful?
CT or IVP
**renal stone dz
IVP dye can cause:
worsening renal function
When would you get imaging on a pt w/ pyelonephritis (fever, flank pain, nausea, dysuria, pyuria)?
abscess is suspected or pt is diabetic
Rib fracture of 12th rib, - suspect:
kidney trauma
Most common cancer of kidneys? Study of choice?
renal cell carcinoma; CT scan
**blood in urine and flank pain; can have cysts
Best way to evaluate hydronephrosis
1. US
**due to obstruction at junction between collection system and ureter
dilatation of the distal ureter (cobra head deformity)
Ureterocele
Initial study for suspected bladder cancer
cystoscopy
In patient w/ pelvic fracture - must think _____________ as well
bladder rupture
Bladder elevated centrally is due to:
bilateral bladder hematomas
Study of choice for bladder trauma
CT scan w/ cystogram
Rupture of bladder can be:
extraperitoneal or intraperitoneal (which will outline loops of bowel)
Recurrent bladder infection (cystitis) - do:
IVP
Emphysematous cystitis (gas in the wall or lumen of bladder) is common in:
diabetic pts
Most bladder tumors
transitional cell carcinoma (male smokers)
Study of choice for bladder tumors
cystoscopy
**follow up w/ CT to see surrounding lymph nodes
study of choice for looking at metastases
bone scan
useful for evaluating suspicious area of prostate (and locating area for biopsy)
transrectal US
first line study for any testicular problem
US
What imaging is used for visualizing testicular torsion
color doppler US
**Torsion is clinical diagnosis (sudden onset of pain)
What is used for staging of testicular CA
CT or CXR
Most common and useful study of female pelvis
US
**Transabdominally or transvaginally
What is used to visualize early or ectopic pregnancy, tubo-ovarian abscess, measurement of endometrial stripe, and ovarian torsion
transvaginal US
Study of choice for pregnancy
US
o Size/date discrepancy
o Vaginal bleeding
o Suspected congenital abnormalities
o Maternal dz
o Suspected fetal demise
o Preterm labor or rupture of membranes
Suspicion for ectopic pregnancy
positive pregnancy test but see nothing in the uterus at 5 weeks or positive pregnancy test and mass on uterus
Most common pelvic tumor of uterus
fibroid (benign)
What type of cancer is difficult to assess by radiological studies (need biopsy)
endometrial CA
_______ is usually detected by PAP smear w/ f/u colposcopy
cervical CA
**further eval w/ CT or MRI
Screening tool for ovarian CA
no effective screening tool right now!
Bloating, weight gain, vaginal bleeding on physical exam
Can do US to recognize mass (CT done to look closely at tumor and look for metastases)
What is used to look at Adrenal glands
CT scan
Most common cancer of adrenal glands
adenoma
**can also have tumors from metastases
What do you get if there is suspected retroperitoneal adenopathy
CT scan
Use oblique views for:
joints, hands, feet
Use CT for:
skull, spine, pelvis
Use MRI for:
muscles, ligaments, spinal cord, cartilage
Use Bone scan for:
metastases, osteomyelitis, occult fractures
Widening of soft tissue line above C3, suspect:
pathology
(4-5 mm at C3 and 10-20mm below C4)
When will you add swimmer's view?
Cannot visualize C7-T1 joint space
Spinal fractures from trauma are most likely from:
MVA
If head CT is indicated, __________ is also done
C-spine CT
Common areas of degenerative changes
C4-C7
Trauma from thoracic spine is usually from:
MVA or osteoporosis
Degenerative changes of thoracic spine
o Spurs
o Calcification of anterior spinal ligament (DISH)
o Calcification of intervertebral disc
Parts of Scotty Dog
o Transverse process - nose
o Pedicle - eye
o Inferior articular facet - front leg
o Superior articular facet - ear
o Pars interarticularis - neck
Lumbar spine degenerative changes
o Loss of disc space
o Hypertrophic spurs (osteophytes)
o Disk calcification
o Herniated/protruding discs
Best study for suspected herniated or protruding disks
MRI
______ is indicated if there is localized pain, elevated ESR, fever, elevated WBC or positive blood culture (indicating a spinal infection)
MRI
Neoplasms in the spine are usually:
metastatic from somewhere else (can be lytic or sclerotic)
**usually arise in bone marrow
Ankylosing Spondylitis is often associated w/:
ulcerative colitis (and patients will usually have HLA antigen)
Primary osteoporosis is mainly caused by:
aging and estrogen deficiency in women
DEXA measures:
bone density
Acute monoarticular joint pain is due to:
Chronic monoarticular joint pain is due to:
Acute: septic arthritis or trauma
Chronic: DJD or aspectic necrosis (get MRI)
Acute polyarticular joint pain is due to:
Chronic polyarticular joint pain is due to:
Acute: viral infection or systemic arthritis
Chronic: osteoarthritic (plain films are good)
thickening of periosteum (white on x-ray)
periosteal reaction
Giant cell tumor is usually in:
long bones
What do you need to get in cases of osteomyelitis?
culture (for diagnosis)
Septic arthritis is usually in the ______. What is used for the diagnosis?
knee
Dx: joint aspiration
**joint films are indicated also
Best true lateral view
axillary view (arm is abducted)
What can be seen in scapular Y view?
coracoid, spine and body of scapula (humeral head should be in center of Y)
3rd most common site for osteogenic sarcoma
humerus
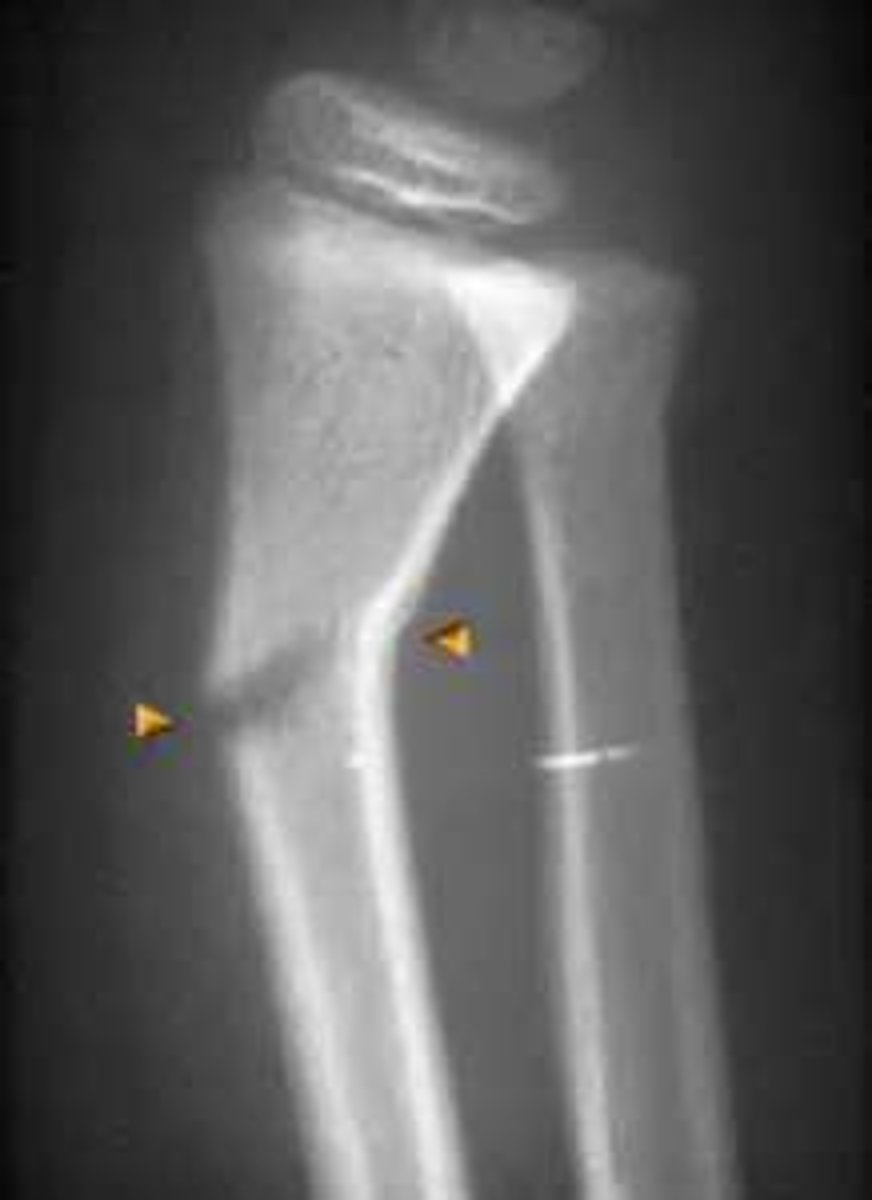
Incomplete fracture due to flexibility of young bones
Greenstick fracture