Disorders of Haemostasis - Embolism, DIC, Shock
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
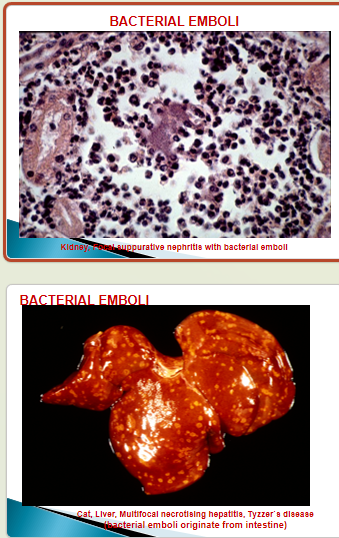
Describe bacterial emboli
E.g. bacterial endocarditis —> bacterial embolus in pulmonary & systemic circulation
What is an embolic-metastatic neoplasm?
A neoplasm caused by emboli aggregation at different sites in the systemic circulation (often caused by bacterial emboli).
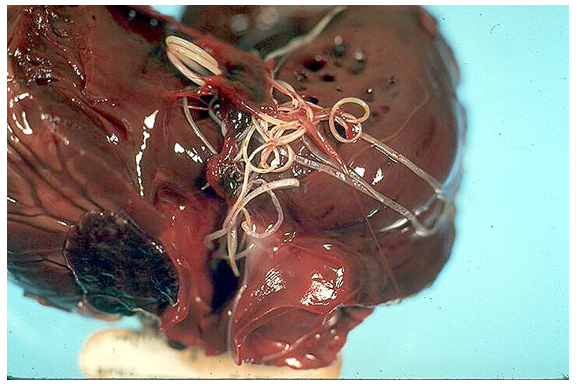
What does this show?
Parasitic embolism (heartworm disease in heart of dog)
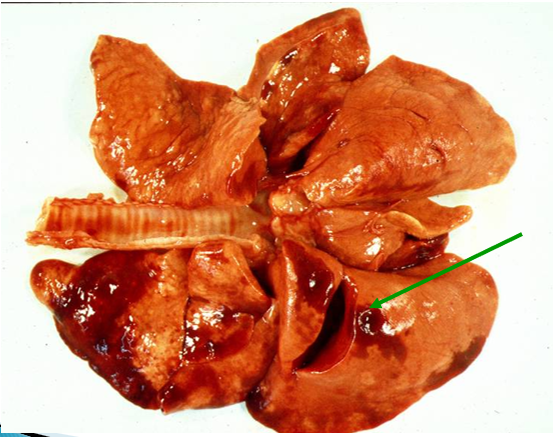
What does this show?
Fat droplet embolism (after pelvic fracture) in lung of dog
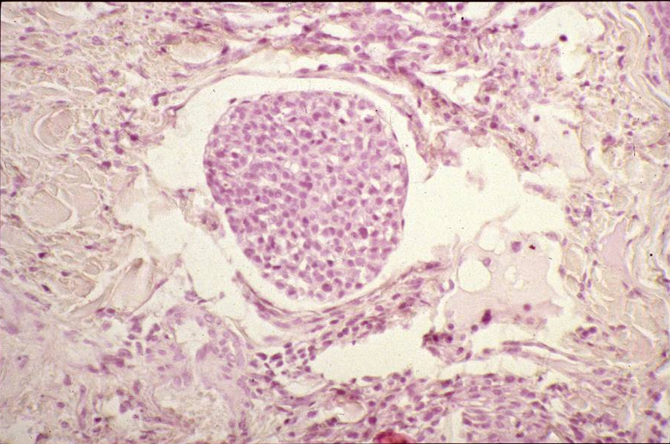
What does this show?
Tumour cell embolus within vein
What is disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)?
Acute, subacute or chronic thrombo-haemorrhagic disorder occuring as a secondary complication (severe end of disease spectrum)
What occurs with DIC?
activation of the coagulation cascade
formation of micro-thrombi throughout microcirculation
consumption of platelets, fibrin and coagulation factors —> activation of fibrinolysis
Microthrombi cause occlusion of the capillaries throughout the body.
What clinical signs are associated with DIC?
Tissue hypoxia
Infarction
Haemorrhagic disorder (due to consumption coagulopathy)
What are the underlying mechanisms of DIC?
Caused by:
Release of tissue factor or thromboplastic substances into the circulation
Widespread endothelial damage (so coagulation cascade activation)
Summarise the pathogenesis of DIC with a flow diagram
DIC pathogenesis
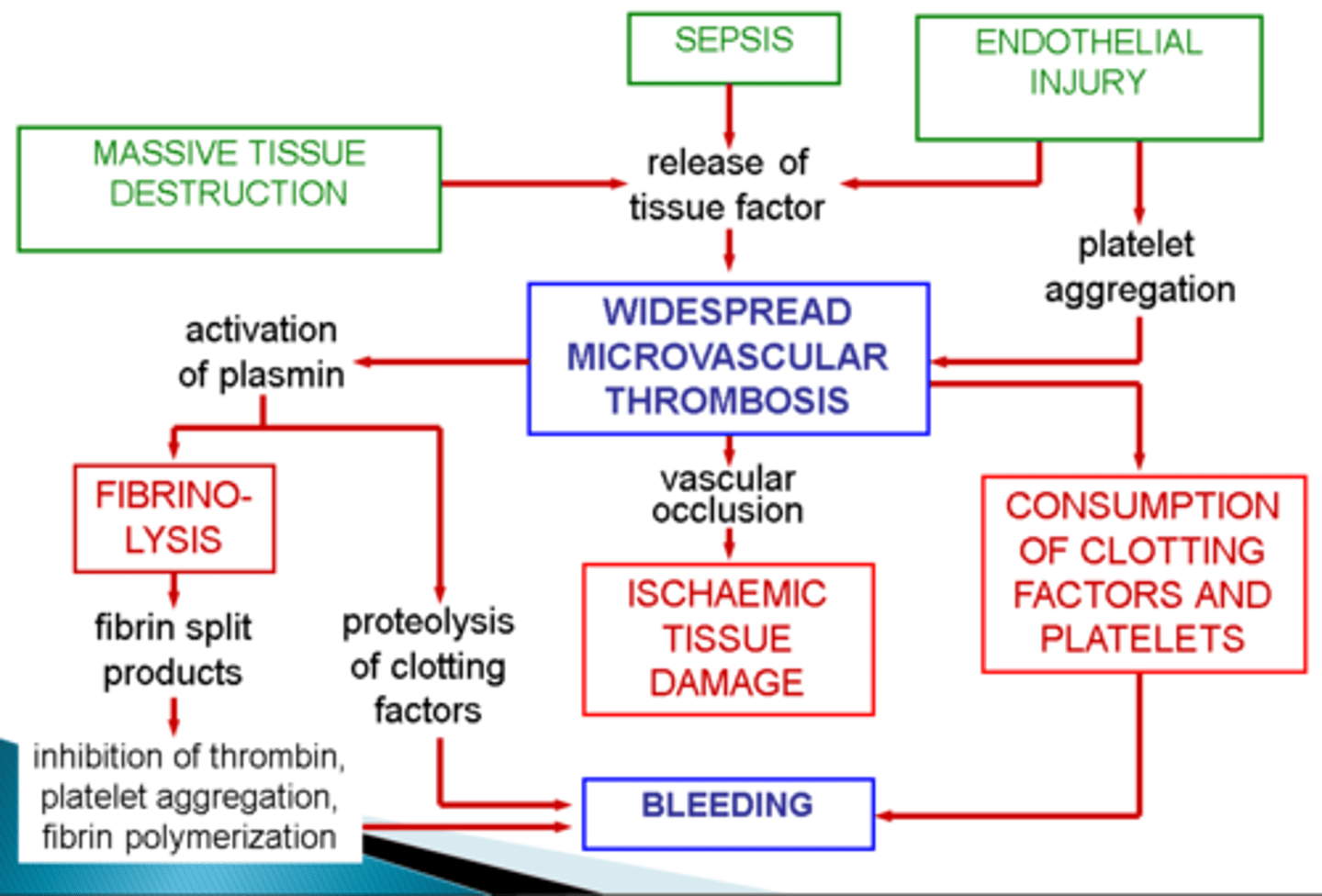
List at least 2 underlying causes of DIC
severe systemic infections due to direct endothelial cell injury or via immune complex deposition
septic (endotoxic) shock
neoplastic diseases
extensive trauma or burns
following extensive surgery
How do some gram negative bacteria cause DIC?
Express LPS on cell wall (endotoxin)
Causes monocytes to increase synthesis and release of tissue factor (also of IL-1 and TNF)
This causes endothelial cells to increase the expression of tissue factor and decrease expression of thrombomodulin
Overall cause is activation of the clotting cascade and inhibition of clotting control
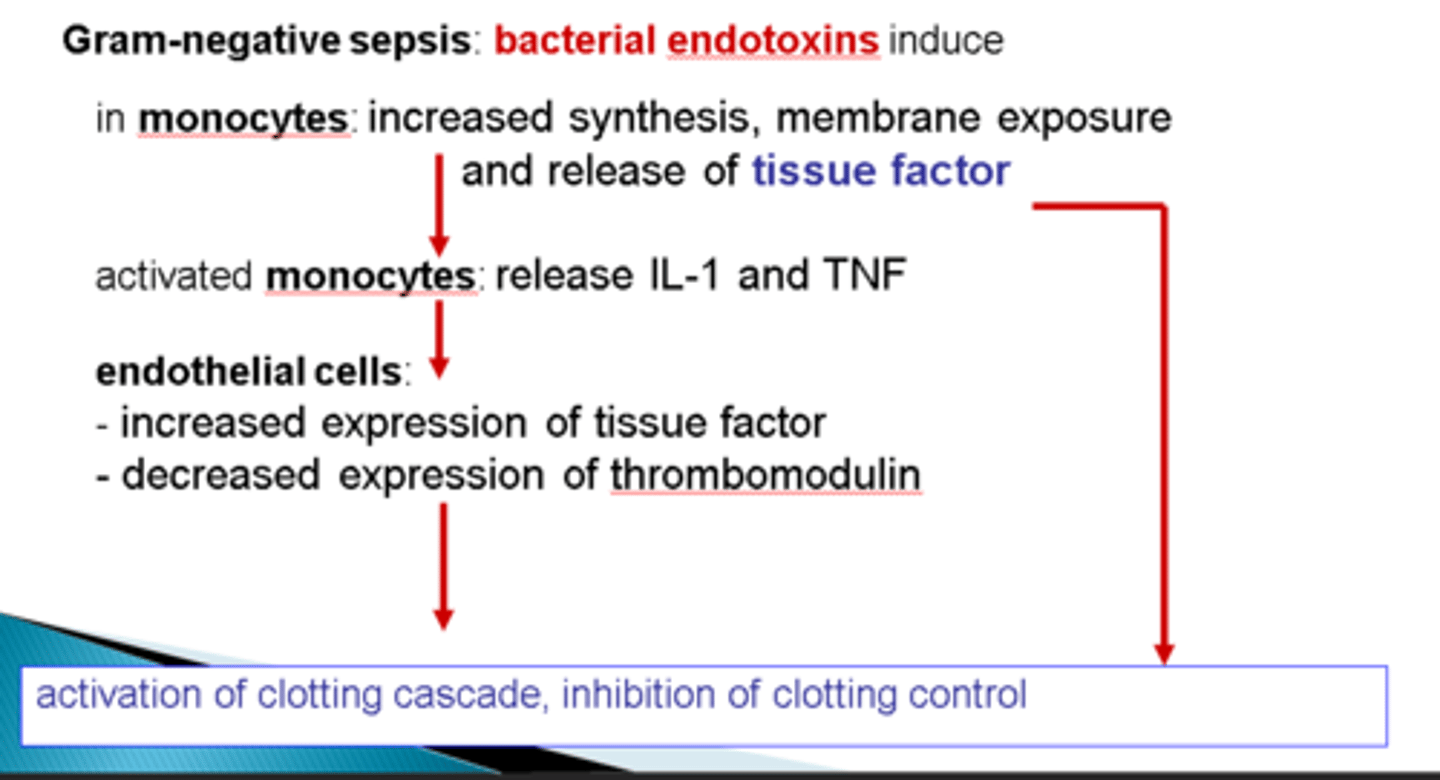
How do some gram-positive bacteria cause DIC?
Bacterial factors (e.g. glycoproteins) cause excessive cytokine prodcution by monocytes
This causes a systemic inflammatory response → to clotting → DIC
How do some gram-positive bacteria cause shock?
Neutrophils adhere to endothelial cells (which have bacteria glycoproteins on)
They release proteases and oxygen radicals to eliminate glycoproteins
Causes capillary damage & haemorrhage → shock (if sustained)
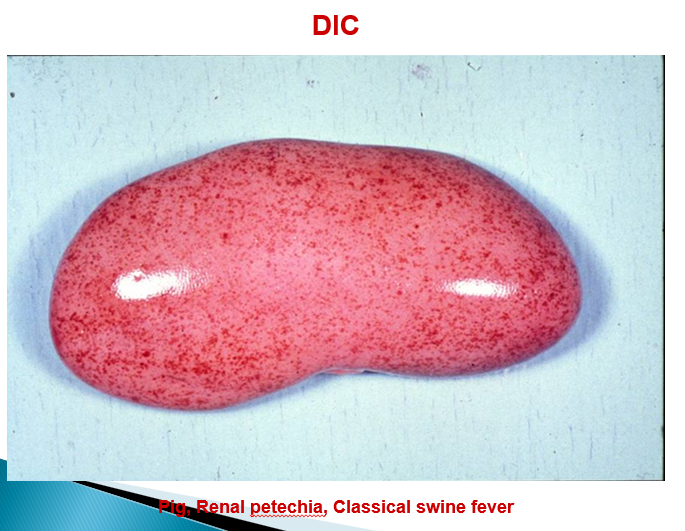
Describe endothelial alterations in classical swine fever (capillaries vs arteries)
Capillaries —> swelling of endothelial cells, hyalinisation, complete obstruction
Arteries —> thrombosis, necrosis
Describe rabbit haemorrhagic disease
Massive necrosis of hepatocytes, DIC
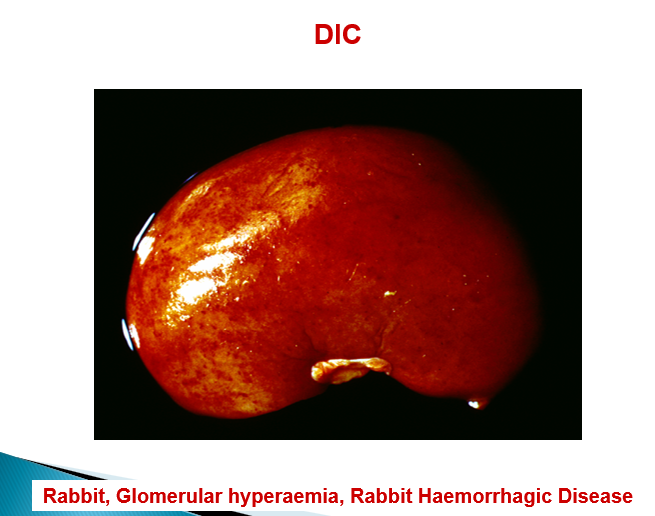
Describe the pathogenesis of immune-complex mediated DIC
Immune complex deposition in vessel walls
Activates compliment system which incidentally damages the endothelial cells
Causes the activation of the coagulation cascade
What is shock?
Complete cardiovascular collapse (so unable to perfuse the tissues of the body).
What are the broad causes of systemic hypoperfusion?
Reduced CO
Reduced effective circulating blood volume
What are the main causes of shock (list at least 2)?
severe haemorrhage
microbial sepsis
extensive trauma or burns
large infarction
massive pulmonary embolism
What is the end result of shock?
Hypotension, impaired tissue perfusion, cellular hypoxia
List at least 2 categories of shock and what their cause is
cardiogenic shock (failure of myocardial pump)
hypovolaemic shock (loss of blood / plasma volume)
septic shock (systemic microbial infection; bacteria, fungi)
neurogenic shock (depression of vasomotor centre)
anaphylactic shock (generalised IgE-mediated hypersensitivity)
List the stages of shock
1) Non-progressive stage
2) Progressive stage
3) Irreversible stage
4) Death
Summarise the pathogenesis of septic shock
Animal exposed to endotoxin (e.g. LPS of gram-negative bacteria)
Stimulates cells of innate immune system to destroy the toxins
If there is lots of toxin —> damages endothelium of blood vessels (due to activation of acquired immune response)
Leads to DIC, haemorrhage or reduced cardiac contractility and systemic vasodilation (latter due to cytokine and inflammatory modulators action)
In what condition do fat emboli typically arise?
Long bone fracture
What it the typical morphological pattern of metastatic neoplasia?
Large primary tumour, disseminated smaller tumours in other organs