Software 3372 Final
1/328
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
329 Terms
How do we indicate a Singleton instance in a class diagram?
With a '1' in the upper right-hand corner
A sequence diagram describes
only the interactions between objects; it does not describe what happens inside of an object.
Which of the following statements about UML dependencies are true? (MULT ANS)
-A dependency represents a transient relationship between class objects.
-When an object A creates another object B, a create dependency exists between the objects A and B.
-If an object of class A is passed in as a parameter to a method defined in class B, then a dependency exists between class A and class B.
A lifeline in a sequence diagram
represents an instance.
To handle the logic (e.g., looping) required for a sequence being modeled, we can use frames with appropriate operators (e.g., loop for looping), which is formally called “sequence diagram fragments”. Which one of the following statements about sequence diagram fragments is NOT true?
A neg fragment describes interactions that are optional.
Which one of the following is NOT true for an association?
A binary relationship between two classes must be represented by two separate associations.
Which one of the following is a true statement about synchronous messages?
When an object sends a synchronous message, it must wait for a response.
Which one of the following is NOT a true statement about subsystem design?
Note: While the architectural modeling is done to show static/dynamic relations among subsystems, the subsystem modeling shows the design of each subsystem.
A subsystem design describes only the signatures of operations in a subsystem's interface.
What type of modeling are interaction diagrams used for?
Dynamic
Which of the following is NOT illustrated in UML class diagrams?
Lifelines
"Interaction diagram" in a design model is a generalization used to refer to more specialized UML diagram types. What are those types? (MULT ANS)
-Sequence diagram
-Communication diagram
Communication diagrams work well for which of the following?
-UML as sketch
-Formal modeling
-Agile modeling environment
True or false. It is NOT possible to nest frames in a frame within a sequence diagram.
False
How are asynchronous messages shown in sequence diagrams?
Stick arrow with solid line
When the class diagram notation is used for the purpose of representing a problem domain, what do we call it?
Domain class diagram
Which one of the following are true statements about UML stereo types? Select all correct answers.
-destroy and create (used on sequence diagrams) are examples of stereotypes.
-A stereotype represents a refinement of an existing modeling concept.
-A stereotype is defined within in a UML profile.
-The Object Management Group (OMG) provides many pre-defined stereotypes in the UML specification.
We show a strong aggregation (composition) with which type of arrow in association?
Solid diamond arrow
What is the acronym for UML's formal specification language for constraints?
OCL (Object Constraint Language)
True or false. UML class diagrams support showing template classes that are typically known as templates or parameterized types in many programming languages.
True
____ is the ability of one object to "see" or have a reference to another object.
Visibility
With regard to the creator pattern, we should assign class B the responsibility of creating an instance of class A if which of the following conditions are true.(MULTIPLE ANSWERS)
-B records A
-B closely uses A
Who are the four authors who wrote the "Bible" of design pattern books, often referred to as the GoF, "Gang-Of-Four".
-Erich Gamma
-Richard Helm
-Ralph Johnson
-John Vlissides
Which of the following statements about GRASP is correct? (MULTIPLE ASNWERS)
-GRASP is a methodology for object-oriented design based on responsibility-driven design
-GRASP consists of a collection of design patterns that help us think in terms of object-oriented design
Which of the following is true? (MULTIPLE ASNWERS)
-If A uses B closely, then A is a creator of B.
-A facade could be any concept which the designer chooses to represent the whole system or a subsystem.
Which of the following is true?
Controller pattern decides what first object after UI layer should receive the message from UI layer.
Which GRASP pattern could we use when we are concerned about change in the system and its impact?
-High Cohesion
-Low Coupling
When there are other design alternatives, the book suggests to take a look at what?
-Coupling
-Cohesion
When talking about the GRASP Controller pattern the book mentions two types of controllers, what are they? (MULTIPLE ASNWERS)
-Session Controller
-Facade Controller
What does "RDD" stand for?
Responsibility-Driven Design
True of false. Patterns help to facilitate communication.
True
In the Low Coupling example in textbook, which of the following is a true statement as a solution in assigning responsibilities? (MULTIPLE ANSWERS) (See Sec. 17.12)
-We remove the call to create() from Register to Payment and place that responsibility with Sale
-Because Register no longer has to know about Payment and only about Sale, instead of both, we have decreased the coupling of our objects
True or False. A low cohesive object with many source lines of code probably collaborates with many other objects and all that interaction tends to also create high coupling.
True
What is the best phrase that can fill the given blank? (see Sec. 18.1)
"A use case realization describes how a particular use case is realized within the Design Model, in terms of ." [from The Rational Unified Process Product]
The collaborating objects
See "calculating sale total" example on pg. 336 of printed book (pg. 484 of pdf, under Figure 18.9).
Which object should be responsible for calculating the sale total?
Sale
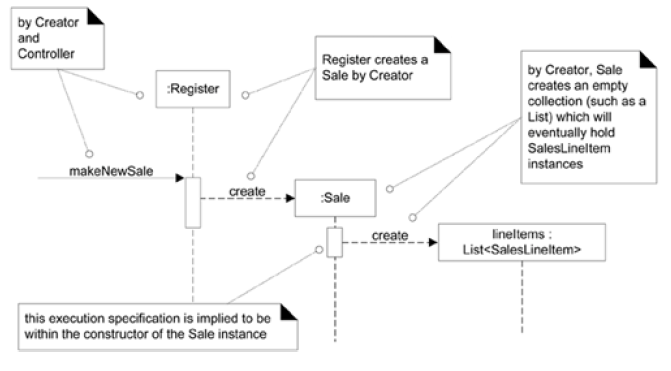
Consider Figure 18.6 on pg. 330 (copied below from Larman textbook), which message is the system operation message?
makeNewSale
Which of the following is a FALSE statement?
Exit and entry actions of a state are performed when an internal transition is made on the state.
The following is an example of an event: after(license period). What type of event is this?
Time event
Which one of the following is TRUE about a state model?
A do event is an on-going behavior that is performed as long as the modeled statement is in the state or until the computation specified by the expression is completed.
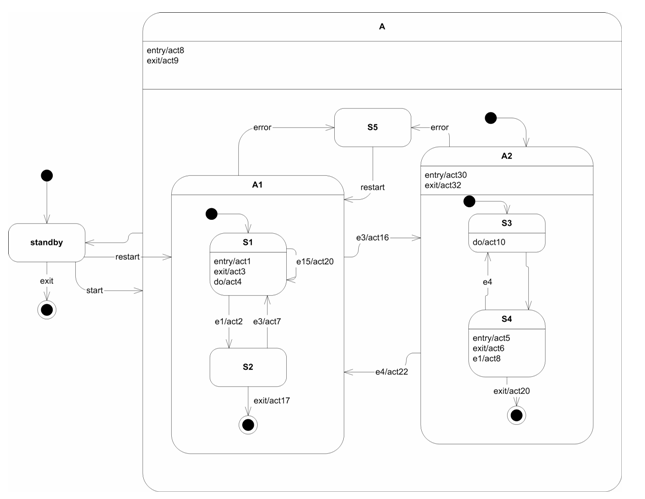
The following figure shows a state machine. If the state machine is in state S1 what is the sequence of actions performed when the event e3 occurs?
act4, act3, act16, act30, act10
Which one of the following is a FALSE statement about active objects?
An active object cannot be terminated by another object.
Which one of the following statements about a state machine event is TRUE?
An event can mark a significant occurrence at some point in time.
Which one of the following is a FALSE statement about run-to-completion semantics?
A high priority event received by a state machine interrupts the state machine when it is handling a low priority event and takes the event that is currently being processed from the pool.
Which one of the following is TRUE about a state model or statechart?
A state chart diagram shows method of execution on receipt of message and activities used in the method.
What is the GRASP
General Responsibility Assignment Software Pattern
-a set of guidelines for assigning responsibilities to classes and objects in OO design.
Information Expert
Assign responsibility to the class that has the necessary information.
Creator
Assign the responsibility to create an instance to the class that has or closely uses it.
Controller
Assign responsibility for handling system events to a controller class (not UI!)
Polymorphism
Use polymorphic behavior to handle alternatives (like different shapes or payment types).
Pure Fabrication
Add a non-real-world class just to support low coupling/high cohesion
Indirection
Use a mediator or handler to decouple two classes.
Low Coupling
Keep classes independent so they're easier to maintain/change
High Cohesion
Keep responsibilities focused; don't overload a class.
What does the Controller in GRASP mainly recommend?
The Controller recommends using a class to handle input/system events. It shouldn’t be the UI or business logic class—it’s a mediator.
-Makes code easier to understand and test
-Changes in one class have minimal effects on others
-Supports reuse and parallel development
How can we better handle alternative types in OO design?
Use dependency injection to swap components easily, and follow the Open/Closed Principle to extend behavior without modifying existing code. Also, use patterns like Strategy or Observer, keep components loosely coupled, and drive behavior with configuration or plugins to support dynamic loading.
How can we create pluggable software components so that a system can be easily extensible?
Designing to interfaces, using dependency injection, and applying patterns like Strategy or Observer. This keeps components loosely coupled and allows new features to be added without changing existing code
How is each operation contract used later in design modeling?
To guide the creation of class methods, responsibility assignments, and sequence diagrams
State Pattern Intent
Allow an object to change its behavior when its internal state changes.
State Pattern Applicability
Use it when an object's behavior depends on its state and it must change behavior at runtime.
State Pattern Consequences
-Eliminates massive switch statements
-Localizes behavior per state, can lead to lots of small classes
Deficiencies in modeling using the original state pattern itself
The basic state pattern doesn't handle complex transitions, concurrency, or history tracking well → UML Statecharts fix this.
Basic State Model Concepts
states, transitions, events, actions
Advanced State Model Concepts
nested states, parallel states, history
State Model Event Types
-Call event: method call
-Signal event: asynchronous notification
-Time event: timeout
-Change event: condition becomes true
Transition Types
-Group: shared transitions
-Default: fallback transition
-Completion: occurs automatically when state completes
Action Key Words
-entry: action on entering a state
-exit: action on exiting
-do: ongoing activity while in the state
Composite States
Sequential and Concurrent substates
Substates vs. Concurrent Substates
-Sequential substates: only one active at a time
-Concurrent substates: active in parallel
Orthogonality in State Models
Multiple independent regions within a composite state that don't interact (unless explicitly defined).
Interactions between parallel states
Happen when a composite state is split into concurrent substates, and each substate has its own independent state machine.
State Model Transformations
-State merging: combine states with shared behavior
-Parallel ⇔ Flat: translate between complex concurrent models and simplified sequential versions
History Pseudo-States
-Shallow: remembers last active substate at one level
-Deep: remembers nested substates recursively
Entry/Exit Points
Used to control entry and exit to composite states when multiple options exist—like checkpoints or gateways into deeper states.
Conditional Branching
Static: redefined decisions (like a switch-case or if-else logic)
Dynamic: evaluated at runtime based on object state or conditions (e.g., checking object property values before deciding path)
Objects' Dynamic Semantics
Passive - waits for method calls; just responds (like most Java objects)
Active - has its own thread or runs in a state machine loop (e.g., in real-time systems or simulations)
What is Run-to-Model Completion Model?
Once an event is being processed by an object, it will fully complete before the next event is handled.
How does a Run-To-Completion Model work on one active object?
No other events interrupt until the current one's finished.
How does a Run-To-Completion Model work in a multi-tasking environment on a uni-processor system?
Only one active object is running at a time. Objects take turns (e.g., cooperative multitasking or queued events).
What are software patterns?
Reusable solutions to common problems in software design.
What are typical problems many patterns intend to solve?
-Object creation (Factory, Builder)
-Object interaction (Observer, Mediator)
-Behavior delegation (Strategy, State)
-Extensibility and flexibility
Different Pattern Types and Examples
-Creational: how objects are created (e.g., Singleton, Factory)
-Structural: object composition (e.g., Decorator, Adapter)
-Behavioral: communication and control flow (e.g., Command, Observer)
Patterns vs Architectures vs Frameworks
-Patterns: abstract solutions (small-scale)
-Architectures: high-level structure (big-picture)
-Frameworks: reusable code libraries with predefined architecture
GoF design pattern classification: scope vs. purpose
-Scope: class-level vs. object-level
-Purpose:
Creational (object creation), Structural (object composition), Behavioral (object interaction)
Singleton Pattern
ensures a class has only one instance
Factory Method Pattern
subclasses decide which class to instantiate
Observer Pattern
one-to-many dependency, objects get notified of changes
Strategy Pattern
encapsulate interchangeable behavior
Command Pattern
encapsulate a request as an object
Decorator
dynamically add behavior to objects
Adaptor Pattern
makes incompatible interfaces work together
State Pattern
alters behavior based on internal st
What is Unified Process (UP)?
An iterative, incremental, and architecture-centric software development framework
Phases of UP
Inception, Elaboration, Construction, Transition
Inception
Define project scope and key requirements
Elaboration
Plan and develop architecture
Construction
Build and test the software
Transition
Deploy and maintain the system
Workflows in UP?
Business Modeling, Requirements, Analysis & Design, Implementation, Testing, Deployment
Business Modeling
Understand the business domain
Requirements
Define system functionality
Analysis & Design
Structure system architecture